ONECUT 转录因子在消化系统器官发育和疾病发生中的功能研究
2015-12-31郭正阳陈香梅鲁凤民
郭正阳,陈香梅,鲁凤民
北京大学医学部病原生物学系,北京100191
ONECUT(OC)蛋白作为转录因子,能广泛调节与细胞增殖、迁移、黏附、分化以及细胞物质代谢相关的蛋白表达,在哺乳动物的器官形成和胚胎发育过程中发挥着重要作用。近年来研究发现OC 蛋白不仅参与肝、胰的发育调控过程,还参与肿瘤、炎症、组织再生等多个生理及病理过程的调控,因此研究OC 蛋白的功能和异常对理解消化系统的器官发育和疾病发生具有重要意义。
1 OC 转录因子的结构特征
OC 转录因子家族含有3 个成员,分别是HNF-6、OC-2 和OC-3。哺乳动物肝细胞核因子6(Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-6,HNF-6)也被称为ONECUT-1(OC-1),于1996 年首次在大鼠中被克隆[1]。HNF-6 作为转录因子能与DNA 结合形成蛋白-DNA 复合物,其DNA 结合结构域包括一个cut 结构域和一个非典型的同源结构域,与其他同源结构域蛋白不同,其非典型同源结构域的48 位为苯丙氨酸,50 位为甲硫氨酸(F48M50)[2]。OC-2 与OC-3 的结构特征与HNF-6 相同,氨基酸序列与HNF-6 具有较大的相似性。三种OC 转录因子的cut 结构域和同源结构域的序列保守性提示其可能结合相同的基因,而许多HNF-6 的DNA 结合位点也在OC-2 和OC-3 中被证实存在[3-4]。
2 OC 转录因子的功能
三种OC 因子的表达具有组织特异性,但也有一定的重叠。在人体中,HNF-6 主要在肝胰岛组织中表达,睾丸和皮肤表达相对较低。OC-2 在肝组织和皮肤呈高表达,在大脑枕叶皮质和睾丸呈较低程度的表达[3]。OC-3 在小鼠大脑和胃肠中表达,在人体内的表达分布尚不清楚[5]。OC 转录因子的功能涉及多个方面,三种OC 因子在功能上即有协同作用,也有各自的特点。
2.1 参与细胞周期和细胞增殖的调控 目前有关OC转录因子调控细胞增殖的研究主要集中在HNF-6。研究表明,HNF-6 能刺激肝再生时的细胞增殖,在小鼠肝再生过程中,HNF-6 高表达能使进入DNA 复制期(S期)的肝细胞数量显著增多。相反,当用siRNA 技术敲减Hepa1-6 小鼠肝癌细胞系HNF-6 的表达后,S 期细胞则减少了50%。
在机制方面,HNF-6 促肝细胞分裂增殖作用可能与其对肿瘤生长因子α(TGF-α)、细胞周期蛋白D1(Cyclin D1)和转录因子Foxm1 的表达上调作用相关,已有研究证实TGF-α、Cyclin D1、Cdc25A、Cdk2 和E2F1 的基因启动子区均存在HNF-6 蛋白的直接结合位点[6-7],提示HNF-6 可通过调控这些基因的表达来发挥其促细胞增殖作用。此外,HNF-6 也可以直接结合甲胎蛋白(AFP)基因增强子,或与维甲酸相关孤核受体α(RORα)发挥协同激活作用,上调AFP 表达[8]。AFP 是肝癌细胞特有的标志物,近年研究发现AFP 可结合和运输多种配体,促进肿瘤和正常细胞的增殖,包括影响细胞分化、生长调控和肿瘤发生进程等[9-11]。
值得注意的是,HNF-6 对细胞增殖的调控作用具有一定的组织特异性,如在结肠腺癌细胞Caco-2 中过表达HNF-6 能抑制细胞周期进程[12];胆管结扎损伤后维持HNF-6 表达能使正常胆管上皮细胞在胆管堵塞后增殖减少[13]。
2.2 参与细胞分化和器官发育的调节 小鼠发育过程中,OC 因子在内胚层按HNF-6、OC-2、OC-3 的时间顺序开始表达,且HNF-6 能够结合并刺激OC-3 基因表达[14]。在小鼠胚胎第9 天,HNF-6 在肝脏、原肠和神经系统表达;在胚胎第10.5 天,HNF-6 在胰上皮细胞表达。OC-2 在发育中的神经系统和肠内胚层中表达,之后在肝和胰中表达,表现出组织局限性和阶段特异性[15]。
