钙敏感受体介导的信号传导通路及生理功能
2015-12-21赵秀英杭苏琴朱伟云
赵秀英 杭苏琴 朱伟云
(南京农业大学消化道微生物研究室,南京 210095)
钙是机体内最重要的元素之一,是机体各项生理活动不可缺少的元素,除构成骨骼和牙齿外[1],参与一切生命活动,维系着细胞的正常生理功能,特别在维持细胞膜2侧生物电位、正常神经及神经-肌肉传导功能和正常的肌肉伸缩与舒张功能方面发挥重要作用。同时,它也是细胞活动必不可少的第二信使。Brown等[2]首次从牛甲状旁腺细胞中克隆出钙敏感受体(calcium-sensing receptor,CaSR),随后在人甲状旁腺[3]和大鼠的肾脏[4]中也发现了CaSR的表达,进一步研究发现机体内钙离子(Ca2+)可以作为CaSR的天然内源性配体,具有细胞外第一信使的作用[5-7]。当Ca2+等与CaSR结合后,激活CaSR,启动相关信号通路,调控细胞增殖、分化及多种激素的分泌。
1 CaSR的发现
Sherwood等[8]利用放射免疫方法研究影响甲状旁腺激素(parathyroid hormone,PTH)分泌的因素时发现,血清Ca2+浓度上升导致PTH分泌下降,相反,血清 Ca2+浓度下降导致 PTH分泌增加。Care等[9]体外培养甲状旁腺细胞也发现了同样现象,即细胞外Ca2+浓度上升或下降可引起PTH呈相反的变化。然而,细胞外Ca2+为何会影响PTH的分泌?细胞膜上存在电压门控钙通道,是否通过这条途径而引起?研究发现,当钙通道被阻断时,这种变化关系不受影响[10]。当甲状旁腺细胞外Ca2+浓度上升时,胞内Ca2+浓度相应上升,而该细胞PTH的分泌却被抑制[11],后来的研究发现,细胞外Ca2+浓度升高可激活磷脂酰肌醇磷脂酶C(PI-PLC),继而细胞内1,4,5三磷酸肌醇(inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate,IP3)和二酰甘油(diacylglycerol,DAG)浓度上升,随后胞内 Ca2+浓度也上升,而IP3和DAG被证明是与受体介导的Ca2+动员有关的成分[12-14]。Nemeth 等[15]使用荧光指示剂Fura-2发现,牛甲状旁腺细胞外的二价阳离子在无Ca2+跨膜内流的情况下可引起细胞Ca2+的快速动员。上述研究表明,甲状旁腺细胞表面存在一种对细胞外Ca2+浓度敏感的受体,通过影响胞内 Ca2+浓度调节 PTH 分泌[16]。1993 年,Brown等[2]首次克隆了具有上述特性的受体,并命名为CaSR,其功能是维持机体钙稳态和调控PTH的表达。人的CaSR由Garrett等[3]首次从甲状旁腺中克隆出来,与牛的CaSR有93%的相似性。除了牛和人,发现CaSR也广泛存在于其他脊椎动物,如大 鼠[4]、兔[17]、小 鼠[18]、狗[19]、猫[20]、鸡[21]、蝾螈[22]和鱼[23]等。
2 CaSR的结构
CaSR与代谢型谷氨酸受体(metabotropic glutamate receptors,mGluR)、γ-氨基丁酸 B 型受体(GABA)B受体、味觉受体第一家族(T1R)1~3及孤儿G蛋白偶联受体(G protein-coupled receptors,GPCRs)一起,组成了化学感应系统中的GPCRs C家族。它能够感应细胞外Ca2+浓度的改变,介导与之相关联的细胞活动[24]。近来研究发现,它还能感应氨基酸和肽,进而影响细胞生长、增殖及分化、胃肠激素分泌和肠道运动[25-26]。
牛甲状旁腺的CaSR由1 085个氨基酸残基构成,分为 3个独立的区域(图 1)[27]。
细胞外结构域(extracellular domain,ECD):约含600个氨基酸残基,由膜周围ECD和富含半胱氨酸的ECD 2部分组成[28];而呈二裂片状的捕虫夹(venus-flytrap,VFT)结构域也位于此,含450~500个氨基酸残基。该结构域可以结合营养性配体,包括多价阳离子、聚胺及芳香族L型氨基酸等,进而活化CaSR,启动下游信号通路,实现其对细胞的调节功能。
跨膜结构域(membrane spanning domain):约由250个氨基酸残基构成,包括GPCRs特有的7个疏水性的跨膜螺旋(transmembrane domains,TMDs)和3 个细胞内环(intercellular loops,ICLs)。CaSR第一和第二细胞外环路的2个半胱氨酸Cys677和Cys765对维持CaSR构象很关键[29],并且跨膜结构域包含附加的Ca2+结合位点[30],负责ECD和G蛋白之间信号传递作用。除了其在信号传导中的作用外,该跨膜结构域还通过非共价相互作用参与受体二聚化[31]。
