Changes and Influencing Factors of Maize Production Pattern in China
2016-01-11,
,
College of Economics and Management, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
ChangesandInfluencingFactorsofMaizeProductionPatterninChina
HaiyangTANG*,JinZHOU
College of Economics and Management, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, China
Since the founding of new China, the maize production pattern took on characteristic of "northern expansion and western movement": there were great changes in ranking of main producing provinces; southern planting area gradually shrank, while central and northern planting area gradually expanded; apart from traditional main producing regions such as northeastern, north China, and southwestern regions, Shanxi-Shaanxi region and northwest region are gradually forming. To further analyze factors promoting changes in maize production pattern, based on 1987-2013 panel data, we carried our empirical study and obtained five influencing factors: resource endowment, economic environment, market environment, technical conditions, and policies. Per capita farmland, multiple cropping index, water conservancy and irrigation, and benefit cost ratio, and traffic and transportation policies exert positive effect, non-agricultural employment level exerts negative effect, and the significance of natural disasters, market price, and science and technology are inadequate.
Maize, Production pattern, Influencing factors
1 Introduction
Maize is one of the three largest grain crops in China. With changes in consumption structure such as grain ration consumption, feed consumption, industrial consumption, and seed consumption, the consumption demands for maize are increasing. Since 2010, China has changed to net importer of maize from net exporter. How to stably organize maize production and ensure supply of maize products concerns the national grain security. China has a long history and wide area of maize planting, finding out regional pattern of grain production and influencing factors is of great significance for formulating reasonable grain production and trade policies[1]. Optimizing maize production distribution not only can bring into play regional comparative advantages, increase production efficiency, and improve maize quality, but also can promote cultivation and development of related industries and raise competitive power of maize products. Therefore, the study on changes in maize production pattern and influencing factors can depict characteristics of maize production distribution in China, is helpful for grasping rules of changes, analyzing reasons for changes, and will play a significant role in adjusting agricultural structure, further optimizing maize production pattern, and formulating regional agricultural policies. The importance of agricultural production distribution is increasingly outstanding, and many scholars have made extensive researches on this issue in recent years[2-6]. The existing domestic literature about production distribution of grain crops focuses on rice, and there are few researches about spatial distribution of maize, especially about quantitative analysis. Therefore, on the basis of analyzing rules of changes in maize production pattern since the founding of new China, we made an empirical analysis on factors influencing maize production pattern using panel data of main maize production provinces in 1987-2013. This will be favorable for making clear adjustment direction of production structure and increase allocation efficiency of limited resources according to rules of changes in maize production pattern. Besides, it will be favorable for fully using advantages of each factor, improving maize production pattern, promoting maize production, and stabilizing development of maize industry.
2 Analysis on changes in maize production pattern of China
2.1AnalysisofmaizedevelopmentstagesBefore the reform and opening up, China’s maize planting was mainly restricted by natural endowment and planting habits. The planting area slowly grew to 19961000 ha from 12953000 ha. Therefore, we selected data from reform and opening up to the present to analyze development of maize planting area. From Fig. 1, we can know that China’s maize production experienced slow decline, fluctuation growth, and rapid rise stages in 1978-2013. The first stage is slow decline (1978-1985): the maize planting area shrank from 19961000 ha to 17694000 ha, with annual decline of 323900 ha; the second stage is fluctuation with growth (1986-2003): the maize planting area grew from 19124000 ha to 24068000 ha with annual growth of 274700 ha; the third stage is rapid rise (2004-2013): maize planting area realized 10 consecutive growth, from 25446000 ha to 36318000 ha with annual growth up to 1087300 ha. In general, maize planting area has been increasing since the reform and opening up, increasing from 19961000 ha in 1978 to 36318000 ha in 2013, annual growth of 467300 ha.
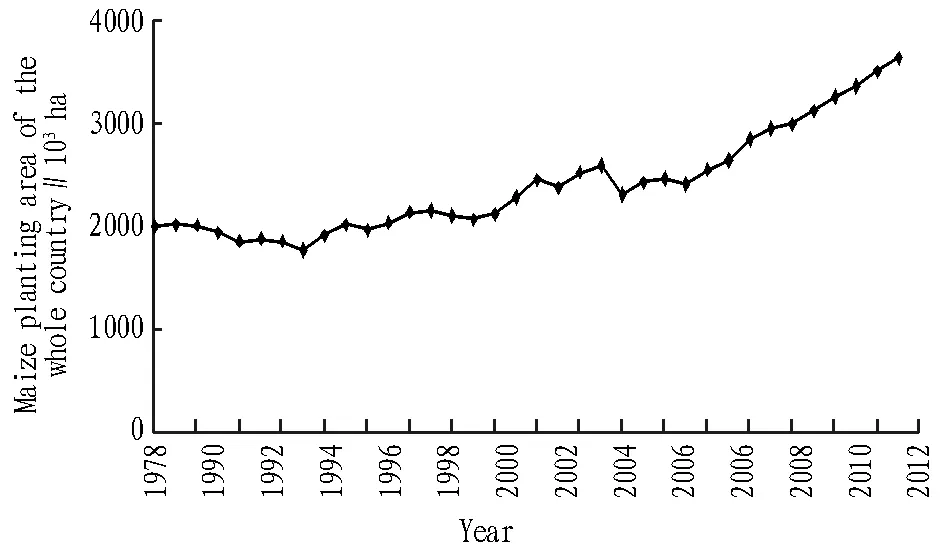
Fig.1 Changes in maize planting area in 1978-2013
2.2Analysisoncharacteristicsofmaizeproductionpattern
2.2.1Changes in main maize production provinces. In this study, we applied the production concentration indicator to measure changes in main maize production provinces. The maize production concentration is the ratio of maize yield of certain region to total maize yield of the whole country in the same period. Main maize production provinces are provinces with maize production concentration higher than 5%[7]. We screened out provinces with maize production concentration higher than 3% and ranked from big to small in Table 1.