OC 因子在小鼠肝脏发育中发挥了重要作用。HNF-6 和OC-2 在前肠内胚层和肝母细胞中表达,HNF-6 参与了肝内胚层向肝母细胞的增殖和分化[16],并控制基膜的适时降解。此外,HNF-6 与OC-2 还共同参与了肝母细胞分化的调控。研究表明,HNF-6 和OC-2 能协同调节TGF-β 二型受体(tbrⅡ)基因的表达,抑制肝实质中的activin/TGF-β 信号,使肝细胞正常分化[17]。胆管细胞的分化也需要转录因子HNF-6和OC-2 参与。在人和斑马鱼的发育过程中,HNF-6能刺激hnf-1β 启动子并控制HNF-6、HNF-1β 级联反应,或者与Notch 信号通路相互作用调控下游分子的表达,参与肝脏内外胆管系统的发育[18-19]。胚胎发育13 ~15 d,HNF-6 和OC-2 可调节早期肝胆细胞系的分离,并减弱未成熟的胆管上皮细胞的分化。因此缺失HNF-6、OC-2、HNF1β 的胎肝出现过大的胆囊,而不能形成适当的肝内胆管系统[17]。
OC 因子在胰腺发育中也发挥重要的调控作用。vHNF-1、HNF-6 和Pdx-1 顺序性激活调控胰腺祖细胞的生成[20],其中HNF-6 能直接刺激Pdx-1 启动子,促进其在腹侧和背侧内胚层表达,以调控内胚层细胞的胰腺特性[21];也能直接激活前内分泌因子Ngn-3 表达,参与内分泌细胞的分化[22]。在胰腺形态形成和内分泌祖细胞分化中,OC-2 与HNF-6 发挥协同作用[23]。研究表明,在胰岛生成过程中,HNF-6 的持续表达会干扰内分泌细胞在胰岛中的空间结构,使葡萄糖转运体GLUT2 缺失或严重减少,破坏β 细胞的生理功能,导致糖尿病[24]。出生后HNF-6 的持续表达同样导致β细胞功能不全[25]。因此,在β 细胞发育过程中,HNF-6的表达下调对β 细胞功能的成熟具有重要意义。
2.3 调节细胞迁移和细胞基质黏附 肝脏发育时肝母细胞增殖并侵袭横膈,然后才能分化为肝细胞或胆管细胞。HNF-6 和OC-2 通过调控某些蛋白的表达而影响这一过程中的细胞迁移和基质黏附。在HNF-6、OC-2 双敲除胚胎中,E-钙黏素和Thbs-4 表达上调,OPN 表达下调[26],肝母细胞能够增殖,但是基底膜未能降解,细胞仍然陷在肝原基中而不发生迁移,引起小鼠胎肝发育不全。有研究表明E-钙黏素在成年肝细胞中是HNF-6 的直接靶基因[27],表明至少一部分细胞迁移黏附相关的基因网络受到OC 因子的直接调控。
体外实验表明,HNF-6 的过表达能抑制结肠癌细胞系SW620 的侵袭、转移能力[28]。受肝脏微环境的影响,HNF-6 在肝内转移的结肠癌细胞中被激活表达,但以非乙酰化HNF-6 为主,刺激DNA 转录的能力较弱。FoxA2 在结肠癌肝转移中高表达,其与HNF-6 之间的蛋白相互作用能抑制后者DNA 结合能力。可见,尽管HNF-6 在结肠癌肝转移细胞中表达上调,但其功能却受到抑制[29]。HNF-6 因子是否影响结肠癌细胞的肝转移仍需深入探究。
OC-2 可能与结直肠癌细胞的迁移、侵袭相关。通过上调mik-429 抑制OC-2 在SW620 和SW480 中的表达,可下调TGF-β1诱导的EMT 标志物的表达水平,并抑制细胞迁移、侵袭,提示OC-2 可能在结肠癌细胞EMT 的初始阶段发挥促进作用[30]。
2.4 调节物质代谢 OC 因子能够通过调节代谢相关基因的转录,参与葡萄糖稳态、胆固醇代谢、胆汁酸清除与转运等代谢过程。
在糖代谢方面,HNF-6 能结合葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶(G6Pase)、葡萄糖激酶(glucokinase)等糖代谢酶以及葡萄糖转运体2(Glut-2)的启动子,并激活这些基因转录[31-33],促进糖异生、糖原合成与分解及葡萄糖转运等过程。此外,HNF-6 能与糖皮质激素受体相互作用,抑制受糖皮质激素激活的肝脏糖代谢酶6-磷酸果糖-2激酶(6-phosphofructo-2 kinase)和磷酸烯醇丙酮酸羧激酶(phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase)基因的表达,通过间接作用抑制糖皮质激素的基因转录刺激功能,调节糖酵解和糖异生等过程[34]。胰岛β 细胞的Granuphilin/Slp4 是一个Rab GTP 酶效应器,能够对胰岛素释放发挥抑制作用[35-36]。OC-2 能结合Granuphilin 基因启动子并抑制其转录活性,当OC-2 转录因子的表达被抑制后,Granuphilin/Slp4 的表达水平增加,使胰岛素的细胞分泌减少,血糖升高[37]。