胞内结构域(intercellular domains,ICDs),约由200个氨基酸残基构成,包含3个ICLs和1个羧基(—COOH)尾部。每个CaSR单体含有5个蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C,PKC)和2个蛋白激酶A(protein kinase A,PKA)的磷酸化作用位点[32-33],蛋白激酶与CaSR相应的蛋白激酶磷酸化作用位点结合即可发生磷酸化,引起下游信号通路的激活,传递CaSR的感应信息。
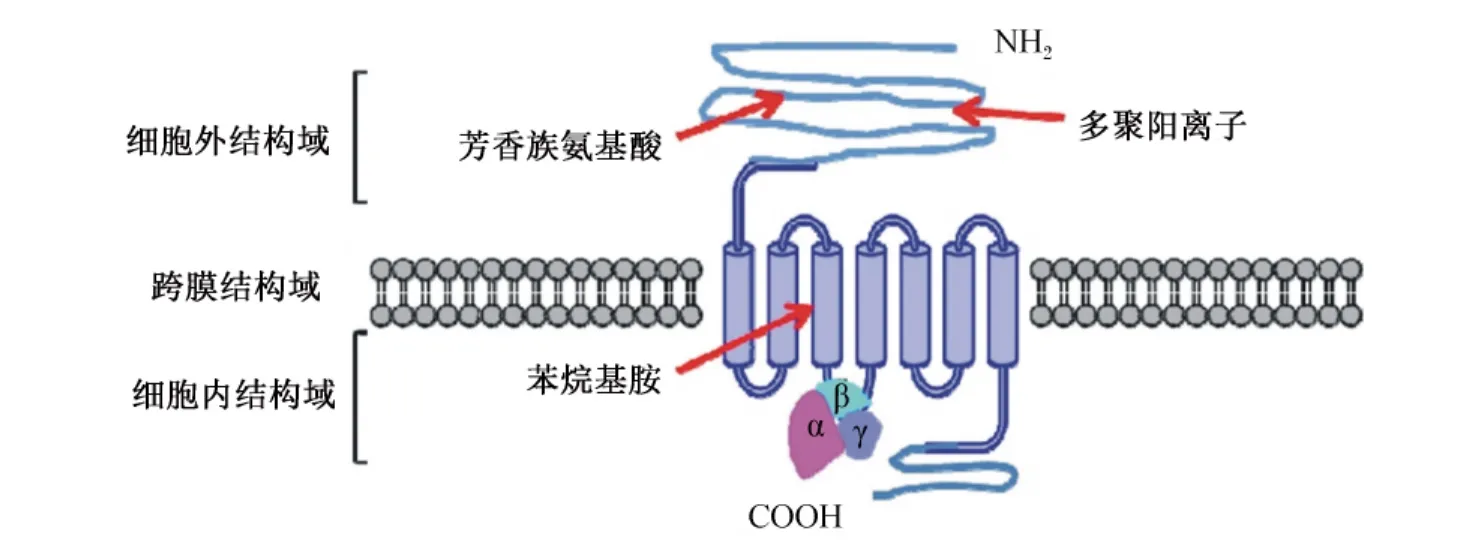
图1 CaSR单体结构图Fig.1 Monomer structure of CaSR[27]
3 CaSR介导的信号活动
CaSR表达受细胞外Ca2+浓度的调节,它在调节细胞钙稳态、渗透平衡和水的吸收方面具有重要作用[34-35]。CaSR作为多功能调节器参与调节细胞生长、分化、凋亡、离子通道开放、细胞分泌等,已成为疾病治疗或预防潜在的治疗靶点[36]。
3.1 CaSR 活化
CaSR胞外氨基(-NH2)末端结构域是配体结合区,包含主要的配体激动剂、抑制剂或正负变构调节剂等的结合位点[24,37-38],CaSR 可被激活剂和变构调节剂活化,激活剂包括多种阳离子[39-40]、带正电荷的氨基葡糖苷类抗生素[41]和聚胺类物质[42]等;变构调节剂包括正向变构调节剂(拟钙剂)[如 L型芳香族氨基酸[43]、钙模拟药物、Calindol]和负向变构调节剂(溶钙剂)[如苯烷基胺衍生物、Calhex231等](表 1)。
芳香族氨基酸和γ-谷氨酰基肽结合CaSR的VFT结构域可适度激活该受体,调节包括细胞内Ca2+释放的CaSR介导的信号传导活动[44-45],而苯烷基胺衍生物可与CaSR跨膜结构域结合,并且碱性多肽与CaSR带负电荷的区域可能存在相互作用[46]。当前,CaSR激动剂特别是变构调节剂的生理学意义尚未完全研究清楚。CaSR介导的信号传导可能会改变由不同激动剂的刺激引起CaSR的构象变化。
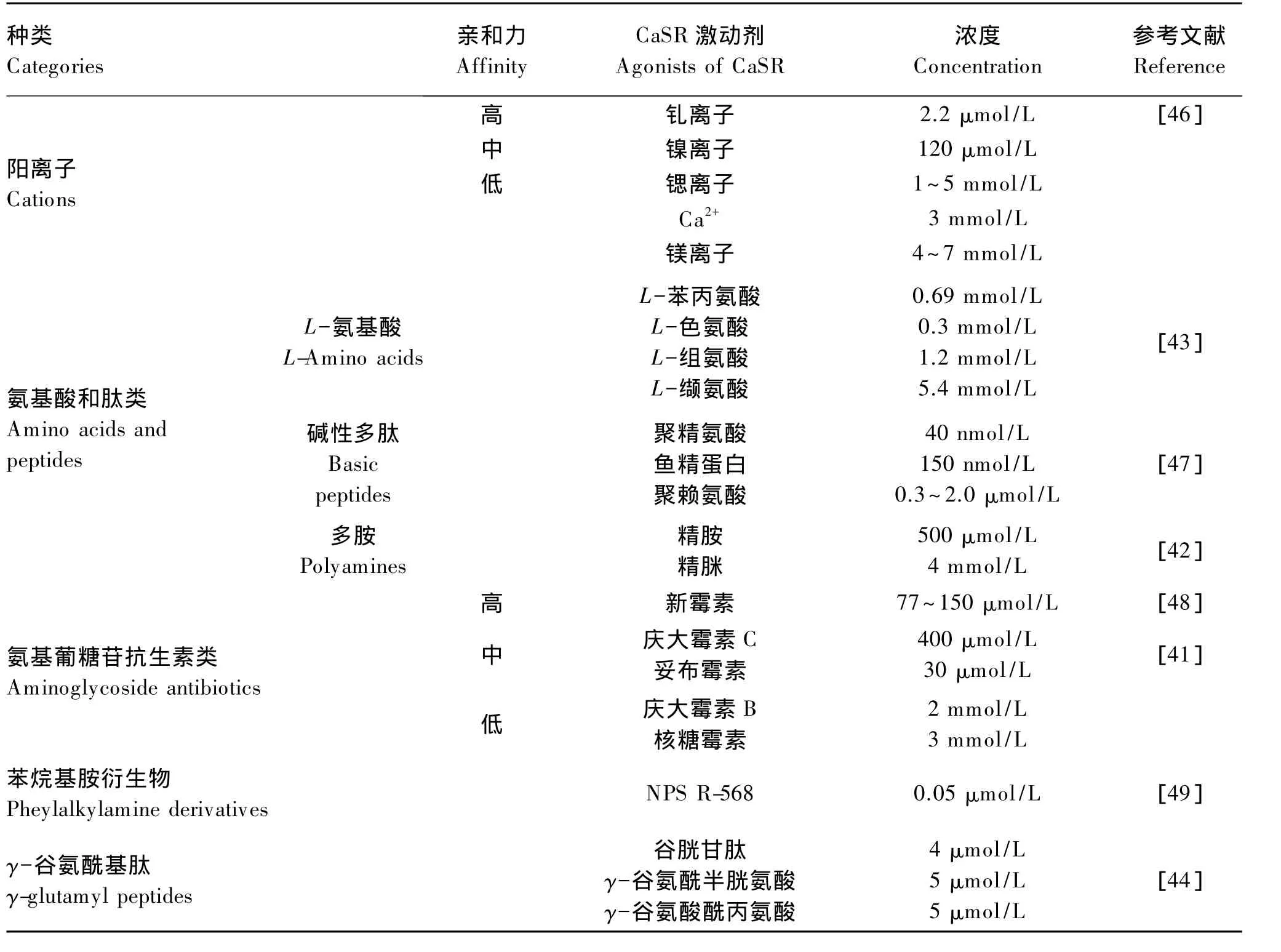
表1 CaSR激动剂的种类Table 1 Categories of CaSR agonists[27]
3.2 CaSR活化介导的细胞信号传导
G蛋白介导的信号传导和GPCRs激酶(GRKs)诱导的脱敏(变构酶不丧失酶活性而失去对变构效应物的敏感性,称为脱敏作用)是CaSR依赖性的2种信使活化途径(图2)[50]。CaSR作为GPCRs能够响应于激动剂的刺激而直接引起G蛋白偶联介导的下游信号传导,主要包括以下3个阶段:首先,激动剂激活CaSR,引起G蛋白介导的磷脂酶C(PLC)和磷脂酰肌醇二磷酸盐(phosphatidylinositol bisophosphate,PtdInsP2)水解,进而释放IP3和DAG,由于IP3扩散并与内质网(endoplasmic reticulum,ER)表面的特异性受体结合,使内部钙贮库释放 Ca2+[6];随后,由升高的细胞内Ca2+浓度或DAG诱导激活PKC,再激活Ras蛋白触发相关联的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)信号传导[36],活化的CaSR也能激活MAPK途径上的多种信号蛋白,例如c-Jun氨基末端激酶(JNK)、p38 MAPK和胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)1/2(表2)[51];最后,CaSR介导的信号终止于一类控制遗传信息表达的转录因子复合物,如核转录因子кB(NF-кB)、激活物蛋白-1(AP-1)等。MAPK 信号传导会激活NF-κB信号通路并提高AP-1的表达,进而抑制细胞凋亡,促进细胞增殖、分化和转化[52-53]。因此,CaSR参与调节生理和病理条件下与其他细胞内信号传导级联相互作用的细胞增殖、分化和凋亡的细胞过程。

图2 激动剂激活的细胞内CaSR信号级联反应示意图Fig.2 Schematic presentation of agonists-activated CaSR signal cascades in cells[27]
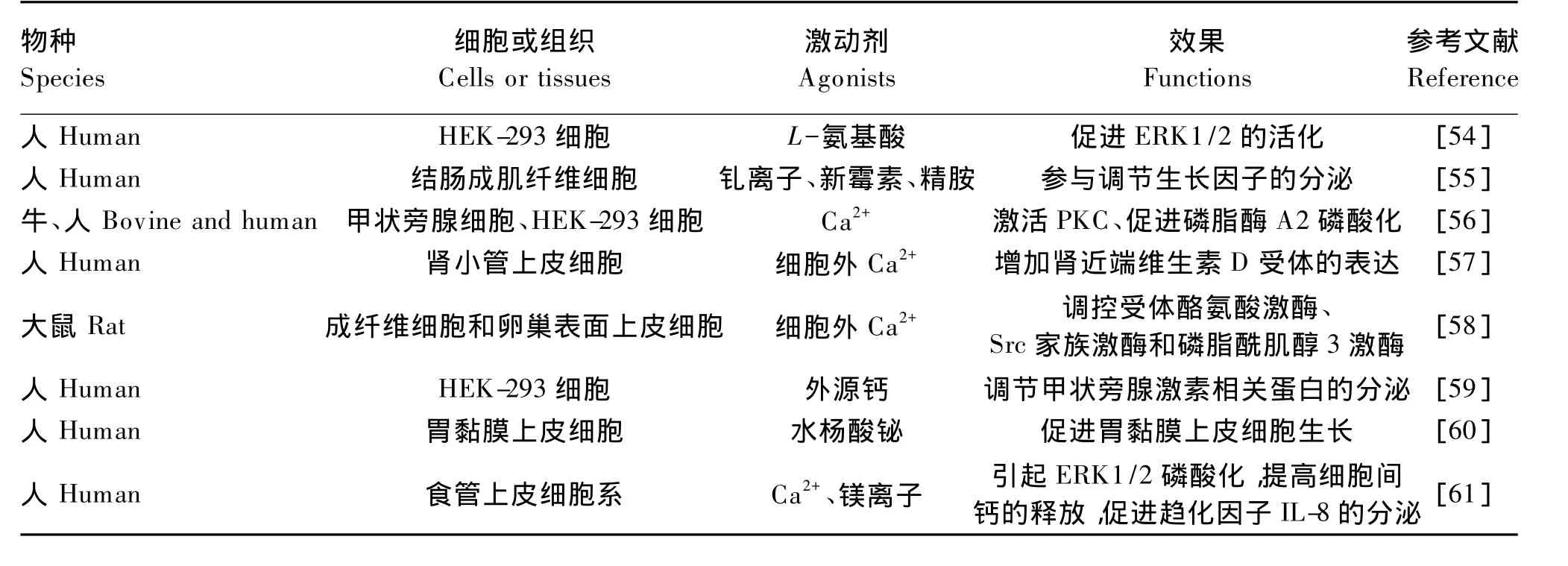
表2 CaSR激活MAPK途径引发的生理效应Table 2 Physiology function mediated by MAPK signaling pathway through CaSR activation
3.3 CaSR 活化的 β-抑制蛋白(β-arrestins)介导的信号传导
