Experimental research on physical properties of saline soil subgrade filler in Chaerhan region
2015-12-19YuZhangJianHongFangJianKunLiuAnHuaXu
Yu Zhang ,JianHong Fang ,JianKun Liu ,AnHua Xu
1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou,Gansu 730070,China
2.Qinghai Research Institute of Transportation,Xining,Qinghai 810001,China
3.China School of Civil Engineering,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
1 Introduction
Saline soil is a special kind of three-phase soil,making it different from general soil mass.When a saline soil phase change occurs,such as after soil salt dissolves in water,it will affect the physical and mechanical properties of the soil,including its strength,particle composition,salt content,salt type,and water content.Of these,salt content and salt type are the internal causes of strength changes of saline soil,whereas water content and penetration,the soluble filter function of dynamic water,and temperature are the external causes of strength changes of saline soil.Soil strength changes are the result of physical changes and chemical reactions,and they appear as structure reforming,expansion or contraction,dispersion,increase of strain rate,decrease of strength,and change of the hydraulic permeability of saline soil
(Shiet al.,1999;Zhouet al.,2006).Frost heaving,leaching,and corrosion cause special geological problems for certain kinds of engineering constructions,such as slope instability,building cracks,underground metal pipeline corrosion,and the need for subgrade mud pumping,all of which seriously harm transportation lines,water conservancy,and buildings in saline soil areas and cause huge economic losses for society(Luo,2004).It is important to identify the change laws between salt content and some basic physical parameters in order to prevent the future emergence of wet saline soil subgrade problems.
2 Natural and geographical background in test section
Our study area was a 40-km-long section of the highway between Golmud and Chaerhan in Qinghai Province in May 2012,which is located in the Chaerhan salt lake region.Its elevation range is 2,625–3,350 m.Its geomorphic type is flat lacustrine plain in which the Quaternary sediments are very thick,reaching 1 km or more.We controlled the deep substrata of the test section as the silty clay layer,with the natural state of soil below the surface appearing plastic,revealing a thickness range of 1.70–11.70 m.The surface was covered with a thin salt crust,and its engineering geological properties were poor:rich brine underground distribution,with chlorine salt type and strong saline to excessive saline soil being predominant along the highway.
The study region is located in the southwest/central part of the continent.Warm and humid air is prevented from entry due to the surrounding high mountains.Therefore,the region's climate characteristics are dry,nearly rainless,and uneven precipitation distribution,which is typical of the cool and dry continental climate of the plateau.The region has abundant solar radiation and heat.Day and night temperatures change drastically and the maximum daily temperature difference reaches 30.6 °C;the extreme minimum temperature is-33.6 °C and the extreme highest temperature is 35.5 °C.The highway between Golmud and Chaerhan is located in the westerly jet zone,where winds are strong and last for a long time,with the wind direction being mainly westerly.The average wind speed is 2.8 m/s and the extreme wind speed is 42.1 m/s,and this region is most windy from April to June.
Being influenced by climate,topography,stratigraphic properties,and many other factors,the average annual rainfall of this region is only 41 mm,and average annual evaporation capacity is 2,504 mm.Rainfall decreases by degrees from the surrounding mountains to the central regions,while the amount of evaporation increases by degrees from the surrounding mountains to the central regions.Rainfall is mainly concentrated in the months of May to September each year,accounting for more than 80% of the annual precipitation.
3 Investigation of the soil basic physical parameters
We tested six physical properties of the saline soil in this study area:the total salt content,specific gravity of soil,liquid limit,plastic limit,maximum dry density,and optimal water content,in accordance with the "Test Methods of Soils for Highway Engineering(JTGE40-2007)"(Ministry of Transportation Highway Research Institute,2007)requirements.According to the results of saline soil soluble salt chemical tests,the salt classifications were mainly chlorine saline soil and sulfite saline soil;the salt content ranged from 0.221% to 48.464%,rendering the samples as either excessive saline soil or strong saline soil.The results of the saline soil soluble salt chemical tests are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 The results of the saline soil soluble salt chemical tests
3.1 Specific gravity of soil
The relationship between the specific gravity of the soil and the salt content is shown in Figure 1.With increasing salt content,the specific gravity of the soil is gradually reduced.
To understand the variation law between the specific gravity of soil and the salt content,a regression equation was derived:
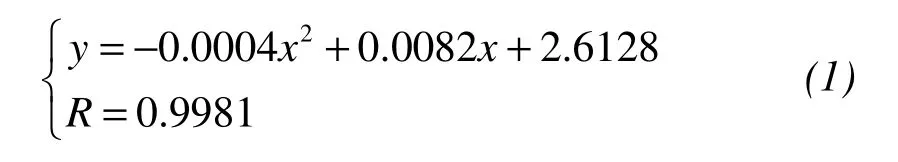
whereyis the specific gravity of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis the correlation coefficient.
