近五年非酒精性脂肪肝运动疗法的研究进展
2016-05-11于洋朱琳胡敏
于洋,朱琳,胡敏
(广州体育学院 运动与健康系,广东 广州 510500)
近五年非酒精性脂肪肝运动疗法的研究进展
于洋,朱琳,胡敏
(广州体育学院 运动与健康系,广东 广州 510500)
非酒精性脂肪肝(NAFLD)是全球普遍流行的肝疾病,近年来呈低龄化发病趋势,与肥胖、糖尿病、高脂血、心脑血管疾病以及人们生活方式密切相关。目前临床上通常采用减轻患者体重,与肥胖、糖尿病等疾病同时治疗的方式,尚缺乏单一治疗NAFLD的方法。运动对NAFLD治疗的有效性已得到多数学者的认同,且相比于手术、药物等疗法更加经济、安全,被誉为NAFLD绿色疗法。以近五年来国内外研究文献为依据,总结不同运动方式、运动强度、运动持续时间对NAFLD治疗的作用。
运动;非酒精性脂肪肝;代谢疾病
非酒精性脂肪肝(Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD)是一种无过量饮酒史,肝细胞脂肪变性和脂肪贮积为特征的临床病理综合症,是肝病变为特征的代谢综合症,是全球较为普遍流行的肝疾病。西方国家NAFLD发病率为20%~50%[1,2],与肥胖增长率和静坐生活方式密切相关[3],肥胖或2型糖尿病患者中NAFLD发病率高达75%~100%[4,5]。近20年来亚洲国家NAFLD增长迅速且呈低龄化发病趋势,随着经济的快速发展,我国发达地区如上海、广州等地成人NAFLD患病率约为15%[6],已成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病。
1 NAFLD的自然发展过程
按照组织病理学变化NAFLD可发展成为单纯性脂肪肝、脂肪性肝炎(Nonalcohalic steatohepatitis, NASH)和脂肪性肝纤维化,最终可演变成肝硬化和肝癌(图1)。伴有肥胖、糖尿病、高脂血等其他代谢疾病的NAFLD患者,NAFLD发展成为NASH的几率加大;伴有腹部肥胖、高血压、胰岛素抵抗等NASH患者发展成为脂肪性肝纤维化的几率大于单纯性NASH患者。随着年龄的增长,脂肪性肝纤维化患者容易病变成为肝硬化,引发肝癌[7]。不仅如此,肝内铁蛋白含量增加、天门冬氨酸转氨酶(AST)与丙氨酸转氨酶(ALT)比高于0.8,也会增加肝纤维化转化为肝硬化的几率。另有研究指出,patatin样磷脂域3基因(PNPLA3)具有多态位点,其中I148M多态位点与血清甘油三酯、AST、ALT以及肝脂肪含量相关,对NAFLD发展起重要作用[8-11]。
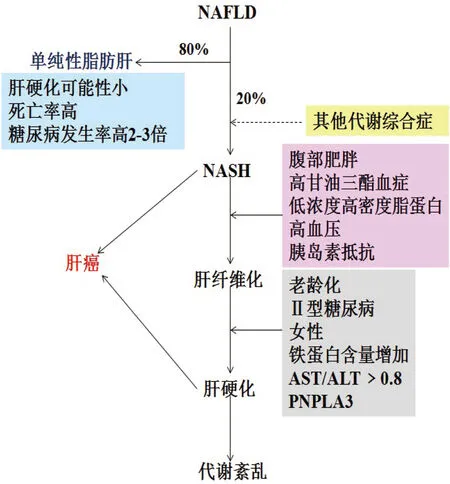
图1 非酒精性脂肪肝的自然发展过程
2 NAFLD的治疗
早期人们治疗NAFLD主要是防止心血管综合症和肝恶化引发的死亡[13]。随着研究的深入,人们发现NAFLD与肥胖、糖尿病、高脂血等代谢疾病密切相关,多采用治疗肥胖、糖尿病等手段同时治疗NAFLD,但却缺少仅针对NAFLD的治疗方法。减轻体重是NAFLD治疗的首要任务,因此临床上采用手术、药物以及内窥镜治疗方式减轻患者体重,从而达到治疗NAFLD的目的[12]。此外,2012年版美国非酒精性脂肪肝诊治指南、中华医学会肝病学分会发布的《非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指南(2010修订版)》和中华医学会内分泌学会制订的《非酒精性脂肪性肝病与相关代谢紊乱诊疗共识(2013版)》认为改变生活方式可以降低肝酶水平和改善肝脂肪病变[14-16]。对于非酒精性脂肪肝患者,减少静坐时间,增加运动时可有效防治NAFLD[17,18]。与手术、药物等治疗方式相比,运动是更加经济、安全的绿色疗法,同时还可以治疗肥胖等其他代谢性疾病。以下主要阐述不同运动方式、运动强度以及运动持续时间对NAFLD的治疗作用。
2.1 运动方式
2.1.1 有氧运动
有氧运动和干预生活方式引起的体重减轻是治疗NAFLD的重要方法。Sullivan等让18位NAFLD患者以45%~55%最大耗氧量进行上肢运动,每周5次,每次30~60 min,共运动16周。运动组和对照组均不限制饮食。研究结果发现,虽然运动组体重没有减轻,但是其肝内TG含量明显减少,同时ALT降低[19]。Oh等将有氧运动结合饮食管理与单纯饮食控制进行比较,52名NAFLD伴肥胖患者以大于40%最大耗氧量进行走步或慢跑运动,每周3次,每次90 min,根据营养师建议患者每天摄入1680 kcal食物。结果发现,运动结合饮食控制组血清炎症标记物、肝脂肪变性、皮下脂肪以及IR均较单纯控制饮食组得到明显改善[20]。上述表明,有氧运动可有效治疗NAFLD。
