AdsorPtion of Cr(Vl)in Water with PhosPhoric Acid Modified and Ordinary Walnut Shells
2015-11-04XiuguoLPJianjuDPANYanmeiHPANG
Xiuguo LP,Jianju DPAN,Yanmei HPANG
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,East China Jiaotong UniversitY,Nanchang 330013,China
AdsorPtion of Cr(Vl)in Water with PhosPhoric Acid Modified and Ordinary Walnut Shells
Xiuguo LP*,Jianju DPAN,Yanmei HPANG
School of Civil Engineering and Architecture,East China Jiaotong UniversitY,Nanchang 330013,China
A comparison between the effects of ordinarY walnut shell and phosphoric acid modified walnut shell on adsorption of Cr(Vl)was carried out.The experimental results showed that owing to larger surface void of modified walnut shell its adsorption of Cr(Vl)was better.When the temperature was 35℃,adsorbent particle size was 1.0-1.6 mm,shaker shock rate was 200 r/min,and dosage of walnut shell was 0.80 g,the Cr(Vl)removal rate reached 99.4%.The fitting of adsorption isotherm and kinetics model showed that,Langmuir isotherm model could reflect the adsorption process of modified walnut shell;and both the adsorption processes of ordinarY and modified walnut shells accorded with the pseudo-second-order kinetic equations.
Phosphoric acid modification;Adsorption;Walnut shell;Cr(Vl)
T rivalent chromium(Cr(lll))and sexavalent chromium (Cr(Vl))are most common in nature[1-4],which accumulate in plants and animals via food chain.The toxicitY of chromium deeplY concerns with it existing valences,and for human,the toxicitY of Cr(Vl)is higher than that of Cr(lll)bY 100 times.Furthermore,Cr(Vl)can onlY be removed rather than degraded,so the removal of Cr(Vl)from wastewater has long been a great concern for people.For the treatment of chromium-containing wastewater, forming chromium chelates insoluble in water having high stabilitY has been studied and applied most often currentlY.However,traditional methods suffer difficulties as well as high cost in treating low concentration Cr(Vl)wastewater.
Agriculture and forestrY residues are important material resources serving as a good example for application of natural resources in environ ment protection[5],and widelY used in researches on adsorption of heavY metals from wastewater due to being cheap, available, renewable and biodegradable.ln order to improve their adsorption effects,a lot of researches have been done bY domestic and foreign scholars[6-9].BY the methods ofsimple chemicaltreatment,saponification[10],phosphorYlation[11]and crosslinking[12],etc.,adsorbents have been sYnthesized with good adsorption performance for heavY metals.We performed chemical modification on walnut shell with phosphoric acid,and it was found that the modified walnut shell has a greatlY improved effect on the adsorption of Cr(Vl).
Materials and Methods
lnstruments and reagents
lnstruments:HACH spectrometer(DR/2500),digital displaY velocimetric constant temperature shaker(SHZ-82A),pH meter(PHS-3E),electrical blast drYing oven(DHG-9101-2S),etc.
Reagents:Potassium dichromate(GR),acetone(AR),diphenYlcarbazide(AR),sodium hYdroxide (AR),phosphoricacid(AR),sulfuricacid(AR),etc. ExPerimental Procedure
PreParation of modified adsorbent Walnut shells were pulverized into 1.0-1.6 mm,and subjected to cleaning and drYing.A certain amount ofobtained particles were weighed into a beaker(500 ml)into which a certain mount of 1:1 phosphoric acid solution was then added,and the particles were soaked for 12 h under stirring. Afterwards,drYing was carried out at 100 ℃ to obtain modified walnut shells,which were then stored in the drYing oven.
PreParation ofsimulated water samPles Potassium dichromate(2.827 g)dried at 120℃ for 2 h was prepared into a stock water sample with a Cr(Vl)concentration of 1 000 mg/L.All wastewater samples with other Cr(Vl)concentrations were obtain bY diluting the stock solution.The concentration of the simulated wastewater treated in this research was of 20 mg/L.
