新型Pd/HZSM-5-N催化剂的制备及其在苯甲醇氧化反应中的应用
2016-06-12王玉宝陈玉静
王玉宝, 陈玉静
(鲁东大学 化学与材料科学学院,山东 烟台 264025)
·快递论文·
新型Pd/HZSM-5-N催化剂的制备及其在苯甲醇氧化反应中的应用
王玉宝*, 陈玉静
(鲁东大学 化学与材料科学学院,山东 烟台264025)
摘要:以分子筛HZSM-5为前驱体,氨气为氮源,直接高温氮化制得掺氮分子筛HZSM-5-N(1);以Pd(OAc)2为钯源,1为载体,采用溶胶-固载法制备了一系列不同钯负载量(α)的新型Pdα/1催化剂,其结构和性质经SEM, FT-IR,元素分析,XRD, N2-BET和ICP表征。以苯甲醇氧化成苯甲醛反应为探针反应,研究了α, Pdα/1用量,反应时间和反应温度对Pdα/1催化性能的影响。结果表明:在最优反应条件(Pd2/1 40 mg,于120 ℃反应180 min)下,苯甲醇转化率为66.7%,苯甲醛选择性为92.9%。 Pd2/1重复使用性能较好,循环使用5次,催化活性保持不变。
关键词:掺氮分子筛; 钯催化剂; 苯甲醇氧化反应; 制备; 催化性能
醇类选择性氧化反应在药物合成,染料开发和中间体制备等领域应用非常广泛,受到化学工作者们的热切关注。如苯甲醇氧化反应,其产物苯甲醛是重要的有机中间体[1-4]。制备苯甲醛的方法主要有:甲苯直接氧化法[5]、苄氯水解氧化法[6]和苯氧化法[7]等。这些方法不仅工艺复杂,且苯甲醇转化率和苯甲醛选择性均较低[8-9]。近年来,苯甲醇直接氧化制备苯甲醛的方法被认为是一种很有潜力的合成路线,发展较为迅速[10]。
负载型金属催化剂常用于苯甲醇氧化反应,如Ru[11], Pd[12], Pt[13], Ag[14]和Au[15]等。其中钯催化剂具有钯源较广、制备过程简单和催化活性较好等优点。
ZSM-5系列高硅铝比分子筛是研究较为深入的一种分子筛[16]。该类分子筛经改性后,应用性能有较大提高。改性方法有:氧化物改性[17]、酸碱液改性[18]和掺杂原子(P, N等)改性[19]等。Guan等[19]采用氮化法对ZSM-5进行改性,并应用于乙苯和乙醇的烷基化反应。结果表明:分子筛氮化后,虽导致乙苯转化率降低,但可有效抑制催化剂表面积炭形成,降低催化剂失活速率。Jia等[18]发现HZSM-5经NaOH溶液改性后,固有晶相和微孔结构均不变,Si—OH—Al骨架发生断裂,形成 Lewis 酸中心,增大了比表面积,提高了催化性能(苯甲醇转化率53%,苯甲醛选择性86%)。但该方法存在反应时间较长,催化剂用量较多,HZSM-5骨架可能发生坍塌等缺点。
为克服这一缺点,本文拟通过直接掺杂氮原子,解决分子筛骨架结构坍塌的问题。以HZSM-5为前驱体,氨气为氮源,直接高温氮化制得掺氮分子筛HZSM-5-N(1);以Pd(OAc)2为钯源,1为载体,采用溶胶-固载法制备了一系列不同钯负载量(α)的新型Pdα/1催化剂,其结构和性质经SEM, FT-IR,元素分析,XRD, N2-BET和ICP表征。以苯甲醇氧化反应为探针反应(Scheme 1),研究了α, Pdα/1用量,反应时间和反应温度对Pdα/1催化性能的影响。