HNF-6 能调节肝细胞色素P450 酶超家族成员CYP7A1[38]和CYP3A4[39]的表达,参与胆固醇代谢以及多种生化反应。此外,HNF-6 和OC-2 参与了包括HNF-4 和HNF-3β 等肝脏转录因子的调节网络[3,40],而HNF-4 和HNF-3β 能够协同刺激载脂蛋白AI(apoAI)的增强子活性[41],因此,HNF-6 可能间接调节apoAI 的表达。HNF-6 的过表达可上调有机阴离子转运多肽1(Oatp1)的表达水平,并可能因此加强肝细胞对胆汁酸的摄取和清除,缓解胆汁淤积[42]。
3 OC 转录因子的异常表达与疾病
HNF-6 可能与慢性炎症的进展有关。在胆管结扎诱导的肝脏慢性炎症中可观察到HNF-6 表达减少[13]。而HNF-6 的表达能通过下调TGFb2R 的水平抑制慢性炎症向肝纤维化进展[43],并且在HNF-6 缺失的小鼠胚胎肝脏中TGF-β 信号的增强和TGFb2R的表达上调[44],支持HNF-6 抑制TGFb2R 表达和调节慢性炎症的可能。
HNF-6 在肝细胞癌中的异常低表达与肝癌细胞的低分化程度相关。在肝癌细胞中过表达HNF-6 可诱导分化相关标志物的表达,并抑制肝细胞癌的迁移、侵袭,而敲除HNF-6 则作用相反,提示HNF-6 可能是肝细胞癌中的抑癌基因[45]。
HNF-6 可能对胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)的发生和发展发挥负调控作用。腺泡-导管化生(ADM)和胰腺上皮内肿瘤(PanIN)是发生PDAC 的主要危险因素[46]。研究表明,胰腺内HNF-6 失活的小鼠存活到成年后,表现出胰腺导管细胞增生、ADM、鳞状细胞化生以及胰腺炎的特征[47],提示HNF-6 缺失小鼠更易发生PDAC。此外,在PanIN 中HNF-6 的表达下降,且其表达水平与PanIN 病变严重程度呈负相关,HNF-6的低表达可能加快PanIN 向PDAC 的进展[49]。与上述结果一致的是,HNF-6 的表达水平在PDAC 组织中显著低于正常胰腺组织。体外实验进一步证实,将HNF-6 转染入胰腺癌细胞后,胰腺癌细胞的转移和侵袭力降低[48]。因此,HNF-6 可能是胰腺癌中的抑癌基因,其在胰腺的表达缺失可能会提高PDAC 的患病风险。然而也有研究报道HNF-6 对于ADM 具有促进作用,如在人的ADM 腺泡细胞中过表达HNF-6 能抑制Mist1、Ptf1a 等腺泡标志物的表达,诱导Sox-9、CK19 和OPN 等导管标志物的表达,调控与ADM 相关的细胞极性变化[50]。
4 OC 转录因子的作用机制
HNF-6 和OC-2 的作用机制主要有:(1)结合基因的启动子直接调控基因的转录,如HNF-6 可直接激活HNF-1β 的启动子和转录表达[18];(2)与其他转录因子协同发挥作用,如HNF-6 和HNF-3β 协同刺激Cyp2c12 的启动子,转录激活明显强于单独作用[51];(3)作为辅助刺激因子间接刺激基因转录,如HNF-6能刺激FoxM1(HNF-3β)结合内源的Cyclin D1 启动子区,HNF-6-FoxM1 复合物可刺激FoxM1 依赖的靶基因表达[6];(4)调节其他信号通路,如通过TGF-β 信号通路间接影响LETF 的表达[52]。这些转录因子在肝胰发育、代谢调节、疾病发生和进展等生理病理过程中相互影响,发挥转录调节功能[3,53-54]。
5 OC 转录因子调控网络