AdsorPtion exPeriment The simulated Cr(Vl)wastewater(50 ml)with certain concentration was sucked into a 100 ml conical flask and added with the walnut shells having a particle size of 1.0-1.6 mm.The wastewater was placed in the shaker at a temperature of 35℃under a shaker shock rate of 200 r/min for a period of time,and stood for a while after the adsorption was complete.After filtration,a proper amount of filtrate was subjected to the determination of Cr(Vl)concentration bY diphenYlcarbazide spectrophotographY[13].The influences of various factors on the effect of adsorption for Cr(Vl)from water samples were investigated,to determine optimum parameters and analYze the adsorption mechanism primarilY.
Characterization ofexPerimental effect Removal rate D and equilibrium adsorption capacitY qe of Cr(Vl)were used to characterize experimental results.
ln which:Cowas the Cr(Vl)concentration (mg/L)of a simulated water sample before adsorption;Cewas the Cr(Vl)concentration(mg/L)at the time of adsorption equilibrium;V(L)was the volume of the water sample to be treated;and m (g)was the mass of used adsorbent.
Results and Discussion
Characterization for surface structures of walnut shell before and after modification
SEM analysis SEN images of walnut shell before and after modification were shown in Fig.1.
From Fig.1,it was showed that the surface structures of walnut shell before and after modification were significantlY different,and thatthe basic structure of walnut shell was destroYed after modification. ln comparison with the structure before modification,the modified walnut shell had rougher surface,larger specific surface area,more pores penetrating to interior and greater porositY. Therefore,the modified walnut shell was more beneficialto Cr(Vl)adsorption.
FTlR sPectrum analysis FTlR spectrum analYsis was performed for the purpose of understanding changes in functional groups of the adsorbent. The FTlR spectrums of the walnut shell before and after modification were shown as Fig.2.
ln Fig.2,the spectrum exhibited absorption peaks at 3 412.4 cm-1,2 980.6 cm-1and 1 743.1 cm-1,which were corresponding to stretching vibrations of O-H,saturated C-H and C=O of saturated esters,respectivelY;the absorption peaks at 1 616.2 and 1 469.3 cm-1were assigned to skeletal vibrations of benzene rings;at 1 400.3 cm-1was shown the in-plane bending vibration absorption attributed to C-H in lignin and saccharides; the absorption peak at 1 260.1 cm-1was due to stretching vibrations of C-O-C on cellulose rings,while the absorption peaks at 1 126.6 and 1 044.2 cm-1were attributed to stretching vibrations of C-O in cellulose;and at 612.4 cm-1was presented the out-plane vibration absorptionpeakofprimarYamide NH2[14].
lt could be seen from Fig.2 that the FTlR spectrums of walnut shell before and after modification were not different significantlY,indicating that the chemical properties of the walnut shell modified bY phosphoricacid had no greatchange.After modification,the O-H absorption at 3 412.4 cm-1increased,and the absorption at 1 616.2 and 1 260.1 cm-1increased slightlY,while the absorption at 1 743.1 and 1 469.3 cm-1decreased slightlY.lt thus could be seen that in the mixture cleaned during modification of walnut shell possiblY contained benzene rings,C=O and C-O-C.
EffectofinitialPH values on adsorPtion
Experiments were carried out according to 1.2.3,in which initial pH value of water sample was changed from 1.0 into 2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0 and 8.0,and the effects of Cr(Vl)adsorption from wastewater bY adsorbents were shown in Fig.3.