Figure 1 Salt content vs.specific gravity of soil
3.2 Liquid limit,plastic limit,and plasticity index
The change relationships among the liquid limit,plastic limit,plasticity index,and the salt content are presented in Figure 2.Clearly,with increasing salt content,the liquid limit,the plastic limit,and plasticity index are gradually reduced.
The variation laws of salt content vs.liquid limit(ωL),plastic limit(ωP),and plasticity index(IP)were also fit to regression Equations(2)through(4):
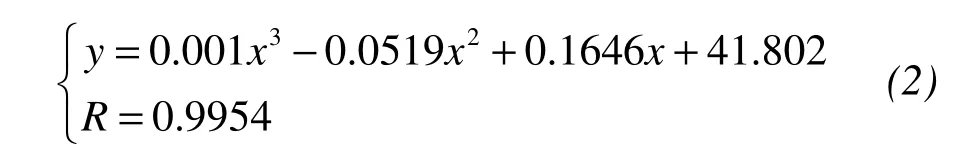
whereyis the liquid limit of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis correlation coefficient.
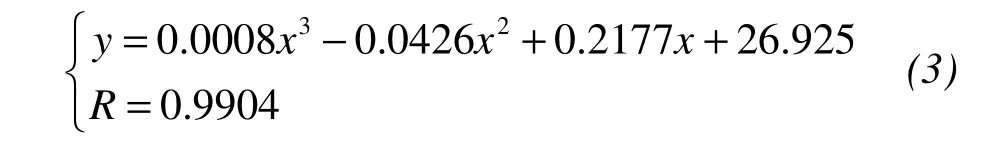
whereyis the plastic limit of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis the correlation coefficient.
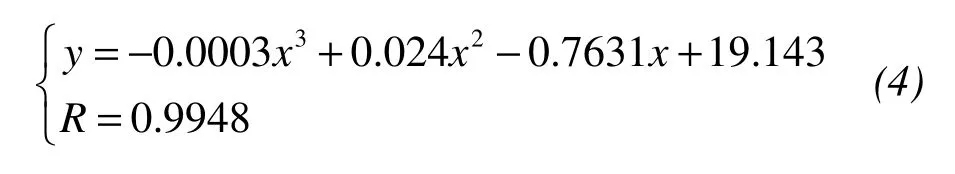
whereyis the plasticity index of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis the correlation coefficient.
3.3 Optimal water content and maximum dry density
The changing relationship among optimal water content,maximum dry density,and the salt content is shown in Figures 3 and 4.Clearly,with increasing salt content,the optimal water content and the maximum dry density are both gradually reduced.
The variation law of salt content vs.optimal water content was fit to regression Equation(5):
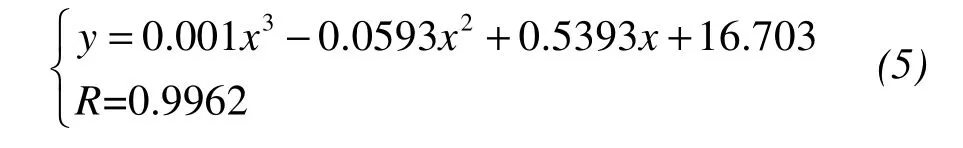
whereyis the optimal water content of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis the correlation coefficient.
The variation law of salt content vs.maximum dry density was fit to regression Equation(6):
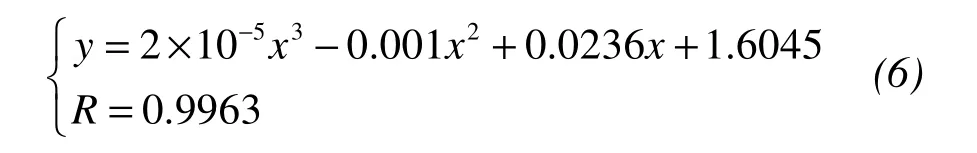
whereyis the maximum dry density of saline soil,xis the salt content of saline soil,andRis the correlation coefficient.
3.4 Particle analysis
The physical and mechanical properties of soil have a certain relationship with the size of the soil particles and the proportion of the various grain-size groups.The results of our saline soil particle analysis are shown in Table 2.In accordance with the "Test Methods of Soils for Highway Engineering(JTG E40-2007)"(Ministry of Transportation Highway Research Institute,2007)requirement,the selected soil samples were low-liquid-limit clay in combination with other physical indicators.