Scheme 1
1实验部分
1.1仪器与试剂
Nexus 670型红外光谱仪(KBr压片);Perkin-Elmer series Ⅱ2400 CHNS型元素分析仪;S-4800型高分辨扫描电镜;D8 Advance型X-射线粉末衍射仪;Thermo Scientific iCAP 6300型等离子体发射光谱仪;Autosorb-3B型自动物理吸附仪。
HZSM-5按文献[20]方法制备;其余所用试剂均为分析纯。
1.2制备
(1) 1的制备
在石英管中加入HZSM-5 1.0 g,缓慢升温至500 ℃,以20 mL·min-1速率通氮气4 h,除去二氧化硅表面吸附的水分;于800 ℃停止通氮,以100 mL·min-1速率通氨气8 h;以20 mL·min-1速率通氮气,冷却至室温得1。
(2) Pdα/1的制备(以Pd2/1的制备为例)
在烧杯中加入1.0 mg·mL-1Pd(OAc)2溶液5 mg,搅拌下依次滴加1%PVA溶液0.6 mL和0.1 mol·L-1新制NaBH4溶液3 mL,滴毕(约30 min),剧烈搅拌下加入1 0.25 g,反应1 h。抽滤,滤饼用高纯水(3×2 mL)洗涤,于120 ℃干燥过夜得灰白色固体Pd2/1{[VPd(OAc)2×cPd(OAc)2×MPd]/[MPd(OAc)2×ms]=2}。
用类似的方法制得灰白色固体Pd1/1, Pd3/1, Pd4/1, Pd5/1。
1.3苯甲醇氧化反应
在三颈烧瓶中加入Pd2/1 40 mg和苯甲醇4 g,搅拌(1 200 r·min-1)下于120 ℃(浴温)通入氧气(20 mL·min-1),反应180 min。按文献[4]方法计算苯甲醇产率和苯甲醛转化率。
2结果与讨论
2.1表征
(1) SEM
图1为HZSM-5和1的SEM照片。由图1可见,虽然高温氮化使晶粒变大,但晶粒形状和分散度基本无变化。这说明1晶型较好,骨架结构完整。

HZSM-51
图1 HZSM-5和1的SEM照片
Figure 1 SEM images of HZSM-5 and 1
(2) FT-IR(图略)
由HZSM-5的FT-IR分析可知,3 646 cm-1和3 606 cm-1处吸收峰分别为Si—OH中OH振动峰和Si—OH—Al振动峰[21],3 502 cm-1和3 453 cm-1处吸收峰为吸附水的OH振动峰,3 406 cm-1和3 360 cm-1处没有出现明显的吸收峰。
由1的FT-IR分析可知,3 606 cm-1处吸收峰消失,这可能是由于Si—OH—Al中的O被N取代,形成Si—NH—Al, 3 406 cm-1和3 360 cm-1处出现新的吸收峰可能归属Si—NH—Si和Si—NH—Al中NH伸缩振动峰。
(3) XRD
图2为HZSM-5, 1和Pd2/1的XRD谱图。由图2可见,HZSM-5, 1和Pd2/1在2θ7~10°和22~25°处均有特征峰,说明1和Pd2/1结晶度均较好。此外,1在2θ22~25°处衍射峰减弱,Pd2/1则无明显变化。说明高温氮化对分子筛结构有一定影响,但不会使骨架坍塌。

