颅脑损伤患者外周血miRNA-124与Treg细胞和IL-10表达的关系
2016-04-11周贵勤陈新寿师宁田冰锋
周贵勤,陈新寿,师宁,田冰锋
颅脑损伤患者外周血miRNA-124与Treg细胞和IL-10表达的关系
周贵勤1,陈新寿1,师宁2,田冰锋3
目的:研究颅脑损伤后外周血小RNA(miRNA)-124与调节性T细胞(Treg)及白细胞介素-10(IL-10)表达的关系,探讨miRNA-124在颅脑损伤中的作用及其机制。方法:纳入颅脑损伤患者109例,根据GCS评分分为轻度损伤组35例,中度损伤组45例,重度损伤组29例,同时纳入正常体检者20例为对照组。受伤后24 h分别采集各组的外周静脉血,采用流式细胞术检测Treg细胞的表达;实时荧光定量聚合酶联反应检测miRNA-124表达;酶联免疫吸附试验检测IL-10的水平。结果:各组颅脑损伤患者外周血Treg比例、miR-124表达及IL-10水平均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),中、重度颅脑损伤组高于轻度损伤组(P<0.05),重度组高于中度组(P<0.05);重度损伤组患者外周血miR-124和Treg比例呈正相关。结论:颅脑损伤后,miRNA-124可能参与对Treg细胞增殖的调节,调控炎症反应。
颅脑创伤;微小RNA-124;调节性T淋巴细胞;白细胞介素-10
颅脑损伤过程中,一些特异生物化学标志物出现改变[1,2]。有研究表明,小RNA(microRNAs,miRNAs)在血浆中的表达与颅脑损伤发生发展有一定的相关[3-5]。本研究旨在研究miRNA-124和颅脑损伤的关系,并通过测定和分析调节性T细胞(T regulatory cells,Tregs)和白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-10,探究miR-124在颅脑损伤患者外周血肿的作用机制。miR-124为脑组织特异性的miRNA,而IL-10是一种多功能负性调节因子,主要辅助T细胞(helper T cell,Th)2细胞和单核巨噬细胞产生,相关标志物的选择,旨在阐明炎症反应通过特异性的miRNA改变,影响颅脑损伤康复过程的作用。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2008年3月至2014年3月我院神经外科收治的颅脑外伤急诊非手术患者109例。排除标准:临床资料不完善;年龄<18岁或>75岁;曾经有颅脑损伤史;缺血性心脏病、严重肝肾功能不全、各种急慢性感染性疾病及其他应激、甲状腺功能异常、2型糖尿病等疾病;血管畸形、药物、肿瘤、血液系统疾病、颅脑损伤诊断不明。所有纳入对象均接受身高、尿粪常规、肝肾功能、血脂、血糖及常规心电图、胸片、心脏彩超等检查。根据患者格拉斯哥昏迷量表(Glasgow coma scale,GCS)评分,分为轻度损伤组(GCS评分13~15分)35例,中度损伤组(GCS评分9~12分)45例,重度损伤组(GCS评分3~8分)29例。同时纳入20例正常体检者为对照组。4组一般资料差异无统计学意义,具有可比性(P>0.05);颅脑损伤各组GCS评分低于对照组,重度损伤组GCS评分低于轻、中度损伤组(P<0.05),见表1。

表14 组患者一般情况及GCS评分比较
1.2 方法
1.2.1 外周血T淋巴细胞亚群测定Ficoll密度梯度法分离出外周血单个核细胞(PBMC),取20 μL细胞悬液加20 μL锥虫蓝;调节细胞密度为1×106/mL,加入1mLFoxp3固定/破膜液,充分混匀后室温孵育20 min;加10 μL抗人Foxp3抗体混匀后暗处孵育30 min,流式细胞仪检测。仪器及试剂盒购自美国BD公司。采用CellquestPro软件进行分析。
1.2.2miRNA-124的检测 于发病24 h抽取静脉血10 mL,肝素抗凝,采用TRIzo提取总RNA,紫光分光光度计检测其浓度。并反转录合成cDNA于-20℃保存备用,用胶回收法纯化DNA片段作为标准品,采用荧光RT-PCR法测定外周血中单个核细胞中miRNA-124的表达量。采用标准曲线法计算miRNA表达量,并计算其相对表达量(β-actin校正值)。
