人脸特征提取与识别
2015-11-01comparativestudyoftexturemeasureswithclassificationbasedonfeaturedistributions
A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions
Ojala,T; Pietikainen,M; Harwood,D
Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using class specific linear projection
Belhumeur,PN; Hespanha,JP; Kriegman,DJ
Robust real-time face detection
Viola,P; Jones,MJ
PCA versus LDA
Martinez,AM; Kak,AC; et al.
人脸识别技术综述
张翠平,苏光大
(清华大学电子工程系“智能技术与系统”国家重点实验室图形图象分室,北京 100084)
人脸识别技术综述
张翠平,苏光大
热点追踪
人脸特征提取与识别
·编者按·
人脸识别,也称作面部识别或人像识别,是利用计算机技术,基于人的脸部特征信息进行身份识别的技术,主要包括三个主要环节,即人脸检测、脸部特征点定位和特征提取和识别。广义的人脸识别研究范围主要包括人脸检测、人脸表征、人脸鉴别、表情姿态分析和生理分类等,该研究同属于生物特征识别、计算机视觉、人工智能等多个领域,涉及到模式识别、图象处理及生理、心理学等多方面的知识。狭义的人脸识别是将待识别人脸所提取的特征与数据库中人脸的特征进行对比,根据相似度判别分类。本专题侧重关注狭义人脸识别,即人脸特征提取与识别技术。
与指纹、视网膜、虹膜、基因等其他人体生物特征识别系统相比,人脸识别具有简便、友好、直接的特点,更易于为用户所接受,并且还能够获得一些额外信息,因而,该技术在许多领域有着广阔的应用前景。人脸识别可用于安全验证系统、公安系统、人机交互系统等,此外还可用于档案管理、医学领域、金融领域以及视频会议等方面。
人脸识别技术的具体实现方法是将检测出的人脸图像信息与数据库中的人脸图像进行对比,从中找出与之匹配的人脸。人脸识别的理论研究以正面图像输入模式为主,主要经历了三个阶段。第一阶段主要研究人脸识别所需要的面部特征,主要的研究者以Bertillon、Allen和Parke为代表;第二阶段主要研究人机交互识别,主要的研究者有Goldstion,Harmon和Lesk;第三阶段开启了机器自动识别技术研究,主要包括基于几何特征、基于代数特征和基于连接机制的三种识别技术。常用的人脸特征提取与识别方法主要包括:基于主元分析的人脸识别方法、基于奇异值分解的人脸识别方法、基于几何结构特征与灰度特征融合的人脸识别方法、非线性建模人脸识别方法、基于隐马尔可夫模型的人脸识别方法和基于图像重建和图像融合的人脸识别方法。
目前,深度学习和大数据是人脸识别研究的一个主要热点方向,现有的大规模人脸数据集合包括:北京旷视科技(Megvii)有限公司旗下的新型视觉服务平台Face++的5 million images of 20000 subjects,谷歌公司的人工智能系统FaceNet的100-200 million images of 8 million subjects,腾讯公司的优图团队Tencent-BestImage的1 million images of 20000 subjects,以及中国科学院自动化研究所的494414 images of 10575 subjects。
本专题得到了谭铁牛院士(中国科学院自动化研究所)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年5月7日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以人脸识别为词条检索到的期刊文献分别为4612与4795条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)
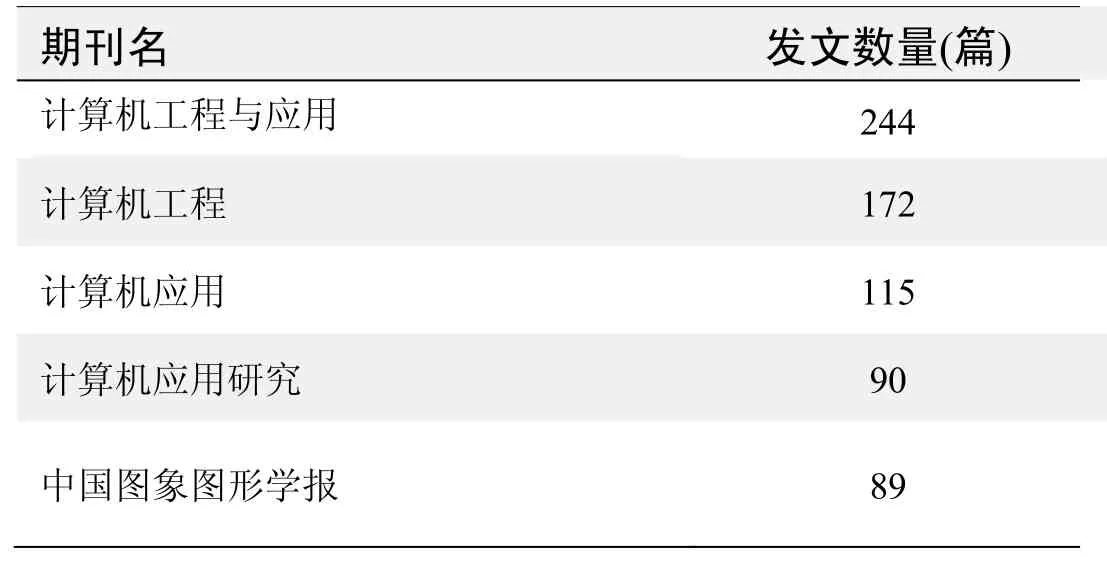
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
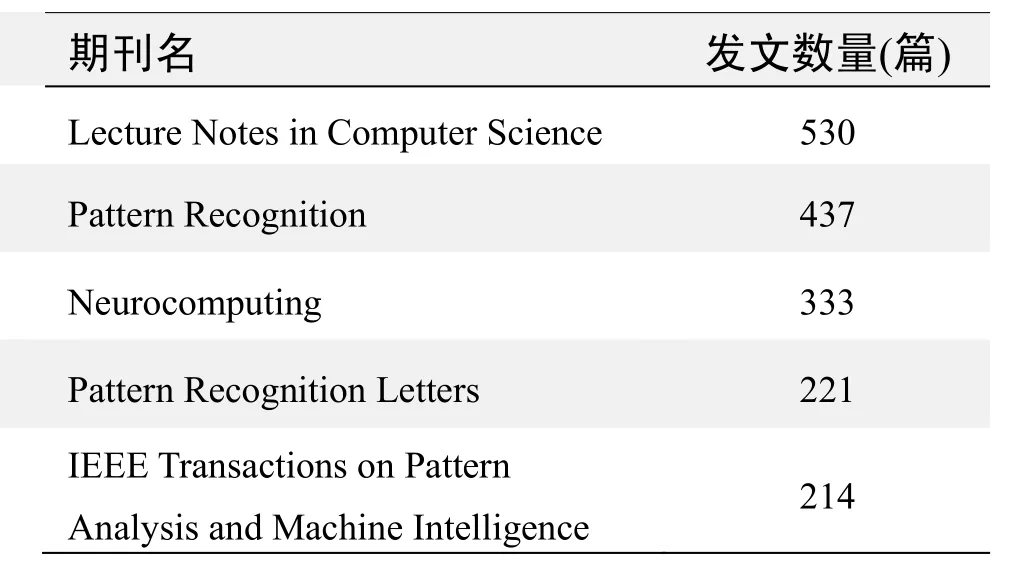
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以人脸识别为词条检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
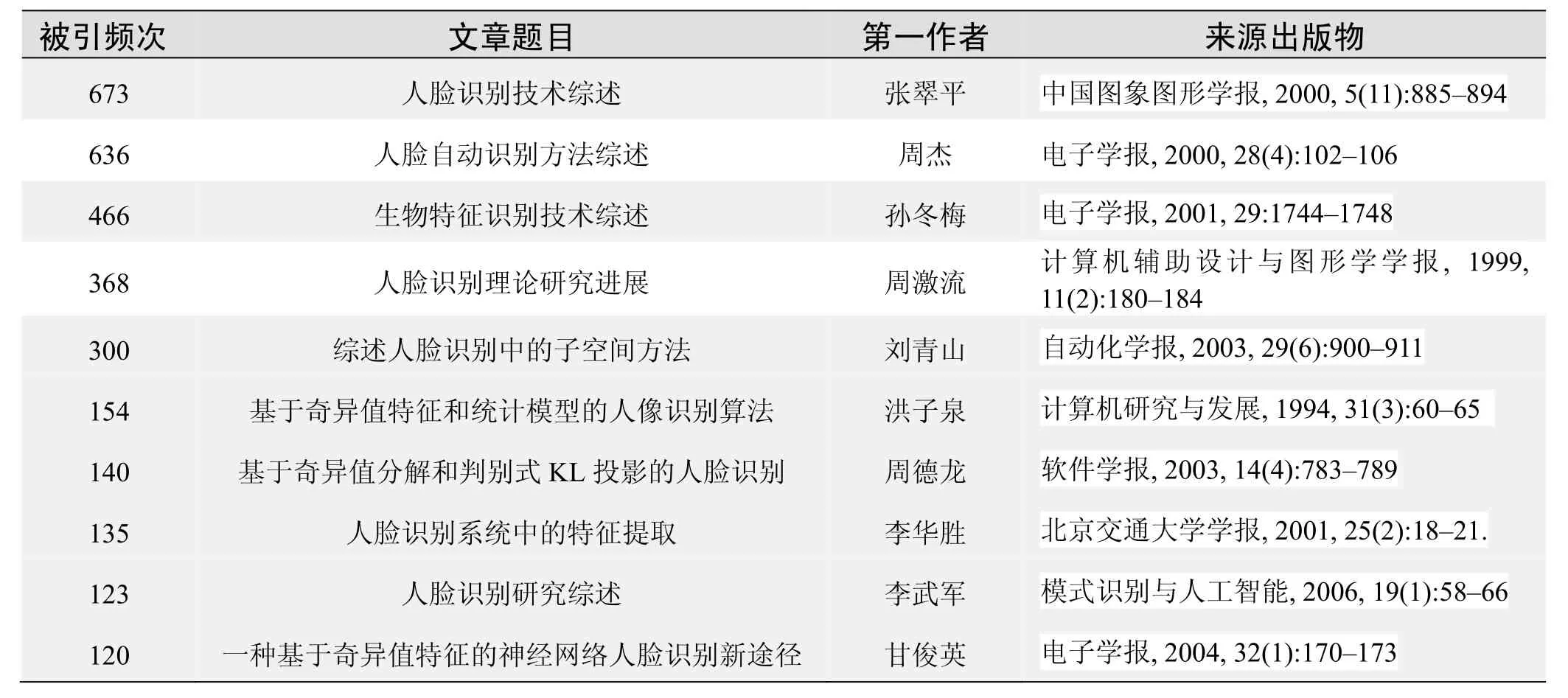
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以人脸识别为词条检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 30文献作为节点进行分析,并结合专家意见,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience,1991,3(1):71-86
A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions
Ojala,T; Pietikainen,M; Harwood,D
Abstract: This paper evaluates the performance both of some texture measures which have been successfully used in various applications and of some new promising approaches proposed recently. For classification a method based on Kullback discrimination of sample and prototype distributions is used. The classification results for single features with one-dimensional feature value distributions and for pairs of complementary features with two-dimensional distributions are presented.