Table1ChangesinmainmaizeproductionprovincessincethefoundingofnewChina
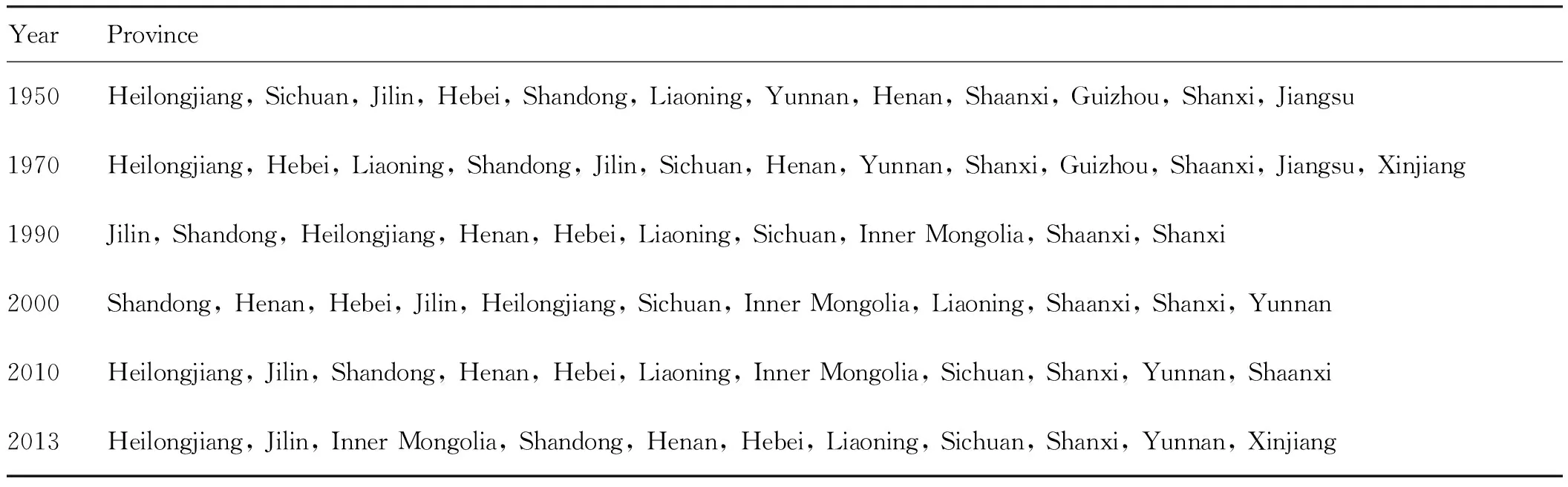
YearProvince1950Heilongjiang,Sichuan,Jilin,Hebei,Shandong,Liaoning,Yunnan,Henan,Shaanxi,Guizhou,Shanxi,Jiangsu1970Heilongjiang,Hebei,Liaoning,Shandong,Jilin,Sichuan,Henan,Yunnan,Shanxi,Guizhou,Shaanxi,Jiangsu,Xinjiang1990Jilin,Shandong,Heilongjiang,Henan,Hebei,Liaoning,Sichuan,InnerMongolia,Shaanxi,Shanxi2000Shandong,Henan,Hebei,Jilin,Heilongjiang,Sichuan,InnerMongolia,Liaoning,Shaanxi,Shanxi,Yunnan2010Heilongjiang,Jilin,Shandong,Henan,Hebei,Liaoning,InnerMongolia,Sichuan,Shanxi,Yunnan,Shaanxi2013Heilongjiang,Jilin,InnerMongolia,Shandong,Henan,Hebei,Liaoning,Sichuan,Shanxi,Yunnan,Xinjiang
From Table 1, we can see that since the founding of new China, there are few changes in main maize production provinces. The quantity of provinces remained about 11, but there are great changes in order of main production provinces. From the founding of new China to the reform and opening up, the maize yield of Heilongjiang Province remained the first place. However, in 1980-2005, it was exceeded by Shandong and Jilin, and rose to the first place till 2010. Jilin Province experienced several times of fluctuation, ranked in the second place; Shandong Province increased maize yield since the reform and opening up, but in recent years, there is slow decline trend; Sichuan Province dropped to the eighth place from the second place in 2010; Yunnan also dropped to the end position; Guizhou, Guangxi, and Jiangsu have exited from main maize production provinces. The ranking of Shanxi and Shaanxi was relatively steady and it has the trend of exceeding Yunnan in recent years; since 2000, the Inner Mongolia developed rapidly and ascended to main maize production provinces; Xinjiang also joined the ranks of main maize production provinces. Generally, there are many provinces having high maize yield in China, but there is decline trend; the ranking of main maize production provinces has large fluctuation, and main maize production provinces are concentrated in northern regions.