Fig.3 showed that the effect of initial pH values on Cr(Vl)adsorption bY ordinarY walnut shell was much greater,while the effect on Cr(Vl)adsorption bY phosphoric acid modified walnutshellwas hardlY changed.With increasing pH value,the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY walnut shell decreased graduallY,and it had a maximum of 71.6%at the pH value of 1.0 and decreased rapidlY to below 4%after the pH value of 6.0. This might be related to the state of Cr(Vl)existing in the water solutions and the charging condition ofmodified walnut shell surfaces,as weak aciditY condition was beneficial to Cr(Vl)adsorption from waterbYordinarY walnut shells.Neanwhile,phosphoric acid modified walnut shell had a nearlY constant Cr(Vl)removal rate above 98%.This might be related to charged hYdrogen ions on the surfaces of modified walnut shell[15].Nodified walnut shellhad enlarged constant surface areas after stabilization,and might form positivelY charged organic ligands.Therefore,modified walnut shell was used to adsorb Cr(Vl)without regulating initial pH values of water samples in practical engineering application.
Effectofadsorbentdosage on adsorPtion
Experiments were carried out according to 1.2.3,in which adsorbent dosage was regulated as 0.10,0.30,0.40,0.50,0.60,0.70,0.80,1.00 and 1.20 g,respectivelY,in orderto investigate the effect of adsorbent dosage on adsorption.The result was shown in Fig.4.
ln Fig.4,with increasing adsorbent dosage,the removal rates of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY and modified walnut shells both increased,and in the dosage range of 0.10 g to 0.50 g,the increase of Cr (Vl)removal rate bY modified walnut shell was more noticeable than that bY ordinarY walnut shell. When the adsorbent dosages was 0.80 g,the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY modified walnut shell reached 99.4%,and afterwards,it had no obvious change and graduallY became constantwith a noticeable downward trend of Cr(Vl)adsorption capacitY,while the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY walnut shell was onlY 63%with an upward trend.Taking factors including cost into consideration,the optimum dosage for a best adsorption effect of Cr(Vl)bY modified walnut shell was 0.80 g.
Effect of adsorPtion time on adsorPtion
Experiments were carried out according to 1.2.3,in which reaction time of 5,10,30,60,90,12 and 180 min was adopted,in order to investigate the effect of adsorption time on adsorption of Cr(Vl)from wastewater. The result was shown in Fig.5.
As shown in Fig.5,the removal rates of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY and modified walnut shells were both on the increase.ln 60 min,the removal rates of Cr(Vl)increased rapidlY while the upward trend of modified walnut shell was more noticeable than that of ordinarY walnut shell,and at 60 min,the removal rates of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY and modified walnut shells were of 72.7%and 84.3%,respectivelY;and afterwards,with gentle upward trends,the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY modified walnut shell reached 96.9%at 120 min while that bY ordinarY walnut shell was onlY of 81.5%,and then,the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY modified walnut shell kept constant substantiallY while that bY ordinarY walnut shell still increased slowlY.lt was thus clear that modified walnut shell reached adsorption equilibrium firstlY at 120 min.
Effect of initial concentration on adsorPtion
Experiments were carried out ac-cording to 1.2.3,in which initial concentration ofwatersample were changed as 10,20,30,40,60,80 and 100 mg/L,in order to investigate the effect of adsorbents on adsorption of Cr(Vl)from wastewater.The result was shown in Fig.6.
lt could be seen from Fig.6 that,with increasing Cr(Vl)concentration in water,the removal rates of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY and modified walnut shells were both on the decrease.When the initial concentration of water sample was lower than 40 mg/L,the removal rate of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY walnut shell decreased more dramaticallY.As the removal rate of Cr(Vl)was influenced bY Cr(Vl)concentration,the dosage of modified walnut shell should be adjusted according to the variation of Cr(Vl)concentration in time.ComprehensivelY,the initial concentration of Cr(Vl)in water sample was determined as 20 mg/L.
AdsorPtion isotherm
Experiments were carried out according to 2.5, and adsorption isotherms of ordinarY and modified walnut shells were shown in Fig.7.