除G蛋白介导的经典信号通路外,GRK-β-抑制蛋白类偶联系统也是调节GPCRs活性的关键。CaSR激活可触发β-抑制蛋白2的募集反应并与细胞内的G蛋白偶联,当拮抗剂与GPCRs结合时启动β-抑制蛋白依赖的脱敏作用诱导GRK磷酸化,从而介导β-抑制蛋白与其受体之间相互作用[50],结果是G蛋白和GPCRs之间的相互作用受阻。此外,β-抑制蛋白作为多功能骨架蛋白和连接蛋白,参与调节许多信号传导网络,包括JNK、p38 MAPK、ERK、丝氨酸-苏氨酸蛋白激酶(AKT)、磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(PI3K)和与Ras同源家族成员 A(RhoA)途径[62]。已经发现,β-抑制蛋白作为信号传导的骨架蛋白可以直接结合关键的靶分子,如 ERK1/2、JNK、NF-κB 抑制蛋白 α(IκBα)以及 TRAF6,并可能参与调控促炎症途径[63-64]。此外,β-抑制蛋白通过协调细胞中的NF-κB依赖型信号传导途径调节免疫应答。在多种细胞类型中,如 HEK293、HEK-TLR4、HeLa、THP-1细胞,β-抑制蛋白能直接与IκBα产生关联从而抑制 NF-κB 的转录活性[63,65-66],可能是变构激活的CaSR引起GRK活化,导致β-抑制蛋白的募集从而减弱G蛋白介导的信号事件,从而调节对生理改变有反应的整体信号级联反应。
4 CaSR的生理作用
自发现牛甲状旁腺细胞CaSR可通过感应细胞外Ca2+浓度上升或下降调控PTH分泌和钙的重吸收以来,许多研究发现CaSR广泛表达于不同组织的多种细胞内,包括甲状旁腺[2]、神经系统[67]、骨组织[68]、胃肠道[69]、肾脏[70]及心血管系统[71]等,它在不同的组织中可能调控相同的信号通路,但却发挥不同的生理功能。
4.1 胃肠道
CaSR广泛分布于胃肠道。在小肠和大肠中,CaSR调节响应于细胞外钙的吸收或分泌,细胞外钙浓度主要是由1,25-二羟维生素 D3水平所影响[72]。
在人和大鼠胃中,胃泌素分泌细胞(G细胞)顶端的膜和基底外侧膜、黏液分泌细胞中以及壁细胞的基底外侧膜都可检测到CaSR[73-75],G细胞中表达的CaSR通过PLC信号通路调控胃泌素的分泌[76]。壁细胞中表达的CaSR通过对多种多价阳离子或氨基酸产生反应调控胃酸产生的关键成分即 H+-K+-ATP酶的活性[77-78],而且,它还参与胃中离子泵转运过程的活化,从而影响胃酸的分泌和胃泌素的释放[79]。
在小肠中,CaSR主要表达于十二指肠神经系统的神经丛、神经突和神经纤维[80],I细胞的基底外侧膜和顶膜[81],在K细胞和 L细胞中也有表达,但尚不清楚具体的表达部位[82]。肠神经系统中表达的CaSR对于肠道的运动和肠内液体的分泌有影响[80],由于CaSR在调节肠内液体分泌和吸收方面发挥作用,所以CaSR活化的调控可能会减轻腹泻。CaSR在I、K和L细胞中活化后可促进胆囊收缩素(cholecystokinin,CCK)、葡萄糖促胰岛素肽(gluco-indulinotropic peptide,GIP)、胰高血糖素样肽1(glucagon-like peptide 1,GLP-1)和酪酪肽(peptide tyrosine tyrosine,PYY)的分泌,从而调控小肠的消化和吸收[81-82]。在整个小肠中,上皮细胞中表达的CaSR在感应养分和调节养分吸收过程中发挥了较大作用。
在人大肠,CaSR主要表达于隐窝和绒毛的上皮细胞顶膜和基底外侧膜[69,83-84],结肠隐窝基部的内分泌细胞中也能检测到CaSR[85]。但也有研究报道,CaSR在正常的结肠上皮细胞和Caco-2细胞中表达[86],结肠隐窝顶部高表达,而有高增殖率细胞的隐窝底部没有表达[87]。正常结肠上皮细胞中的CaSR能够使该细胞感应细胞外Ca2+浓度的变化[86],隐窝顶部表达的CaSR具有促进细胞分化的作用。结肠上皮细胞中CaSR可被微生物代谢产物如多胺激活,从而促进结肠液体的分泌[69]。这表明,结肠中表达的CaSR对某些营养素具有响应功能从而调节肠道健康。已经证明,结肠的成肌纤维细胞中Ca2+诱导的CaSR活化能够促进细胞的分化从而刺激肠内屏障的再生[88]。因此,CaSR可直接参与调节结肠上皮细胞的增殖和分化。在结肠癌患者的结肠组织中发现CaSR表达下调[86]。食物中钙吸收增加可通过CaSR介导的通路信号促进结肠黏膜上皮细胞分化,抑制结肠癌的发生[69,89]。所以,CaSR 活化有利于维持结肠完整性和减少结肠癌的发生,并参与调节肠道的生理反应以保持稳态。
总之,CaSR表达于胃肠道,CaSR对调节生理活动的细胞外环境能够做出反应的功能性化学感应体。胃肠道中现有的研究在胃、十二指肠、结肠较多,主要集中在人、大鼠和小鼠等,而关于猪及其他家畜胃肠道中CaSR表达及相关生理作用的研究目前还很少。
4.2 心血管系统