2.2.2Analysis on changes in maize belt of China. Since the founding of new China, there have been constant changes in maize production situation of every province. To visually reflect changes in maize production pattern of China, we took maize planting area of every province as an indicator to analyze maize production situation and variation trend of maize production pattern. From Fig. 2, it is known that, on the whole, China has established a "Northeast - Huang-Huai-Hai - Southwest" narrow maize belt before the founding of new China, and Jilin, Heilongjiang, Hebei, Shandong, Henan, and Sichuan remain the traditional main maize production areas, while there are great changes in other maize production provinces. As to stages: in 1950-1978, the maize planting area greatly shrank in southern part (Guizhou and Guangxi) and central area of maize belt (Hubei and Jiangsu); in 1978-2000, maize planting area had certain decline in southern part (Yunnan) and central area of maize belt (Shaanxi), while it greatly increased in northern area (Inner Mongolia); from 2000 to the present, the maize planting area continued shrinking in southern area, especially in Guizhou and Sichuan, while it expanded in central area (for example, Shanxi), in northern part, Inner Mongolia gradually became a main production province, and Xinjiang also expanded maize planting area. In sum, for over 6 decades, maize planting area was constantly increasing: the planting area in southern part was shrinking, while it was gradually expanding in central and northern parts.
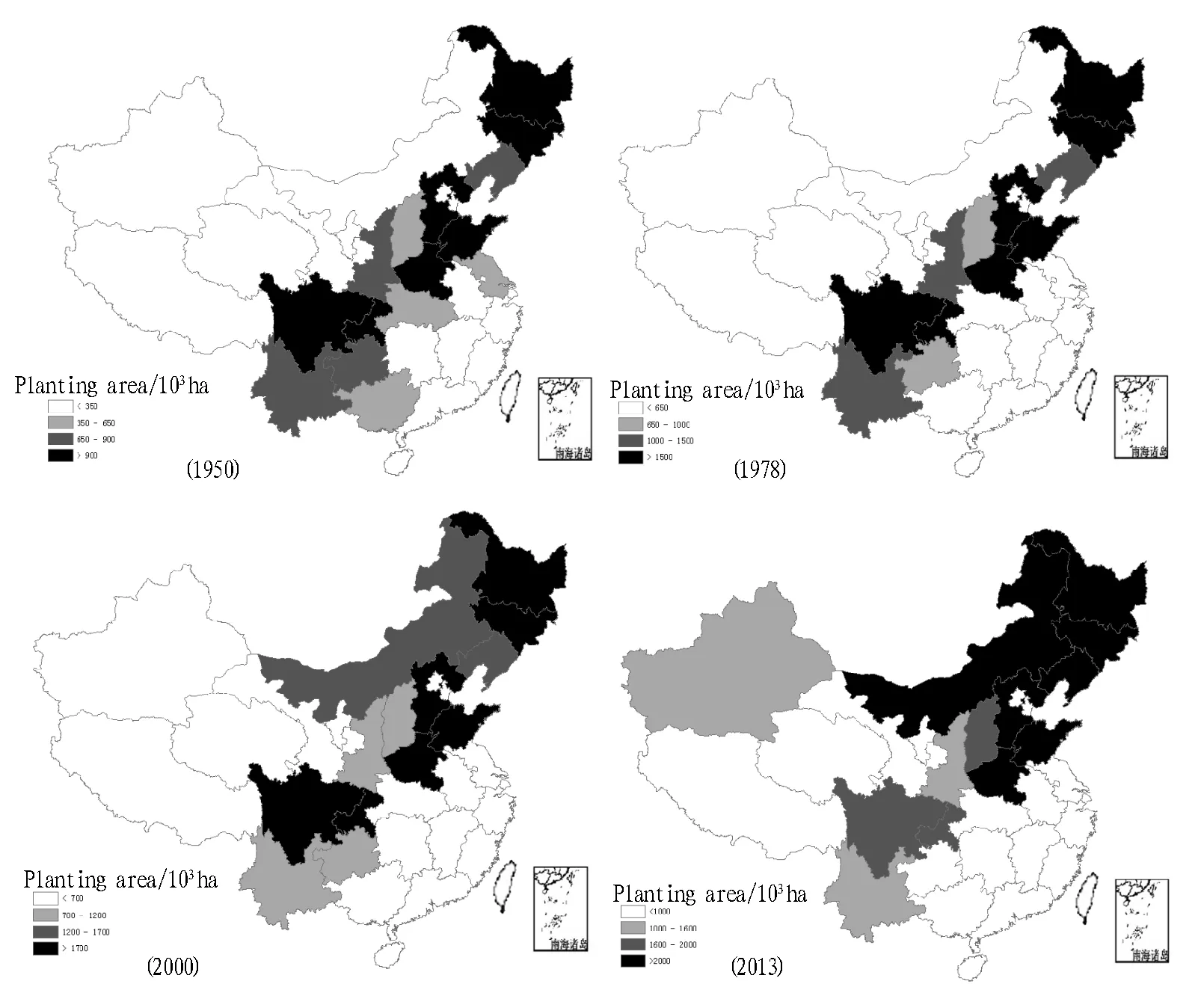
Fig.2 Maize production pattern (1950, 1978, 2000, and 2013)
2.2.3Changes in main maize production areas. Vast in territory, China is different in natural environment and farming rules from the north to the south and from the east to the west, and maize production conditions are also varied. To fully analyze changes in distribution of maize production areas, we divided maize planting areas into southern and northern areas, 4 big areas (eastern, central, western, and northeastern), and 8 first-level planting areas, with reference to division of Chai Binfeng (2007) and Jiang Hao (1998). The 8 first-level planting areas are northeastern areas (including Heilongjiang, Jilin, Liaoning, and Inner Mongolia), North China (Hebei, Shandong, and Henan), Jin-shan area (Shanxi and Shaanxi), East China (Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui), and Central China (Jiangxi, Hubei, and Hunan), South China (Fujian, Guangdong, and Guangxi), and southwest (Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan), and northwest (Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang).