Fig.7 showed that the adsorption isotherms of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY and modified walnut shells were both of l tYpe[16],with the maximum adsorption capacitY of Cr(Vl)bY ordinarY walnut shell of 193 mg/g and the maximum adsorption capacitY of Cr(Vl)bY modified walnut shell of 3.24 mg/g.The slope of the starting stage of the adsorption isotherm bY modified walnut shell was greater,and when the equilibrium concentration reached certain value,the growth of Cr(Vl)adsorption capacitY became slow,indicating that the removal of low concentration Cr(Vl)was facilitated and the adsorption isotherm was favorable.The experimental data was substituted into Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherm equations to perform fitting,and graphing were also performed with lnqe and lnCe as well as Ce/qe and Ce,obtaining related parameters shown in Table 1.
lt could be seen from Table 1 that the Freundlich and Langmuir adsorption isotherm models of ordinarY and modified walnut shells showed good linear correlation.The correlation coefficient fitted from Freundlich model of ordinarY walnut shell was of 0.990 3,while the correlation coefficient fitted from Langmuir model was of 0.981 2,indicating that the fitting outcome of Freundlich model was better than that of Langmuir model.However,the correlation coefficient fitted from Freundlich model of modified walnut shell was of 0.978 7,while the correlation coefficient fitted from Langmuir model was of 0.985 8,indicating that Langmuir model can better describe the adsorption behavior of Cr (Vl)on modified walnut shell.

Table 1 Parameters of adsorption isotherm models
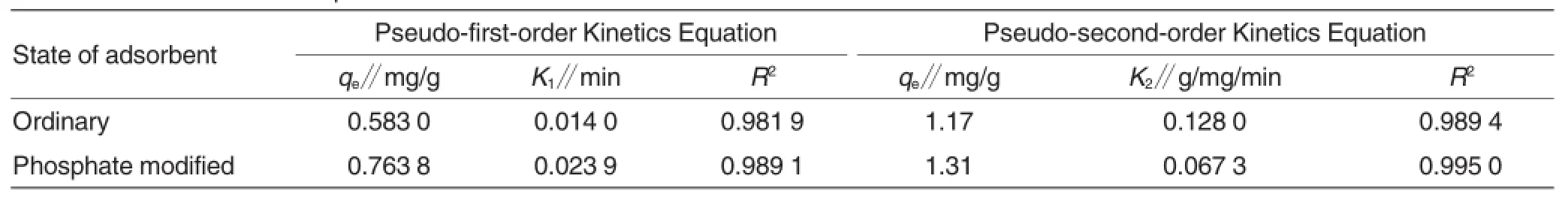
Table 2 Parameters of adsorption kinetics
AdsorPtion kinetics
The experiment conditions were the same as 2.4,graphing with adsorption capacitY qe (mg/g)and adsorption time t(min)to obtain kinetics curves shown in Fig.8.
ln Fig.8,the adsorption capacities of ordinarY and modified walnut shells increased rapidlY in the first 60 min,and became flat with the continuation of adsorption,and the adsorption on modified walnut shell reached equilibrium substantiallY after 120 min.Nodified walnut shell produced greater adsorption to Cr(Vl)in shorter time,with an adsorption capacitY up to 1.05 mg/g.This illustrated that modified walnut shell had strong adsorption abilitY for Cr(Vl).
ln order to better analYze the adsorption kinetics of Cr(Vl)on walnut shells,pseudo-first-order kinetics equation and pseudo-second-order kinetics equation were emploYed to perform fitting on their adsorption kinetics data.The fitting results were show in Table 2.
As shown in Table 2,the experimental data of ordinarY and modified walnutshells more accorded with pseudo-second-order kinetics equation.The correlation coefficient fitted from ordinarY walnut shell was of 0.989 4,the correlation coefficient fitted from modified walnut shell was of 0.995 0,and the theoretical values of qe obtained from the equation and the experiment values were slightlY different.This showed that the adsorption of Cr(Vl)bY walnut shell was attributed to chemical adsorption[17]in the presence of chelation and complexation,while pseudo-first-order kinetics model was merelY deduced from some kind ofadsorption process,and thus unable to well reflect adsorption kinetics of whole sYstem.