1.2.3 IL-10的检测 将已分离的血浆标本从冰箱取出置于室温下,待溶解后离心取上清,应用ELIAS检测血清中IL-10的含量。在450 nm处测吸光度(A)值,所有测得值减去空白值后再行计算。通过绘制标准曲线,计算各样本IL-10的含量。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS18.0软件处理数据,计量资料以(χ±s)表示,组间比较采用方差分析,计数资料以率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验,Pearson作相关性分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
各组颅脑损伤患者外周血Treg比例、miR-124表达及IL-10水平均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),中、重度损伤组高于轻度损伤组(P<0.05),重度组高于中度组(P<0.05),见表2。
Pearson相关分析提示重度损伤组患者外周血miR-124和Treg比例呈正相关(R=0.64,P=0.006);miR-124和IL-10呈正相关(R=0.70,P=0.001),而轻、中度颅脑损伤患者无明显相关关系,见图1。
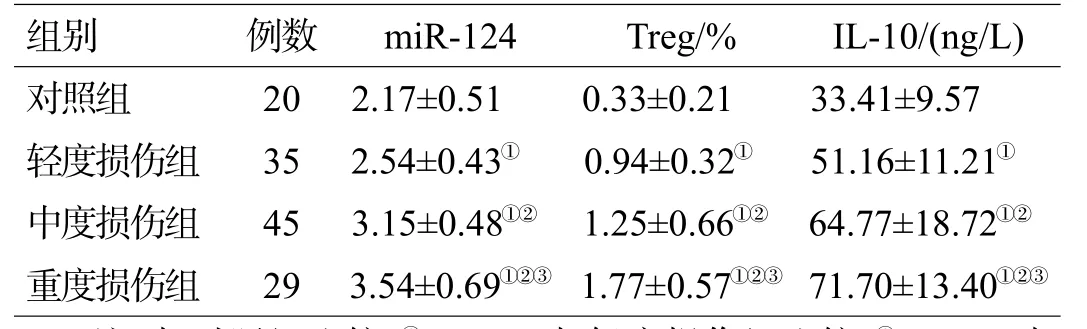
表2 不同组别患者血清Treg比例、miR-124及IL-10表达(χ±s)
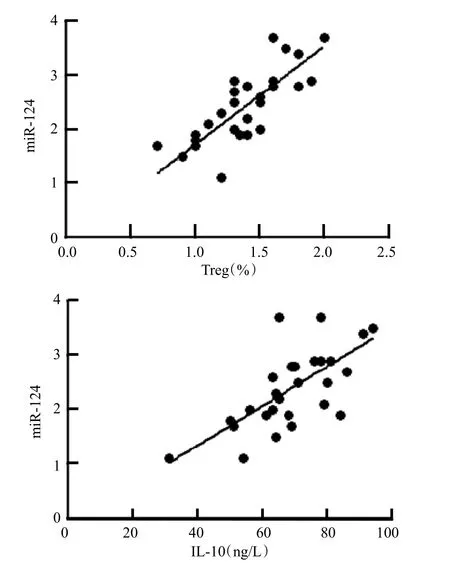
图1 重度颅脑损伤患者外周血miR-124和Treg、IL-10水平Pearson相关分析
3 讨论
miRNAs是在真核生物中发现的一类内源性具有调控功能的非编码RNA,其大小长约20~25个核苷酸。miRNA与个体发育、机体代谢及多种疾病的发生发展密切相关[6-9]。颅脑损伤后血浆中miRNA出现改变,其可能的机制[10-12]:①受伤组织直接释放或其它组织反应性释放miRNA进入血液,其中miR-124为脑组织特异性的miRNA。miR-124能调节Th1/Th17细胞的分化,对活化的T细胞分泌的细胞因子也有调节作用。②miR-124可通过靶基因调控AT1R及转录因子,改善炎性损伤和内皮细胞迁移期体内miR-124表达升高,此过程能促进机体释放促炎因子、特异性抗体和产生效应性T细胞。但miR-124过度激活可能导致促炎因子的爆发性释放,免疫细胞过度活化,同时miR-124作用于Treg细胞,参与免疫抑制。
IL-10是一种多功能负性调节因子,主要由Th2细胞和单核巨噬细胞产生,能抑制前炎症细胞因子产生;抑制MHC-II类分子和B-7分子的表达;抑制T细胞合成IL-2、IFN-γ等细胞因子;可促进B细胞分化增殖。IL-10在严重感染性疾病、肿瘤及自身免疫性疾病和移植免疫等多种疾病的发生过程中发挥了重要的作用[13]。IL-10可抑制细胞免疫应答,其机制可能是通过抑制活化的T细胞产生细胞因子,特别是抑制TH1细胞产生IL-2和IFN-γ等细胞因子。因此,IL-10曾称为细胞因子合成抑制因子。本研究验证了其在随着颅脑创伤程度加重,在患者外周血中出现下降趋势,其机制可能是通过负反馈机制抑制颅脑损伤患者血清炎症反应[14,15]。因此,我们认为调控炎症反应在颅脑损伤修复过程中的作用值得进一步研究。
本研究表明miR-124在脑损伤组里明显升高,其在重度颅脑损伤患者的Treg表达和IL-10呈正相关,但在轻度和中度颅脑损伤康复过程中并无明显相关关系。这一结果证实了炎症反应在重度颅脑损伤后修复过程中的作用,并且证实了miR-124可能通过作用于Treg细胞,调节颅内炎症反应,这种调节作用可能和患者脑损伤的严重程度密切相关。随着病情发展,当miR-124调节Treg的增殖加强,抗炎反应失控性增强,抗炎反应占主导地位[16]。此时,患者可能处于免疫反应亢进、免疫抑制和促炎、抗炎反应的动态演变之中。由于多种因素的共同作用,患者体内表现出一种复杂的免疫紊乱和动态失衡状态[17-18]。同时,还有研究表明miR-124还具有调控急性炎症及Treg增殖的双重作用,起到一定的免疫抑制作用[19-20]。
综上,miR-124可能是颅脑损伤患者免疫失衡调控网络中的重要位点,但具体调控机制和其影响因素仍不清楚。本研究结果还证实,颅脑损伤后的炎症反应与患者病情严重程度密切相关,miR-124有潜力成为颅脑损伤预后的预测指标。