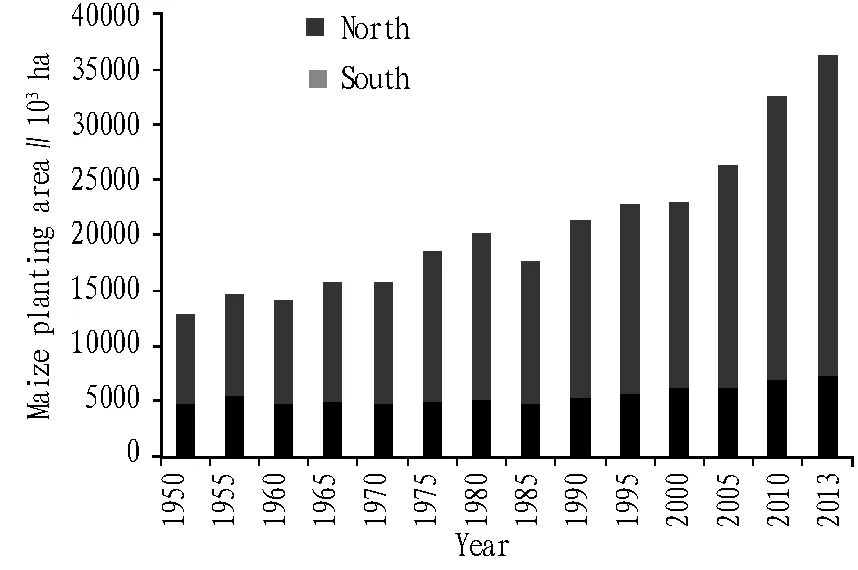
Fig.3 Maize planting area of southern and northern areas
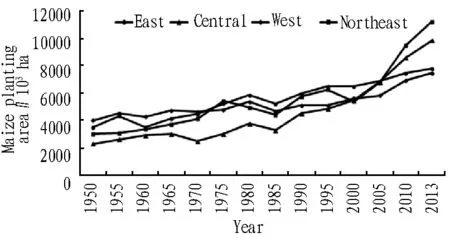
Fig.4 Maize planting area of east, central, west, and northeast
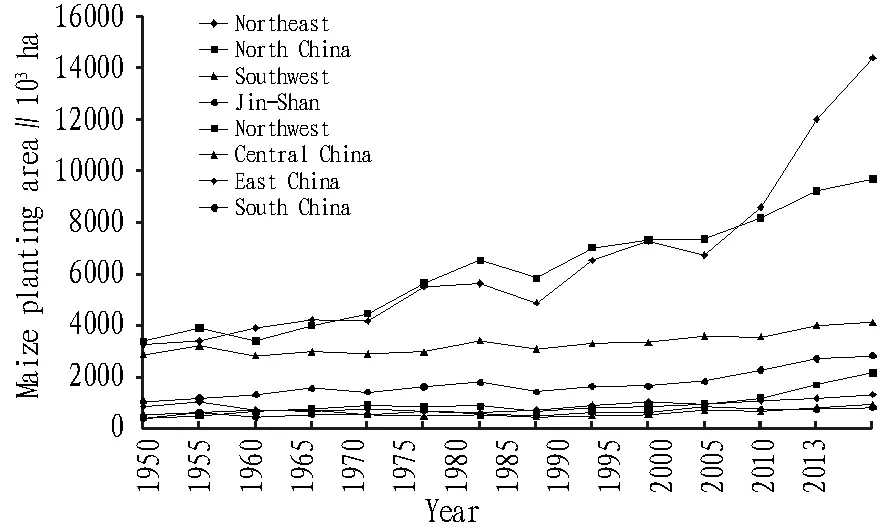
Fig.5 Maize planting area of 8 first-level planting regions
From Fig. 3, China’s maize planting area is gradually increasing, the northern planting are is higher than southern planting area, especially after 2000, the northern planting area rapidly grows, while the southern planting area grows slowly, the gap between southern and northern areas is widening, from 1.7 times to 4.0 times, and the maize production areas go northwards, and there is northern expansion and southern withdrawal.
From Fig. 4, we can know that before the reform and opening-up, the maize sown area in four parts of China steadily grows at the rate below 50%, the gap in between is small; however, the implementation of household contract responsibility system fully stimulates enthusiasm of farmers for planting grain, and grain sown area grew substantially. In particular, after 2000, the maize planting area of central and northeastern areas grew sharply, the percentage of central maize sown area to the whole country rose from 18% in the early stage of founding of new China to 27% in 2013, and the percentage of three northeastern provinces rose from 23% to 31%, they became the largest two maize production areas in China.
From Fig. 5, it can be known that since the founding of new China, main maize production areas of China are still northeastern, North China, and southwestern areas. The maize planting area in the 8 first level planting areas has different level of growth, but the difference is great in growth level. From the founding of new China to 1970s, China’s maize planting area grew slowly, but the planting was relatively decentralized. As stated by Huang Qizheng (1995)[8], the maize production distribution was scatter at the first stage, many areas not suitable for planting maize also planted maize, while suitable areas planted little. In 1970-2000, with guidance of national policies, changes of market environment, and improvement of scientific and technological level, as well as frequent occurrence of natural disasters, maize planting area in China fluctuated greatly. In the fluctuation, planting area in northeastern and North China expanded substantially for 1.6 times. After 2000, the maize planting area took on rigid growth. In 2000-2013, it grew about 1.58 times, while the northeastern and northwestern areas grew more than 2 times. Within 63 years, China has established a narrow "northeastern - Huang-Huai-Hai - southwestern" maize planting belt[3]. However, there is great difference between three traditional maize planting areas: the growth rate in northeastern area is up to 4.4 times, and it is up to 2.9 times in North China; in southwestern area, the growth rate is only 1.4 times; the maize planting belt in China takes on the trend of northward expansion and westward movement.
