芋螺毒素的毒理学和药理学研究
2016-02-15戴秋云
戴秋云
(军事医学科学院生物工程研究所,北京 100071)
芋螺毒素的毒理学和药理学研究
戴秋云
(军事医学科学院生物工程研究所,北京 100071)
戴秋云,博士,军事医学科学院生物工程研究所研究员,博士生导师。中国生物毒素专业委员会常务委员,海洋生物化学与分子生物学专业委员会理事。主要从事芋螺毒素的基因克隆、毒素分离、结构、功能及药物开发研究。已发现新芋螺毒素序列400余个,测定了7个毒素的溶液结构,发现多个芋螺毒素的新功能及多个芋螺毒素的新框架,其中一个作用于N-型钙通道的芋螺多肽SO-3已完成临床前研究,正在申报临床试验批件。另一个I类抗病毒药物获军特药临床批件。在PNAS,JACS,JBC,J MolBiol,Sci Rep,Neurophamarcology和J Virol等国内外学术刊物上发表论文120余篇,参编专著2部,获军队科技进步二等奖2项,获授权国家发明专利16项。
芋螺毒素由芋螺毒液管和毒囊内壁的毒腺所分泌,多数由12~40个氨基酸组成,富含二硫键。其多变的一级序列、特异二硫键配对方式和特殊修饰氨基酸与陆生动物分泌的多肽或蛋白质显著不同,作用靶点涵盖钠、钾和钙离子通道等及多种膜受体。根据芋螺毒素保守的信号肽序列及半胱氨酸框架,芋螺毒素分为A,M,O,P,S,T,I,V,Y,J,D,C和L等20多个超家族,根据药理学作用靶点,其进一步可分为α、μ、ω、κ、δ、ψ、σ、ρ、γ、加压素、惊厥剂和睡眠肽等药理家族。本文着重介绍了芋螺毒素的分类与多样性,简要总结了作用于烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体、钙、钠离子通道和N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体的几类芋螺毒素的毒理学和药理学研究进展。这些毒素有的毒性很高,有的已发展为药物或正在开发中,一些毒素已成为神经药理学的强大研究工具。期望该综述对从事毒素或相关神经生物学的研究者有所裨益。
芋螺毒素;毒理学;药理学;离子通道;乙酰胆碱受体;天冬氨酸受体
芋螺属腹足纲软体动物,全世界约有500种,遍布世界各暖海区[1]。我国有芋螺80余种,主要分布在西沙群岛、海南岛及台湾海域等热带海洋浅水区[2]。芋螺毒素由芋螺毒液管和毒囊内壁的毒腺所分泌,每种芋螺的毒液中含50~200个活性多肽,不同品种芋螺所含的活性肽各不相同,即使同种芋螺因海域不同,其毒素成分也可存在差异,理论上估计约存在5万多种不同活性的多肽[3]。芋螺毒素多数由12~40个氨基酸组成,富含二硫键,包括了迄今为止最小的神经毒素。其多变的一级序列(如Cys排列)、特异二硫键配对方式和特殊修饰氨基酸与陆生动物分泌的多肽或蛋白质显著不同,对发展多肽结构理论很有意义。它们虽然分子质量小,但活性及选择性高,能特异性作用于乙酰胆碱受体、其他神经递质的各种受体亚型及钠、钾和钙等多种离子通道,对发展神经生物学和新型靶向特异性药物十分重要。
1 芋螺毒素的分类和结构特征
根据芋螺食性的不同可分为食鱼、食虫和食螺3种。其中,食虫芋螺数量最多,占全部芋螺种类的70%左右;其次是食软体动物芋螺。食鱼芋螺的毒性最大。芋螺毒素由含70~120个氨基酸残基的前体肽加工而来,前体肽含信号肽、Pro区及成熟肽区。成熟肽一般含13~46个氨基酸及多对二硫键,同一超家族的芋螺毒素信号肽保守,成熟肽则超变异,存在多种陆生毒素不常见的修饰,如D-氨基酸和溴化等。根据芋螺毒素保守的信号肽序列及二硫键骨架,将芋螺毒素分为A,M,O,P,S,T,I,V,Y,J,D,C和L等20多个超家族[4],再根据其药理学作用靶点,进一步可分为α、μ、ω、κ、δ、ψ、σ、ρ、γ、加压素、惊厥剂和睡眠肽等药理家族。目前发现的芋螺毒素主要超家族及半胱氨酸框架见表1[1,4-11]。
芋螺毒素的半胱氨酸框架(目前超过26种)及二硫键配对的多样性导致其结构多样性,显著高于其他动物毒素,如蛇毒、蝎毒和蜘蛛毒等。这里仅以M家族毒素为例说明结构多样性(图1),该家族毒素目前发现9个半胱氨酸框架[4,12-15],其中框架Ⅲ(CCX4-6CX4-5CX1-5CC,数字代表氨基酸残基数目)的第4和第5个半胱氨酸之间的非半胱氨酸残基数目不同,可将其进一步分为5个分支M-1~M-5,这些亚家族的二硫键连接方式有些不同或作用靶点有区别。目前,已确定M-4、M-5及框架XVI毒素的作用靶点,其他有待测定。
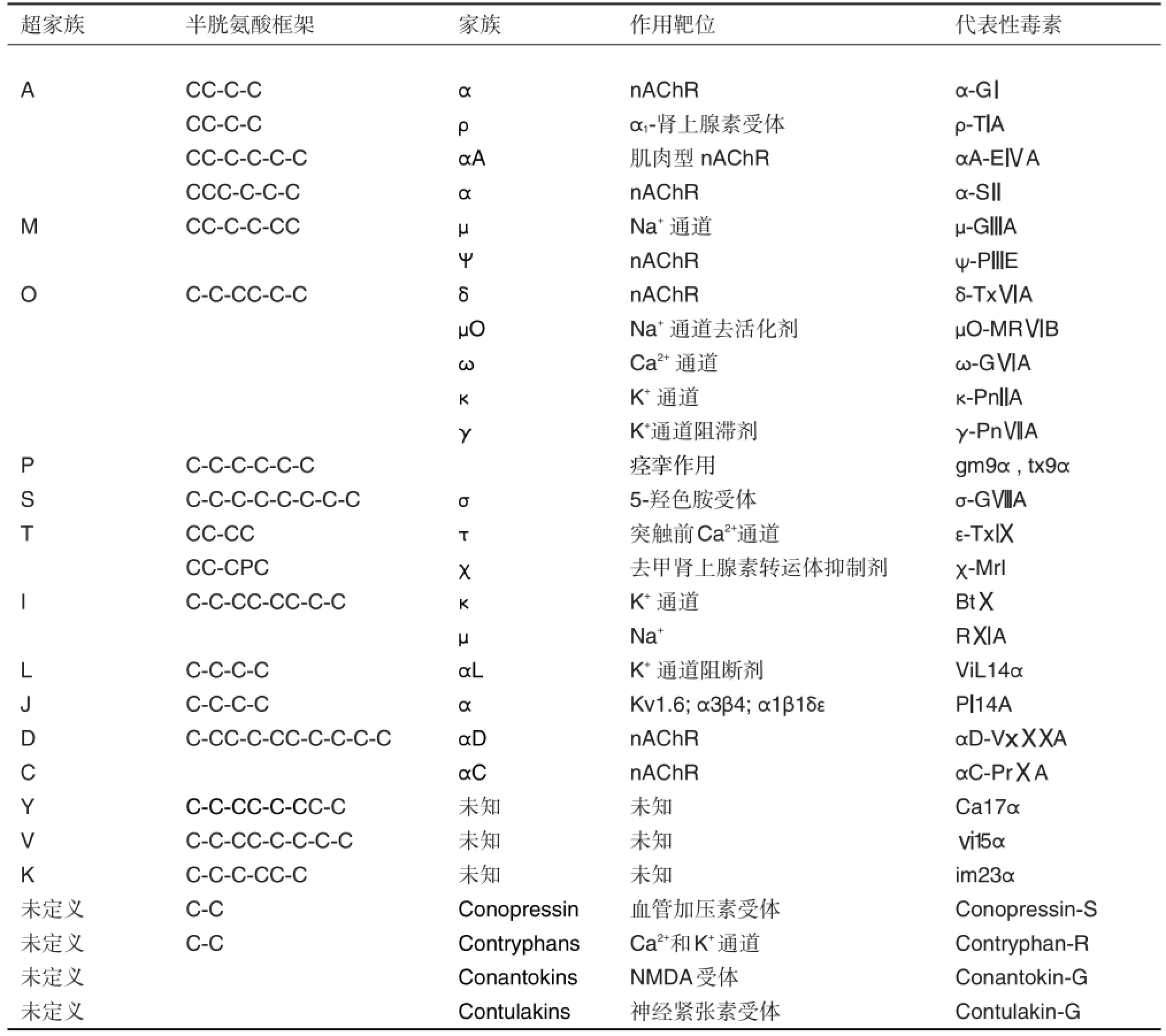
表1 芋螺毒素的分类[1,4-11]

图1 芋螺毒素M超家族分类和靶点[4,12-15]
2 芋螺毒素的作用靶点
目前发现芋螺毒素的作用靶标主要为乙酰胆碱受体,钠、钾和钙离子通道,N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(N-methyl-D-aspartic acid,NMDA)受体,肾上腺素受体和激素受体等,其中作用于乙酰胆碱受体、钠和钙离子通道及NMDA受体的最多,而作用于其他受体或离子通道(如钾离子通道)的芋螺毒素较少,显著不同于蝎毒素。本文就研究最多、靶点重要的α、μ、ω和睡眠肽药理家族芋螺毒素的毒理学药理学研究进展作简要介绍。