[1]Hu T,Zhou FJ,Chang YF,et al.miR21 is Associated with the Cognitive Improvement Following Voluntary Running Wheel Exercise in TBIMice[J].J Mol Neurosci,2015,57:114-122.
[2]Rodriguez A,Chuang DC,Chen KT,et al.Comparative study of single-,double-,and triple-nerve transfer to a common target:experimental study of rat brachial plexus[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2011,127:1155-1162.
[3]Schenck TL,Stewart J,Lin S,et al.Anatomical and histomorphometric observations on the transfer of the anterior interosseous nerve to the deep branch of the ulnar nerve[J].J Hand Surg Eur Vol,2015,40:591-596.
[4]亢晓燕,李耀华,陈芳莲,等.大鼠脑创伤后损伤区miRNA-21的差异表达及干预研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013,6:171-147.
[5]Yang JW,Hu ZP.Neuroprotective effects of atorvastatin against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J].Neural Regen Res,2015,10:1239-1244.
[6]Khurana S,Gupta S,Bhalla H,et al.Comparison of anti-inflammatory effect of atorvastatin with rosuvastatin in patients of acute coronary syndrome[J].J Pharmacol Pharmacother,2015,6:130-135.
[7]Potey C,Ouk T,Petrault O,et al.Early treatment with atorvastatin exerts parenchymal and vascular protective effects in experimental cerebral ischaemia[J].Br J Pharmacol,2015,172:5188-5198.
[8]Kumar N,Chaurasia S,Patel RR,et al.Atorvastatin calcium encapsulated eudragit nanoparticles with enhanced oral bioavailability,safety and efficacy profile[J].Pharm Dev Technol,2015,11:1-12.
[9]An LP,An SK,Wei XH,et al.Atorvastatin improves cardiac function ofratswith chronic cardiac failure via inhibiting Rac1/P47phox/ P67phox-mediated ROS release[J].Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2015,19: 3940-3946.
[10]Dalli J,Chiang N,Serhan CN.Elucidation of novel 13-series resolvins that increase with atorvastatin and clear infections[J].Nat Med, 2015,21:1071-1075.