Keywords: texture analysis; classification; feature distribution; Brodatz textures; Kullback discriminant; performance evaluation
来源出版物:Pattern Recognition,1996,29(1): 51-59
Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using class specific linear projection
Belhumeur,PN; Hespanha,JP; Kriegman,DJ
Abstract: We develop a face recognition algorithm which is insensitive to large Variation in lighting direction and facial expression. Taking a pattern classification approach,we consider each pixel in an image as a coordinate in a high-dimensional space. We take advantage of the observation that the images of a particular face,under varying illumination but fixed pose,lie in a 3D linear subspace of the high dimensional image space - if the face is a Lambertian surface without shadowing. However,since faces are not truly Lambertian surfaces and do indeed produce self-shadowing,images will deviate from this linear subspace. Rather than explicitly modeling this deviation,we linearly project the image into a subspace in a manner which discounts those regions of the face with large deviation. Our projectionmethod is based on Fisher's Linear Discriminant and produces well separated classes in a low-dimensional subspace,even under severe variation in lighting and facial expressions. The Eigenface technique,another method based on linearly projecting the image space to a low dimensional subspace,has similar computational requirements. Yet,extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed ''Fisherface'' method has error rates that are tower than those of the Eigenface technique for tests on the Harvard and Yale Face Databases.
Keywords: appearance-based vision; face recognition; illumination invariance; Fisher's linear discriminant
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1997,19(7): 711-720
Robust real-time face detection
Viola,P; Jones,MJ
Abstract: This paper describes a face detection framework that is capable of processing images extremely rapidly while achieving high detection rates. There are three key contributions. The first is the introduction of a new image representation called the "Integral Image" which allows the features used by our detector to be computed very quickly. The second is a simple and efficient classifier which is built using the AdaBoost learning algorithm(Freund and Schapire,1995)to select a small number of critical visual features from a very large set of potential features. The third contribution is a method for combining classifiers in a "cascade" which allows background regions of the image to be quickly discarded while spending more computation on promising face-like regions. A set of experiments in the domain of face detection is presented. The system yields face detection performance comparable to the best previous systems(Sung and Poggio,1998;Rowley et al.,1998; Schneiderman and Kanade,2000; Roth et al.,2000). Implemented on a conventional desktop,face detection proceeds at 15 frames per second.
Keywords: face detection; boosting; human sensing
来源出版物:International Journal of Computer Vision,2004,57(2): 137-154
PCA versus LDA
Martinez,AM; Kak,AC; et al.
Abstract: In the context of the appearance-based paradigm for object recognition,it is generally believed that algorithms based on LDA(Linear Discriminant Analysis)are superior to those based on PCA(Principal Components Analysis). in this communication,we show that this is not always the case. We present our case first by using intuitively plausible arguments and,then. by showing actual results on a face database. Our overall conclusion is that when the training data set is small,PCA can outperform LDA and,also,that PCA is less sensitive to different training data sets.
Keywords: face recognition; pattern recognition; principal components analysis; linear discriminant analysis; learning from undersampled distributions; small training data sets
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001,23(2): 228-233
·推荐综述·
人脸识别技术综述
张翠平,苏光大
(清华大学电子工程系“智能技术与系统”国家重点实验室图形图象分室,北京 100084)
摘编自《中国图像图形学报》2015年5卷11期:885~894页,图、表、参考文献已省略
0引言
计算机人脸识别技术也就是利用计算机分析人脸图象,进而从中提取出有效的识别信息,用来“辨认”身份的一门技术。人脸识别技术应用背景广泛,可用于公安系统的罪犯身份识别、驾驶执照及护照等与实际持证人的核对、银行及海关的监控系统及自动门卫系统等。虽然人类的人脸识别能力很强,能够记住并辨别上千个不同人脸,可是计算机则困难多了。其表现在:人脸表情丰富;人脸随年龄增长而变化;人脸所成图象受光照、成象角度及成象距离等影响;而且从二维图象重建三维人脸是病态(illposed)过程,目前尚没有很好的描述人脸的三维模型。另外,人脸识别还涉及到图象处理、计算机视觉、模式识别以及神经网络等学科,也和人脑的认识程度紧密相关。这诸多因素使得人脸识别成为一项极富挑战性的课题。