2.1.2 无氧运动(抗阻力运动)
有氧运动虽然能够有效治疗NAFLD,但对于心肺功能低下、体重过大、缺少运动耐力的NAFLD患者来说,他们不适合进行有氧运动,可选择抗阻力运动方式。Hallsworth等人使具有静坐习惯的NAFLD患者每天进行约1 h的剧烈运动,但不干预他们的饮食。8周后发现,虽然患者体重没有变化,但肝脂肪变性明显降低,血糖和脂质氧化得到明显改善[21]。Zelber-Sagi等利用超声和肝肾指数检测抗阻力运动对NAFLD的影响发现,抗阻力运动3个月后肝肾指数下降11%,血清铁蛋白和胆固醇也明显降低[22]。上述表明,抗阻力运动可有效治疗NAFLD,对于不适宜有氧运动NAFLD患者可采用抗阻力运动方式治疗。
2.1.3 混合运动
对于重度肥胖者、丧失运动能力以及年纪较大的NAFLD患者来说,有氧或抗阻力运动都不适宜,可选择混合运动方式。混合运动包括肌肉收缩和电刺激。Kawaguchi等人采用下肢屈伸运动形式,患者无需站立,在床上也可进行训练。研究结果显示,35位患者经过12周(每周2次)运动后,体脂肪、血清ALT、肝脂肪变性以及IR都明显降低,但对血清脂质和基础代谢率无显著影响[23]。
2.1.4 加速运动
对于不喜欢运动的NAFLD患者还可以采用加速运动方式。加速运动是通过振动方式增加作用于骨骼肌物理刺激的加速度,是一种新型训练方式。受试者既可以通过维持姿势也可以通过力量运动刺激肌肉纤维,增加肌肉耐力和长度。Oh等人选择18名NAFLD伴肥胖受试者,进行为期12周的加速运动训练,期间不限制饮食。管理结束后发现,受试者的胞内脂质和脂质含量明显得到改善,肝内脂肪变性下降了8.7%,然而肝酶无显著变化[24]。
综上所述,根据NAFLD患者的身体条件,选择适合自己的运动方式可实现治疗NAFLD的目的。不仅如此,优化运动强度和运动持续时间将更有助于NAFLD的治疗。
2.2 运动强度
Oh等研究者不仅发现加速运动可改善肝脂肪变性,还指出中度到剧烈运动有益于NAFLD患者的抗氧化和抗炎作用[24,25]。根据不同强度的加速运动,研究者将NAFLD患者分为3组:每周运动少于150 min组,每周运动150~250 min组以及每周运动超过250 min组。各组均运动管理12周,并限制饮食每天摄入1680 kcal食物。结果发现,各组受试者体重和身体质量指数(BMI)均降低;其中每周运动少于150 min组体重减少12.4%,肝脂肪变性减少。每周运动超过250 min组除了肝脂肪变性减少外,铁蛋白和炎症标记物含量也降低。Kistler等人研究指出,中度到剧烈运动可减轻肝纤维化和脂肪性肝炎[26]。此外,他们还认为运动强度对NAFLD的治疗作用优于运动时间和运动量。另有学者认为低强度运动可以有效改善人体成分,降低体脂含量及体脂百分比,降低血脂[27,28]。
2.3 运动持续时间
为了探寻运动持续时间对NAFLD的治疗作用,Haus等人进行了一周短期的运动管理。他们筛选17名NAFLD伴肥胖和17名NAFLD受试者,指导受试者进行7天走步或慢跑,每天以80%~85%最大心率运动50~60 min。疗程结束核磁共振检测发现,7天运动后受试者肝不饱和脂肪酸含量和血清脂联素含量增加,抗炎因子调控脂质氧化[29]。结果表明,短期有氧运动同样对NAFLD改善其作用。
3 结论
近年来随着经济快速发展,我国人民生活质量大幅提高,生活方式也随之发生变化,高热量饮食、久坐和高强度工作状态以及运动或身体锻炼减少,这些往往引发代谢性疾病。目前NAFLD已然成为与肥胖、糖尿病、高脂血等密切相关的代谢性疾病,成为仅次于病毒性肝炎的第二大肝病。对于大多数NAFLD患者来说病情是可以逆转的。迄今为止,除手术、药物等治疗方式外,运动疗法的有效性已得到很多学者的认可。运动对NAFLD的治疗具有综合性、全面性的治疗特点[30],且相对于手术、药物等治疗来说更加经济、安全,同时还可治疗伴有肥胖、高脂血等其他代谢疾病。由于运动疗法具有个性化,因此运动处方的设计和制定,优化运动强度和运动持续时间等仍需进一步深入研究。