2.1 α-芋螺毒素
α-芋螺毒素主要包括A,B3,D,J,L,M和S芋螺毒素基因超家族,其中研究最充分的为A超家族[4,16]。属于A超家族的α-芋螺毒素约有数十种,其结构通式可表示为GCCXmCXnC,二硫键的主要连接方式为C1~C3,C2~C4(个别含3对二硫键)。根据m和n的数目不同,将α-芋螺毒素细分为几个亚家族:α3/5,α4/3,α4/4,α4/6,α4/7,α4/8和α5/5。其中α3/5亚家族主要作用于肌肉型乙酰胆碱受体,其他亚家族作用于神经元型乙酰胆碱受体,一些主要的α-芋螺毒素作用靶标及选择性见表2和表3。
在作用于肌肉型乙酰胆碱受体的α-芋螺毒素中(表2),GI及MI的毒性最高。GI来自于剧毒性海洋地纹芋螺,仅含13个氨基酸和2对二硫键,能专一性抑制肌肉型烟碱乙酰胆碱受体,造成中毒者器官麻木、呕吐、眼花、呼吸衰竭,直至死亡,对小鼠的致死剂量为8~12 mg·kg-1(ip)[20],目前还无药物用于GI中毒治疗。该类毒素第一个loop环含HPA或NPA 3个氨基酸残基是其显著特征。

表2 芋螺毒素对神经肌肉型乙酰胆碱受体的作用活性[5,16-19]
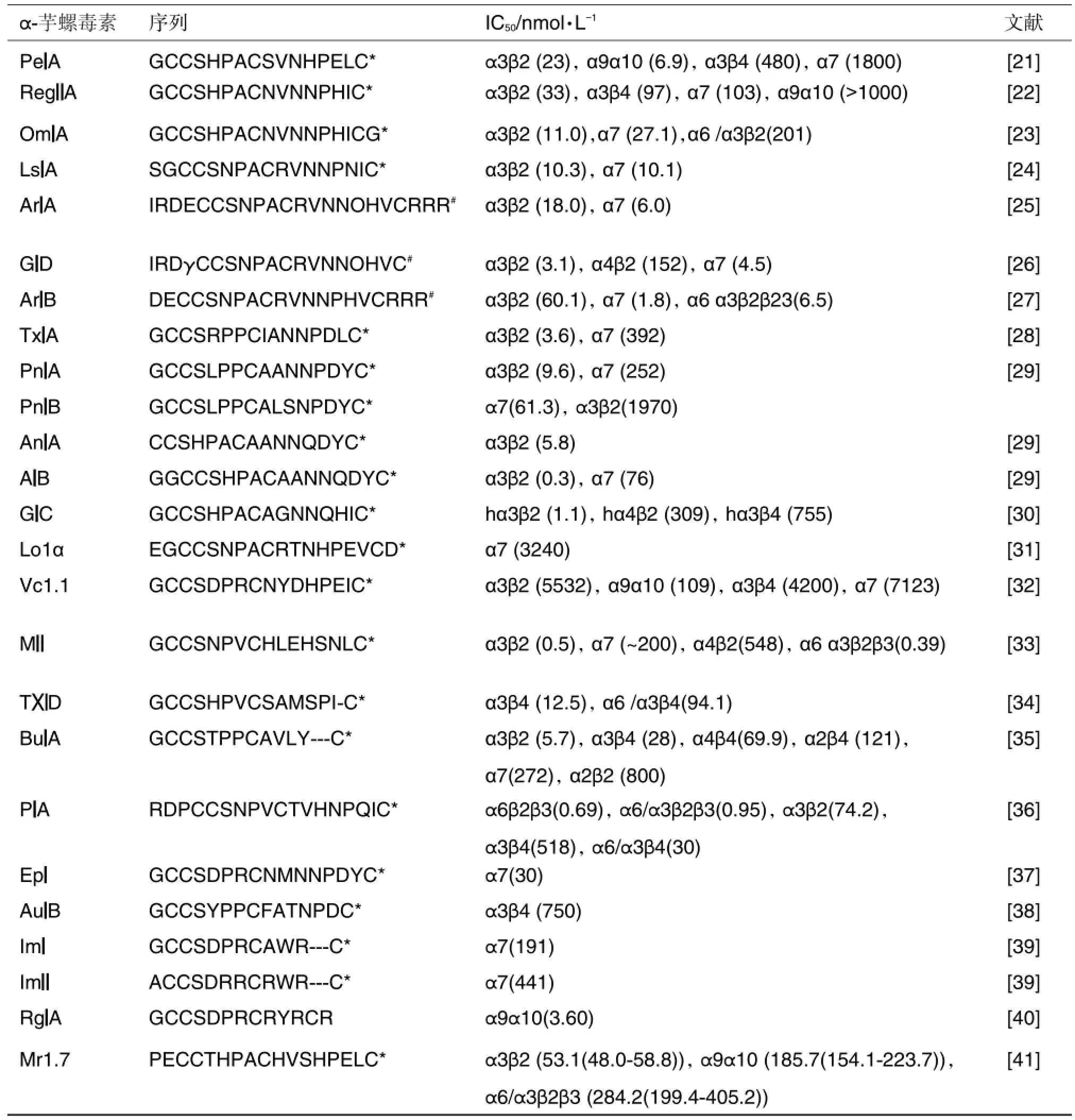
表3 α-芋螺毒素对神经元型乙酰胆碱受体的作用活性
目前对作用于神经元型乙酰胆碱受体亚型α7、α9α10、α3β2及γ-氨基丁酸B(γ-aminobutyric acid B,GABAB)受体介导N-钙通道的α-芋螺毒素已进行很多工作[21-41],涵盖结构-活性关系及镇痛和神经性疾病应用研究等多个方面。本课题组发现了数个新型α-芋螺毒素并测定了其作用靶点[42-43],研究了Mr1.7等芋螺毒素的结构-活性关系,观察到N端前2个氨基酸残基PE对毒素的活性及选择性具有影响。此外,还发现一些α-芋螺毒素可作用于多种靶点,相关论文正在发表中。
2.2 ω-芋螺毒素
ω-芋螺毒素是由24~29个氨基酸和3对二硫键构成的刚性小肽。自从1984年Olivera首先报道以来,至今已从地纹芋螺(C.geographus)、魔术家(C.magus)、线纹(C.straius)及织锦芋螺(C.textile)等分离出20余种ω-芋螺毒素,其作用靶点及选择性见表4[44-59]。ω-芋螺毒素能特异地阻断并区分不同的电压敏感钙通道,不仅在镇痛和神经保护等神经疾病治疗中具有巨大应用价值,而且为神经生物学提供了一系列研究工具。第1个芋螺毒素药物MⅦA已于2004年12月28在美国上市,用于顽固性慢性疼痛、晚期癌痛及艾滋病疼痛患者的镇痛[60]。
ω-芋螺毒素涉及的基因超家较少,主要为O1及O2,其二硫键框架为Ⅵ/Ⅶ,ⅩⅥ和ⅩⅩⅥ。Ⅵ/Ⅶ框架为C-C-CC-C-C,二硫键排列方式为“1-4,2-5,3-6”,ⅩⅥ和ⅩⅩⅥ分别为“C-C-CC”及“C-C-C-C-CCCC”,后二者很少见。作用的钙通道亚型主要为L-,N-及P/Q型,其中N-型钙通道最引人关注。
不同的ω-芋螺毒素对小鼠的毒性相差很大,毒性反应亦不相同。GⅥA~GⅥB,GⅦA~GⅦB,MⅦA和SⅥA对小鼠脑内给毒只引起震颤,剂量在每公斤数微克到数百微克之间;MⅦC和MⅦD则对小鼠有很高的毒性,每只小鼠给毒1 mg即可致死;SⅥB也可致死,但剂量稍高。目前所有的ω-芋螺毒素都难以穿过小鼠的血脑屏障,腹腔给毒的毒性很小,但ω-芋螺毒素对金鱼腹腔给毒可致死,LD50为15~60 mg·kg-1,ⅤⅹⅦ,PnⅥA和PnⅥB对脊椎动物的毒性低。
MⅦA虽已用于镇痛,且不成瘾,但MⅦA具有严重的副作用,如幻想、共济失调及震颤等,降低了其用药适从性。最近本课题组研究了MⅦA的毒性来源,发现Met12可能是毒性的主要来源氨基酸[51]。SO-3是本实验室从中国南海线纹芋螺(Conus stria⁃tus)发现的新ω-芋螺多肽[61],也含有25个氨基酸和3对全交叉二硫键(表4)。SO-3与MⅦA具有71%的结构同源性,也选择性作用于N-型钙通道,结合活性与MⅦA相似[51,56],但其对小鼠的震颤毒性、自发活动和运动功能的影响显著低于MⅦA。目前SO-3已完成临床前研究,正在申报临床试验批件。CVID的毒性也比MⅦA低,毒性低可能是第5和第6半胱氨酸之间的氨基酸差异所致。

表4 主要ω-芋螺毒素的作用靶标和选择性
2.3 μ-芋螺毒素
μ-芋螺毒素主要来自M超家族,由17~22个氨基酸残基组成,二硫键骨架为CC-C-C-CC,连接方式也为“C1-C4,C2-C5,C3-C6”,目前已分离到20多种(表5)[62~76]。其余的μ-芋螺毒素来自于O1和T家族,半胱氨酸框架为“CC-C-C-C-C”、“CC-CC”及“C-C-CC-C-C”。一些μ-芋螺毒素与河豚毒素(te⁃trodotoxin,TTX)和石房蛤毒素(saxitoxin,STX)竞争性结合α亚单位连接环区域的位点1,专一阻断肌肉河豚毒素敏感型(tetrodotoxin-sensitive,TTX-S)的电压敏感性钠通道(voltage sensitive sodium channel,VSSC),抑制动作电位的产生[6,77],其阻断骨骼肌型钠通道的活性比阻断心脏和大脑钠通道的活性高2个数量级,而TTX/STX对大脑和骨骼肌的活性比心脏通道高3个数量级。而另一些μ-芋螺毒素能专一作用于TTX不敏感型(TTX-resistant,TTX-R)钠通道,如SmⅢA,SⅢA和KⅢA等。