研究表明,CaSR在成年大鼠的整个心脏组织和培养的心室肌细胞都有表达。Wang等[90]发现,在成年大鼠心脏中,当细胞外Ca2+浓度或其他CaSR激动剂(如钆离子或精胺)升高后,细胞内Ca2+浓度呈剂量依赖性的升高,并且在钠离子-钙离子交换体和L型钙通道(L-type calcium channel)阻断的情况下也存在该现象,而U73122(磷脂酶C抑制剂)和肌浆网钙泵抑制剂Thapsigargin可减弱或消除该现象,且心脏中的CaSR通过调控G蛋白-PLC-IP3-IP3受体(IP3R)-Ca2+信号传导途径,引起细胞内钙Ca2+浓度上升,参与兴奋收缩偶联机制。研究发现,CaSR活化启动MAPK(包括p38 MAPK、JNK和ERK)-细胞色素c-天冬氨酸特异性半胱氨酸蛋白酶(cysteine-containing aspartate-specific proteases,caspase)-3 通路和 Fas受体死亡通路,诱导心肌细胞凋亡[91-96]。
4.3 肾脏
文献表明,CaSR在肾脏也有表达,并且是发挥维持钙稳态重要作用的另一个器官[4]。Butters等[17]和 Riccardi等[97]利用免疫组化和 RNA 分离技术,发现CaSR广泛表达于肾单位的主要部位,如近曲小管、髓袢升支粗段、远曲小管和集合管,但肾单位各段之间CaSR表达模式有所不同[98]。在近端小管,CaSR位于刷状缘膜的基部,在髓袢升支粗段,其表达于基底膜,在内髓集合管,其表达于细胞的顶膜[17,97]。
由于肾单位的每段都具有特定的功能,因此推测各段中CaSR具有特定的作用。PTH抑制近端小管对无机磷酸盐的吸收,CaSR的活化可以使这种抑制作用解除[98]。在髓袢升支粗段,发现CaSR活化可降低细胞顶膜钾通道的活性,导致钾的重吸收减少[27]。Aslanova等[99]研究发现,CaSR通过依赖氯化物的方式调控髓袢升支粗段细胞内的pH,在髓袢升支粗段的上皮细胞,CaSR通过Gi和Gq偶联信号在产生肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor,TNF)过程中发挥作用,其主要是通过PKC依赖途径,并且需要T细胞、CaSR介导的环磷腺苷(cAMP)积聚降低的钙调磷酸酶和核因子的活化共同参与[100]。在皮质附近的升支,CaSR活化可能是通过抑制cAMP的累积而抑制依赖PTH的钙吸收[101-102]。在集合管,CaSR调节水通道蛋白2的活性,并通过2种不同方式参与肾上皮细胞的水重吸收[27,34]。Procino 等[103]用 CaSR 激动剂处理稳定表达水通道蛋白2的集合管细胞后发现,通过降低cAMP水平,激活PKC信号通路,增加肌动蛋白纤维水平抑制了毛喉素(forskolin)诱导的水通道蛋白2的转运。而Bustamante等[35]的研究发现,CaSR的活化可通过抑制cAMP的信号传导减弱8-精氨酸加压素诱导的水通道蛋白2的表达。Topala等[104]通过远曲小管和连接小管的CaSR和瞬时受体电位香草酸亚型5通道(transient receptor potential vanilloid-subtype 5 channel,TRPV5)共定位的研究表明,该受体活化可导致TRPV5通道活性升高。
肾脏中CaSR生理作用的研究表明了该受体的多效性,这与它在同一器官的不同类型细胞中的定位及功能不同有关。
5 小结
CaSR广泛分布于不同组织内多种类型的细胞中,包括甲状旁腺、神经系统、骨、胃肠道和肾脏。它参与多种细胞活动的调控,如细胞的分泌、增殖、分化、凋亡和离子通道活性,但这些研究主要集中于人、小鼠和大鼠,家畜方面的研究还很少,它对家畜生长、生殖等各种生命活动的调节作用均不是很明确,特别是在家畜胃肠道中CaSR对营养物质感应与营养转运体转运之间的联系及对胃肠道消化吸收方面是否有作用,有何调节作用目前都尚未深入研究。因此,解析家畜胃肠道中CaSR对营养物质的感应机理,对营养物质消化和吸收的调控作用,及明确CaSR感应营养物质发挥调控作用的机理,对提高家畜饲料利用率和家畜生产性能具有重要的生产实际意义。
[1] JOHANSSON S,KINDMARK A.Vitamins are not always good![J].Lakartidningen,2001,98(11):1252-1255.
[2] BROWN E M,GAMBA G,RICCARDI D,et al.Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid[J].Nature,1993,366(6455):575-580.
[3] GARRETT J E,CAPUANO I V,HAMMERLAND L G,et al.Molecular cloning and functional expression of human parathyroid calcium receptor cDNAs[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1995,270(21):12919-12925.
[4] RICCARDI D,PARK J,LEE W S,et al.Cloning and functional expression of a rat kidney extracellular calcium/polyvalent cation-sensing receptor[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America,1995,92(1):131-135.