计算机人脸识别技术是近20a才逐渐发展起来的,90年代更成为科研热点。仅1990年到1998年之间,EI可检索到的相关文献就多达数千篇。由于人脸识别实验所采用的人脸库通常不大,最常见的人脸库仅包括100幅左右的人脸图象,如MIT库、Yale库、CMU库等人脸库均为小型库,且由于不同人脸库之间的输入条件各异,因此不同的识别程序之间很难进行比较。为促进人脸识别算法的深入研究和实用化,美国国防部发起了人脸识别技术(FaceRecognition Technology简称FERET)工程[1],它包括一个通用人脸库和一套通用测试标准。该FERET库可用于各种人脸识别算法的测试比较。1997年,FERET人脸库存储了取自1199个人的14126幅图象,其中同一人的图象差异,包括不同表情、不同光照、不同头部姿态以及不同时期(相隔18个月以上)拍摄差异等。如今FERET人脸库仍在扩充,并定期对各种人脸识别程序进行性能测试,其分析测试结果对未来的工作起到了一定的指导作用。由于 FERET库中包括军人的图片,不能在美国以外获得,因此其他国家的研究只能采用本地的人脸库,如英国的Manchester人脸库[2]。
通常,人类进行人脸识别依靠的感觉器官包括视觉,听觉,嗅觉,触觉等,一般人脸的识别可以用单个感官完成,也可以是多感官相配合来存储和检索人脸,而计算机的人脸识别所利用的则主要是视觉数据。另外,计算机人脸识别的进展还受限于对人类本身识别系统的认识程度。研究表明[2],人类视觉数据的处理是一个分等级的过程,其中最底层的视觉过程(视网膜功能)起信息转储的作用,即将人眼接收的大量图象数据变换为一个比较规则的紧凑表达形式。生理学的研究表明,人眼视网膜上存在着低层次和高层次的细胞。其中,低层次的细胞对空间的响应和小波变换的结果相似[2];而高层次的细胞则依据一群低层次细胞的响应,而作出具体的线、面乃至物体模式的响应。以此为依据,在计算机人脸识别中,可以将那些通过大量图象数据简单处理后获得的特征定义为低层次特征,而将线、面、模式等描述特征定义为高层次特征。由此,图象KL变换后的系数特征、小波变换特征及一些统计特征均属低层次特征的范畴,而人脸部件形状分析的结果则为高层次特征。由于视觉数据经传输后的重建,需依赖于人脑中早期形成的先验知识,因此在人的识别系统中,人脸的检测是一个整体识别和特征识别共同作用的结果[3];具体说来,远处辨认人,主要是整体识别,而在近距离的人脸识别中,特征部件的识别则更重要。另外,人脸的各部件对识别的贡献也不相同,如眼睛和嘴巴的重要程度大于人的鼻子,人脸上半部分重要性大于人脸下半部分,其中特别的人脸更容易被识别记住[3],比如说歪嘴,或是独眼龙等人脸就更容易为人记起,没有个性的人脸相对就需要更长的时间来辨认。根据对人脑的研究表明[3],人脸的表情识别和人脸识别虽然存在联系,但总体说是分开的、并行的处理过程。这些结论对于设计有效的识别方法起到了一定启发作用。在现有的识别算法中,特征脸方法[4]和神经网络方法[5]是基于整体人脸的识别,而基于提取眼睛等部件特征而形成特征向量[6]的方法就是基于人脸特征的识别。
人脸识别的研究始于60年代末,最早的研究见于文献[7],Bledsoe以人脸特征点的间距、比率等参数为特征,建成了一个半自动的人脸识别系统。而且早期人脸识别研究主要有两大方向:一是提取人脸几何特征的方法[7],包括人脸部件规一化的点间距离和比率以及人脸的一些特征点,如眼角、嘴角、鼻尖等部位所构成的二维拓扑结构;二是模板匹配的方法,主要是利用计算模板和图象灰度的自相关性来实现识别功能。Berto在1993年对这两类方法作了较全面的介绍和比较后认为,模板匹配的方法优于几何特征的方法[8]。目前的研究也主要有两个方向:其一是基于整体的研究方法,它考虑了模式的整体属性,包括特征脸(Eigenface)方法、SVD分解的方法[9]、人脸等密度线分析匹配方法[10]、弹性图匹配(elastic graph matching)方法[11]、隐马尔可夫模型(Hidden Markov Model)方法[12]以及神经网络的方法等;其二是基于特征分析的方法,也就是将人脸基准点的相对比率和其它描述人脸脸部特征的形状参数或类别参数等一起构成识别特征向量。这种基于整体脸的识别不仅保留了人脸部件之间的拓扑关系,而且也保留了各部件本身的信息,而基于部件的识别则是通过提取出局部轮廓信息及灰度信息来设计具体识别算法。文献[8]认为基于整个人脸的分析要优于基于部件的分析,理由是前者保留了更多信息,但是这种说法值得商榷,因为基于人脸部件的识别要比基于整体的方法来得直观,它提取并利用了最有用的特征,如关键点的位置以及部件的形状分析等,而对基于整个人脸的识别而言,由于把整个人脸图象作为模式,那么光照、视角以及人脸尺寸会对人脸识别有很大的影响,因此如何能够有效地去掉这些干扰很关键。虽然如此,但对基于部件分析的人脸识别方法而言也有困难,其难点在于如何建立好的模型来表达识别部件。近年来的一个趋势是将人脸的整体识别和特征分析的方法结合起来,如Kin-Man Lam提出的基于分析和整体的方法[13],Andreas Lanitis提出的利用可变形模型(Flexible Models)来对人脸进行解释和编码的方法[14]。
在介绍重要的人脸识别方法之前,先扼要说明一下应用于人脸识别的其它方法。其中SVD方法和特征脸识别方法同属统计分析的范畴,都是将表达人脸的大量图象数据降维后进行模式分类,其区别仅是变换基的给出不同;而等密度线的分析方法则试图通过从二维的人脸图上抽取等密度线(即等灰度线)来反映人脸的三维信息,其根据是地图上的等高线能反映地形特征,那么通过不同人脸的等密度线也可比较人脸的相似度;HMM 是语音处理中成功的一种统计方法;而神经网络方法通常需要将人脸作为一个一维向量输入,因此输入节点庞大,其识别重要的一个目标就是降维处理。根据文献[15]对于自组织神经网络方法的分析,该文认为可采用自组织神经网络的P个节点来表达原始的N个输入(P < N),但由于将P个输出进行分类,其识别的效果仅相当于提取人脸空间特征向量后进行的识别分类,因此采用此类神经网络进行识别的效果只能是特征脸的水平,所以本文将不对神经网络作专门介绍。需要说明的是,由于人脸处于高维空间,如100×100的图象为10000维,这样神经网络的输入节点将很庞大,因此实际训练网络的时候参数繁多,实现起来很困难,但神经网络方法的优点是可以针对特定的问题进行子空间设计,如神经网络的方法可以用作性别识别等问题[15]。
1常用的人脸识别方法简介
1.1基于KL变换的特征脸识别方法
1.1.1基本原理
KL变换是图象压缩中的一种最优正交变换。人们将它用于统计特征提取,从而形成了子空间法模式识别的基础。若将KL变换用于人脸识别,则需假设人脸处于低维线性空间,且不同人脸具有可分性。由于高维图象空间KL变换后可得到一组新的正交基,因此可通过保留部分正交基,以生成低维人脸空间。而低维空间的基则是通过分析人脸训练样本集的统计特性来获得。KL变换的生成矩阵可以是训练样本集的总体散布矩阵,也可以是训练样本集的类间散布矩阵,即可采用同一人的数张图象的平均来进行训练,这样可在一定程度上消除光线等的干扰,且计算量也得到减少,而识别率不会下降。
也就是说,根据总体散布矩阵或类间散布矩阵可求出一组正交的特征向量μ1,μ2,…,μn,其对应的全部特征值分别为λ1,λ2,…,λn,这样,在新的正交空间中,人脸样本X就可以表示为

若通过选用m(m < n)个特征向量作为正交基,则在该正交空间的子空间中,就可得到以下近似表达式

如将子空间的正交基按照图象阵列排列,则可以看出这些正交基呈现人脸的形状,因此这些正交基也被称作特征脸,这种人脸识别方法也叫特征脸方法。关于正交基的选择有不同的考虑,即与较大特征值对应的正交基(也称主分量)可用来表达人脸的大体形状,而具体细节还需要用与小特征值对应的特征向量(也称次分量)来加以描述,因此也可理解为低频成分用主分量表示,而高频成分用次分量表示。其中,采用主分量作正交基的方法称为主分量方法(PCA)。同时,也有人采用m个次分量作为正交基,原因是所有人脸的大体形状和结构相似,真正用来区别不同人脸的信息是那些用次分量表达的高频成分。由训练得到特征脸后,将待识别人脸投影到新的m维人脸空间,即用一系列特征脸的线性加权和来表示它,这样即得到一投影系数向量来代表待识别人脸,这时候,人脸识别问题已转化为m低维空间的坐标系数矢量分类问题,而分类最简单的做法是最小距离分类。
KL变换在90年代初受到了很大的重视,实际用于人脸识别也取得了很好的效果,其识别率从70~100%不等,这取决于人脸库图象的质量。从压缩能量的角度来看,KL变换是最优的,它不仅使得从n维空间降到m维空间前后的均方误差最小,而且变换后的低维空间有很好的人脸表达能力,然而这不是说已经具有很好的人脸辨别能力。选择训练样本的散布矩阵作为KL变换的生成矩阵,是由于其最大特征向量抓住了该样本集合的主要分布,但这是图象统计,而不是人脸统计方法。它虽然考虑了图象之间所有的差异,但由于它不管这样的差异是由照明、发型变更或背景导致,还是属于人脸的内在差异,因此特征脸识别的方法用于人脸识别存在理论的缺陷。研究表明,特征脸的方法随着光线、角度及人脸的尺寸等因素的引入,识别率急剧下降。虽然可通过采用同一人的训练样本的平均来计算类间散布矩阵,但也只能在一定程度上纠正这个缺点。研究结果表明,主分量的方法使得变换后表达能力最佳,次分量的方法则考虑了高频的人脸区分能力。由于对KL变换而言,外在因素带来的图象差异和人脸本身带来的差异是不加任何区分的,因此,不管如何选择正交基,也不能根本解决问题。其改善的一个思路是针对干扰所在,对输入图象作规范化处理,其中包括将输入图的均值方差归一化、人脸尺寸归一化等;另一种改进是考虑到局部人脸图象受外在干扰相对较小,在进行人脸识别时,除计算特征脸之外,还可利用KL变换计算出特征眼睛、特征嘴巴等。然后将局部特征向量加权进行匹配,就能够得到一些好的效果。
1.1.2对特征脸方法的改进
一种较好的特征脸改进方法是fisher脸方法(fisherface)[17],众所周知,fisher线性判别准则是模式识别里的经典方法,一般应用fisher准则是假设不同类别在模式空间是线性可分的,而引起它们可分的主要原因是不同人脸之间的差异。fisher的判别准则是:不同类样本尽可能远,同类样本尽可能近。文献[17]对用KL变换和fisher准则分别求出来的一些特征脸进行比较后得出如下结论,即认为特征脸很大程度上反映了光照等的差异,而fisher脸则能压制图象之间的与识别信息无关的差异。Belhumeur的试验[17],是通过对160幅人脸图象(一共16个人,每个人10幅不同条件下的图象)进行识别,若采用KL变换进行识别,其识别率为81%;若采用fisher方法则识别率为99.4%,显然fisher方法有了很大的改进。 Chengjun Liu在KL变换基础上提出了PRM(Probalistic Reasoning Models)模型[18],并在PRM中采用了贝叶斯分类器,它是利用最大后验概率进行分类,其类条件概率密度的方差参数用类内散布矩阵来估计,而且,PRM是采用马氏距离,而不是采用最小欧氏距离的判别准则,并且特征脸和fisher脸均可以看成是PRM的特殊情况。