[1] Browning J D,Szczepaniak L S,Dobbins R,et al. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity[J]. Hepatology,2004,40(6):1387—1395.
[2] Bedogni G,Miglioli L,Masutti F,et al. Incidence and natural course of fatty liver in the general population: the Dionysos study[J]. Hepatology,2007,46(5):1387—1391.
[3] Williams C D,Stengel J,Asike M I,et al. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middleaged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: a prospective study[J]. Gastroenterology,2011,140(1):124—131.
[4] Sheth S G,Gordon F D,Chopra S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Ann Intern Med,1997,126(2):137—145.
[5] Ludwig J,Viggiano T R,McGill D,B,et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease[J]. Mayo Clin Proc,1980,55(7):434—438.
[6] 王丽娟,孙苗芳.非酒精性脂肪肝病运动疗法的研究进展[J].中华护理杂志,2014,49(5):588—592.
[7] Argo C K,Northup P G,Al-Osaimi A M,et al. Systematic review of risk factors for fibrosis progression in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol,2009,51(2):371—379.
[8] Kotronen A,Johansson L E,Johansson L M,et al. A common variant in PNPLA3, which encodes adiponutrin, is associated with liver fat content in humans[J]. Diabetologia,2009,52(6):1056—1560.
[9] Wang C W,Lin H Y,Shin S J,et al. The PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism is associated with insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a normoglycaemic population[J]. Liver Int,2011,31(9):1326—1331.
[10] Kollerits B,Coassin S,Kiechl S,et al. A common variant in the adiponutrin gene influences liver enzyme values[J]. J Med Genet,2010,47(2):116—119.

[12] Popov V B,Lim J K. Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Medical, Surgical, and Endoscopic Weight Loss[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol,2015,3(3):230—238.
[13] Whitsett M,VanWagner L B. Physical activity as a treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review[J]. World J Hepatol,2015,7(16):2041—2052.