[11]Ma Q,Zhou Y,Zhai G,et al.Meta-Analysis Comparing Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin in Reducing Concentration of C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Hyperlipidemia[J].Angiology,2015,13:15-17.
[12]Hsue PY,Bittner VA,Betteridge J,et al.Impact of female sex on lipid lowering,clinical outcomes,and adverse effects in atorvastatin trials[J]. Am J Cardiol,2015,115:447-453.
[13]Gao C,Du H,Hua Y,et al.Role of red blood cell lysis and iron in hydrocephalus after intraventricular hemorrhage[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2014,34:1070-1075.
[14]Yi R,Xiao-Ping G,Hui L.Atorvastatin prevents angiotensin II-induced high permeability of human arterial endothelial cell monolayers via ROCK signaling pathway[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2015,459: 94-99.
[15]Yang JW,Hu ZP.Neuroprotective effects of atorvastatin against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through the inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J].Neural Regen Res,2015,10:1239-1244.
[16]Khurana S,Gupta S,Bhalla H,et al.Comparison of anti-inflammatory effect of atorvastatin with rosuvastatin in patients of acute coronary syndrome[J].J Pharmacol Pharmacother,2015,6:130-135.
[17]雷平,张建宁,张亮,等.利用miRNA芯片筛选大鼠颅脑创伤后皮层差异表达的miRNA[J].中华神经外科杂志,2009,25:1138-1141.
[18]李爱林,王琼,只达石.血浆miRNA-124和miRNA-765作为重型颅脑创伤患者生物标记物的研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013,12: 125-127.
[19]Potey C,Ouk T,Petrault O,et al.Early treatment with atorvastatin exerts parenchymal and vascular protective effects in experimental cerebral ischaemia[J].Br J Pharmacol,2015,172:5188-5198.
[20]Dalli J,Chiang N,Serhan CN.Elucidation of novel 13-series resolvins that increase with atorvastatin and clear infections[J].Nat Med, 2015,21:1071-1075.
[21]Hsue PY,Bittner VA,Betteridge J,et al.Impact of female sex on lipid lowering,clinical outcomes,and adverse effects in atorvastatin trials[J]. Am J Cardiol,2015,115:447-453.
(本文编辑:唐颖馨)
Relationship among MiRNA-124,Treg Cells and IL-10 expression in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury
ZHOUGui-qin1,CHENXin-shou1,SHINing2,TIANBing-feng3.1.DepartmentofNeurosurgery,ForestIndustryProfessionalHospital,Shanxi716000,China;2.Departmentof Neurosurgery,AffiliatedHospitalofYanAnuniversity,Shanxi716000,China;3.DepartmentofNeurosurgery, HanzhongCentral Hospital,Hanzhong723000
Objective:To evaluate the relationship among microRNA(miRNA)-124,T regulatory cells(Treg) and interleukin(IL)-10 levels in the peripheral blood of patient with traumatic brain injury.Methods:One hundred and nine patients with traumatic brain injury were enrolled and divided into mild group(n=35),moderate group(n=45)and severe group(n=29)according to their Glasgow coma scale(GCS)scores.Twenty healthy volunteers were enrolled into controls.The level of miRNA-124,Treg cells and IL-10 were calculated by RT-PCR, flow cytometry and ELISA respectively.Results:The levels of miRNA-124,Treg cells and IL-10 in the mild, moderate and severe groups were significantly higher than those in the controls(P<0.05).The levels of miRNA-124,Treg cells and IL-10 in the mild group were lower than those in the moderate and severe groups(P< 0.05).In the severe group,miRNA-124 is positively correlated with Treg cell and IL-10.Conclusion:miRNA-124 could regulate Treg cells and the inflammation response which play an important role in the recovery process of traumatic brain injury.
traumatic brain injury;microRNA-124;T regulatory cells;interleukin(IL)-10
R741;R741.02
A DOI 10.16780/j.cnki.sjssgncj.2016.06.016
1.陕西省森林工业职业医院神经外科西安710031
2.延安大学附属医院神经科陕西 延安716000
3.汉中市中心医院神经外科汉中 723000
2016-01-20
田冰锋bingfeng98@sihu. com