近年来的研究发现,OC 因子参与了由转录因子和microRNA 组成的基因调控网络[55-56]。如图1 所示,在长激素(GH)的刺激下,肝细胞表达HNF-6[57],HNF-6 和OC-2 可转录激活miR-122,而miR-122 能直接或间接地刺激肝特异基因和大部分肝富含的转录因子(LETF)的表达,包括HNF-6[58],因此适宜水平的miR-122 利于肝细胞的分化进程。肝细胞癌中miR-122 表达水平较正常肝细胞显著下降,提示增加miR-122 水平可能成为肝细胞癌的治疗策略之一[59]。另有研究表明HNF-6 和OC-2 是miR-9、miR-495 和miR-218 的靶基因,其表达可被miR-9、miR-495 和miR-218抑制[36,60-61]。此 外,OC-2 能 促 进HNF-3β 表 达,而HNF-6 则可刺激HNF-3β 和HNF-4 的表达,并且可以直接或间接刺激HNF-1 的表达[3,18,40]。多种转录因子和microRNA 相互调节,保障了细胞状态和功能的稳定性。
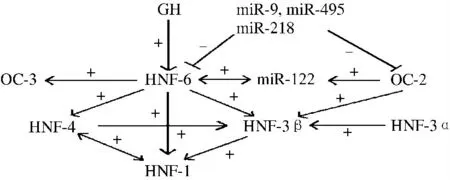
图1 ONECUT 转录因子调控网络Fig 5 Regulatory network of transcription factor of ONECUT
6 总结与展望
OC 因子在细胞周期调控和增殖、细胞迁移和黏附、细胞分化、物质代谢、炎症和化生等病理过程中发挥了重要的调节作用,但目前多数研究结果都是来自于HNF-6 的功能研究,OC-2 和OC-3 的功能研究尚处于起步阶段。因此,未来的研究应该深入探索不同OC因子发挥功能的分子机制及基因调控网络。此外,OC因子的结构和功能异常与临床疾病的关系尚未阐明,特别是其与糖尿病、高胆固醇血症、肝纤维化以及癌症发生、发展的关系还需要更深入的研究。
[1] Lemaigre FP,Durviaux SM,Truong O,et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6,a transcription factor that contains a novel of homeodomain and a single cut domain[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,1996,93(18):9460-9464.
[2] Lannoy VJ,Bürglin TR,Rousseau GG,et al. Isoforms of hepatocyte nuclear factor-6 differ in DNA-binding properties,contain a bifunctional homeodomain,and define the new ONECUT class of homeodomain proteins[J]. J Biol Chem,1998,273(22):13552-13562.
[3] Jacquemin P,Lannoy VJ,Rousseau GG,et al. OC-2,a novel mammalian member of the ONECUT class of homeodomain transcription factors whose function in liver partially overlaps with that of hepatocyte nuclear factor-6[J]. J Biol Chem,1999,274(5):2665-2671.
[4] Vanhorenbeeck V,Jacquemin P,Lemaigre FP,et al. OC-3,a novel mammalian member of the ONECUT class of transcription factors[J].Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2002,292(4):848-854.