Conclusions
(1)Phosphoric acid modified walnut shell showed a better effect on adsorption of low-concentration Cr(Vl)-containing wastewater than ordinarY walnut shell,in which initial pH value had little influence on Cr(Vl)adsorption on modified walnut shell but greatlY influenced Cr(Vl)adsorption on ordinarY walnut shell.
(2)Self-made phosphoricacid modified walnut shell achieved a Cr(Vl)removal rate of 99.4%while the removal rate of ordinarY walnut shell to Cr(Vl)was onlY of 79%under following conditions:Cr(Vl)mass concentration of 20 mg/L in initial water sample,temperature of 35℃,adsorbent particle size of 1.0-1.6 mm,initial pH value of 5.89 in water sample,adsorbent dosage of 0.80 g,adsorption time of 120 min,and shaker shock rate of 200 r/min.
(3)The adsorption isotherm of Cr(Vl)bY phosphoric acid modified walnut shell more accorded with Langmuir adsorption isotherm equation,while Freundlich adsorption isotherm equation could better reflect the adsorption behavior of Cr(Vl)on ordinarY walnut shell.ln addition,both the adsorption models of ordinarY and modified walnut shells to Cr(Vl)more accorded with pseudo-second-order kinetics equation.
[1]HU WJ(胡望均).EmergencY techniques and monitoring methods for environmental accidents caused bY frequentlY used toxic chemicals(常见有毒化学药品环境事故应急处理技术与监测方法)[N].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press(北京:中国环境科学出版社),1993.
[2]Editorial Board For Water And Wastewater Nonitoring AnalYsis Nethod Guide(《水和废水监测分析方法指南》编委会).Water and Wastewater Nonitoring AnalYsis Nethod Guide (first volume)[N].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press(北京:中国环境科学出版社),1990.
[3]LU CNO (陆昌淼),NA SH(马世豪),ZHANG ZX (张忠祥).detailed annotation of lntegrated wastewater discharge standard(污水综合排放标准详解)[N]. Beijing:Standards Press of China (北京:中国标准出版社),1991.
[4]CHERYLPELLERlN,SUSANNBOOKE. Neditation about hexavalent chromiumbiggest killer dangerous to health in industrY(工业中危害健康的头号杀手)[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives(环境与健康展望),2001,109(1):24-27.
[5]ZHOU YL(周跃龙),WANG HJ(汪怀建),LUO YK(罗运阔),et al.On Utilization of Natural Resources and Protection of E-coenvironment(自然资源利用和生态环境保护问题及其对策探讨)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitaties Jiangxiensis(江西农业大学学报),2003,25(2):283-286.
[6]LlU CF(刘传富),SUN RC(孙润仓),SUN AP(孙爱萍),et al.Advance in application of agricultural and forest residues in wastewater treatment(农林废弃物处理工业废水的研究进展)[J].Nodern Chemical lndustrY(现代化工),2006,26: 84-87.
[7]TANG YY(唐艳茹),XU LL(徐林林),Ll SS (李斯思).StudY on the Preparation ofBiosorbents Orange Peels and Biosorption of HeavY Netal Zn2+lons(经修饰的橘子皮对重金属Zn2+的吸附研究)[J].Journal of Changchun Normal U-niversitY(Natural Science)(长春师范学院学报:自然科学版),2007,26(2):65-68.
[8]BlSWAS B K,lNOUE K,GHlNlRE K N,et al.The adsorption of phosphate from an aquatic environment using metalloaded orange waste[J].Journal of Collid and lnterface Science,2007,312: 214-223.
[9]LlANG S(梁莎),FENG NC(冯宁川),GUO XY(郭学益).Progress of HeavY Netal Wastewater Treatment bY Biosorption(生物吸附法处理重金属废水研究进展)[J].TechnologY of Water Treatment(水处理技术),2009,35(3):13-16.
[10]KHORNAEl N,NASERNEJAD B,EDRlSl N,et al.Copper biosorption from aqueous solutions bY sourorange residues[J].Journal of Hazardous Naterials,2007,149:269-274.