The above data indicate that China’s maize production is mainly in northern areas, main maize production areas have certain increase, but the traditional main maize production areas are still northeastern, North China, and southeastern areas, while Jin-Shan and northwestern areas are forming. In sum, China’s maize production pattern has the trend of northern expansion and western movement.
3 Analysis on factors influencing changes in maize production pattern of China
3.1TheoreticalanalysisAccording to agricultural regional element theory, regional planning theory and new spatial economics, the production pattern of maize planting will be influenced by resources, economy, market, technology, environment, and policies; these factors influence formation and evolution of maize production pattern in different form, approaches and degrees[9]; according to hypothesis of rational man and theory of producer behavior, farmers, as subjects of agricultural production, take pursuing maximum profit as objectives, and the changes of micro-decision making behavior will lead to variation of agricultural production structure, consequently promote changes in maize production pattern. In this situation, we made theoretical assumptions and empirical analysis on factors influencing China’s maize production pattern from resources, economy, market, technology, and policy.
(i) Natural endowment of resources. Regional distribution of agriculture takes natural laws as precondition. Natural factors, such as moisture, sunshine, and soil, directly influence varieties of crops, suitable growth areas, and production situations. China’s maize production is the production of natural reproduction, and the maize planting is restricted by natural endowment of resources and resource conditions, especially farmland resources. Per capita farmland, multiple cropping index, natural disasters, and water conservancy projects will influence enthusiasm of farmers for planting maize, and accordingly influence maize production pattern.
(ii) Economic environment. With advance in industrialization and urbanization, non-agricultural employment opportunities and income of farmers will constantly increase. As economic men, farmers will leave hometown and engage in non-agricultural sectors, reduce or even give up farming. Decrease of agricultural labor will increase production cost of maize planting. Besides, based on hypothesis of rational men, when deciding whether to plan maize or not, farmers will compare the relative economic benefits of maize with other grain crops. There is outstanding difference in regional economic development level, non-agricultural employment opportunity, and crop cultivation. These factors will influence maize production pattern through influencing farmers’ behavior.
(iii) Market environment. With constant deepening of economic system reform, market plays a decisive role in resource allocation. On the one hand, with increase in the proportion of industrial consumption of maize, the maize demand takes on rigid growth. On the other hand, with development of urbanization, the demands of farmers for coarse grain and meat, eggs and dairy products are increasing. However, as grain ration and feed material, the maize continually increases in demands. Powerful market demand is primary force for regional, large-scale, and specialized development of maize production in China. Besides, according to new spatial economics, traffic condition is an essential factor influencing industrial distribution, and the improvement of transport carrying capacity can weaken influence of geographical location on selection of agricultural production space, and consequently affect maize production pattern.
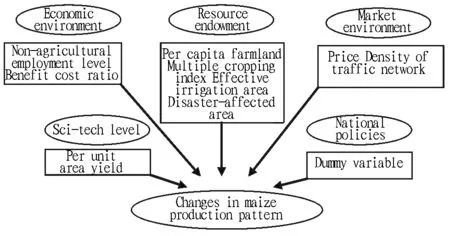
Fig.6 Hypothesis of factors influencing maize production pattern
(iv) Science and technology level. Science and technology are the primary productivity and also important driving force for agricultural progress. Progress and extension of agricultural science and technology will not only influence the per unit area yield, but also weaken restriction of natural conditions to crops, so as to promote changes in regional pattern of crop production. Progress of agricultural science and technology increases the per unit area yield, multiple cropping index, and promotes mechanization progress. The level of agricultural science and technology is different in different areas, and the influence degree of scientific and technological progress on maize planting is also different.
(v) Policy factor. China’s agricultural products are greatly influenced by national policies. In 2004, China started to abolish agricultural tax, and issued preferential policies such as minimum grain purchase price and increasing subsidies for purchasing agricultural machinery and fine seeds. From 2008, temporary maize reserve policy greatly inspired enthusiasm of farmers for planting grain. Only in 2004-2013, the growth rate of maize planting area was up to 43%, and the maize planting area grew explosively. However, different areas have great difference in influence of national policies, which will exert great influence on China’s maize production pattern.
3.2Empiricalanalysis
3.2.1Setting of variables and building of econometric model. According to the above theoretical assumptions, combining with similarities between natural situations and maize planting structure, and with reference to study and experience of other planting crop production distribution, we included resource endowment, economic environment, market environment, technology condition, and policy into the control variables, as listed in Table 2.