文献[19]的改进方法是将人脸图象进行差异分类,即分为脸间差异和脸内差异,其中脸内差异属于同一个人脸的各种可能变形,而脸间差异则表示不同人的本质差异,而实际人脸图的差异为两者之和。通过分析人脸差异图,如果脸内差异比脸间差异大,则认为两人脸属于同一人的可能性大,反之属不同人的可能性大。 假设该两类差异都是高斯分布,则先估计出所需的条件概率密度[19],最后也归为求差图在脸内差异特征空间和脸间差异特征空间的投影问题。如果说fisher脸的方法是试图减少光照等的外在干扰,那么文献[19]则是解决表情干扰的一点有效尝试,虽然这样的尝试还很初步。文献[19]中提到,ARPA在1996年进行的FERET人脸识别测试中,该算法取得了最好的识别效果,其综合识别能力优于其它任何参加测试的算法。
1.1.3特征脸方法小结
如今特征脸方法用于人脸识别仍存在如下一些弊病:首先,由于作为一种图象的统计方法,图象中的所有象素被赋予了同等的地位,可是角度、光照、尺寸及表情等干扰会导致识别率急剧下降,因此较好的识别算法[19]都对人脸进行了矫正处理,且只考虑裸脸;其次,根据文献[2],人脸在人脸空间的分布近似高斯分布,且普通人脸位于均值附近,而特殊人脸则位于分布边缘。由此可见,越普通的人脸越难识别,虽然特征脸的方法本质上是抓住了人群的统计特性,但好的表达能力不等于好的区分能力;特征脸虽反映了特定库的统计特性,但不具有普遍代表性,而广泛的应用,则需要训练出的特征脸具有普遍意义;采用此方法的重要假设是人脸处于低维线性空间,即人脸相加和相减后还是人脸[2],显然这是不可能的,因为即使在定位和尺寸相同的情况下,由于部件的相对位置不同,相加、相减后的人脸也一样存在模糊,因此文献[14]提出形状无关人脸(shapeless face)的概念,即依据脸部基准点将人脸变形到标准脸,再进行特征脸处理。总之,有效的特征脸识别方法需要做大量预处理,以减少干扰。而如何表达,并去除表情因素则是识别的另一关键。
1.2形状和灰度分离的可变形模型
文献[14]提出了一个形状和灰度分离的模型,即从形状、总体灰度、局部灰度分布3个方面来描述一个人脸(如图1、图2、图3所示)。其中,点分布模型(图1)用来描述人脸的形状特征,该点分布模型中是用每点的局部灰度信息(图3是采用耳朵上一点附近的方向投影)来描述人脸的局部灰度特征;然后用点分布模型将图象进行变形,以生成形状无关人脸(图2),再做特征脸分析,从而得到人脸的总体灰度模式分布特征。这种三者相结合的识别方法,识别率为92%(300个人脸),虽然该方法作了一些改进,但构成该方法的基础仍是KL变换。一般在特征脸的方法中,是由行或列扫描后的人脸图象数据来生成特征脸子空间,这里则对应于3种由不同类型参数生成的3种特征子空间。该方法首先是循序取每点坐标位置信息,并将其排列成待训练数据以生成形状特征子空间;然后对点分布模型的每一点(如图3中耳朵附近一点)取局部投影信息来代表该点附近的局部灰度特征,再通过训练后生成与该点相对应的局部灰度分布特征子空间。若将所有人脸的关键点都变形到规定位置,则生成形状无关人脸,然后对所有的形状无关人脸进行特征脸分析,以生成特征脸子空间。虽然每一个特征子空间都可以单独用来识别人脸,但若要完整地描述一个人脸,则需要 3个特征子空间的人脸参数。文献[14]还试图通过形状特征子空间来分离和表情相关的参数,而设计形状和灰度分离的模型是希望能够有一个好的人脸模型。试验中,将这样的模型用于三维姿态复原、身份识别、性别识别、表情识别以及人脸的重建,均取得了一定的效果。
1.3基于小波特征的弹性匹配方法
1.3.1基本原理
在KL变换中,待识别人脸X和库中人脸C之间采用了通常的欧氏距离来进行匹配。虽然欧氏距离计算简单,但是当X和C只有位移、膨胀(如affine变换)或是表情不同时,则欧氏距离不会等于零,甚至很大,此外,若C作为人脸库中的已知人脸模板,应该是描述人脸的关键特征,它的维数并不需要和待识别人脸一样,因而此时欧氏距离就不合适;而弹性图匹配法是在二维的空间中定义了这样一个距离,它对通常的人脸变形具有一定的不变性,也不要求C、X维数一定相同。可采用属性拓扑图来表达人脸(图4采用的是规则的二维网格图),其拓扑图的任一顶点均包含一特征矢量,它记录了人脸在该顶点位置的分布信息(如图5),如文献[11]中介绍的二维拓扑图的顶点矢量就是人脸经小波变换后的特征矢量。在图象的敏感位置(如轮廓线、突出点等),小波变换后生成的特征矢量的模较大。用拓扑图分别代表已知和待识别人脸,还可根据匹配拓扑图算出它们的“距离”,作为人脸的相似度准则。由于篇幅所限,详细的拓扑图生成过程文献[11]、[15]。
人脸的相似度可用拓扑图的“距离”来表示,而最佳的匹配应同时考虑顶点特征矢量的匹配和相对几何位置的匹配。由图 6(和图5一样,它们的每一顶点均为一特征矢量)可见,特征匹配即:S1上的顶点i,与S中相对应的顶点j(j= M(i),M为匹配函数),其特征的匹配度则表示i和j顶点的特征矢量相似度,而几何位置的匹配则为S中相近的两顶点,匹配后,S1中对应的两顶点也应该相近,因此文献[11]用了以下能量函数E(M)来评价待识别人脸图象矢量场和库中已知人脸的矢量场之间的匹配程度

式中的第一项是计算两个矢量场中对应的局部特征Xj和Ci的相似程度,第二项则是计算局部位置关系和匹配次序。由此可见,最佳匹配也就是最小能量函数时的匹配。
在求能量函数实现匹配的时候,可以有如下两种匹配的方法:其中一种是严格的匹配方法;另一种匹配即所谓弹性图匹配方法(见图7)。由图7可见,网格S经过了变形,即由原来网格S中的一点对S1中一点的严格匹配,变成了S中一点和S1中一点领域范围内的匹配,其目的是为了进一步减小能量函数,通过最终收敛到一个最小值,来实现弹性匹配,正是这样的匹配容忍了表情的细微变化。
根据Jun Zhang[15]对综合MIT、Olivetti、W wizmann、和Bem等人脸库所形成的包括272幅照片的综合人脸库,分别用KL方法和弹性匹配方法进行识别试验比较[15],所得的识别率分别为66%和93%。其中KL变换的识别率很低,其原因主要是由于综合库里来自4个人脸库的人脸图象在光照上有很大的差异所造成的,文献[15]之所以作出了弹性图形匹配优于KL变换的结论,其原因之一是由于拓扑图的顶点采用了小波变换特征,因为它对于光线、变换、尺寸和角度具有一定的不变性。大家知道,小波特征分析是一种时频分析,即空间—频率分析,若空间一点周围区域的不同的频率响应构成该点的特征串,则其高频部分就对应了小范围内的细节,而低频部分则对应了该点周围较大范围内的概貌。根据该原理,文献[20]提出了用数学形态学上的腐蚀扩张方法形成的多尺度(多分辨率)特征矢量来取代小波特征,并证明了它具有和小波特征相似的效果,它能够反映空间一点周围的高低频信息。现已证明,弹性图形匹配能保留二维图象的空间相关性信息,而特征脸方法在将图象排成一维向量后,则丢失了很多空间相关性信息。 这些都是弹性匹配方法优于特征脸方法的原因,如向人脸库中加入新的人脸时,由于不能保证已有特征脸的通用性,因而有可能需要重新计算特征脸;而对于弹性匹配的方法,则不需要改变已有的数据,通过直接加入新的模板数据即可,但计算较复杂是弹性匹配的一大缺点。根据引言中提出的低层次特征和高层次特征的定义,这里的小波特征类似于外界景物在人眼视网膜上的响应,属低层次特征,没有线、面、模式的概念。 由于低层次特征中信息的冗余不仅使得计算复杂,而且由于大量与识别无关的信息没有过滤掉,因而识别率会大打折扣,另外特征脸也存在这样的问题,其中典型的无用信息就是头发。
针对弹性匹配方法的缺陷,可从以下两方面进行改进:一是降低计算复杂度,即对表达人脸的二维矢量场进行特征压缩和提取;二是减少冗余信息,即将所提取出来的低层次特征和高层次特征(如眼角、鼻端的位置等)结合起来,以突出关键点的识别地位。
1.3.2对弹性匹配方法的改进及分析
文献[20]提出了一种弹性匹配的改进方法,即将KL变换应用于小波变换,来生成二维网格中顶点的矢量串,以减少其维数,从而大大减少了表达一幅人脸所需要的特征数量,而识别率不会明显下降。
文献[21]是采用人脸基准点,而不是采用二维网格作为拓扑图的节点,同时节点特征也是小波变换特征,即它忽略了除重要人脸部件以外的特征数据,把研究的重点直接定位到感兴趣的区域(参照图8)。
文献[21]还采用了和文献[11]不同的结构来存储人脸特征(如图9所示)。
由于文献[11]中特征库的存储是面向人脸的,即对每一张人脸都需要存储描述该人脸的整个拓扑图,因而导致了人脸的特征库很庞大,文献[21]中特征库的存储是面向人脸基准点的(如图9),且对应每个基准点有一串的特征矢量,当由某一人脸的对应基准点提取出来的矢量不同于库中已有的任意矢量时,就添入到该结构中存储起来,并编号。这样识别每个人脸只需知道人脸对应基准点在该存储结构中的特征矢量序号即可。该存储结构一个主要优点是,由于不同人脸在同一个基准点所对应的特征矢量可能相同,因此和面向人脸的存储形式相比,数据量会大大减少;另一优点是该存储结构有很强的表达潜力,设有10个基准点,如库中每一基准点都存储了50个特征矢量,那么该存储结构能表达5010个不同的人脸。由此可见,文献[21]对文献[11]方法的一大改进是结合了人脸的高层次特征。
另外,弹性匹配方法在实现时,需要考虑具体的参数选择,如二维网格的大小、小波变换参数的选择等,这些参数都会影响识别的效果。毫无疑问,有效的识别效果依赖于关键识别信息的提取,如采取多大的人脸分辨率?能否对提取出来的特征(具体的或抽象的)进行筛选?经验知识使我们关注人脸部件及其附近的特征,而能否再次对这些特征进行筛选?并有何依据?文献[2]正是希望能够回答这些问题。
文献[2]的方法称为紧凑多层图形方法,它是采用三维的拓扑图来表达人脸(如图10)。