[5] CHATTOPADHYAY N.Biochemistry,physiology and pathophysiology of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor[J].The International Journal of Biochemistry& Cell Biology,2000,32(8):789-804.
[6] HOFER A M,BROWN E M.Extracellular calcium sensing and signalling[J].Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2003,4(7):530-538.
[7] ZHAO X,PEI Z M,HE Y K.Extracellular Ca2+signaling:first messenger in animals and plants[J].Hereditas,2007,29(3):269-275.
[8] SHERWOOD L M,POTTS J T,CARE A D,et al.E-valuation by radioimmunoassay of factors controlling the secretion of parathyroid hormone:intravenous infusions of calcium and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid in the cow and goat[J].Nature,1966,209(5018):52-55.
[9] CARE A D,SHERWOOD L M,POTTSJT,Jr.,et al.Perfusion of the isolated parathyroid gland of the goat and sheep[J].Nature,1966,209(5018):55-57.
[10] LÓPEZ-BARNEO J,ARMSTRONG C M.Depolarizing response of rat parathyroid cells to divalent cations[J].The Journal of General Physiology,1983,82(2):269-294.
[11] SHOBACK D,THATCHER J,LEOMERUNO R,et al.Effects of extracellular Ca2+and Mg2+on cytosolic Ca2+and PTH release in dispersed bovine parathyroid PETI[J].Endocrinology,1983,113(1):424-426.
[12] KIFOR O,BROWN E M.Relationship between diacylglycerol levels and extracellular Ca2+in dispersed bovine parathyroid cells[J].Endocrinology,1988,123(6):2723-2729.
[13] BROWN E,ENYEDI P,LEBOFF M,et al.High extracellular Ca2+and Mg2+stimulate accumulation of inositol phosphates in bovine parathyroid cells[J].FEBS Letters,1987,218(1):113-118.
[14] SHOBACK D M,MEMBRENO L A,MCGHEE J G.High calcium and other divalent cations increase inositol trisphosphate in bovine parathyroid cells[J].Endocrinology,1988,123(1):382-389.
[15] NEMETH E F,SCARPA A.Rapid mobilization of cellular Ca2+in bovine parathyroid cells evoked by extracellular divalent cations.Evidence for a cell surface calcium receptor[J].Journal of Biological Chemistry,1987,262(11):5188-5196.