2θ/(°)
(4) 元素分析和N2-BET
表1为HZSM-5, 1和Pd2/1的氮含量和织构性质。
表1HZSM-5, 1和Pd2/1的氮含量和织构性质

Table 1 The nitro content and texture properties of HZSM-5, 1 and Pd2/1
*P/P0=0.995。
由表1可见,1和Pd2/1的氮含量为1.12%,略低于文献值[21]。此外,1和Pd2/1的比表面积和孔体积无明显变化,说明其结构保持完好,与文献[22]结果吻合,与XRD结果一致。
(5) ICP
表2为Pdα/1的钯含量(α)。由表2可见,高温氮化后,α增大,负载效率先升高后降低。当α=2.00%时,负载效率最高(89.0%)。这说明1表面的含氮量一定时,提高α反而不利于Pd有效负载。
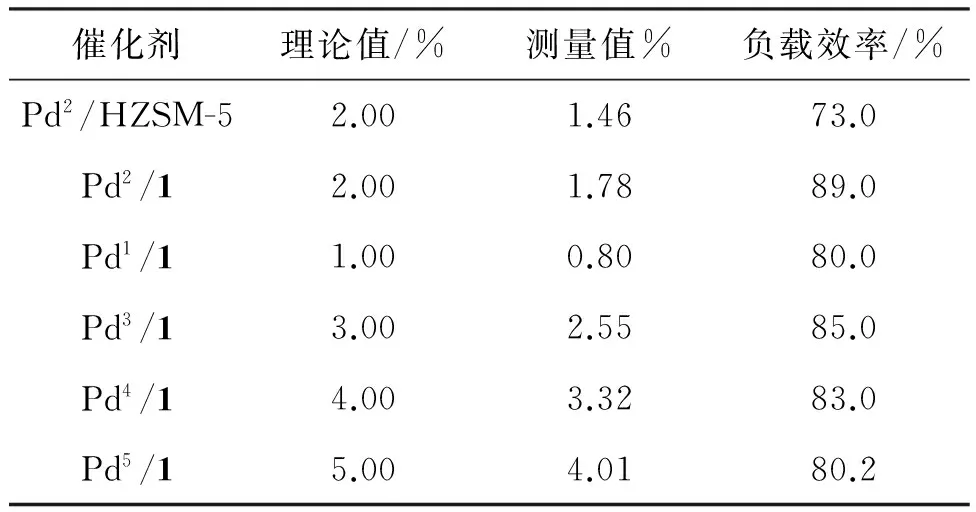
表2 Pdα/1的钯含量
综上可见,高温氮化不会破坏分子筛的骨架结构,N成功取代了部分O,形成—NHx,提高了Pd负载量。
2.2苯甲醇氧化反应的条件优化
为优化苯甲醇氧化反应条件,研究了α, Pdα/1用量,反应时间和反应温度对Pdα/1催化性能的影响,寻找最佳反应条件。
(1)α
Pdα/1 40 mg,其余反应条件同1.3,考察α对Pdα/1催化性能的影响,结果见表3。由表3可见,α增大,苯甲醇转化率逐渐提高,苯甲醛选择性缓慢降低,说明α增大有利于提高转化率,但苯甲酸等副产物也增多,导致选择性降低。当α为2%时,转化率和选择性最高(66.7%, 92.9%)。因此最佳α为2%,即Pd2/1催化性能最佳。

表3 α对Pdα/1催化性能的影响*
*Pdα/1 40 mg,其余反应条件同1.3。
(2) Pd2/1用量
Pd2/1为催化剂,其余反应条件同2.2(1),考察Pd2/1用量对催化性能的影响,结果见表4。由表4可见,当Pd2/1用量为40 mg时,转化率和选择性分别为66.7%和92.9%。继续增加Pd2/1用量,转化率基本不变,选择性逐渐降低。因此Pd2/1的最佳用量为40 mg。

表4 Pd2/1用量对催化性能的影响*
*Pd2/1为催化剂,其余反应条件同表1。
(3) 反应温度
Pd2/1 40 mg,其余反应条件同2.2(1),考察反应温度对苯甲醇氧化反应的影响,结果见表5。由表5可见,当反应温度为100 ℃时,转化率仅为35.5%,可能是由于该温度未达到苯甲醇氧化反应所需活化能。当反应温度为120 ℃时,转化率为66.7%;继续升高温度,转化率变化不大,选择性则逐渐降低。温度过高,会使苯甲醛继续发生氧化反应,生成苯甲酸和苯甲酸苄脂等副产物,导致苯甲醛选择性降低。因此最佳反应温度为120 ℃。