该图构成了一个金字塔的人脸模型,而且每一层中节点的特征矢量也是小波变换的结果。通过这样的金字塔模型就实现了同一个人脸的多分辨率表达。另外,文献[2]有如下两点创新:(1)将高低层特征联系起来,并通过手工选择一些关键点(如眼角、嘴角等)来定位三维拓扑图,同时去除了背景、头发等所在节点;(2)对三维拓扑图的特征进行了特征选择,选出了活跃的特征(包括节点内的特征分量和不同节点之间两种活跃性能比较),还去除了相当多的贡献不大的特征,从而形成了人脸的稀疏表达。由于特征选择后,不同人脸的拓扑图保留的节点不完全一样,因此用于比较的两个人脸的三维拓扑图在数值上和结构上都不相同,为此,文献[2]定义了一种距离来计算它们的相似度。为提取活跃特征,我们曾尝试利用那些手工提取的关键点,来生成训练库的形状无关模型(不是形状无关人脸),即通过插值小波变换后生成的二维拓扑图来形成人脸的连续表达模型,并假设所有人的脸内差异相同(即表情等),然后根据训练库的统计形状无关模型,在一人一张照片的情况下,估计出个人表达模型中的活跃特征。打个比方,人的眼睛都是相似的,假设眼睛的分布为高斯分布,那么一个眼睛离平均眼睛越远,这个眼睛的特征就越显著,即,若有一定的与众(平均眼)不同性,就可以认为是该人的活跃特征,详细内容参考文献[2],该文有很多创新,它是以人脑对人脸的识别为依据,因此有很好的参考价值。
通过上述的介绍分析,可看出弹性匹配方法比特征脸识别方法前进了一大步。它是采用小波变换特征来描述人脸的局部信息,并和人眼视网膜对图象的响应相似[2],而且一定程度上容忍光线等干扰,对细微表情也不敏感。而且弹性匹配中的人脸模型还考虑了局部人脸细节,并保留了人脸的空间分布信息,且它的可变形匹配方式一定程度上能够容忍人脸从三维到二维投影引起的变形。目前还没有见到国内有利用弹性匹配进行识别的相关报道,但是从国外众多的关于弹性匹配的研究结果来看,它在人脸识别众方法中具有重要地位。
1.4传统的部件建模的方法
文献[8]认为在人脸识别中,模型匹配方法要优于基于相对距离的特征分析方法。尽管如此,传统的部件分析方法还是被一些研究室用于人脸识别,究其原因,一方面是由于其它方法还处于摸索阶段,另一方面是利用曲线去拟合部件、分析部件的形状比较直观,也容易取得一定的成果[6]。
在各种人脸识别方法中,定位眼睛往往是人脸识别的第一步,由于两眼睛的对称性以及眼珠呈现为低灰度值的圆形,因此在人脸图象清晰端正的时候,眼睛的提取是比较容易的,如从400幅人像库上可取得96%的眼睛定位率[6],但是如果人脸图象模糊,或者噪声很多,则往往需要利用更多的信息(如眼睛和眉毛、鼻子的相对位置等),而且这将使得眼睛的定位变得很复杂。由于通常眼睛的形状模型为椭圆[22],嘴巴的形状模型为抛物线[22],因此椭圆和抛物线的参数和位置能够用作表达当前人脸的特征,文献[6]考虑到眼睛用椭圆表达过于简单,故又采用了二值化,并通过跟踪以得到眼睛形状的方法,由于眉毛和脸形的形状具有任意性,因此在一些研究中曾采用snake动态能量曲线来逼近形状[13,22],如脸颊的形状采用了折线,下巴采用抛物线的模型。这些都是传统的提取和分析形状的方法。虽然人脸是刚体,可实际图象中,部件未必轮廓分明,有时人用眼看也只是个大概,计算机提取就更成问题。另外,由于用抛物线、椭圆或者直线作为模型也不能很好的表达反映变化多端的人脸部件,且由于人脸识别还受到表情的影响,且不能在模型中表达表情,因而导致描述同一个人的不同人脸时,其模型参数可能相差很大,而失去识别意义,这也是部件建模识别方法近年受冷落的原因。尽管如此,在正确提取部件以及表情变化微小的前提下,该方法依然奏效,因此在许多方面仍可应用,如对标准身份证照的应用。
2人脸识别方法的分析和总结
2.1特征来源以及特征的后处理
众所周知,人脸的结构大体相同,所不同的是一些细节上的差异,原始的人脸图象不仅数据庞大,而且还会随着拍摄条件及表情神态变化而变化,这就使得人脸的识别成为模式分析中的一个难题。一般从人脸图象上进行有效的识别需要提取稳定的人脸特征,目前所利用的特征可以概括为形状、灰度分布、频域特征3种。其中,形状特征包括人脸各部件的形状以及人脸各部件之间的相对位置,这是最初研究所采用的特征;灰度分布特征,即将人脸图象看成一维或二维灰度模式,所计算出的不同灰度模式之间的距离就是整体的灰度分布特征,例如特征脸的方法,此外还有描述局部关键点领域的灰度分布特征的分析方法;频域特征,即将人脸图象变换到频域后所做的特征脸分析方法就是频域特征脸方法,此时的特征即为频域特征,如小波特征就是频域特征。虽然形状特征是3个特征中最具体形象的特征,但是它也和灰度特征一样受到光照、角度和表情的影响,而频域特征虽然相对较稳定,但作为低层次特征,不易直接用于匹配和识别,因此对它进行进一步的解释是目前需要解决的问题。
在弹性匹配中,若对每个节点运用KL变换,则能够减少特征数,而不降低识别率。其特征后处理的一个重要方面是特征的选择,也就是需选出最活跃的识别特征,去除对识别不重要的信息。在人脸识别的特征选择中,生物心理学家首先研究了人脸各部件对识别的重要性,接着文献[2]从模式识别的角度出发,结合人脸各部件信息,并运用最大后验概率,对表达人脸的低层次特征进行了筛选,从而减少了人脸信息的存储量,并改善了识别的效果。
2.2人脸的定位问题
虽然人脸定位问题是人脸识别的第一步,但在前面介绍各种人脸识别方法的时候,并没有介绍具体的定位问题。事实上,对大多数方法而言,人脸的定位过程也就是人脸识别特征的生成过程,而且定位算法也是和识别算法密切相关的。为了说明这一点,下面给出一些人脸识别所采用的定位方法:
方法1特征脸的方法也可用于定位人脸,这是因为人脸模式在特征脸子空间的投影系数基本相似,若先将子图在特征脸空间投影后重建,然后比较原图和重建图,就能够说明原图是否是人脸,这是因为特征脸空间能反映人脸的分布,而对于非人脸则没有很好的表达力,因此重建图和原图的差异会较大。
方法2最初的模板匹配方法是直接计算人脸图象和模板人脸图象之间的相似度,匹配最好时,即是人脸在原图中的位置,如弹性图形匹配中,采用的也是一种模板匹配,但是其参与匹配的是用小波特征表达的二维(或三维)拓扑图,若将模板拓扑图在全图生成的拓扑图上移动匹配(严格的或弹性的),则其最佳匹配就给出了人脸的位置,如文献[2]就采用了多分辨率的三维模型,其定位的时候是从最低分辨率开始定位,然后依次增加分辨率,直到位置不变为止,这是由于文献[2]考虑的是定位的分辨率可以远小于识别所需要的分辨率。
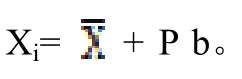
方法3在定位人脸的同时也就定位出了具体的部件位置,虽然方法1和方法3的基本原理不需要定位人脸的部件,而依赖于部件分析来进行人脸识别的方法[6]通常是应用一些先验知识(如眼睛的投影直方图形状、人脸的部件分布比例等)来初步给出人脸的大致位置,然后再精确定位人脸的各个部件。这里部件的定位通常使用投影方法、hough变换的方法以及构造模型能量函数的匹配方法。
2.3识别效果的比较
由于采用的人脸库不同,因此不同识别算法之间的优劣没有可比性,前面的论述也是尽量从理论上进行比较。根据Moghaddam等在1996年进行的FFEIT人脸库测试[19],结果说明区别脸内差异和脸间差异的Bay esian特征脸方法的表现最佳,即从5000幅待识别人像中,第一候选的识别率为89.5%,而灰度和形状分离的可变形模型在300幅人像中的识别率达到92%。另根据文献[15]的测试,在2000幅人脸图象的综合库中,利用小波特征弹性图形匹配的方法获得了93%的识别率,而PCA识别率只达66%。
3结论
人脸识别是一个跨学科富挑战性的前沿课题,但目前人脸识别还只是研究课题,尚不是实用化领域的活跃课题。人脸识别难度较大,主要难在人脸都是有各种变化的相似刚体,由于人脸部件不仅存在各种变形,而且和皮肤之间是平缓过渡,因此人脸是不能用经典的几何模型来进行识别分类的典型例子。如今人脸识别研究人员已经慢慢地将研究重点从传统的点和曲线的分析方法,过渡到用新的人脸模型来表达和识别人脸,其中弹性图匹配就是较成功的尝试。虽然人脸识别算法的开发需要工程人员的努力,但也和解剖学、生理学等的研究密切相关。从目前的研究成果来看,就二维图象而言,成功的人脸识别至少需要考虑以下几个方面:(1)由于外部干扰不可避免,预处理的效果将会影响到识别结果,好的人脸模型应能够在识别的同时,抑制分离外在干扰的影响;(2)细节是区分不同人脸的关键,因此很多识别方法都十分注重细节,如弹性图匹配中的局部细节,就是通过节点的小波变换特征加以表达,而在灰度形状分离的可变形模型中,局部灰度投影分布也描述了人脸细节,另外,传统的点和曲线的方法更是直接从局部细节入手,可是特征脸方法则缺少对细节的考虑,故需和别的方法相结合,才能取得好的识别效果;(3)在匹配的时候,不仅要考虑各种因素所导致的人脸微小变形,而且在容忍变形的同时,还不能损害到人脸识别的有效性,如弹性图匹配的方法不论从特征的选择上,还是从匹配的方法上都力图遵循这一原则。由此可见,人脸变形在人脸识别中具有重要意义,因为人脸丰富的变形就是导致传统的点线分析方法失败的原因;(4)对于表达人脸的各种特征需要进行比较和选择,以找出人脸最活跃的特征。这可以通过如下两种途径:一是比较同一个人的多张图片,以得到稳定的特征;另一种方法就是比较不同人的图片,以得出该人最“与众不同”之处[2]。
此外,实用的识别系统还必须考虑计算复杂度,现有的识别方法中,通过从人脸图中提取出特征串,来对数据库进行检索的方法速度快,而利用拓扑属性图匹配来确定匹配度的方法则相对慢,而且随数据库增加,前者的识别率要比后者下降得快,因此改进的思路是将两者相结合,首先用快速的特征串匹配,来缩小检索范围,再进行拓扑图慢匹配,此外,用减小拓扑图存储量的方法也能够加快匹配速度,但这需要提取有效特征和去掉冗余信息。
本文介绍和分析的各种人脸识别方法同样可用于摄像机输入人脸的识别,而对于摄像机图象而言,人脸的定位和表情的分析还可以利用序列图象之间的相关性信息,如从摄像机输入动态图可以进行二维及三维的运动估计,从而建立三维的人脸模型。 由于从摄像机动态输入图中得到的信息很多,故还有可能进行有效的表情分析,以作为身份辨认的辅助手段。本文只是对目前应用于人脸识别的技术作了选择性的介绍,也是对文献[3]、[15]的一点补充。由于人脸识别的理论还不完善,具体算法的实现也有很多的因素待研究,因此计算机人脸识别的实用化还需要众多研究人员的不懈努力。
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:673
人脸识别技术综述
张翠平,苏光大