Table2Modelvariablesandtheirinfluentialeffect
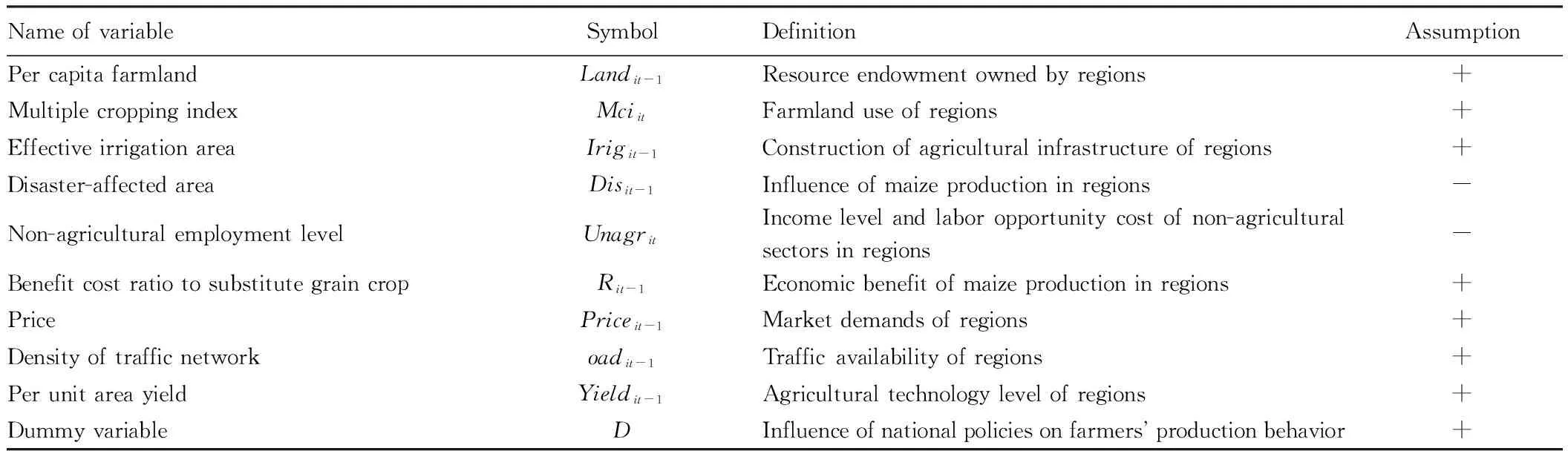
NameofvariableSymbolDefinitionAssumptionPercapitafarmlandLandit-1Resourceendowmentownedbyregions+MultiplecroppingindexMciitFarmlanduseofregions+EffectiveirrigationareaIrigit-1Constructionofagriculturalinfrastructureofregions+Disaster-affectedareaDisit-1Influenceofmaizeproductioninregions-Non-agriculturalemploymentlevelUnagritIncomelevelandlaboropportunitycostofnon-agriculturalsectorsinregions-BenefitcostratiotosubstitutegraincropRit-1Economicbenefitofmaizeproductioninregions+PricePriceit-1Marketdemandsofregions+Densityoftrafficnetworkoadit-1Trafficavailabilityofregions+PerunitareayieldYieldit-1Agriculturaltechnologylevelofregions+DummyvariableDInfluenceofnationalpoliciesonfarmersproductionbehavior+
Based on the above variable setting and panel data, we established the model for influential factors of maize production space pattern in China. The general form is as follows:
Yi=α+β1LnLandit-1+β2LnMciit+β3LnIrigit-1+β4LnDisit-1+β5LnUnagrit+β6LnRit-1+β7LnPriceit-1+β8LnRoadit-1+β9LnYieldit-1+β10D+μi
wheret= 1, 2,… ,26;i= 1,2,… , 19.
3.2.2Data source and description. Considering our purpose and data availability, the data we used were long series panel data consisted of time series and section data of main maize production provinces in 1987-2014.Yis the proportion of maize planting area of the provinceiin the yeartto the maize planting area of the whole country; data of main production provinces and maize planting area came fromChinaRuralStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014). The per capita farmland area (Landit-1) was calculated from total farmland area of each province divided by agricultural population, the multiple cropping index (Mciit) was calculated from grain sown area divided by total local farmland area, and the total farmland, grain sown area and agricultural population data were selected fromChinaRuralStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014). At present, there is no statistical data of effective irrigation area and disaster affected area of maize. With reference to processing methods of other scholars, the effective irrigation area and disaster affected area of maize were estimated according to maize planting area, crop planting area, effective irrigation area, and disaster affected crop area. All data came fromChinaRuralStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014) and the calculation method is as follows:
Effective irrigation area of maize (Irigit-1) = effective irrigation area × (maize planting area ÷ total crop planting area)
Disaster affected maize area (Disit-1) = disaster affected crop area × (maize planting area ÷ total crop planting area)
Besides, non-agricultural employment level (Unagrit) was calculated the balance of rural labors deducting those engaged in agricultural labor divided by total rural labor. These data were selected fromChinaRuralStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014). The benefit cost ratio to substitute grain crop (Rit-1) was calculated from the ratio of net maize output value to net rice/wheat output value, and price of maize, rice, and wheat (Priceit-1) was selected fromCompilationofNationalCostBenefitDataofAgriculturalProducts(1988-2014). The traffic network density (Roadit-1) was calculated from total mileage of road plus railway divided by administrative area, and the data came fromChinaStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014). The per unit area yield (Yieldit-1) was calculated from grain yield of each province divided by the sown area, and the data came fromChinaStatisticalYearbook(1988-2014). The temporary maize purchasing policy is dummy variable (D). Taking the year 2008 as the line, before 2008, it is 0, and after 2008, it is 1; μiis the random perturbation term of the regioni.β1,β2,β3,β4,β5,β6,β7,β8,β9, andβ10denote coefficient of respective variables.
3.2.3Model estimation results and analysis. We made regression of panel data by Stata12.0. Through Hausman test, the statistic was 85.86. At 1% level, it rejected the hypothesis that there is no difference between fixed effect model and random effect model, so adopting the fixed effect model is better than random effect model. The regression estimation results are listed in Table 3.