表5 反应温度对Pd2/1催化性能的影响*
*Pd2/1 40 mg,其余反应条件同表1。

表6 反应时间对Pd2/1催化性能的影响*
*Pd2/1 40 mg,反应温度120 ℃,其余反应条件同表1。
(4) 反应时间
Pd2/1 40 mg,反应温度为120 ℃,其余反应条件同2.2(1),考察反应时间对Pd2/1催化性能的影响,结果见表6。
由表6可见,转化率随反应时间延长而逐渐增大。当反应时间为180 min时,转化率为66.7%;继续延长反应时间,转化率基本不变。选择性随反应时间延长而逐渐降低,反应时间为180 min时,选择性最好(92.2%)。因此,最佳反应时间为180 min。
综上所述,苯甲醇氧化反应的最佳反应条件为:Pd2/1 40 mg,于120 ℃反应180 min,苯甲醇转化率为66.7%,苯甲醛选择性为92.2%。
2.3Pd2/1的循环性能
在最佳反应条件下完成反应。反应液离心,Pd2/1用无水乙醇和丙酮洗涤多次,于100 ℃干燥备用。考察Pd2/1的循环使用效果,结果见表7。

表7 Pd2/1的循环性能
由表7可见,Pd2/1循环性能较好,重复使用5次,催化性能基本不变。此外,我们对使用前后的Pd2/1的Pd含量进行了ICP检测,结果表明: Pd含量在反应前后无明显变化;反应液离心后,上清液中也未检测出Pd。这说明反应过程中无Pd流失现象。
制备了一系列不同钯负载量(α)的新型掺氮钯催化剂Pdα/1。以苯甲醇氧化反应为探针反应,研究了α, Pdα/1用量,反应时间和反应温度对Pdα/1催化性能的影响。结果表明:在最优反应条件(Pd2/1 40 mg,于120 ℃反应180 min)下,苯甲醇转化率为66.7%,苯甲醛选择性为92.9%。 Pd2/1重复使用性能较好,循环使用5次,催化活性保持不变。
参考文献
[1]Brink G T, Arends I W C E, Sheldon R A. Green,catalytic oxidation of alcohols in water[J].Science,2000,287:1636-1639.
[2]Abad A, Concepcion P, Corma A,etal. A collaborative effect between gold and a support induces the selective oxidation of alcohols[J].Angew Chem Int Ed,2005,44:4066-4069.
[3]Dimitratos N, Lopez-Sanchez J A, Morgan D,etal. Solvent-free oxidation of benzyl alcohol using Au-Pd catalysts prepared by sol immobilization[J].Phys Chem Chem Phys,2009,11:5142-5153.
[4]Miedziak P J, He Q, Edwards J K,etal. Oxidation of benzyl alcohol using supported gold-palladium nanoparticles[J].Catal Today,2011,163:47-54.
[5]Jhonstone A, Rowbottom K T, Sanderson W R. Oxidition of alkylaromatics:US 5 473 101[P].1995.
[6]王毅,乔旭. 氯化苄制备苯甲醛的研究[J].精细化工中间体,2005,35:44-46.
[7]Zhuo F L, Jiang X Z. Selective carbonylation of benzene to benzaldehyde[J].Catal Lett,2003,87:225-227.
[8]Pagliaro M, Campestrini S, Ciriminna R. Ru-based oxidation catalysis[J].Chem Soc Rev,2005,34:837-845.
[9]Sankar M, Nowicka E, Tiruvalam R,etal. Controlling the duality of the mechanism in liquid-phase oxidation of benzyl alcohol catalysed by supported Au-Pd nanoparticles[J].Chem Eur J,2011,17:6524-6532.
[10]Chaudhari M P, Sawant S B. Kinetics of heterogeneous oxidation of benzyl alcohol with hydrogen peroxide[J].Chem Eng J,2005,106:111-118.
[11]García-Suárez E J, Tristany M, García A B,etal. Carbonsupported Ru and Pd nanoparticles:Efficient and recyclable catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol in water[J].Micropor Mesopor Mater,2012,153:155-162.
[12]Chen Y T, Zheng H J, Guo Z,etal. Pd catalysts supported on MnCeOxmixed oxides and their catalytic application in solvent-free aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol:Support composition and structure sensitivity[J].J Catal,2011,283:34-44.
[13]Chen H, Tang Q H, Chen Y T,etal. Microwave-assisted synthesis of PtRu/CNT and PtSn/CNT catalysts and their applications in the aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol in base-free aqueous solutions[J].Catal Sci Technol,2013,3:328-338.