[5] Vaisse C,Kim J,Espinosa R 3rd,et al. Pancreatic islet expression studies and polymorphic DNA markers in the genes encoding hepatocyte nuclear factor-3alpha,-3beta,-3gamma,-4gamma,and -6[J]. Diabetes,1997,46(8):1364-1367.
[6] Tan Y,Yoshida Y,Hughes DE,et al. Increased expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 stimulates hepatocyte proliferation during mouse liver regeneration[J]. Gastroenterology,2006,130(4):1283-1300.
[7] Odom DT,Zizlsperger N,Gordon DB,et al. Control of pancreas and liver gene expression by HNF transcription factors [J]. Science,2004,303(5662):1378-1381.
[8] Nacer-Cherif H,Bois-Joyeux B,Rousseau GG,et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-6 stimulates transcription of the alpha-fetoprotein gene and synergizes with the retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan receptor alpha-4[J]. Biochem J,2003,369 (Pt 3):583-591
[9] Muehlemann M,Miller KD,Dauphinee M,et al. Review of growth inhibitory peptide as a biotherapeutic agent for tumor growth,adhesion,and metastasis[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev,2005,24(3):441-467.
[10] Vakharia D,Mizejewski GJ. Human alpha-fetoprotein peptides bind estrogen receptor and estradiol,and suppress breast cancer [J].Breast Cancer Res Treat,2000,63(1):41-52.
[11] Wang S,Jiang W,Chen X,et al. Alpha-fetoprotein acts as a novel signal molecule and mediates transcription of Fn14 in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol,2012,57(2):322-329.
[12] Lehner F,Kulik U,Klempnauer J,et al. Inhibition of the liver enriched protein FOXA2 recovers HNF6 activity in human colon carcinoma and liver hepatoma cells[J]. PLoS One,2010,5(10):e13344.
[13] Holterman AX,Tan Y,Kim W,et al. Diminished hepatic expression of the HNF-6 transcription factor during bile duct obstruction [J].Hepatology,2002,35(6):1392-1399.
[14] Pierreux CE,Vanhorenbeeck V,Jacquemin P,et al. The transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-6/Onecut-1 controls the expression of its paralog Onecut-3 in developing mouse endoderm[J]. J Biol Chem,2004,279(49):51298-51304.
[15] Jacquemin P,Pierreux CE,Fierens S,et al. Cloning and embryonic expression pattern of the mouse Onecut transcription factor OC-2[J].Gene Expr Patterns,2003,3(5):639-644.
[16] Landry C,Clotman F,Hioki T,et al. HNF-6 is expressed in endoderm derivatives and nervous system of the mouse embryo and participates to the cross-regulatory network of liver-enriched transcription factors[J]. Dev Biol,1997,192(2):247-257.
[17] Clotman F,Jacquemin P,Plumb-Rudewiez N,et al. Control of liver cell fate decision by a gradient of TGF beta signaling modulated by Onecut transcription factors [J]. Genes Dev,2005,19 (16):1849-1854.
[18] Clotman F,Lannoy VJ,Reber M,et al. The onecut transcription factor HNF6 is required for normal development of the biliary tract[J].Development,2002,129(8):1819-1828.
[19] Vanderpool C,Sparks EE,Huppert KA,et al. Genetic interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factor-6 and Notch signaling regulate mouse intrahepatic bile duct development in vivo[J]. Hepatology,2012,55(1):233-243.
[20] Poll AV,Pierreux CE,Lokmane L,et al. A vHNF1/TCF2-HNF6 cascade regulates the transcription factor network that controls generation of pancreatic precursor cells [J]. Diabetes,2006,55(1):61-69.
[21] Jacquemin P,Lemaigre FP,Rousseau GG. The Onecut transcription factor HNF-6 (OC-1)is required for timely specification of the pancreas and acts upstream of Pdx-1 in the specification cascade[J].Dev Biol,2003,258(1):105-116.
[22] Jacquemin P,Durviaux SM,Jensen J,et al. Transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 regulates pancreatic endocrine cell differentiation and controls expression of the proendocrine gene ngn3[J]. Mol Cell Biol,2000,20(12):4445-4454.
[23] Vanhorenbeeck V,Jenny M,Cornut JF,et al. Role of the Onecut transcription factors in pancreas morphogenesis and in pancreatic and enteric endocrine differentiation[J]. Dev Biol,2007,305(2):685-694.