[16] NEMETH E F,CARAFOLI E.The role of extracellular calcium in the regulation of intracellular calcium and cell function[J].Cell Calcium,1990,11(5):319-321.
[17] BUTTERS R R Jr,CHATTOPADHYAY N,NIELSEN P,et al.Cloning and characterization of a calciumsensing receptor from the hypercalcemic New Zealand white rabbit reveals unaltered responsiveness to extracellular calcium[J].Journal of Bone and Mineral Research,1997,12(4):568-579.
[18] ODA Y,TU C L,CHANG W,et al.The calcium sensing receptor and its alternatively spliced form in murine epidermal differentiation[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2000,275(2):1183-1190.
[19] SKELLY B J,FRANKLIN R J M.Mutations in genes causing human familial isolated hyperparathyroidism do not account for hyperparathyroidism in Keeshond dogs[J].The Veterinary Journal,2007,174(3):652-654.
[20] GAL A,RIDGE T K,GRAVES T K.Cloning and sequencing of the calcium-sensing receptor from the feline parathyroid gland[J].Domestic Animal Endocrinology,2010,38(1):57-61.
[21] DIAZ R,HURWITZ S,CHATTOPADHYAY N,et al.Cloning,expression,and tissue localization of the calcium-sensing receptor in chicken(Gallus domesticus)[J].The American Journal of Physiology,1997,273(3):R1008-R1016.
[22] CIMA R R,CHENG I,KLINGENSMITH M E,et al.Identification and functional assay of an extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in Necturus gastric mucosa[J].The American Journal of Physiology,1997,273(5):G1051-G1060.
[23] LORETZ C A.Extracellular calcium-sensing receptors in fishes[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A:Molecular& Integrative Physiology,2008,149(3):225-245.
[24] BROWN E M,MACLEOD R J.Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling[J].Physio-logical Reviews,2001,81(1):239-297.
[25] RASOAMANANA R,DARCEL N,FROMENTIN G,et al.Nutrient sensing and signalling by the gut[J].Proceedings of the Nutrition Society,2012,71(4):446-455.
[26] BRENNAN SC,DAVIES T S,SCHEPELMANN M,et al.Emerging roles of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in nutrient sensing:control of taste modulation and intestinal hormone secretion[J].British Journal of Nutrition,2014,111(Suppl.1):S16-S22.
[27] ZHANG H.Anti-inflammatory effects of allosteric agonist peptides of calcium-sensing receptor in intestinal mucosal system[D].Ph.D.Thesis.Guelph:The University of Guelph,2013:35-46.
[28] BAI M,QUINN S,TRIVEDI S,et al.Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca2+-sensing receptor[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1996,271(32):19537-19545.
[29] RAY K,GHOSH S P,NORTHUP J K.The role of cysteines and charged amino acids in extracellular loops of the human Ca2+receptor in cell surface expression and receptor activation processes[J].Endocrinology,2004,145(8):3892-3903.
[30] HU JX,REYES-CRUZ G,CHEN W Z,et al.Identification of acidic residues in the extracellular loops of the seven-transmembrane domain of the human Ca2+receptor critical for response to Ca2+and a positive allosteric modulator[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2002,277(48):46622-46631.
[31] ZHANG Z X,SUN S,QUINN SJ,et al.The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor dimerizes through multiple types of intermolecular interactions[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2001,276(7):5316-5322.
[32] BAI M,TRIVEDI S,BROWN E M.Dimerization of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor(CaR)on the cell surface of CaR-transfected HEK293cells[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1998,273(36):23605-23610.
[33] CHATTOPADHYAY N,YAMAGUCHI T,BROWN E M.Ca2+receptor from brain to gut:common stimulus,diverse actions[J].Trends in Endocrinology &Metabolism,1998,9(9):354-359.
[34] WANG W H,LU M,HEBERT S C.Cytochrome P-450 metabolites mediate extracellular Ca2+-induced inhibition of apical K+channels in the TAL[J].The A-merican Journal of Physiology,1996,27(1):C103-C111.
[35] BUSTAMANTE M,HASLER U,LEROY V,et al.Calcium-sensing receptor attenuates AVP-induced aquaporin-2 expression via a calmodulin-dependent mechanism[J].Journal of the American Society of Nephrology,2008,19(1):109-116.
[36] SHOBACK D M,BILEZIKIAN JP,TURNER SA,et al.The calcimimetic cinacalcet normalizes serum calcium in subjects with primary hyperparathyroidism[J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology&Metabolism,2003,88(12):5644-5649.
[37] PIN J P,GALVEZ T,PRÉZEAU L.Evolution,structure,and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors[J].Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2003,98(3):325-354.
[38] SAIDAK Z,BRAZIER M,KAMEL S,et al.Agonists and allosteric modulators of the calcium-sensing receptor and their therapeutic applications[J].Molecular Pharmacology,2009,76(6):1131-1144.
[39] MCGEHEE D S,ALDERSBERG M,LIU K P,et al.Mechanism of extracellular Ca2+receptor-stimulated hormone release from sheep thyroid parafollicular cells[J].The Journal of Physiology,1997,502(1):31-44.
[40] BROWN E M.The calcium-sensing receptor:physiology,pathophysiology and CaR-based therapeutics[J].Sub-Cellular Biochemistry,2007,45:139-167.
[41] MCLARNON S J,HOLDEN D,WARD D T,et al.Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce pH-sensitive activation of the calcium-sensing receptor[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2002,297(1):71-77.
[42] QUINN S J,YE C P,DIAZ R,et al.The Ca2+-sensing receptor:a target for polyamines[J].The American Journal of Physiology,1997,273(4):C1315-C1323.
[43] CONIGRAVE A D,MUN H C,DELBRIDGE L,et al.L-amino acids regulate parathyroid hormone secretion[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2004,279(37):38151-38159.
[44] BROADHEAD G K,MUN H C,AVLANI V A,et al.Allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor by γ-glutamyl peptides:inhibition of PTH secretion,suppression of intracellular cAMP levels,and a common mechanism of action with L-amino acids[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2011,286(11):8786-8797.
[45] OHSU T,AMINO Y,NAGASAKI H,et al.Involvement of the calcium-sensing receptor in human taste perception[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2010,285(2):1016-1022.
[46] BREITWIESER G E,MIEDLICH S U,ZHANG M.Calcium sensing receptors as integrators of multiple metabolic signals[J].Cell Calcium,2004,35(3):209-216.