GⅢA,GⅢB和GⅢC对脊椎动物骨骼肌的TTX-S的VSSC Nav1.4选择性很高,显示强烈毒性,Arg13是功能关键残基。μ-PⅢA作用于骨骼肌TTX-S的Nav1.4通道(IC50=40 nmol·L-1),对神经元Nav1.2亚型(IC50=690 nmol·L-1)和大鼠外周神经PN1亚型也表现出一定的活性,能够区分大鼠脑部的各种VSSC亚型[64],Arg14是其结合骨骼肌VSSC亚型的关键残基。μ-SmⅢA是从芋螺中发现的第一个可作用于TTX-R钠通道的毒素,特异阻断两栖类动物交感神经元和感觉神经元TTX-R型VSSC[67],以及选择性抑制大鼠背根神经节细胞上TTX-R型VSSC。SmⅢA的Arg和Lys的平面取向对结合TTX-R钠通道起关键作用,Trp15和Arg17也是重要功能残基。μ-SⅢA和KⅢA也能阻断两栖动物交感神经元和背根神经节TTX-R钠通道。SⅢA中Trp12和His16(KⅢA中为Trp8和His12)也对它们结合TTX-R通道起着重要作用。作用于TTX-R VSSC的芋螺毒素SmⅢA和SⅢA等,已被发现具有显著的镇痛作用,如SⅢA10 nmol能有效抑制小鼠的炎症痛[78]。
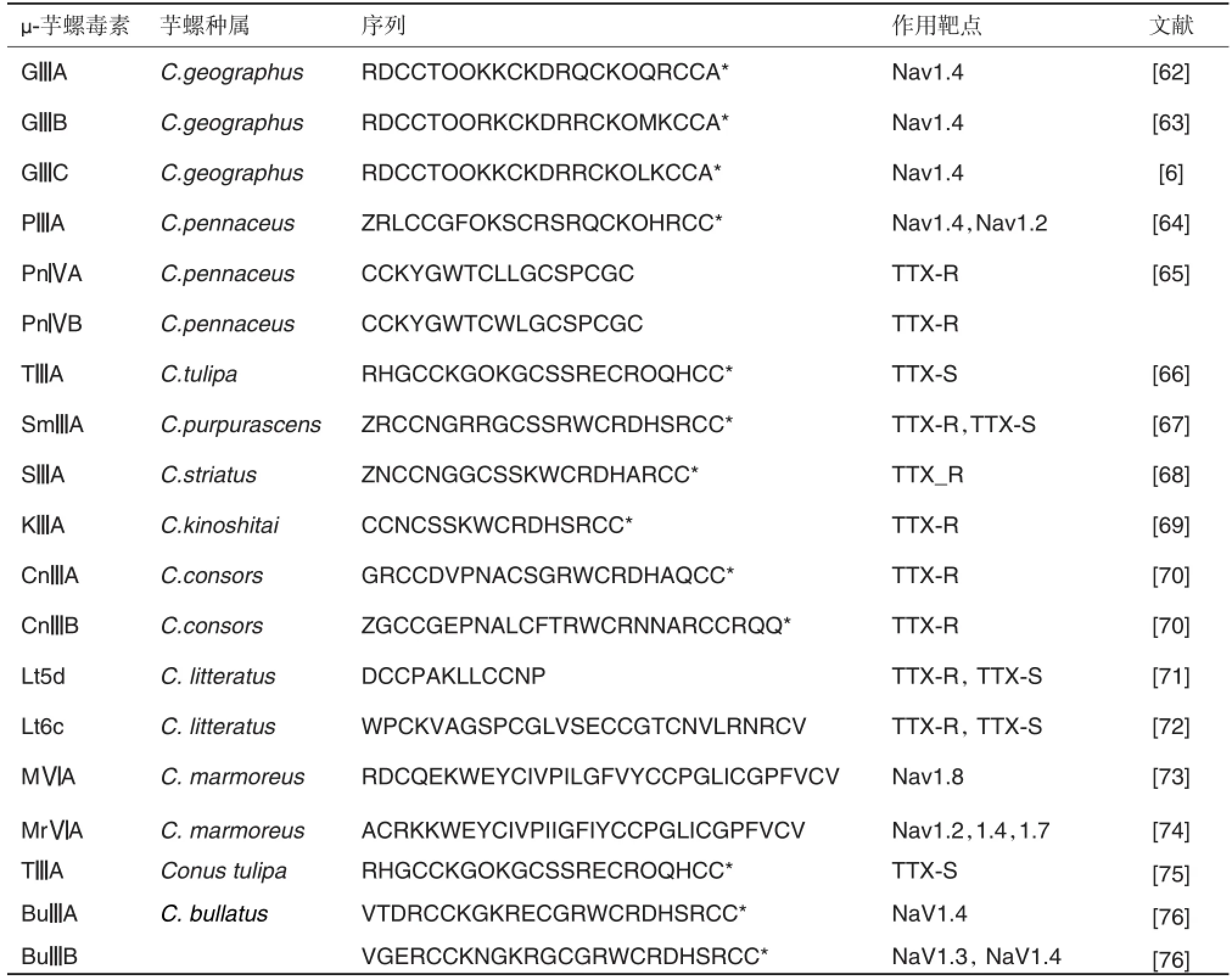
表5 作用于钠通道的μ-芋螺毒素
从结构来看,μ-芋螺毒素是由一段α螺旋、一个β发夹和n个转角组成的紧密CSαβ模体(cysteine stablilized αβ motif),分子中常含有Hyp,构成重要的功能结构域,Arg是关键氨基酸。
μO-芋螺毒素μO-MrⅥA/B属于O超家族,能特异阻断TTX-R型Nav1.8通道,还可以阻止TTX-S Nav1.4通道,高浓度时可与TTX-S Nav1.2通道和钙通道作用,其对TTX-R电流活性的阻断作用比对TTX-S约强10倍。但μO-MrⅥA不与TTX和STX竞争结合钠通道的Site1位点[79],这与μ-芋螺毒素不同。μO-MrⅥA虽作用于钠通道,但并不降低钠通道去活化,主要作用于结构域-3孔道loop环的C端。大鼠神经性和慢性炎症痛疼痛模型实验表明,MrⅥB 0.03~3 nmol鞘内注射能显著减轻神经性慢性疼痛和其他疼痛,且副作用较低[6]。
2.4 睡眠肽(conatokin)
上述芋螺毒素富含二硫键,二硫键对稳定结构及发挥活性非常重要。睡眠肽不含或只含1对二硫键,其作用生物活性并不与二硫键有关。该类多肽能特异性作用于NMDA受体及其亚型。早期发现该类肽能致小鼠睡眠,所以亦称“睡眠肽”。睡眠肽的结构显著特点是含有4-5个γ-羧基谷氨酸(γcarboxyl glutamic acid,Gla)残基,一些Gla是重要功能基团。目前为止,已发现20余个睡眠肽,其中有些已确定靶点(表6)[80-88]。一些多肽的核磁共振结构及关键残基对NMDA受体亚基NR2A/NR2B和NR2C的选择性已测定。
睡眠肽是目前唯一已知的具有NMDA受体选择抑制作用的天然多肽,对NMDA受体的亚基具有很高的选择性[8]。本课题组在睡眠肽结构及新的药理功能研究方面开展了系列工作[89-100],研究了睡眠肽与磷脂膜的作用机机制[89],观察到钙离子诱导Con-G及Con-T突变体α-双螺旋[90-92]。该螺旋与已报道的一般双螺旋结构及金属离子诱导蛋白质形成双螺旋结构的机制不同,其作用力来自于与Gla络合的钙离子,Con-G/Ca晶体结构证实其确为双螺旋结构[95],分子中除Gla残基外,其他残基对螺旋二聚体的形成也有影响[96,98-99]。上述研究拓展了双螺旋的基础理论,并为其应用提供新模型。
在应用方面,本课题组开展了睡眠肽及其突变体的镇痛及戒毒功能研究,用4种镇痛模型研究了10多个睡眠肽突变体的的镇痛活性[97],首次观察到某些睡眠肽及突变体具有很高的戒毒活性[93],其作用活性显著高于其他戒毒药,如美金胺及艾芬地尔。最近又观察到Con-T[M8Q]能显著降低吗啡的耐药性[100]。
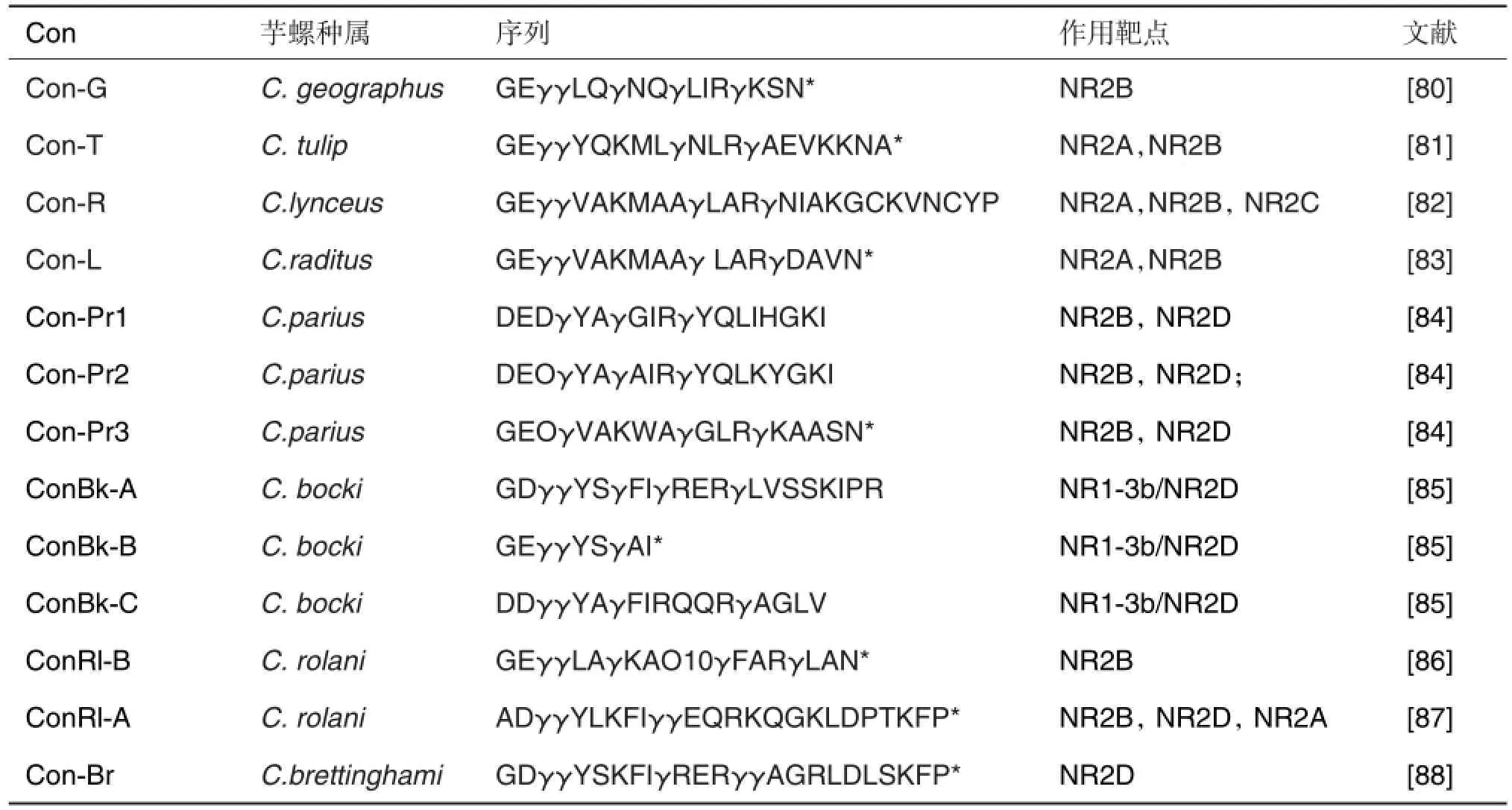
表6 睡眠肽(conatokin,Con)对NMDA受体的选择性
3 芋螺毒素的应用
目前,芋螺毒素的应用研究主要集中在药物发展及药理学研究工具开发2个方面[101]。前言中谈到的ω-芋螺毒素MⅦA已用于晚期癌症及顽固性慢性疼痛治疗,本课题组开发的ω-芋螺毒素SO-3已完成临床研究,基于该药的毒性降低改造或给药途径改进也在进行中。作用于神经元烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体α7亚基的α-芋螺毒素在治疗精神分裂方面具有应用价值[102],α4β2,α3β2和α9α10在镇痛方面有一定潜力[102],已发现一些α-芋螺毒素的具有多靶点功能,如作用于神经元型乙酰胆碱受体及其他受体和通道(钾离子通道和GABAB介导的钙离子通道等)的毒素可能在镇痛方面具有更好效果。睡眠肽已发现具有很好的镇痛和戒毒功能,但其给药途径需要改进。