首先对计算机人脸自动识别技术的研究背景及发展历程做了简单回顾,然后对人脸正面像的识别方法,按照识别特征的不同进行了分类综述,主要介绍了特征脸(Eigenface)方法、基于小波特征的弹性匹配(ElasticMatching)的方法、形状和灰度模型分离的可变形模型(Flexible Model)以及传统的部件建模等分析方法。通过对各种识别方法的分析与比较,总结了影响人脸识别技术实用化的几个因素,并提出了研究和开发成功的人脸识别技术所需要考虑的几个重要方面,进而展望了人脸识别技术今后的发展方向。
人脸识别;特征脸;小波特征;形状无关模型
来源出版物:中国图象图形学报,2000,5(11):885-894
被引频次:636
人脸自动识别方法综述
周杰,卢春雨,张长水,等
摘要:人脸自动识别是模式识别、图像处理等学科的一大研究热点,近几年来关于人脸识别的研究取得了很大进展。本文重点对近三、四年来人脸识别的研究进行综述并对各种方法加以评论。
关键词:人脸自动识别;人脸检测;人脸定位
来源出版物:电子学报,2000,28(4):102-106
被引频次:466
生物特征识别技术综述
孙冬梅,裘正定
摘要:生物特征识别技术作为一种身份识别的手段,具有独特的优势,近年来已逐渐成为国际上的研究热点。本文综述了各种生物特征识别技术的基本原理和一些关键技术,对每种生物特征的优势和不足进行了分析,并对生物特征识别技术中存在的问题和未来的研究方向进行了讨论。
关键词:生物特征识别;身份识别;身份认证;人脸识别 指纹识别;虹膜识别;手形识别;掌纹识别;签名识别;说话人识别
来源出版物:电子学报,2001,29:1744-1748
被引频次:368
人脸识别理论研究进展
周激流,张晔
摘要:综述了人脸识别理论的概念和研究现状,讨论了其中的关键技术和难点以及应用和发展前景,最后对人脸识别研究中应注意的问题提出了我们的看法。
关键词:人脸识别;面部特征提取;表情/姿态分析
来源出版物:计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,1999,11(2):180-184
被引频次:300
综述人脸识别中的子空间方法
刘青山,卢汉清,马颂德
摘要:如何描述每个个体人脸的特征,使之区别于其他个体,是人脸识别研究中的关键问题之一。近年来提出了大量的方法,其中随着主元分析在人脸识别中的成功应用之后,子空间分析因其具有描述性强、计算代价小、易实现及可分性好的特点,受到了广泛的关注。文中结合近年来已发表的文献,按照线性和非线性的划分,对子空间分析在人脸识别中的应用作一回顾、比较和总结,以供其他人参考。
关键词:主元分析;子空间分析;人脸识别
来源出版物:自动化学报,2003,29(6):900-911
被引频次:154
基于奇异值特征和统计模型的人像识别算法
洪子泉,杨静宇
摘要:人像识别是模式识别领域中的一个前沿课题。目前多数研究者采用人脸的一维和二维几何特征来完成识别任务。人脸的几何特征抽取以及这些特征的有效性都面临着很多问题,至今人像识别的研究仍然处于较低的水平。作者证明了图象矩阵的奇异值特征矢量具备了代数上和几何上的不变性以及稳定性,提出用它作为识别人脸的代数特征。本文的人像识别算法是基于奇异值特征矢量建立Sammon最佳鉴别平面上的正态Bayes分类模型。在本文的实验中,我们用9张人像照片建立的统计模型能完全正确地识到这9张照片。对同一个人的不同历史时期的照片,本文也给出识别实验结果。
关键词:人像识别;奇异值特征;图象识别;代数特征抽取;鉴别向量;维数压缩
来源出版物:计算机研究与发展,1994,31(3):60-65
被引频次:140
基于奇异值分解和判别式KL投影的人脸识别
周德龙,高文,赵德斌
摘要:脸识别是计算机视觉和模式识别领域的一个活跃课题,有着十分广泛的应用前景。提出了一种新的彩色人脸识别方法。该算法采用模拟K-L变换、奇异值分解、主分量分析和Fisher线性判别分析技术来提取最终特征,可以使分类器的设计更加简洁、有效,使用较少的特征向量数目就能取得较高的识别率。仿真结果表明了该方法的有效性。
关键词:人脸识别;特征提取;K-L变换;奇异值特征向量;主分量分析;Fisher线性判别分析
来源出版物:软件学报,2003,14(4):783-789
被引频次:135
人脸识别系统中的特征提取
李华胜,杨桦,袁保宗
摘要:研究了人脸识别系统中正面人脸的特征提取。通过区域增长从人脸图像中分割出人脸,再利用边缘检测、Hough变换、模板匹配和方差投影技术可以快速有效地提取出人脸面部器官眼睛、鼻子和嘴巴特征。实验结果表明本文所采用的方法具有较高的准确率和光照鲁棒性。
关键词:人脸识别;Hough变换;模板匹配;方差投影
来源出版物:北京交通大学学报,2001,25(2):18-21
被引频次:123
人脸识别研究综述
李武军,王崇骏,张炜,等
摘要:人脸识别已成为多个学科领域的研究热点之一。本文对人脸识别的发展历史、研究现状进行了综述,系统地对目前主流人脸识别方法进行了分类。针对人脸识别面临的挑战,着重对近几年来在光照和姿态变化处理方面的研究进展进行了详细论述,并对未来人脸识别的发展方向进行了展望。
关键词:人脸识别;人脸检测;模式识别
来源出版物:模式识别与人工智能,2006,19(1):58-66
被引频次:120
一种基于奇异值特征的神经网络人脸识别新途径
甘俊英,张有为
摘要:本文在ZHong等人使用的奇异值分解(SVD)基础上,将人脸图像矩阵的奇异值作为识别特征,解决了奇异值处理、神经网络训练策略和竞争选择问题;运用BP网络进行识别,提出了一种基于奇异值特征的神经网络人脸识别新方法。基于ORL人脸数据库的多次反复实验结果表明,在大样本情况下,识别方法具有实现简单、识别速度快、识别率高的特点,为人脸的实时识别提供了一种新途径。
关键词:人脸识别;奇异值特征;神经网络;模式识别
来源出版物:电子学报,2004,32(1):170-173
被引频次:4503
Eigenfaces for recognition
Turk,M; Pentland,A
Abstract: 参见“经典文献推荐”栏目
被引频次:3890
Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using class specific linear projection
Belhumeur,PN; Hespanha,JP; Kriegman,DJ
Abstract: 参见“经典文献推荐”栏目
被引频次:1936
Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts
Belongie,S; Malik,J; Puzicha,J
Abstract: We present a novel approach to measuring similarity between shapes and exploit it for object recognition. In our framework,the measurement of similarity is preceded by 1)solving for correspondences between points on the two shapes,2)using the correspondences to estimate an aligning transform. In order to solve the correspondence problem,we attach a descriptor,the shape context,to each point. The shape context at a reference point captures the distribution of the remaining points relative to it,thus offering a globally discriminative characterization. Corresponding points on two similar shapes will have similar shape contexts,enabling us to solve for correspondences as an optimal assignment problem. Given the point correspondences,we estimate the transformation that best aligns the two shapes;regularized thin-plate splines provide a flexible class of transformation maps for this purpose. The dissimilarity between the two shapes is computed as a sum of matching errors between corresponding points,together with a term measuring the magnitude of the aligning transform. We treat recognition in a nearest-neighbor classification framework as the problem of finding the stored prototype shape that is maximally similar to that in the image. Results are presented for silhouettes,trademarks,handwritten digits,and the COIL data set.
Keywords: shape; object recognition; digit recognition; correspondence problem; MPEG7; image registration; deformable templates
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001,24(4):509-522
被引频次:1614
Robust face recognition via sparse representation
Wright,J; Yang,AY; Ganesh,A; et al.