[24] Gannon M,Ray MK,Van Zee K,et al. Persistent expression of HNF6 in islet endocrine cells causes disrupted islet architecture and loss of beta cell function[J]. Development,2000,127(13):2883-2895.
[25] Tweedie E,Artner I,Crawford L,et al. Maintenance of hepatic nuclear factor 6 in postnatal islets impairs terminal differentiation and function of beta-cells[J]. Diabetes,2006,55(12):3264-3270.
[26] Margagliotti S,Clotman F,Pierreux CE,et al. The Onecut transcription factors HNF-6/OC-1 and OC-2 regulate early liver expansion by controlling hepatoblast migration [J]. Dev Biol,2007,311(2):579-589.
[27] Odom DT,Dowell RD,Jacobsen ES,et al. Tissue-specific transcriptional regulation has diverged significantly between human and mouse[J].Nat Genet,2007,39(6):730-732.
[28] Geng H,Xiao Q,Xu D,et al. Effect of a recombinant lentiviral vector carrying hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 gene on migration and invasion abilities of SW620 cells[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao,2012,32(1):66-70.
[29] Lehner F,Kulik U,Klempnauer J,et al. The hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 (HNF6)and FOXA2 are key regulators in colorectal liver metastases[J]. FASEB J,2007,21(7):1445-1462.
[30] Sun Y,Shen S,Liu X,et al. MIR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting onecut2 in colorectal carcinoma [J]. Mol Cell Biochem,2014,390(1-2):19-30.
[31] Streeper RS,Hornbuckle LA,Svitek CA,et al. Protein kinase A phosphorylates hepatocyte nuclear factor-6 and stimulates glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene transcription[J]. J Biol Chem,2001,276(22):19111-19118.
[32] Lannoy VJ,Decaux JF,Pierreux CE,et al. Liver glucokinase gene expression is controlled by the onecut transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-6[J]. Diabetologia,2002,45(8):1136-1141.
[33] Tan Y,Adami G,Costa RH. Maintaining HNF6 expression prevents AdHNF3beta-mediated decrease in hepatic levels of Glut-2 and glycogen[J]. Hepatology,2002,35(4):790-798.
[34] Pierreux CE,Stafford J,Demonte D,et al. Antiglucocorticoid activity of hepatocyte nuclear factor-6[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,1999,96(16):8961-8966.
[35] Coppola T,Frantz C,Perret-Menoud V,et al. Pancreatic beta-cell protein granuphilin binds Rab3 and Munc-18 and controls exocytosis[J].Mol Biol Cell,2002,13(6):1906-1915.
[36] Gomi H,Mizutani S,Kasai K,et al. Granuphilin molecularly docks insulin granules to the fusion machinery[J]. J Cell Biol,2005,171(1):99-109.
[37] Plaisance V,Abderrahmani A,Perret-Menoud V,et al. MicroRNA-9 controls the expression of Granuphilin/Slp4 and the secretory response of insulin-producing cells [J]. J Biol Chem,2006,281 (37):26932-26942.
[38] Wang M,Tan Y,Costa RH,et al. In vivo regulation of murine CYP7A1 by HNF-6:a novel mechanism for diminished CYP7A1 expression in biliary obstruction [J]. Hepatology,2004,40(3):600-608.
[39] Sasaki T,Takahashi S,Numata Y,et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 activates the transcription of CYP3A4 in hepatocyte-like cells differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells[J]. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet,2013,28(3):250-259.
[40] Landry C,Clotman F,Hioki T,et al. HNF-6 is expressed in endoderm derivatives and nervous system of the mouse embryo and participates to thecross-regulatory network of liver-enriched transcription factors[J]. Dev Biol,1997,192(2):247-257.
[41] Harnish DC,Malik S,Kilbourne E,et al. Control of apolipoprotein AI gene expression through synergistic interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factors 3 and 4 [J]. J Biol Chem,1996,271 (23):13621-13628.
[42] Maher JM,Slitt AL,Callaghan TN,et al. Alterations in transporter expression in liver,kidney,and duodenum after targeted disruption of the transcription factor HNF1alpha[J]. Biochem Pharmacol,2006,72(4):512-522.