芋螺毒素的高选择性已用作神经生物学的研究工具,用于确定一些离子通道和受体的亚型及它们的生理功能。不同的α-芋螺毒素可选择性区分肌肉型及神经元型的乙酰胆碱受体的亚型(如α1δ,α1γ,α3β2,α3β4和α7等),ω-芋螺毒素可选择性区分N,P/Q,R和L型钙通道,μ-和δ-芋螺毒素可选择性作用于钠通道中6个不同的功能区。ω-芋螺毒素GⅥA、μ-芋螺毒素SmⅢA和SⅢA等是非常好的N-钙通道与钠通道的探针,PeIA能区分α9α10与α7烟碱型受体亚型,其区分α-银环蛇毒素敏感的α9α10与α7烟碱型受体亚型的选择性高达260倍[103]。
基于芋螺毒素的结构模体开展的类肽或小分子功能化合物研究也受到关注[104]。迄今为止,基于ω-芋螺毒素的功能团的研究已发现了小分子N型-钙离子通道抑制剂(目前活性或选择性还不能与天然肽相比),一些基于芋螺毒素的环肽的研究也发现其具有其他功能,如抑制登革病毒蛋白酶[105]。
4 结语
芋螺毒素相对于其他动物多肽毒素而言,序列更短,结构多样性更高,目前研究的多肽还不及其预测毒素量的1%,因此还有很大研究空间。目前通过基因测序方法已获得不少毒素序列,但功能未知。本课题组从20世纪90年代中期就开展芋螺毒素研究,国内目前已有数家单位开展芋螺毒素研究,如防化研究院、同济大学、海南大学和中山大学等,我国科学家已在新芋螺毒素的发现、功能鉴定及药物研发方面取得显著进展。今后芋螺毒素的研究重点是毒素的发现、功能鉴定及应用研究。芋螺毒素的作用靶标不限定于神经受体或离子通道,其作为药理学研究工具的应用领域会进一步扩展,一些基于芋螺毒素的非毒素成分也会引起重视(如最近发现的芋螺类胰岛素组分效应更强[106])。芋螺毒素的临床应用将进一步拓展,除镇痛之外,在其他神经性疾病治疗中也会发挥作用。
[1]Akondi KB,Muttenthaler M,Dutertre S,Kaas Q,Craik DJ,Lewis RJ,et al.Discovery,synthesis,and structure-activity relationships of conotoxins[J].Chem Rev,2014,114(11):5815-5847.
[2]Dai QY.Conus snail species in China[M]//Liang SP,Zhang Y.Animal Peptide Toxins of China(中国动物多肽毒素).Beijing:Science Press,2016:385-390.
[3]Nelson L.Venomous snails:one slip,and you′re dead[J].Nature,2004,429(6994):798-799.
[4]Kaas Q,Yu R,Jin AH,Dutertre S,Craik DJ. ConoServer:updated content,knowledge,and discovery tools in the conopeptide database[EB/OL].Nucleic Acids Res,2012,40(Database issue):D325-D330.
[5]Wu RJ,Wang L,Xiang H.The structural features of α-Conotoxin specifically target different isoforms of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].Curr Top Med Chem,2015,16(2):156-169.
[6]Green BR,Bulaj G,Norton RS.Structure and function of μ-conotoxins,peptide-based sodium channelblockers with analgesic activity[J].Future Med Chem,2014,6(15):1677-1698.
[7]Hannon HE,Atchison WD.Omega-conotoxins as experimental tools and therapeutics in pain manage⁃ment[J].Mar Drugs,2013,11(3):680-699.
[8]Huang L,Balsara RD,Castellino FJ.Synthetic conantokin peptides potently inhibitN-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated currents of retinal ganglion cells[J].J Neurosci Res,2014,92(12):1767-1774.
[9]Liu L,Wu X,Yuan D,Chi C,Wang C.Identification of a novel S-superfamily conotoxin from vermivorous Conus caracteristicus[J].Toxicon,2008,51(8):1331-1337.