Table3Estimationresultsoffactorsinfluencingchangesinmaizeproductionpattern
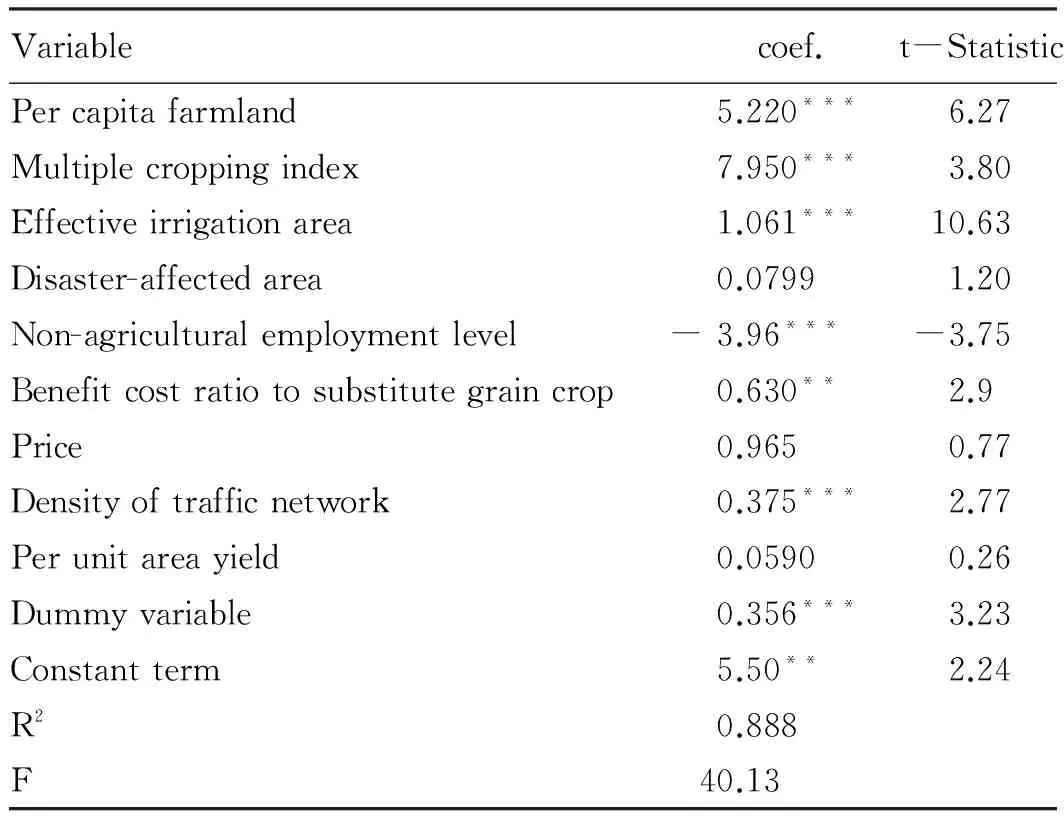
Variablecoef.t-StatisticPercapitafarmland5.220***6.27Multiplecroppingindex7.950***3.80Effectiveirrigationarea1.061***10.63Disaster-affectedarea0.07991.20Non-agriculturalemploymentlevel-3.96***-3.75Benefitcostratiotosubstitutegraincrop0.630**2.9Price0.9650.77Densityoftrafficnetwork0.375***2.77Perunitareayield0.05900.26Dummyvariable0.356***3.23Constantterm5.50**2.24R20.888F40.13
Note:*,**and***signify that variable is significant at 10%, 5% and 1% respectively.
From results reflected in Table 3, the overall estimation effect of the model is excellent, and symbol and significance level of most explanatory variables are consistent with our assumptions. Main conclusions are as follows:
(i) Resource endowment exerts significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. Consistent with the above assumptions, both the farmland volume,i.e. per capita farmland area, and farmland quality,i.e. multiple cropping index, have significantly positive influence on changes in China’s maize production pattern. (ii)Agricultural infrastructure exerts significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. The irrigation condition positively influences changes in maize production pattern and passes significance test. (iii) Natural disasters exert positive but not significant influence on changes in maize production pattern. There is great difference between above assumptions. The influence of natural disasters on maize production pattern is positive, but not significant. The natural disasters of last year did not restrict enthusiasm of farmers for planting maize. (iv) Non-agricultural employment level exerts significantly negative influence on changes in maize production pattern. The coefficient of non-agricultural employment level is negative, and the significance coefficient is below 0, indicating that the higher non-agricultural employment level, the higher non-agricultural employment opportunities, the higher cost for agricultural production, and the more significant negative influence on maize production. (v) Comparative benefit of maize production has significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. The influence of comparative economic benefits of maize to other substitute crops on changes in maize production pattern is positive and significant. Based on rational assumptions, farmers will choose crops with high economic benefits and significant comparative advantages in agricultural production. (vi) Price exerts positive but not significant influence on changes in maize production pattern. As an indicator reflecting market demands, price exerts positive influence on changes in maize production pattern, but it fails to pass the significance test, indicating that market did not play a decisive role in allocation of maize resources. (vii) Traffic network density exerts significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. This is consistent with the above assumption that traffic availability has significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. (viii) The per unit area yield exerts positive but not significant influence on changes in maize production pattern. The per unit area yield has positive effect on changes in maize production pattern, but it fails to pass the significance test, indicating that science and technology level of maize in China is to be improved. From the perspective of scientific and technological input, since the 1990s, the input in agricultural science and technology has been increasing, however the per unit area yield is still very low. In recent years, the growth rate of total power of agricultural machinery dropped from 7-8% to 4-5%, the growth rate of pesticide use dropped from 3-4% to 2-3%; compared with growth rate of 15.6% for the per unit area yield in the United States, China has only 5.5%. From the perspective of scientific and technological extension: on the one hand, most young and middle-aged rural people go to cities and do migrant work, and the average age of farmers takes on aging trend; according to the results of the sixth population census, 40-65 years old farmers account for 42.55% of rural labors and most of them do maize production activities relying on traditional planting methods and experience; on the other hand, farmers have low educational level, farmers with junior middle school and below account for 87.46%; in addition to few related technical trainings, the promotion of agricultural science and technology is not fully brought into play. (ix) National policies exert significantly positive influence on changes in maize production pattern. As expected, the temporary maize purchasing policy significantly and positively influences the maize production pattern. This reflects that positive policy can effectively safeguard farmers’ benefits, inspire enthusiasm of farmers for maize production, and promote changes in maize production pattern.