Abstract: We consider the problem of automatically recognizing human faces from frontal views with varying expression and illumination,as well as occlusion and disguise. We cast the recognition problem as one of classifying among multiple linear regression models and argue that new theory from sparse signal representation offers the key to addressing this problem. Based on a sparse representation computed by l(1)-minimization,we propose a general classification algorithm for(image-based)object recognition. This new framework provides new insights into two crucial issues in face recognition: feature extraction and robustness to occlusion. For feature extraction,we show that if sparsity in the recognition problem is properly harnessed,the choice of features is no longer critical. What is critical,however,is whether the number of features is sufficiently large and whether the sparse representation is correctly computed. Unconventional features such as downsampled images and random projections perform just as well as conventional features such as Eigenfaces and Laplacianfaces,as long as the dimension of the feature space surpasses certain threshold,predicted by the theory of sparse representation. This framework can handle errors due to occlusion and corruption uniformly by exploiting the fact that these errors are often sparse with respect to the standard(pixel)basis. The theory of sparse representation helps predict how much occlusion the recognition algorithm can handle and how to choose the training images to maximize robustness to occlusion. We conduct extensive experiments on publicly available databases to verify the efficacy of the proposed algorithm and corroborate the above claims.
Keywords: face recognition; feature extraction; occlusion and corruption; sparse representation; compressed sensing; l(1)-minimization;validation and outlier rejection
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2008,31(2): 210-227
被引频次:1271
From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose
Georghiades,AS; Belhumeur,PN; Kriegman,DJ
Abstract: We present a generative appearance-based method for recognizing human faces under variation in lighting and viewpoint. Our method exploits the fact that the set of images of an object in fixed pose,but under all possible illumination conditions,is a convex cone in the space of images. Using a small number of training images of each face taken with different lighting directions,the shape and albedo of the face can be reconstructed. In turn,this reconstruction serves as a generative model that can be used to render-or synthesize-images of the face under novel poses and illumination conditions. The pose space is then sampled and,for each pose. the corresponding illumination cone is approximated by a low-dimensional linear subspace whose basis vectors are estimated using the generative model. Our recognition algorithm assigns to a test image the identity of the closest approximated illumination cone(based on Euclidean distance within the image space). We test our face recognition method on 4050 images from the Yale Face Database B; these images contain 405 viewing conditions(9 poses x 45 illumination conditions)for 10 individuals. The method performs almost without error,except on the most extreme lighting directions,and significantly outperforms popular recognition methods that do not use a generative model.
Keywords: face recognition; image-based rendering; appearance-based vision; face modeling; illumination and pose modeling; lighting;illumination cones; generative models
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001,23(6):643-660
被引频次:1248
Face recognition by elastic bunch graph matching
Wiskott,L; Fellous,JM; Kruger,N; et al.
Abstract: We present a system for recognizing human faces from single images out of a large database containing one image per person. Faces are represented by labeled graphs,based on a Gabor wavelet transform. Image graphs of new faces are extracted by an elastic graph matching process and can be compared by a simple similarity function. The system differs from the preceding one in three respects. Phase information is used for accurate node positioning. Object-adapted graphs are used to handle large rotations in depth. Image graph extraction is based on a novel data structure,the bunch graph,which is constructed from a small set of sample image graphs.
Keywords: face recognition; different poses; Gabor wavelets; elastic graph matching; bunch graph; ARPA/ARL FERET database; Bochum database
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1997,19(7): 775-779
被引频次:1147
Face recognition using Laplacianfaces
He,XF; Yan,SC; Hu,YX; et al.
Abstract: We propose an appearance-based face recognition method called the Laplacianface approach. By using Locality Preserving Projections(LPP),the face images are mapped into a face subspace for analysis. Different from Principal Component Analysis(PCA)and Linear Discriminant Analysis(LDA)which effectively see only the Euclidean structure of face space,LPP finds an embedding that preserves local information,and obtains a face subspace that best detects the essential face manifold structure. The Laplacianfaces are the optimal linear approximations to the eigenfunctions of the Laplace Beltrami operator on the face manifold. In this way,the unwanted variations resulting from changes in lighting,facial expression,and pose may be eliminated or reduced. Theoretical analysis shows that PCA,LDA,and LPP can be obtained from different graph models. We compare the proposed Laplacianface approach with Eigenface and Fisherface methods on three different face data sets. Experimental results suggest that the proposed Laplacianface approach provides a better representation and achieves lower error rates in face recognition.
Keywords: face recognition; principal component analysis; linear discriminant analysis; locality preserving projections; face manifold;subspace learning
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2005,27(3): 328-340
被引频次:958
Face recognition - features versus templates
BRUNELLI,R; POGGIO,T
Abstract: Over the last 20 years,several different techniques have been proposed for computer recognition of human faces. The purpose of this paper is to compare two simple but general strategies on a common database(frontal images of faces of 47 people: 26 males and 21 females,four images per person). We have developed and implemented two new algorithms; the first one is based on the computation of a set of geometrical features,such as nose width and length,mouth position,and chin shape,and the second one is based on almost-grey-level template matching. The results obtained on the testing sets(about 90% correct recognition using geometrical features and perfect recognition using template matching)favor our implementation of the template-matching approach.
Keywords: classification; face recognition; karhunen-loeve expansion; template matching
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1993,15(10):1042-1052
被引频次:953
Two-dimensional PCA: A new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition
Yang,J; Zhang,D; Frangi,AF ; et al.
Abstract: In this paper,a new technique coined two-dimensional principal component analysis(2DPCA)is developed for image representation. As opposed to PCA,2DPCA is based on 2D image matrices rather than 1 D vectors so the image matrix does not need to be transformed into a vector prior to feature extraction. Instead,an image covariance matrix is constructed directly using the original image matrices,and its eigenvectors are derived for image feature extraction. To test 2DPCA and evaluate its performance,a series of experiments were performed on three face image databases: ORL,AR,and Yale face databases. The recognition rate across all trials was higher using 2DPCA than PCA. The experimental results also indicated that the extraction of image features is computationally more efficient using 2DPCA than PCA.