[10]Buczek O,Wei D,Babon JJ,Yang X,Fiedler B,Chen P,et al.Structure and sodium channel activity of an excitatory I1-superfamily conotoxin[J].Biochemistry,2007,46(35):9929-9940.
[11]Zhu C,Li L,Dai QY.Progress on the study of new superfamily conotoxins[J].Chin J Mar Drugs,2014,33(2):84-90.
[12]Jacob RB,Mcdougal OM.The M-superfamily of conotoxins:a review[J].Cell Mol Life Sci,2010,67(1):17-27.
[13]Kancherla AK,Meesala S,Jorwal P,Palanisamy R,Sikdar SK,Sarma SP.A disulfide stabilized βsandwich defines the structure of a new cysteine frameworkM-superfamilyconotoxin[J].ACS Chem Biol,2015,10(8):1847-1860.
[14]Zhou M,Wang L,Wu Y,Liu J,Sun D,Zhu X,et al.Soluble expression and sodium channel activity of lt16a,a novel frameworkⅩⅥ conotoxin from the M-superfamily[J].Toxicon,2015,98:5-11.
[15]Jiang H,Wang CZ,Xu CQ,Fan CX,Dai XD,Chen JS,et al.A novel M-superfamily cono⁃toxin with a unique motif from conus vexillum[J].Peptides,2006,27(4):682-689.
[16]Wei JJ,Dai QY.The research progress of struc⁃ture-activity relationship of α-conotoxins[J].Bull Acad Mil Med Sci(军事医学科学院院刊),2006,30(4):389-393.
[17]Quinton L,Servent D,Girard E,Molgó J,Le Caer JP,Malosse C,et al.Identification and functional characterization of a novel α-conotoxin(EIIA)from Conus ermineus[J].Anal Bioanal Chem,2013,405(15):5341-5351.
[18]Teichert RW,López-Vera E,Gulyas J,Watkins M,Rivier J,Olivera BM.Definition and characteriza⁃tion of the short alphaA-conotoxins:a single residue determines dissociation kinetics from the fetal muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptor[J].Bio⁃chemistry,2006,45(4):1304-1312.
[19]López-Vera E,Jacobsen RB,Ellison M,Olivera BM,Teichert RW.A novel alpha conotoxin(alpha-PIB)isolated from C.purpurascens is selective for skel⁃etal muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].Toxicon,2007,49(8):1193-1199.
[20]Gray WR,Rivier JE,Galyean R,Cruz LJ,Olivera BM.Conotoxin MI.Disulfide bonding and conformational states[J].J Biol Chem,1983,258(20):12247-12251.
[21]Mcintosh JM,Plazas PV,Watkins M,Gomez-Casati ME,Olivera BM,Elgoyhen AB.A novel alpha-conotoxin,PeIA,cloned from Conus pergrandis,discriminates between rat alpha9alpha10 and alpha7 nicotinic cholinergic receptors[J].J BiolChem,2005,280(34):30107-30112.