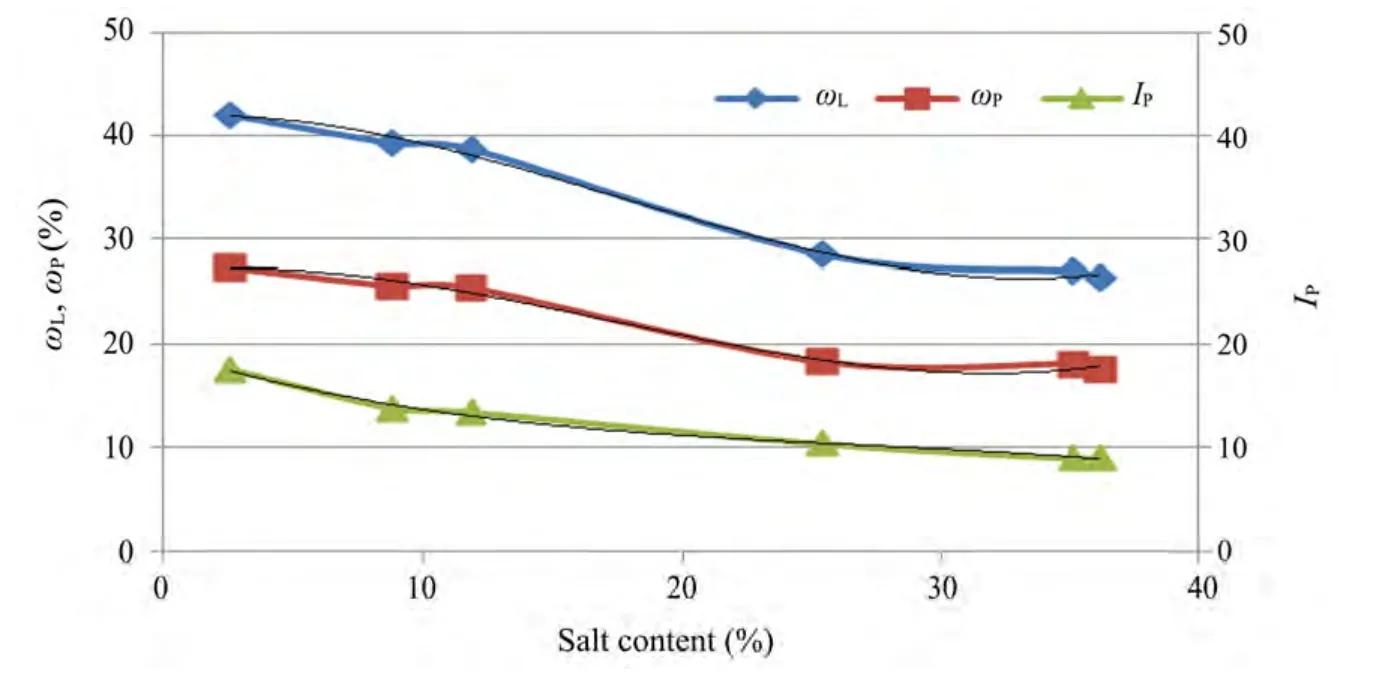
Figure 2 Salt content vs.liquid limit(ωL),plastic limit(ωP),and plasticity index(IP)
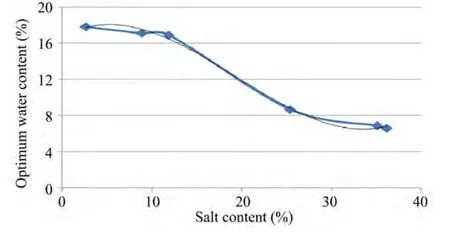
Figure 3 Salt content vs.optimal water content
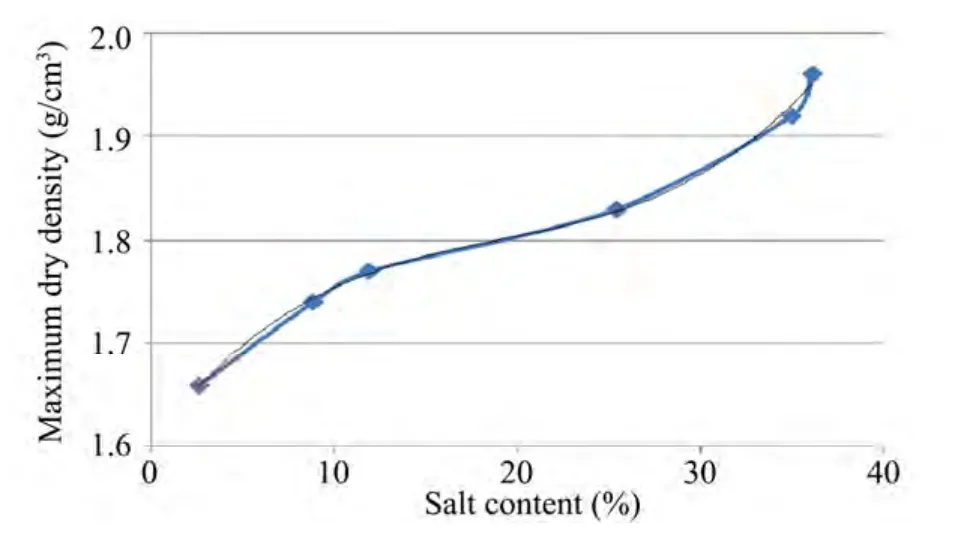
Figure 4 Salt content vs.maximum dry density
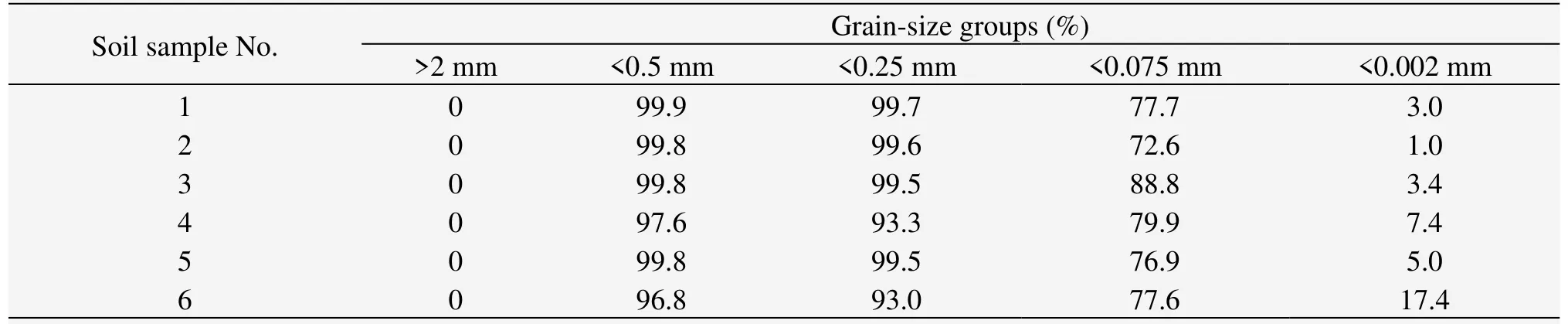
Table 2 The results of particle analysis
4 Conclusions
The physical properties of saline soils in the Chaerhan salt lake region(total salt content,specific gravity of soil,liquid limit,plastic limit,maximum dry density,and optimal water content)were tested and the relationships among them were analyzed.A series of variation laws between these basic physical parameters and salt content were determined,and their regression equations were derived,with all of the correlation coefficients being greater than 0.99.The regression equations enhance understanding of the variation laws of the soil physical properties,enabling improved engineering design and construction in saline soil.This can also help prevent subgrade filler from undermining subgrade stability and producing disease.
The authors wish to acknowledge the support and motivation provided by the Gansu Province Natural Science Foundation(No.145RJZA054)and Lanzhou Jiaotong University Young Scientific Research Fund Project(No.2012032).
Luo QX,2004.Pile Foundation Engineering Testing Manual.Beijing:China Communications Press,pp.55-56.
Ministry of Transportation Highway Research Institute,2007.Test Methods of Soils for Highway Engineering(JTG E40-2007).Beijing:China Communications Press.
Shi PD,1999.Practical Pile Foundation Engineering Manual.Beijing:China Building Industry Press,pp.133-134.
Zhou Q,Han WF,Deng A,et al.,2006.Influences on unconfined compressive strength of stabilized coastal saline soils.Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,28(9):1177–1180.
杂志排行
Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions的其它文章
- Aesthetic evaluation of yardang landforms landscape:the Dunhuang Yardang National Geo-park example
- Comparative studies on leaf epidermal micromorphology and mesophyll structure of Elaeagnus angustifoliaL.in two different regions of desert habitat
- Biomass and water partitioning in two age-related Caragana korshinskii plantations in desert steppe,northern China
- Characterizing stand structure in a spruce forests:effects of sampling protocols
- Characterizing changes in ecosystem service values in China's eastern Loess Plateau
- The characteristics of oasis urban expansion and drive mechanism analysis:a case study on Ganzhou District in Hexi Corridor,China