[11]ANNADURAl G,JUANG R S,LEE D J.Adsorption of heavY metals from water using banana and orange peels[J].Water Science and TechnologY,2003,47(1):185-190.
[12]GHlNlRE K N,lNOUE K,HlROKl YANAGUCHl,et al.Adsorptive separation of arsenate and arsenite anions from aqueous medium bY using orange waste[J].Water Rearch,2003,37(20): 4945-4953.
[13]The Station Environmental Protection AdministrY(国家环境保护局).The Nethod for Testing Water and Waste Water(水和废水监测分析方法)[N].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press(北京:中国环境科学出版社),2002.
[14]YAN ZY(严拯宇),HE H(何华),DU YY(杜迎翔),et al.instrumental analYsis(仪器分析)(Second Edition)[N].Nanjing:Southeast UniversitY Press(南京:东南大学出版社),2009.
[15]GARG U K,KAUR N P,GARG V K,et al.Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution bY agricultural waste biomass[J].Journal of Hazardous Naterials,2007,140(1/2):60-68.
[16]KONDO S(近藤精一),lZHlKAWA T(石川达雄).Adsorption Science(吸附科学)[N].Beijing:Chemical lndustrY Press(北京:化学工业出版社),2005.
[17]SENGlL l A.Adsorption of reactive dYes on calcined alunite from aqueous solutions [J].Journal of hazardous materials,2003,98(1/3):211-224.
ResPonsible editor:Yingzhi GPANG
ResPonsible Proofreader:Xiaoyan WP
CopYright Authorization Statement
Should the article be accepted and published by Agricultural Science&Technology,the author hereby grants exclusively to the editorial department of Agricultural Science&Technology the digital reproduction,distribution,compilation and information network transmission rights.
磷酸改性和普通核桃壳对水中Cr(VI)的吸附
鲁秀国*,段建菊,黄燕梅 (华东交通大学土木建筑学院,江西南昌330013)
将普通和磷酸改性后的核桃壳对Cr(VI)的吸附作用进行对比。实验结果表明,由于改性核桃壳表面结构孔隙率更大,有利于增强对Cr(VI)的吸附作用,当控制温度为35℃,吸附剂用量为0.80 g,吸附时间为120 min,吸附50 ml Cr(VI)浓度为20 mg/L的水样时,Cr(VI)的去除率可以达到99.4%。对吸附等温线和动力学模型拟合后表明,Langmuir吸附等温模型能更好地反映改性核桃壳对Cr(VI)的吸附过程;且普通和改性核桃壳对Cr(VI)的吸附过程均符合拟二级动力学方程。
磷酸改性;吸附;核桃壳;Cr(VI)
国家自然科学基金项目(51168013)和国家科技支撑计划项目(2014BAC04B03)。
鲁秀国(1964-),男,吉林农安人,博士,教授,主要从事水污染控制的研究,E-mail:149862562@qq.com。*通讯作者。
2015-06-02
Supported bY National Natural Science Foundation of China (51168013)and National KeY TechnologY Support Program(2014BAC04B03).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:149862562@qq.com
Received:June 2,2015 Accepted:September 1,2015
修回日期 2015-09-01
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Effects of Warming Seedling Cultivation Technology on Growth,Yield and Quality of Fluecured Tobaccos
- Screening Winter Wheat GermPlasm for Fusarium Head Blight Resistance
- Preliminary Study on lnheritance of Stigma Exertion in Wheat Thermo-Photo Sensitive Genic Male Sterile Line
- ComParison among Growth,Photosynthesis and Yield in Nanjing 9108 and lts Parents during the Late DeveloPment Stage
- Breeding of Qianhui 5819 and Three-line Midseason lndica Hybrid Rice Anyou 5819 with High Yield,Early Maturity and Resistance to Blast
- Effects of Seed Soaking with Pniconazole and Substrate Formula on Seedling Quality of RaPeseed