[22] Franco A,Kompella SN,Akondi KB,Melaun C,Daly NL,Luetje CW,et al.RegIIA:an α4/7-conotoxin from the venom of Conus regius that potently blocks α3β4 nAChRs[J].Biochem Phar⁃macol,2012,83(3):419-426.
[23]Talley T,Olivera BM,Han KH,Christensen SB,Dowell C,Tsigelny I,et al.Alpha-conotoxin OmIA is a potent ligand for the acetylcholinebinding protein as well as alpha3beta2 and al⁃pha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].J Biol Chem,2006,281(34):24678-24686.
[24] Inserra MC,Kompella SN,Vetter I,Brust A,Daly NL,Cuny H,et al.Isolation and character⁃ization of α-conotoxin LsIA with potent activity at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2013,86(6):791-799.
[25]Whiteaker P,Christensen S,Yoshikami D,Dowell C,Watkins M,Gulyas J,et al.Discovery,synthesis,and structure activity of a highly selective alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist[J].Biochemistry,2007,46(22):6628-6638.
[26]Nicke A,Loughnan ML,Millard EL,Alewood PF,Adams DJ,Daly NL,et al.Isolation,structure,and activity of GID,a novel alpha 4/7-conotoxin with an extended N-terminal sequence[J].J Biol Chem,2003,278(5):3137-3144.
[27] Dutertre S,Ulens C,Büttner R,Fish A,Van Elk R,Kendel Y,et al.AChBP-targeted alpha-conotox⁃in correlates distinct binding orientations with nAChR subtype selectivity[J].EMBO J,2007,26(16):3858-3867.
[28] Hopping G, Wang CI, Hogg RC,Nevin ST,Lewis RJ,Adams DJ,et al.Hydrophobic resi⁃dues at position 10 of α-conotoxin PnIA influence subtype selectivity between α7 and α3β2 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2014,91(4):534-542.
[29] Loughnan ML,Nicke A,Jones A,Adams DJ,Alewood PF,Lewis RJ.Chemical and functional identification and characterization of novel sulfated alpha-conotoxins from the cone snail Conus anemone[J].J Med Chem,2004,47(5):1234-1241.
[30] Mcintosh JM,Dowell C,Watkins M,Garrett JE,Yoshikami D,Olivera BM.Alpha-conotoxin GIC from Conus geographus,a novel peptide antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].J Biol Chem,2002,277(37):33610-33615.
[31] LebbeEK,PeigneurS,MaitiM,DeviP,Ravichandran S,Lescrinier E,et al.Structurefunction elucidation of a new α-conotoxin,Lo1a,from Conus longurionis[J].J Biol Chem,2014,289(14):9573-9583.
[32]Halai R, Clark RJ, Nevin T, Jensen JE,Adams DJ,Craik DJ.Scanning mutagenesis of alpha-conotoxin Vc1.1 reveals residues crucial for activity at the alpha9alpha10 nicotinic acetyl⁃choline receptor[J].J Biol Chem,2009,284(30):20275-20284.
[33] Cartier GE,Yoshikami D,Gray WR,Luo S,Olivera BM,Mcintosh JM.A new alpha-conotoxin which targets alpha3beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].J Biol Chem,1996,271(13):7522-7528.
[34]Luo S,Zhangsun D,Zhu X,Wu Y,Hu Y,Christensen S,et al.Characterization of a novel α-conotoxin TxID from Conus textile that potently blocks rat α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors[J].J Med Chem,2013,56(23):9655-9663.
[35]Azam L,Dowell C,Watkins M,Stitzel JA,Olivera BM, McIntoshJM.Alpha-conotoxin BuIA,a novel peptide from Conus bullatus,dis⁃tinguishes among neuronal nicotinic acetylcho⁃line receptors[J].J Biol Chem,2005,280(1):80-87.
[36]Dowell C,Olivera BM,Garrett JE,Staheli ST,Watkins M,Kuryatov A,et al.Alpha-conotoxin PIA is selective for alpha6 subunit-containing nic⁃otinic acetylcholine receptors[J].J Neurosci,2003,23(24):8445-8452.
[37]Nicke A, SamochockiM, Loughnan ML,Bansal PS,Maelicke A,Lewis RJ.Alpha-cono⁃toxins EpI and AuIB Switch subtype selectivity and activity in native versus recombinant nicotin⁃ic acetylcholine receptors[J].FEBS Lett,2003,554(1/2):219-223.
[38] Luo S,Kulak JM,Cartier GE,Jacobsen RB,Yoshikami D,Olivera BM,et al.Alpha-conotoxin AuIB selectively blocks alpha3 beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotine-evoked norepi⁃nephrine release[J].J Neurosci,1998,18(21):8571-8579.
[39]Ellison MA,Mcintosh JM,Olivera BM.Alpha-cono⁃toxins ImI and ImII.Similar alpha 7 nicotinic receptor antagonists actatdifferentsites[J].JBiol Chem,2003,278(2):757-764.
[40]Ellison M, Haberlandt C, Gomez-Casati ME, Watkins M,Elgoyhen AB,McIntosh M,et al. Alpha-RgIA:a novel conotoxin that specifically and potently blocks the alpha9alpha10 nAChR[J].Biochemistry,2006,45(5):1511-1517.
[41]Lebbe EK,Peigneur S,Wijesekara I,Tytgat J. Conotoxins targeting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors:an overview[J].Mar Drugs,2014,12(5):2970-3004.
[42] Wang S, Zhao C,Liu ZG,Wang XS,Liu N,Du WH,et al.Structural and functional charac⁃terization of a novel α-conotoxin Mr1.7 from conus marmoreus targeting neuronal nAChR α3β 2,α9α10 and α6/α3β2β3 subtypes[J].Mar Drugs,2015,13(6):3259-3275.
[43] Li L,Liu N,Ding R,Wang S,Liu ZG,Li HY,et al. A novel 4/6-type alpha-conotoxin ViIA selectively inhibits nAchR α3β2 subtype[J].Acta Biochim Biophys Sin(Shanghai),2015,47(12):1023-1028.
[44]Favreau P,Gilles N,Lamthanh H,Bournaud R,Shimahara T,Bouet F,et al.A new omega-cono⁃toxin that targets N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels with unusual specificity[J].Biochemis⁃try,2001,40(48):14567-14575.
[45]Lewis RJ,Nielsen KJ,Craik DJ,Loughnan ML,Adams DA,Sharpe IA,et al.Novel omega-cono⁃toxins from Conus catus discriminate among neu⁃ronalcalcium channelsubtypes[J].JBiol Chem,2000,275(45):35335-35344.
[46]Berecki G,Motin L,Haythornthwaite A,Vink S,Bansal P,Drinkwater R,et al.Analgesic(omega)-conotoxins CVIE and CVIF selectively and volt⁃age-dependently block recombinant andnative N-type calcium channels[J].MolPharmacol,2010,77(2):139-148.
[47]Lee S,Kim Y,Back SK,Choi HW,Lee JY,Jung HH,et al.Analgesic effect of highly revers⁃ible ω-conotoxin FVIA on N type Ca2+channels[J].Mol Pain,2010,6:97.
[48]Olivera M,Mcintosh M,Cruz J,Luque A,Gray R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic pep⁃tide toxin from Conus geographus venom[J].Biochemistry,1984,23(22):5087-5090.
[49]Olivera M,Gray R,Zeikus R,Mcintosh M,Varga J,Rivier J,et al.Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails[J].Science,1985,230(4732):1338-1343.
[50]Olivera BM,Cruz LJ,de Santos V,LeCheminant GW,Griffin D,Zeikus R,et al.Neuronal calciumchannel antagonists.Discrimination between cal⁃cium channel subtypes using omega-conotoxin from Conus magus venom[J].Biochemistry,1987,26(8):2086-2090.
[51]Wang F,Yan Z,Liu Z,Wang S,Wu Q,Yu S,et al.Molecular basis of toxicity of N-type calcium channel inhibitor MVIIA[J].Neuropharmacology,2016,101:137-145.