[47] BROWN E M,KATZ C,BUTTERSR,et al.Polyarginine,polylysine,and protamine mimic the effects of high extracellular calcium concentrations on dispersed bovine parathyroid cells[J].Journal of Bone and Mineral Research,1991,6(11):1217-1226.
[48] KATZ C L,BUTTERS R R,CHEN C J,et al.Structure-function relationships for the effects of various aminoglycoside antibiotics on dispersed bovine parathyroid cells[J].Endocrinology,1992,131(2):903-910.
[49] PETREL C,KESSLER A,DAUBAN P,et al.Positive and negative allosteric modulators of the Ca2+-sensing receptor interact within overlapping but not identical binding sites in the transmembrane domain[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2004,279(18):18990-18997.
[50] PIERCE K L,LEFKOWITZ R J.Classical and new roles ofβ-arrestins in the regulation of G-protein-coupled receptors[J].Nature Reviews Neuroscience,2001,2(10):727-733.
[51] TFELT-HANSEN J,MACLEOD R J,CHATTOPADHYAY N,et al.Calcium-sensing receptor stimulates PTHrP release by pathways dependent on PKC,p38 MAPK,JNK,and ERK1/2 in H-500 cells[J].A-merican Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism,2003,285(2):E329-E337.
[52] 潘雷,王英华,曾锦旗,等.核转录因子 NF-κB的研究进展[J].现代实用医学,2002,14(4):205-207.
[53] 何庆南.转录因子AP-1的研究进展[J].国外医学:儿科学分册,1999(3):152-155.
[54] LEE H J,MUN H C,LEWIS N C,et al.Allosteric activation of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor by L-amino acids enhances ERK1/2 phosphorylation[J].Biochemical Journal,2007,404(1):141-149.
[55] PEIRIS D,PACHECO I,SPENCER C,et al.The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor reciprocally regulates the secretion of BMP-2 and the BMP antagonist Noggin in colonic myofibroblasts[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2007,292(3):G753-G766.
[56] KIFOR O,MACLEOD R J,DIAZ R,et al.Regulation of MAP kinase by calcium-sensing receptor in bovine parathyroid and CaR-transfected HEK293 cells[J].A-merican Journal of Physiology:Renal Physiology,2001,280(2):F291-F302.
[57] MAITI A,HAIT N C,BECKMAN M J.Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor activation induces vitamin D receptor levels in proximal kidney HK-2G cells by a mechanism that requires phosphorylation of p38α MAPK[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2008,283(1):175-183.
[58] HOBSON SA,WRIGHT J,LEE F,et al.Activation of the MAP kinase cascade by exogenous calcium-sensing receptor[J].Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2003,200(1/2):189-198.
[59] MACLEOD R J,CHATTOPADHYAY N,BROWN E M.PTHrP stimulated by the calcium-sensing receptor requires MAP kinase activation[J].American Journal of Physiology:Endocrinology and Metabolism,2003,284(2):E435-E442.
[60] GILSTER J,BACON K,MARLINK K,et al.Bismuth subsalicylate increases intracellular Ca2+,MAP-kinase activity,and cell proliferation in normal human gastric mucous epithelial cells[J].Digestive Diseases and Sciences,2004,49(3):370-378.
[61] JUSTINICH C J,MAK N,PACHECO I,et al.The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor(CaSR)on human esophagus and evidence of expression of the CaSR on the esophageal epithelial cell line(HET-1A)[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2008,294(1):G120-G129.
[62] DEWIRE S M,AHN S,LEFKOWITZ R J,et al.β-arrestins and cell signaling[J].Annual Review of Physiology,2007,69:483-510.
[63] GAO H,SUN Y,WU Y L,et al.Identification ofβ-arrestin 2 as a G protein-coupled receptor-stimulated regulator of NF-κB pathways[J].Molecular Cell,2004,14(3):303-317.
[64] WANG Y Y,TANG Y W,TENG L,et al.Association ofβ-arrestin and TRAF6 negatively regulates Tolllike receptor-interleukin 1 receptor signaling[J].Nature Immunology,2006,7(2):139-147.
[65] FAN H K,LUTTRELL L M,TEMPEL G E,et al.βarrestins 1 and 2 differentially regulate LPS-induced signaling and pro-inflammatory gene expression[J].Molecular Immunology,2007,44(12):3092-3099.
[66] WITHEROW D S,GARRISON T R,MILLER W E,et al.β-arrestin inhibits NF-κB activity by means of its interaction with the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of United States of America,2004,101(23):8603-8607.
[67] CHATTOPADHYAY N,CHENG I,ROGERS K,et al.Identification and localization of extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor in rat intestine[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,1998,274(1):G122-G130.
[68] JOECKEL E,HABER T,PRAWITT D,et al.High calcium concentration in bones promotes bone metastasis in renal cell carcinomas expressing calcium-sensing receptor[J].Molecular Cancer,2014,13:42.
[69] HEBERT S C,CHENG S,GEIBEL J.Functions and roles of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor in the gastrointestinal tract[J].Cell Calcium,2004,35(3):239-247.
[70] VEZZOLI G,SOLDATI L,GAMBARO G.Roles of calcium-sensing receptor(CaSR)in renal mineral ion transport[J].Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,2009,10(3):302-310.
[71] SMAJILOVIC S,TFELT-HANSEN J.Calcium acts as a first messenger through the calcium-sensing receptor in the cardiovascular system[J].Cardiovascular Research,2007,75(3):457-467.
[72] FAVUS M J,KATHPALIA S C,COE F L,et al.Effects of diet calcium and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on colon calcium active transport[J].The American Journal of Physiology,1980,238(2):G75-G78.
[73] RAY J M,SQUIRES P E,CURTISS B,et al.Expression of the calcium-sensing receptor on human antral gastrin cells in culture[J].Journal of Clinical Investigation,1997,99(10):2328-2333.
[74] RUTTEN M J,BACON K D,MARLINK K L,et al.I-dentification of a functional Ca2+-sensing receptor in normal human gastric mucous epithelial cells[J].The American Journal of Physiology,1999,277(3):G662-G670.
[75] CHENG I,QURESHI I,CHATTOPADHYAY N,et al.Expression of an extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in rat stomach[J].Gastroenterology,1999,116(1):118-126.