[14]Huang X M, Wang X G, Wang X S,etal. P123-stabilized Au-Ag alloy nanoparticles for kinetics of aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol in aqueous solution[J].J Catal,2013,301:217-226.
[15]Pina C D, Falletta E, Rossi M. Highly selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde catalyzed by bimetallic gold-copper catalyst[J].J Catal,2008,260:384-386.
[16]Morey M S, Brein S O, Stucky G D. Hydrothermal and postsynthesis surface modification of Cubic, MCM-48, and ultralarge pore SBA-15 mesoporous silica with titanium[J].Chem Mater,2000,12:898-911.
[17]Zhao T S, Takemoto T. Direct synthesis of propylene and light olefins from dimethylether catalyzed by modified HZSM-5[J].Catal Comm,2006,7:647-650.
[18]Jia A Z, Lou L L, Zhang C,etal. Selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol to benzaldehyde with hydrogen peroxide over alkali-treated ZSM-5 zeolite catalysts[J].J Mol Catal A:Chem,2009,306:123-129.
[19]Guan X X, Li N, Wu G J,etal. Para-selectivity of modified HZSM-5 zeolites by nitridation for ethylation of ethylbenzene with ethanol[J].J Mol Catal A:Chem,2006,248:220-225.
[20]Argauer R J, Landolt G R,etal. Crystalline zeolite ZSM-5 and method of preparing the same:US 3 702 886[P].1972.
[21]Wu G J, Wang X, Yang Y L,etal. Confirmation of NH species in the framework of nitrogen-incorporated ZSM-5 zeolite by experimental and theoretical studies[J].Micropor Mesopor Mater,2010,127:25-31.
[22]Zhang C, Xu Z, Liu Q. Synthesis,characterization and catalytic properties of nitrogen-incorporated ZSM-5 molecular sieves with bimodal pores[J].Appl Catal A,2004,258:55-61.
Preparation of Novel Pd/HZSM-5-N Catalysts and Their Applications in Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation
WANG Yu-bao*,CHEN Yu-jing
(School of Chemistry and Material Science, Ludong University, Yantai 264025, China)
Abstract:The doped nitrogen molecular sieve, HZSM-5-N(1), was obtained by directly high temperature nitridation, using molecular sieve HZSM-5 as precursor and ammonia as nitrogen source. A series of catalysts(Pdα/1) with different Pa loading(α) were prepared by sol-immobilization method, using 1 as supporter and Pd(OAc)2 as Pd source. The structures and properties of Pdα/1 were characterized by SEM, FT-IR, elemental analysis, XRD, N2-BET and ICP. Effects of α, Pdα/1 dosage, reaction time and temperature on catalytic performances of Pdα/1 were investgated, using benzyl alcohol oxidation as the template reaction. The results showed that conversion of benzyl alcohol was 66.7% and selectivity of benzaldehyde was 92.9% under the optimum reaction conditions(Pd2/1 40 mg, reacted at 120 ℃ for 180 min). The catalytic performance of Pd2/1 remain stable after recycling for five times.
Keywords:doped nitrogen molecular sieve; Pd catalyst; benzyl alcohol oxidation; preparation; catalytic property
收稿日期:2015-05-11;
修订日期:2016-03-23
作者简介:王玉宝(1969-),男,汉族,山东聊城人,高级实验师,主要从事分子筛催化剂的研究。 E-mail: rabbit197968@sina.com
中图分类号:O614.82; TQ426.81
文献标志码:A
DOI:10.15952/j.cnki.cjsc.1005-1511.2016.05.15206
