TO-DO LIST FOR 2016
2016-03-28
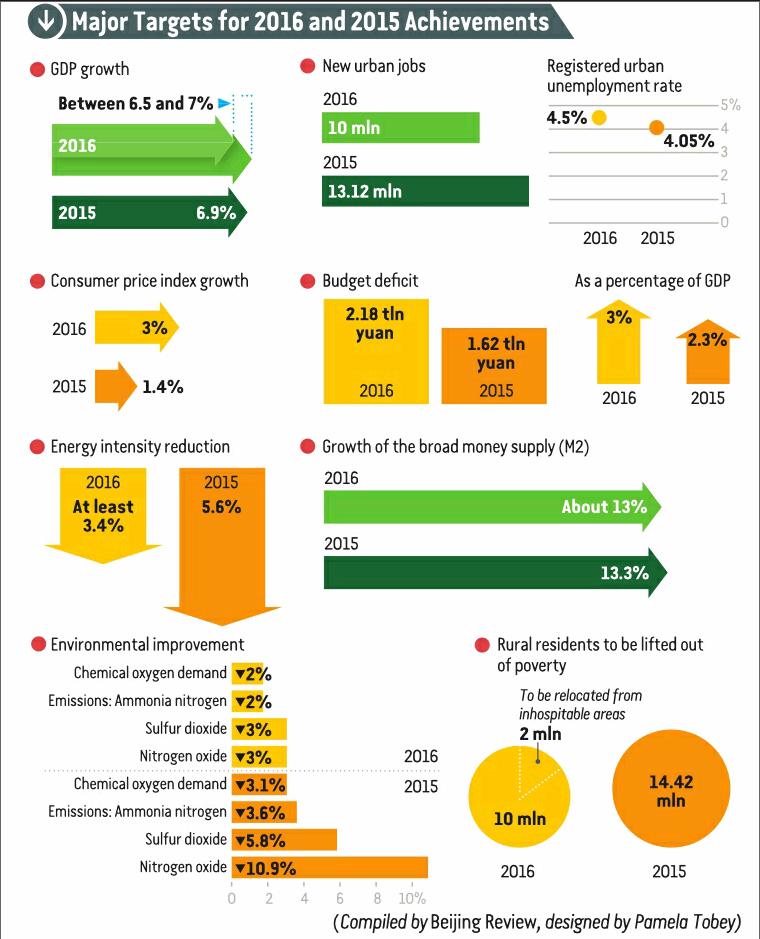
In his Government Work Report de- livered at the opening of the Fourth Session of the 12th National Peoples Congress on March 5, Premier Li Keqiang said that China will face tough challenges in its development this year. He listed the following measures in the governments efforts to boost development.
Macroeconomic Policies
—Implement a more proactive fiscal policy;
—Replace business tax with value-added tax in all sectors;
—Pursue a prudent monetary policy;
—Move faster in the reform efforts to improve the modern financial regulatory system;
—Keep the renminbi exchange rate generally stable at an appropriate and balanced level;
—Move forward with the reform of the stock and bond markets.
Supply-side Structural Reform
—Reduce the number of matters that are subject to government review;
—Pilot a blacklist [that specifies off-limits areas] for market access;
—Implement the strategy of innovationdriven development;
—Encourage business startups and innovation;
—Strengthen the protection of intellectual property rights;
—Address overcapacity in the steel and coal industries;
—Improve the performance of stateowned enterprises (SOEs);
—Diversify types of SOE equity;
—Protect the property rights of entities under all forms of ownership;
—Energize the non-public sector.
Domestic Demand
—Support the growth of consumption in elderly healthcare, health, housekeeping, education, training, cultural and sports services;
—Strengthen the growth of emerging areas of consumption such as information products and services, smart homes and personalized fashion;
—Cut tariffs on some consumer goods;
—Increase the number of duty-free stores;
—Speed up tourism development;
—Invest more than 800 billion yuan ($123 billion) in railway construction projects;
—Invest 1.65 trillion yuan ($254 billion) in road construction projects;
—Start construction on 20 water conservancy projects;
—Develop hydropower, nuclear power, ultrahigh-voltage power transmission, smart grids, pipelines for oil and gas transmission and urban rail transit;
—Improve the public-private partnership models to stimulate private investment;
—Advance new urbanization: Grant urban residency to more people registered to rural households, reform the household registration system, and implement the residence card system.
Agriculture and Rural Income
—Speed up structural adjustments in agriculture;
—Reduce excess stockpiles of food;
—Promote the development of suitably scaled-up agricultural operations in diversified forms;
—Improve public services in rural areas;
—Combat poverty.
Opening Up
—Move ahead with the initiative to build the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21stCentury Maritime Silk Road;
—Promote the innovation-driven development of foreign trade;
—Launch trials in the area of trade in services;
—Adopt a more proactive import policy: Increase the import of advanced technology and equipment, key spare parts and components, as well as energy and raw materials in short supply in China;
—Continue to relax market access restrictions on investment: Further open up the service sector and the general manufacturing sector, and simplify procedures for establishing overseas-funded enterprises;
—Establish more pilot free trade zones;
—Achieve greater industrial-capacity cooperation with other countries;
—Accelerate the implementation of the free trade area strategy;
—Negotiate on the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement;
—Negotiate on the China-Japan-ROK(Republic of Korea) free trade agreement;
—Negotiate on investment agreements between China and the United States and between China and the EU.
Green Development
—Take strong measures against air and water pollution;
—Develop the energy conservation and environmental protection industries;
—Continue to develop ecological barriers;
—Improve mechanisms which compensate for ecological conservation efforts.
Peoples Wellbeing
—Pursue a more proactive employment policy and encourage business startups that create employment;
—Promote fairer access to quality education;
—Allocate a greater share of funds for public education to central and western regions as well as to remote and poor areas;
—Unify the urban and rural mechanisms for funding compulsory education;
—Advance the coordinated reform of medical services, medical insurance and the medicine industry;
—Realize complete coverage of the serious disease insurance scheme;
—Build an extensive and tightly woven social safety net;
—Strengthen and develop new forms of social governance.