[76] BUCHAN A M,SQUIRESPE,RING M,et al.Mechanism of action of the calcium-sensing receptor in human antral gastrin cells[J].Gastroenterology,2001,120(5):1128-1139.
[77] BUSQUE S M,KERSTETTER J E,GEIBEL J P,et al.L-type amino acids stimulate gastric acid secretion by activation of the calcium-sensing receptor in parietal cells[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2005,289(4):G664-G669.
[78] DUFNER M M,KIRCHHOFF P,REMY C,et al.The calcium-sensing receptor acts as a modulator of gastric acid secretion in freshly isolated human gastric glands[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2005,289(6):G1084-G1090.
[79] GEIBEL J P,HEBERT SC.The functions and roles of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor along the gastrointestinal tract[J].Annual Review of Physiology,2009,71:205-217.
[80] CHATTOPADHYAY N,CHENG I,ROGERS K,et al.Identification and localization of extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor in rat intestine[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,1998,274(1):G122-G130.
[81] LIOU A P,SEI Y,ZHAO X L,et al.The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor is required for cholecystokinin secretion in response to L-phenylalanine in acutely isolated intestinal I cells[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2011,300(4):G538-G546.
[82] MACE O J,SCHINDLER M,PATEL S.The regulation of K-and L-cell activity by GLUT2 and the calcium-sensing receptor CasR in rat small intestine[J].The Journal of Physiology,2012,590(12):2917-2936.
[83] CHENG S X.Calcium-sensing receptor inhibits secretagogue-induced electrolyte secretion by intestine via the enteric nervous system[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2012,303(1):G60-G70.
[84] REY O,CHANG W,BIKLE D,et al.Negative crosstalk between calcium-sensing receptor andβ-catenin signaling systems in colonic epithelium[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,2012,287(2):1158-1167.
[85] SHEININ Y,KÁLLAY E,WRBA F,et al.Immunocytochemical localization of the extracellular calciumsensing receptor in normal and malignant human large intestinal mucosa[J].Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry,2000,48(5):595-601.
[86] CHAKRABARTY S,RADJENDIRANE V,APPEL-MAN H,et al.Extracellular calcium and calcium sensing receptor function in human colon carcinomas:promotion of E-cadherin expression and suppression ofβcatenin/TCF activation[J].Cancer Research,2003,63(1):67-71.
[87] CHAKRABARTY S,WANG H,CANAFF L,et al.Calcium sensing receptor in human colon carcinoma:interaction with Ca2+and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3[J].Cancer Research,2005,65(2):493-498.
[88] PACHECO I I,MACLEOD R J.CaSR stimulates secretion of Wnt5a from colonic myofibroblasts to stimulate CDX2 and sucrase-isomaltase using Ror2 on intestinal epithelia[J].American Journal of Physiology:Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2008,295(4):G748-759.
[89] BRESALIER R S.Calcium,chemoprevention,and cancer:a small step forward(a long way to go)[J].Gastroenterology,1999,116(5):1261-1263.
[90] WANG R,XU C Q,ZHAO W M,et al.Calcium and polyamine regulated calcium-sensing receptors in cardiac tissues[J].European Journal of Biochemistry,2003,270(12):2680-2688.
[91] ZHANG W H,FU S B,LU F H,et al.Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor in ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis in rat cardiomyocytes[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2006,347(4):872-881.
[92] SUN Y H,LIU M N,LI H,et al.Calcium-sensing receptor induces rat neonatal ventricular cardiomyocyte apoptosis[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2006,350(4):942-948.
[93] JIANG C M,HAN L P,LI H Z,et al.Calcium-sensing receptors induce apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes during simulated ischemia/reperfusion[J].Cell Biology International,2008,32(7):792-800.
[94] 孙轶华,张力,徐长庆,等.不同鼠龄大鼠心肌组织中钙敏感受体的表达及与缺氧-再灌注损伤的关系[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006,22(8):1506-1509.
[95] 张伟才,张伟华,吴博,等.钙敏感受体与缺血/再灌注损伤诱发心肌细胞凋亡的线粒体途径的关系[J].中华心血管病杂志,2007,35(8):740-744.
[96] 吴博,张伟华,李全凤,等.钙敏感受体在缺氧-复氧诱导的大鼠心肌细胞凋亡中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(7):1249-1253.
[97] RICCARDI D,HALL A E,CHATTOPADHYAY N,et al.Localization of the extracellular Ca2+/polyvalent cation-sensing protein in rat kidney[J].American Journal of Physiology:Renal Physiology,1998,274(3):F611-F622.
[98] BA J M,FRIEDMAN P A.Calcium-sensing receptor regulation of renal mineral ion transport[J].Cell Calcium,2004,35(3):229-237.
[99] ASLANOVA U F,MORIMOTO T,FARAJOV E I,et al.Chloride-dependent intracellular pH regulation via extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in the medullary thick ascending limb of the mouse kidney[J].Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine,2006,210(4):291-300.
[100] ABDULLAH H I,PEDRAZA P L,MCGIFF J C,et al.CaR activation increases TNF production by mTAL cells via a Gi-dependent mechanism[J].American Journal of Physiology:Renal Physiology,2008,294(2):F345-F354.
[101] DE JESUS FERREIRA M C,HÉLIÈS-TOUSSAINT C,IMBERT-TEBOUL M,et al.Co-expression of a Ca2+-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase and of a Ca2+-sensing receptor in the cortical thick ascending limb cell of the rat kidney.Inhibition of hormone-dependent cAMP accumulation by extracellular Ca2+[J].The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1998,273(24):15192-15202.
[102] MOTOYAMA H I,FRIEDMAN PA.Calcium-sensing receptor regulation of PTH-dependent calcium absorption by mouse cortical ascending limbs[J].American Journal of Physiology:Renal Physiology,2002,283(3):F399-F406.
[103] PROCINO G,CARMOSINO M,TAMMA G,et al.Extracellular calcium antagonizes forskolin-induced aquaporin 2 trafficking in collecting duct cells[J].Kidney International,2004,66(6):2245-2255.
[104] TOPALA C N,SCHOEBER JPH,SEARCHFIELD L E,et al.Activation of the Ca2+-sensing receptor stimulates the activity of the epithelial Ca2+channel TRPV5[J].Cell Calcium,2009,45(4):331-339.