4 Conclusions and policy recommendations
4.1ConclusionsSince the founding of new China, the maize production has gradually formed a narrow "northeastern - Huang-Huai-Hai - southwestern" maize planting belt, andthe maize production pattern took on characteristic of "northern expansion and western movement. Per capita farmland, multiple cropping index, water conservancy and irrigation, and economic benefit cost ratio, and traffic and transportation policies exert positive effect, non-agricultural employment level exerts negative effect, and the significance of natural disasters, market price, and science and technology are inadequate. This is possibly because maize is one of the most important grain crops in China, and its price fluctuation directly concerns national security. Maize price is greatly influenced by national policies and the effect of market in price making and resource allocation is not significant. In addition, the contribution of planting area to increase of maize yield is far higher than the per unit area yield, and scientific and technology level is still relatively low.
4.2Policyrecommendations(i) Grasp rules of changes in maize production pattern and optimizing maize production pattern. Due to overall influence of resource endowment, economic environment, market environment, technical conditions, and policies, China’s maize planting is gradually centralized, and the production takes on "northern expansion and western movement" trend. However, in the whole country, there are still many areas not suitable for planting maize, which is not favorable for effectively use of resources. Therefore, it is recommended to formulate differentiated support policies, develop superior areas, and further optimize maize production pattern.
(ii) Strengthening infrastructure construction and creating excellent maize production environment. Initial pattern of maize production mainly relies on natural resources, but economic activities of all regions can improve and optimize production pattern. Therefore, strengthening construction of infrastructure such as capital farmland, water conservancy projects and irrigation can alleviate restriction of natural resources to maize production. Besides, improving field roads and inter-regional traffic network can facilitate maize production and circulation and realize organic combination of resource endowment and economic benefits.
(iii) Improving maize insurance system and stabilizing and promoting maize production. Agricultural insurance provides guarantee for agricultural production in the event of natural disasters and plant diseases and insect pests. It can decentralize and transfer losses of farmers and stabilize farmers’ income. Besides, it can stabilize farmers’ expected income, improve enthusiasm of farmers for planting, and promote agricultural production. Therefore, it is recommended to establish and improve effective maize production insurance, strengthen propaganda of agricultural insurance policies, stabilize maize yield, and promote maize production.
(iv) It is recommended to increase scientific and technological input, and increase the contribution rate to per unit area yield. In 2014, the per unit area yield of maize in China was 5.82 t/ha, having a wide gap with 10.73 t/ha in the United States. Compared with mechanized maize planting and high per unit area yield in developed countries, like the United States, China is still relatively low in maize production mechanization, and the contribution of per unit area yield to the yield increase is very little. Therefore, it is recommended to strengthen scientific researches and speed up research and development of fine maize varieties of resisting drought and lodging, enhance scientific and technological extension, cultivate mechanized production, and increase the per unit area yield.
(v) It is recommended to encourage land circulation and realize mechanized production. Traditional extensive and decentralized operation is a major factor restricting China’s maize production. Encouraging land circulation and guiding centralization of land to large planting households or cooperatives are helpful for realizing centralized and mechanized farming, reducing production cost, increasing production efficiency, and realizing economic benefits.
[1] LUO WC, CHEN YF. Variables affecting grain production in China: Regional patterns[J].Journal of Agrotechnical Economics, 2005(6):58-64. (in Chinese).
[2] JIANG J, AN XN, WANG YM,etal. Modeling analysis of regional comparative dominance in maize production in China[J]. Research of Agricultural Modernization,1998(1):9-12. (in Chinese).
[3] ZHONG FN, LIU SF. Analysis on the variation of the distribution of rice production in China[J]. Chinese Rural Economy,2007(9):39-44. (in Chinese).
[4] GUO QH. The development and evolution of the major maize producing areas in China[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences,2010(1):139-145. (in Chinese).
[5]YANG WJ, CHEN WJ. Studies on the spatial distribution changing of China’s rice production and its influencing factors[J]. Economic Geography, 2011(12):2086-2093. (in Chinese).
[6] DENG ZB, FENG YL, ZHANG JL,etal. Analysis on the characteristics and tendency of grain production’s spatial distribution in China[J]. Economic Geography, 2013(5):117-123. (in Chinese).
[7] ZHANG Y. Analysis on the variation of the distribution of peanut production in China[J]. Chinese Rural Economy,2014(11):73-82, 95. (in Chinese).
[8] HUANG QZ. Thinking on the allocation and transportation of maize in China[J]. China Rural Survey,1995(6): 44-46, 23. (in Chinese).
[9] LIU TJ, FAN Y. Analysis of the influencing factor and layout of major apple production in China[J].Problems of Agricultural Economy,2012(10): 36-42, 111. (in Chinese).
January 4, 2016 Accepted: February 13, 2016
*Corresponding author. E-mail: 13237193370@163.com
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Evaluation of Social Vulnerability to Natural Disasters on a County Scale in Henan Province
- An Empirical Analysis of the Export Competitiveness of Agricultural Products in Hubei Province Based on Inter-provincial Comparison
- The Changes in Guilin Paddy Soil Organic Matter and Rice Yield under Long-Term Fertilization
- Study on the Discipline Reputation of Agricultural Colleges and Universities
- Pricing Power of Agricultural Products under the Background of Small Peasant Management and Information Asymmetry
- Backflow of Migrant Workers in Urbanization: Place Selection and Influencing Factors