[52]Hillyard R,Monje D,Mintz M,Bean P,Nadasdi L,Ramachandran J,et al.A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+channels[J].Neuron,1992,9(1):69-77.
[53]Haack JA,Kinser P,Yoshikami D,Olivera BM. Biotinylated derivatives of omega-conotoxins GVIA and MVIID:probes for neuronal calcium channels[J].Neuropharmacology,1993,32(11):1151-1159.
[54]Ramilo A,Zafaralla C,Nadasdi L,Hammerland G,Yoshikami D,Gray R,et al.Novel alpha-and omega-conotoxins from Conus striatus venom[J].Biochemistry,1992,31(41):9919-9926.
[55] Woppmann A,Ramachandran J,Miljanich P. Calcium channel subtypes in rat brain:biochemical characterization of the high-affinity receptors for omega-conopeptides SNX-230(synthetic MVIIC),SNX-183(SVIB),and SNX-111(MVIIA)[J].Mol Cell Neurosci,1994,5(4):350-357.
[56]Wen L,Yang S,Qiao HF,Liu ZW,Zhou WX,Zhang YX,et al.SO-3,a new O-superfamily conopeptide derived from conus striatus,selec⁃tively inhibits N-type calcium currents in cultured hippocampalneurons[J].BrJPharmacol,2005,145(6):728-739.
[57]Bernáldez J,Román-González SA,Martínez O,Jiménez S,Vivas O,Arenas I,et al.A conus regularis conotoxin with a novel eight-cysteine framework inhibits CaV2.2 channels and displays an anti-nociceptive activity[J].Mar Drugs,2013,11(4):1188-1202.
[58]WangX,BezprozvannayaS,BowersoxS,Nadasdi L,Miljanich G,Mezo G,et al.Peripheral versus central potencies of N-type voltage-sensi⁃tive calcium channelblockers[J].Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,1998,357(2):159-168.
[59]Fainzilber M,Lodder C,Van Der Schors C,Li W,Yu Z,Burlingame L,et al.A novel hydrophobic omega-conotoxin blocks molluscan dihydropyri⁃dine-sensitive calcium channels[J].Biochemistry, 1996,35(26):8748-8752.
[60]Pope E,Deer R.Ziconotide:a clinical update and pharmacologic review[J].Expert Opin Phar⁃macother,2013,14(7):957-966.
[61]Dai QY,Liu FY,Zhou YR,Lu BS,Yu F,Huang PT. The synthesis of SO-3,a conopeptide with high analgesic activity derived from Conus striatus[J].J Nat Prod,2003,66(9):1276-1279.
[62]Li RA,Sato K,Kodama K,Kohno T,Xue T,Tomaselli GF,et al.Charge conversion enables quantification of the proximity between a normallyneutral mu-conotoxin(GⅢA)site and the Na+channel pore[J].FEBS Lett,2002,511(1-3):159-164.
[63]Li RA,Ennis IL,Vélez P,Tomaselli GF,Marbán E. Novel structural determinants of mu-conotoxin(GⅢB)block in rat skeletal muscle(mu1)Na+chan⁃nels[J].J Biol Chem,2000,275(36):27551-27558.
[64]Safo P,Rosenbaum T,Shcherbatko A,Choi DY,Han E,Toledo-Aral JJ,et al.Distinction among neuronal subtypes of voltage-activated sodium channels by mu-conotoxin PⅢA[J].J Neurosci,2000,20(1):76-80.
[65]Fainzilber M,Nakamura T,Gaathon A,Lodder C,Kits S,Burlingame L,et al.A new cysteine frame⁃work in sodium channel blocking conotoxins[J].Biochemistry,1995,34(27):8649-8656.
[66]Lewis RJ,Schroeder CI,Ekberg J,Nielsen KJ,Loughnan M,Thomas L,et al.Isolation and structure-activity of mu-conotoxin TⅢA,a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels[J].Mol Pharmacol,2007,71(3):676-685.
[67]West PJ, Bulaj G, Garrett JE, Olivera BM,Yoshikami D.Mu-conotoxin SmⅢA,a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in amphibian sympathetic and sensory neurons[J]Biochemistry,2002,41(51):15388-15393.
[68]Bulaj G, West PJ, Garrett JE,Watkins M,Zhang MM,Norton RS,et al.Novel conotoxins from Conus striatus and Conus kinoshitai selec⁃tively block TTX-resistant sodium channels[J].Biochemistry,2005,44(19):7259-7265.
[69]Zhang MM,Green BR,Catlin P,Fiedler B,Azam L,Chadwick A,et al.Structure/function characterization of micro-conotoxin KIIIA,an analgesic,nearly irreversible blocker of mammali⁃an neuronal Sodium channels[J].J Biol Chem,2007,282(42):30699-30706.
[70] Zhang MM,Fiedler B,Green BR,Catlin P,Watkins M,Garrett JE,et al.Structural and functional diversities among mu-conotoxins targeting TTX-resistant sodium channels[J].Biochemistry,2006,45(11):3723-3732.
[71] Liu JL,Wu QF,Pi CH,Zhao Y,Zhou MJ,Wang L,et al.Isolation and characterization of a T-superfamily conotoxin from Conus litteratus with targeting tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium chan⁃nels[J].Peptides,2007,28(12):2313-2319.
[72] Wang L,Pi CH,Liu JL,Chen SW,Peng C,Sun DD,et al.Identification and characterization of a novel O-superfamily conotoxin from Conus litteratus[J].J Pept Sci,2008,14(10):1077-1083.
[73] Vetter I, Dekan Z, Knapp O, Adams DJ,Alewood PF,Lewis RJ.Isolation,characteriza⁃tion and total regioselective synthesis of the novel μO-conotoxin MfVIA from Conus magnificus that targets voltage-gated sodium channels[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2012,84(4):540-548.
[74] Ekberg J,Jayamanne A,Vaughan CW,Aslan S,Thomas L,Mould J,et al.muO-conotoxin MrVIB selectively blocks Nav1.8 sensory neuron specific sodium channels and chronic pain behavior without motor deficits[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2006,103(45):17030-17035.
[75] Hill JM,Alewood PF,Craik DJ.Conotoxin TVIIA,a novel peptide from the venom of conus tulipa 2.three-dimensional solution structure[J].Eur J Biochem,2000,267(15):4649-4657.
[76] Kuang Z,Zhang MM,Gupta K,Gajewiak J,Gulyas J,Balaram P,et al.Mammalian neuronal sodium channel blocker μ-conotoxin BuIIIB has a structured N-terminus that influences potency[J].ACS Chem Biol,2013,8(6):1344-1351.
[77] Feng GX,Luo FF,Dai QY.Progress in research on sodium channel conotoxins[J].Bull Acad Mil Med Sci(军事医学科学院院刊), 2007,31(6):564-567.
[78] Green BR,Bulaj G,Norton RS.Structure and function of μ-conotoxins,peptide-based sodium channelblockers with analgesic activity[J].Future Med Chem,2014,6(15):1677-1698.
[79] Prorok M,Castellino FJ.The molecular basis of conantokin antagonism of NMDA receptor function[J].Curr.Drug Targets.2007,8(5):633-642.
[80] Donevan D,Mccabe T.Conantokin G is an NR2B-selective competitive antagonist ofN-methyl-D-aspartate receptors[J].Mol Pharmacol,2000,58(3):614-623.
[81]Warder E,Blandl T,Klein C,Castellino J,Prorok M.Amino acid determinants for NMDA receptor inhibition by conantokin-T[J].J Neuro⁃chem,2001,77(3):812-822.
[82]White S,Mccabe T,Armstrong H,Donevan D,Cruz J,Abogadie C,et al.In vitroandin vivocharacterization of conantokin-R,a selective NMDA receptor antagonist isolated from the venom of the fish-hunting snail Conus radiatus[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2000,292(1):425-432.