[43] Wang M,Chen M,Zheng G,et al. Transcriptional activation by growth hormone of HNF-6-regulated hepatic genes,a potential mechanism for improved liver repair during biliary injury in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2008,295(2):G357-G366.
[44] Plumb-Rudewiez N,Clotman F,Strick-Marchand H,et al. Transcription factor HNF-6/OC-1 inhibits the stimulation of the HNF-3alpha/Foxa1 gene by TGF-beta in mouse liver [J]. Hepatology,2004,40(6):1266-1274.
[45] Sun H,Tang H,Xie D,et al. Krüppel-like factor 4 blocks hepatocelluar carcinoma dedifferentiation and progression through activation of nepatocyte nuclear factor-6[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2015[Epub ahead of print].
[46] Lowenfels AB,Maisonneuve P,Whitcomb DC. Risk factors for cancer in hereditary pancreatitis. International Hereditary Pancreatitis Study Group[J]. Med Clin North Am,2000,84(3):565-573.
[47] Zhang H,Ables ET,Pope CF,et al. Multiple,temporal-specific roles for HNF 6 in pancreatic endocrine and ductal differentiation[J]. Mech Dev,2009,126(11-12):958-973.
[48] Jiang X,Zhang W,Kayed H,et al. Loss of ONECUT1 expression in human pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Oncol Rep,2008,19(1):157-163.
[49] Pekala KR,Ma X,Kropp PA,et al. Loss of HNF6 expression correlates with human pancreatic cancer progression [J]. Lab Invest,2014,94(5):517-527.
[50] Prévot PP,Simion A,Grimont A,et al. Role of the ductal transcription factors HNF6 and Sox9 in pancreatic acinar-to-ductal metaplasia [J].Gut,2012,61(12):1723-1732.
[51] Delesque-Touchard N,Park SH,Waxman DJ. Synergistic action of hepatocyte nuclear factors 3 and 6 on CYP2C12 gene expression and suppression by growth hormone-activated STAT5b. Proposed model for female specific expression of CYP2C12 in adult rat liver[J]. J Biol Chem,2000,275(44):34173-34182.
[52] Plumb-Rudewiez N,Clotman F,Strick-Marchand H,et al. Transcription factor HNF-6/OC-1 inhibits the stimulation of the HNF-3alpha/Foxa1 gene by TGF-beta in mouse liver [J]. Hepatology,2004,40(6):1266-1274.
[53] Rausa F,Samadani U,Ye H,et al. The cut-homeodomain transcriptional activator HNF-6 is coexpressed with its target gene HNF-3 beta in the developing murine liver and pancreas[J]. Dev Biol,1997,192(2):228-246.
[54] Briancon N,Bailly A,Clotman F,et al. Expression of the alpha7 isoform of hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)4 is activated by HNF6/OC-2 and HNF1 and repressed by HNF4alpha1 in the liver[J]. J Biol Chem,2004,279(32):33398-33408.
[55] Hayashi Y,Wang W,Ninomiya T,et al. Liver enriched transcription factors and differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Mol Pathol,1999,52(1):19-24.
[56] Wang K,Holterman AX. Pathophysiologic role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6[J]. Cell Signal,2012,24(1):9-16.
[57] Lahuna O,Fernandez L,Karlsson H,et al. Expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6 in rat liver is sex-dependent and regulated by growth hormone [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,1997,94 (23):12309-12313.
[58] Laudadio I,Manfroid I,Achouri Y,et al. A feedback loop between the liver-enriched transcription factor network and miR-122 controls hepatocyte differentiation [J]. Gastroenterology,2012,142(1):119-129.
[59] Nakao K,Miyaaki H,Ichikawa T. Antitumor function of microRNA-122 against hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol,2014,49(4):589-593.
[60] Simion A,Laudadio I,Prévot PP,et al. MiR-495 and miR-218 regulate the expression of the Onecut transcription factors HNF-6 and OC-2[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2010,391(1):293-298
[61] Luxenhofer G,Helmbrecht MS,Langhoff J,et al. MicroRNA-9 promotes the switch from early-born to late-born motor neuron populations by regulating Onecut transcription factor expression[J]. Dev Biol,2014,386(2):358-370.