[14] Chalasani N,Younossi Z,Lavine J E,et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2012,107(6):811—826.
[15] 范建高. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指南(2010年修订版)[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2010,19(6):483—487.
[16] Gao X,Fan J G. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and related metabolic disorders: consensus by the Study Group of Liver and Metabolism, Chinese Society of Endocrinology[J]. J Diabetes,2013,5(4):406—415.
[17] Takahashi Y,Sugimoto K,Inui H,et al. Current pharmacological therapies for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2015,21(13):3777—3785.
[18] Chalasani N,Younossi Z,Lavine J E,et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology[J]. Gastroenterology,2012,142(7):1592—1609.
[19] Sullivan S,Kirk E P,Mittendorfer B,et al. Randomized trial of exercise effect on intrahepatic triglyceride content and lipid kinetics in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Hepatology,2012,55(6):1738—1745.
[20] Oh S,Tanaka K,Tsujimoto T,et al. Regular exercise coupled to diet regimen accelerates reduction of hepatic steatosis and associated pathological conditions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Metab Syndr Relat Disord,2014,12(5):290—298.
[21] Hallsworth K,Fattakhova G,Hollingsworth K,et al. Resistance exercise improves liver lipid, fat oxidation and glucose control in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease independent of weight loss[J]. J Hepatol,2011(54):S337.
[22] Zelber-Sagi S,Buch A,Yeshua H,et al. Effect of resistance training on non-alcoholic fattyliver disease a randomized-clinical trial [J]. World J Gastroenterol,2014,20(15):4382—4392.
[23] Kawaguchi T,Shiba N,Maeda T,et al. Hybrid training of voluntary and electrical muscle contractions reduces steatosis, insulin resistance, and IL-6 levels in patients with NAFLD: a pilot study[J]. J Gastroenterol,2011,46(6):746—757.
[24] Oh S,Shida T,Sawai A,et al. Acceleration training for managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a pilot study[J]. Ther Clin Risk Manag,2014(10):925—936.
[25] Oh S,Shida T,Yamagishi K,et al. Moderate to vigorous physical activity volume is an important factor for managing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a retrospective study[J]. Hepatology,2015,61(4):1205—1215.
[26] Kistler K D,Brunt E M,Clark J M,et al. Physical activity recommendations, exercise intensity, and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Am J Gastroenterol,2011,106(3):460—468.
[27] Wang Z Z. The research of the women aged 61~65 years suitable exercise intensity [D].Beijing Sport University,2002.
[28] An N,Wang S T,Wang A L,et al. Research on moderate intensity of middle and elder age woman′s physical exercise[J].China Sport Science,2005,25(8):62—66.
[29] Haus J M,Solomon T P,Kelly K R,et al. Improved hepatic lipid composition following short-term exercise in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J ClinEndocrinol Metab,2013,98(7):E1181—E1188.
[30] 郑永才,陈亮,路富林,等.运动疗法治疗非酒精性脂肪肝的临床疗效观察[J].肝脏,2015,20(1):51—53.
Green Therapy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Recent Five Years
YU Yang, ZHU Lin, HU Min
(Key Lab of Exercise Science and Health Promotion, Department of Sports and Health,Guangzhou Institute of Physical Education, Guangzhou 510500, China)
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a overall prevalence hepatic disease. The incidence of NAFLD is increased in recent years with the age decreased. It is associated with obesity, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease and lifestyle. Currently, numerous pharmacologic agents can be used to treat the metabolic derangements such as obesity and diabetes mellitus that often coexist in NAFLD, pharmacologic treatments for NAFLD itself are lacking. Many researchers indicate that exercise is an effective treatment for NAFLD. Exercise is known as green therapy, and it is more secure and inexpensive compared with surgery and pharmacologic therapy. The article summarized the effect of various exercise mode, intensity and duration on NAFLD in recent five years.
exercise; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; metabolic disease
2016-07-12
于洋(1981—),女,黑龙江佳木斯人,讲师。研究方向:运动生理、运动与体质健康。
G804.55
A
1671-1300(2016)04-0101-04