[83]Jimenez EC,Donevan S,Walker C,Zhou LM,Nielsen J,Cruz LJ,et al.Conantokin-L,a new NMDA receptor antagonist:determinants for anti⁃convulsant potency[J].Epilepsy Res,2002,51(1-2):73-80.
[84]Gowd KH,Twede V,Watkins M,Krishnan KS,Teichert RW,Bulaj G,et al.Conantokin-P,an unusual conantokin with a long disulfide loop[J].Toxicon,2008,52(2):203-213.
[85]Platt RJ,Curtice KJ,Twede VD,Watkins M,Gruszczyński P,Bulaj G,et al.From molecular phylogeny towards differentiating pharmacology for NMDA receptor subtypes[J].Toxicon,2014,81:67-79.
[86]Kunda S, Yuan Y, Balsara RD, Zajicek J,Castellino FJ.Hydroxyproline-induced helical dis⁃ruption in conantokin Rl-B affects subunitselective antagonistic activities toward Ion chan⁃nels ofN-methyl-D-aspartate receptors[J].J Biol Chem,2015,290(29):18156-18172.
[87]Gowd KH,Watkins M,Twede VD,Bulaj GW,Olivera BM.Characterization of conantokin Rl-A:molecular phylogeny as structure/function study[J].J Pept Sci,2010,16(8):375-382.
[88]Twede VD, TeichertRW, WalkerCS,Gruszczyński P,Kaz′mierkiewicz R,Bulaj G,et al.Conantokin-Br from Conus brettinghami and selectivity determinants for the NR2D subunit of the NMDA receptor[J].Biochemistry,2009,48(19):4063-4073.
[89]Dai Q,Zajicek J,Castellino FJ,Prorok M.Binding and orientation of conantokins in PL vesicles and aligned PL multilayers[J].Biochemistry,2003,42(43):12511-12521.
[90]Dai Q,Prorok M,Castellino FJ.A new mechanism for metal ion-assisted interchain helix assemblyin a naturally occurring peptide mediated by opti⁃mally spaced gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues[J].J Mol Biol,2004,336(3):731-744.
[91]Dai QY,Castellino FJ,Prorok M.A single amino acid replacement results in the Ca2+-induced selfassembly of a helical conantokin-based peptide[J].Biochemistry,2004,43(41):13225-13232.
[92]Dai QY,Prorok M,Castellino FJ.Role of the hexapeptide disulfide loop in the gamma-carboxy⁃glutamic acid domain of protein C in Ca2+-mediated structural and functional properties[J].Biochem⁃istry,2005,44(37):12508-12514.
[93]Wei JJ,Dong MX,Xiao C,Jiang FC,Castellino FJ,Prorok M,et al.Conantokins and variants derived from cone snail venom inhibit naloxone-induced withdrawal jumping in morphine-dependent mice[J].Neurosci Lett,2006,405(1/2):137-141.
[94]Sheng ZY,Dai QY,Prorok M,Castellino FJ. Subtype-selective antagonism ofN-methyl-D-aspartate receptorion channels by synthetic conantokin peptides[J].Neuropharmacology,2007,53(1):145-156.
[95]Cnudde SE,Prorok M,Dai Q,Castellino FJ,Geiger JH.The crystal structures of the calciumbound con-G and con-T[K7gamma] dimeric peptides demonstrate a metal-dependent helixforming motif[J].J Am Chem Soc,2007,129(6):1586-1593.
[96]Cnudde SE,Prorok M,Dai Q,Castellino FJ,Geiger JH.Helix-helix interactions between homoandheterodimericgamma-carboxyglutamatecontaining conantokin peptides and their deriva⁃tives[J].J Biol Chem,2007,282(17):12641-12649.
[97]Xiao C,Huang YY,Dong MX,Hu J,Hou SS,Castellino FJ,et al.NR2B-selective conantokin peptide inhibitors of the NMDA receptor display enhanced antinociceptive properties compared to non-selective conantokins[J].Neuropeptides,2008,42(5/6):601-609.
[98]Dai QY,Xiao C,Dong MX,Liu ZG,Sheng ZY,Castellino FJ,et al.Non-strict strand orientation of the Ca2+-induced dimerization of a conantokin peptide variant with sequence-shifted gamma-car⁃boxy glutamate residues[J].Peptides,2009,30(5):866-872.
[99]Dai QY,Dong MX,Liu ZG,Prorok M,Castellino FJ. Ca2+-induced self-assembly in designed peptides with optimally spaced gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues[J].J Inorg Biochem,2011,105(1):52-57.
[100]Ren BL,Zhou ZJ,Liu ZG,Li BL,Ou J,Dai QY. Con-T[M8Q]potently attenuates the expression and development of morphine tolerance in mice[J].Neurosci Lett,2015,597:38-42.
[101]Mir R,Karim S,Kamal MA,Wilson CM,Mirza Z. Conotoxins:structure,therapeutic potential and pharmacologicalapplications[J].CurrPharm Des,2016,22(5):582-589.
[102]Lewis RJ,Dutertre S,Vetter I,Christie MJ.Conus venom peptide pharmacology[J].Pharmacol Rev,2012,64(2):259-298.
[103]Cnudde SE,Prorok M,Dai Q,Castellino FJ,Geiger JH.The crystal structures of the calciumbound con-G and con-T[K7gamma]dimeric pep⁃tides demonstrate a metal-dependent helix-form⁃ing motif[J].J Am Chem Soc,2007,129(6):1586-1593.
[104]Duggan J,Tuck L.Bioactive mimetics of conotoxins and other venom peptides[J].Toxins(Basel),2015,7(10):4175-4198.
[105]Xu S,Li H,Shao X,Fan C,Ericksen B,Liu J,et al.Critical effect of peptide cyclization on the potency of peptide inhibitors against Dengue virus NS2B-NS3 protease[J].J Med Chem,2012,55(15):6881-6887.
[106]Safavi-Hemami H, Gajewiak J, Karanth S,Robinson SD,Ueberheide B,Douglass AD,et al. Specialized insulin is used for chemical warfare by fish-hunting cone snails[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2015,112(6):1743-1748.
Progress in toxicology and pharmacology of conotoxins
DAI Qiu-yun
(Institute of Biotechnology,Academy of Military Medical Sciences,Beijing 100071,China)
Conotoxins are secreted by Conus snail,which are mainly composed of 12-40 amino acid residues and several disulfide bridges.Their diversities in sequences,disulfide bond connections and modified amino acids are different from those of peptide toxins and proteins secreted by terrestrial animals,and their targets include sodium,potassium,calcium ion channels and membrane receptors. Conotoxins have been categorized into more than 20 superfamilies,such as A,M,O,P,S,T,I,V,Y,J,D,C and L,which are characterized by consensus signal sequences and cysteine framework. According to pharmacological functions,these superfamilies are further classified into several pharma⁃cological families,such as α,μ,ω,κ,δ,ψ,σ,ρ,γ,conopressin and conantokins.This review briefly introduced the classifications and diversities of conotoxins,and summarized the progresses in the toxi⁃cology and pharmacology of conotoxins targeting calcium,sodium ion channel,nicotinic acetylcholine receptor andN-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor.Some of the above conotoxins are highly poisonous,some have been developed as drugs or drug candidates,or have become powerful research tools for neuro⁃pharmacology.We hope this review will contribute to researches of toxins and related neuropharmacology.
conotoxins;toxicology;pharmacology;ion channel;acetylcholine receptor;aspartic acid receptor
DAI Qiu-yun,E-mail:qy_dai@yahoo.com
R99,R996.3
A
1000-3002-(2016)12-1397-14
10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2016.12.018
Foundation item:The project supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(81173035);National Natural Science Foundation of China(81473192);National High Technology Research and Development Program(2011AA09070108);and National Key Basic Research and Development Program(973 Program)(2010CB529802)
2016-11-23接受日期:2016-12-20)
(本文编辑:齐春会)
国家自然科学基金(81173035);国家自然科学基金(81473192);863高技术项目(2011AA09070108);国家重点基础研究发展计划(973)(2010CB529802)
戴秋云,E-mail:qy_dai@yahoo.com