Keywords: Principal Component Analysis(PCA); eigentaces; feature extraction; image representation; face recognition
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2004,26(1):131 - 137
被引频次:953
PCA versus LDA
Martinez,AM; Kak,AC
Abstract: 参见“经典文献推荐”栏目
·推荐论文摘要·
基于改进ORB特征的多姿态人脸识别
周凯汀,郑力新
摘要:为了克服通过全局特征以及每位个体单个模板样本进行多姿态人脸识别的不足,提出基于改进的ORB局部特征以及每位个体多个模板样本的多姿态人脸识别方法.首先改进ORB算子的采样模式提高算子对人脸视角变化的鲁棒性,并采用每位个体的多个训练样本建立模板库,然后提取并匹配测试样本与模板样本的改进ORB特征。在特征提取阶段,为避免关键点数目变化的干扰,对全部样本提取一致数目的关键点;在特征匹配阶段,采用基于模型和基于方向的双重策略剔除误匹配点对,使用匹配点对数目与平均距离评价测试样本与每个模板样本的吻合程度。对CAS-PEAL-R1和XJTU数据库的实验结果表明,改进的ORB特征具有更好的识别性能;与采用多个训练样本构建个体单个模板样本的方法相比,在训练样本数目相同的条件下,该方法能较好地避免姿态的干扰,具有更好的识别效果。与SIFT算子相比,ORB算子在特征提取与特征匹配2个阶段都具有明显的速度优势。
关键词:人脸识别;多姿态;多视图;ORB;特征匹配
来源出版物:计算机辅助设计与图形学学报,2015,27(2):287-295联系邮箱:郑力新,1050920138@qq.com
基于鉴别稀疏保持嵌入的人脸识别算法
马小虎,谭延琪
摘要:鉴于近年来稀疏表示(Sparse representation,SR)在高维数据例如人脸图像的特征提取与降维领域的快速发展,对原始的稀疏保持投影(Sparsity preserving projection,SPP)算法进行了改进,提出了一种叫做鉴别稀疏保持嵌入(Discriminant sparsity preserving embedding,DSPE)的算法.通过求解一个最小二乘问题来更新SPP中的稀疏权重并得到一个更能真实反映鉴别信息的鉴别稀疏权重,最后以最优保持这个稀疏权重关系为目标来计算高维数据的低维特征子空间.该算法是一个线性的监督学习算法,通过引入鉴别信息,能够有效地对高维数据进行降维.在ORL库、Yale库、扩展Yale B库和CMU PIE库上的大量实验结果验证了算法的有效性。
关键词:人脸识别;稀疏表示;稀疏保持投影;鉴别稀疏保持嵌入
来源出版物:自动化学报,2014,40(1):73-82联系邮箱:马小虎,xhma@suda.edu.cn
一种基于改进BP神经网络的PCA人脸识别算法
李康顺,李凯,张文生
摘要:人脸识别作为模式识别领域的热点研究问题受到了广泛的关注。传统BP算法虽然具有自学习、自适应以及强大的非线性映射能力并且在人脸图像识别准确率上占有很大的优势,但算法具有收敛缓慢、训练过程振荡、易陷入局部极小点等缺点。针对传统BP算法的不足提出一种基于改进BP神经网络的PCA人脸识别算法,该算法采用PCA算法提取图像的主要特征,并结合一种新的权值调整方法改进BP算法进行图像分类识别。仿真实验表明,通过使用该算法对ORL人脸数据库的图像进行识别,其结果比传统算法具有更快的收敛速度和更高的识别率。
关键词:人脸识别;主成分分析;BP神经网络;附加动量;弹性梯度下降法
来源出版物:计算机应用与软件,2014,(1):158-161
基于非下采样Contourlet梯度方向直方图的人脸识别
奉俊鹏,杨恢先,蔡勇勇,等
摘要:针对人脸识别系统准确度不高的问题,提出一种基于非下采样 Contourlet梯度方向直方图(HNOG)的人脸识别算法。先对人脸图像进行非下采样Contourlet变换(NSCT),并将变换后的各系数矩阵进行分块,再计算各分块的梯度方向直方图(HOG),将所有分块的直方图串接得到人脸图像HNOG特征,最后用多通道最近邻分类器进行分类。在YALE人脸库、ORL人脸库上和CAS-PEAL-R1人脸库上的实验结果表明,人脸的HNOG特征有很强的辨别能力,特征维数较小,且对光照、表情、姿态的变化具有较好的鲁棒性。
关键词:非下采样Contourlet变换;梯度方向直方图;人脸识别;最近邻分类器
来源出版物:计算机应用,2014,34(1):158-161联系邮箱:杨恢先,yanghx@xtu.edu.cn
用于人脸识别的相对梯度直方图特征描述
杨利平,辜小花
摘要:由于方向边缘幅值模式(POEM)在剧烈光照变化情况下无法获得足够的特征描述信息,本文分析了相对梯度幅值图像特点,提出了相对梯度直方图特征描述方法。该方法根据图像的梯度方向对相对梯度幅值图像进行分解、滤波、局部二值模式编码和特征降维,形成了对光照变化,尤其是非均匀光照变化具有健壮性的低维直方图特征。在FERET和YaleB子集上的人脸识别实验证实:在光照变化较小时,相对梯度直方图特征描述方法与方向边缘幅值模式的性能相当,均显著优于经典的局部二值模式特征;在光照剧烈变化时,前者的识别精度比方向边缘幅值模式至少高 5%,性能显著优于方向边缘幅值模式和局部二值模式,展示了相对梯度直方图特征描述方法的有效性和对光照变化的良好健壮性。
关键词:人脸识别;相对梯度直方图;局部二值模式;特征描述
来源出版物:光学精密工程,2014,22(1):152-159联系邮箱:杨利平,yanglp@cqu.edu.cn
基于简化脉冲耦合神经网络的人脸识别
聂仁灿,姚绍文,周冬明
摘要:基于简化脉冲耦合神经网络(S-PCNN),提出了一种新颖的人脸识别方法。首先通过对神经元振荡特性的分析,将神经元振荡时间序列(OTS)分解为捕获性振荡时间序列(C-OTS)和自激性振荡时间序列(S-OTS)。然后通过图像几何变换和振荡频图,分析了X-OTS(OTS、C-OTS和S-OTS)的鉴别特性。最后利用C-OTS+S-OTS和余弦距离测度给出了人脸识别的系统结构。人脸库中的实验结果验证了所提方法的有效性,显示了它比其它传统算法具有更好的识别性能。
关键词:简化脉冲耦合神经网络;振荡时间序列;人脸识别
来源出版物:计算机科学,2014,41(2):297-301联系邮箱:聂仁灿,huomu_ren@163.com
基于子模式的Gabor特征融合的单样本人脸识别
王科俊,邹国锋
摘要:针对传统人脸识别方法在单训练样本条件下效果不佳的缺点,提出基于子模式的Gabor特征融合方法并用于单样本人脸识别。首先采用Gabor变换抽取人脸局部信息,为有效利用面部器官的空间位置信息,将Gabor人脸图像分块构成子模式,采用最小距离分类器对各子模式分类。最后对各子模式分类结果做决策级融合得出分类结果。根据子模式构成原则和决策级融合策略不同,提出两种子模式Gabor特征融合方法。利用ORL人脸库和CAS-PEAL-R1人脸库进行实验和比较分析,实验结果表明文中方法有效提高单样本人脸识别的正确率,改善单样本人脸识别系统的性能。
关键词:单样本人脸识别;Gabor变换;局部特征;图像子模式;决策级融合;模糊综合
来源出版物:模式识别与人工智能,2013,26(1):50-56联系邮箱:王科俊,15124551941@139.com
基于低秩子空间恢复的联合稀疏表示人脸识别算法
胡正平,李静
摘要:针对阴影、反光及遮挡等原因破坏图像低秩结构这一问题,提出基于低秩子空间恢复的联合稀疏表示识别算法。首先将每个个体的所有训练样本图像看作矩阵D,将矩阵D分解为低秩矩阵A和稀疏误差矩阵E,其中A表示某类个体的‘干净’人脸,严格遵循子空间结构,E表示由阴影、反光、遮挡等引起的误差项,这些误差项破坏了人脸图像的低秩结构。然后用低秩矩阵A和误差矩阵E构造训练字典,将测试样本表示为低秩矩阵A和误差矩阵E的联合稀疏线性组合,利用这两部分的稀疏逼近计算残差,进行分类判别。实验证明该稀疏表示识别算法有效,识别精度得到了有效提高。
关键词:人脸识别;稀疏表示;联合稀疏;低秩子空间恢复
来源出版物:电子学报,2013,41(5):987-991
基于低分辨率局部二值模式的人脸识别
戴金波,肖霄,赵宏伟
摘要:为提高人脸识别的准确度,提出了一种基于低分辨率局部二值模式的人脸识别方法。该方法将原始人脸图像滤波下采样处理成低分辨率图像,将其划分成若干块矩形块图像,对每一块图像进行局部二值模式计算,统计出每一块LBP图谱的直方图,再连接在一起成为这幅图片的最终特征向量。经实验表明,该算法在ORL和YALE上均取得了更好的识别效果,且对光照、表情、姿势等的变化具备鲁棒性。
关键词:计算机应用;局部二值模式;低分辨率;特征提取;人脸识别
来源出版物:吉林大学学报:工学版,2013,43(2):435-438联系邮箱:赵宏伟,zhaohw@jlu.edu.cn
面向光照可变的人脸识别方法
李昕昕,陈丹,许凤娇
摘要:传统 Retinex算法在侧光严重的情况下难以消除阴影,为此提出一个对数形式的传导函数,取得了很好的光照补偿效果。为提高人脸识别率,将该问题看成一个典型的模式分类问题,提出基于局部二值模式(LBP)特征的支持向量机(SVM)人脸识别方法,使用“一对一”的方法将多类问题转化为SVM分类器可以解决的两类问题,实现了高效的人脸识别。在CMU PIE、AR、CAS-PEAL以及自行采集的人脸库上进行了仿真实验,结果表明该方法能够有效地去除光照影响,相对传统方法具有较优的识别性能。
关键词:人脸识别;光照;局部二值模式;支持向量机;视网膜皮层
来源出版物:计算机应用,2013,33(2):507-510联系邮箱:李昕昕,xinxinli@foxmail.com
Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering
Florian Schroff; Dmitry Kalenichenko; James Philbin
Abstract:Despite significant recent advances in the field of face recognition,implementing face verification and recognition efficiently at scale presents serious challenges to current approaches. In this paper we present a system,called FaceNet,that directly learns a mapping from face images to a compact Euclidean space where distances directly correspond to a measure of face similarity. Once this space has been produced,tasks such as face recognition,verification and clustering can be easily implemented using standard techniques with FaceNet embeddings as feature vectors. Our method uses a deep convolutional network trained to directly optimize the embedding itself,rather than an intermediate bottleneck layer as in previous deep learning approaches. To train,we use triplets of roughly aligned matching / non-matching face patches generated using a novel online triplet mining method. The benefit of our approach is much greater representational efficiency: we achieve state-of-the-art face recognition performance using only 128-bytes per face. On the widely used Labeled Faces in the Wild(LFW)dataset,our system achieves a new record accuracy of 99.63%. On YouTube Faces DB it achieves 95.12%. Our system cuts the error rate in comparison to the best published result by 30% on both datasets.
来源出版物:preprint arXiv:1503.03832,2015
Face Search at Scale: 80 Million Gallery
Dayong Wang; Charles Otto; Anil K. Jain
Abstract:Due to the prevalence of social media websites,one challenge facing computer vision researchers is to devise methods to process and search for persons of interest among the billions of shared photos on these websites. Facebook revealed in a 2013 white paper that its users have uploaded more than 250 billion photos,and are uploading 350 million new photos each day. Due to this humongous amount of data,large-scale face search for mining web images is both important and challenging. Despite significant progress in face recognition,searching a large collection of unconstrained face images has not been adequately addressed. To address this challenge,we propose a face search system which combines a fast search procedure,coupled with a state-of-the-art commercial off the shelf(COTS)matcher,in a cascaded framework. Given a probe face,we first filter the large gallery of photos to find the top-k most similar faces using deep features generated from a convolutional neural network. The k candidates are re-ranked by combining similarities from deep features and the COTS matcher. We evaluate the proposed face search system on a gallery containing 80 million web-downloaded face images. Experimental results demonstrate that the deep features are competitive with state-of-the-art methods on unconstrained face recognition benchmarks(LFW and IJB-A). Further,the proposed face search system offers an excellent trade-off between accuracy and scalability on datasets consisting of millions of images. Additionally,in an experiment involving searching for face images of the Tsarnaev brothers,convicted of the Boston Marathon bombing,the proposed face search system could find the younger brother's(Dzhokhar Tsarnaev)photo at rank 1 in 1 second on a 5M gallery and at rank 8 in 7 seconds on an 80M gallery.
来源出版物:preprint arXiv:1507.07242,2015
Non-rigid visible and infrared face registration via regularized Gaussian fields criterion
Ma,JY; Zhao,J; Ma,Y; et al.
Abstract: Registration of multi-sensor data(particularly visible color sensors and infrared sensors)is a prerequisite for multimodal image analysis such as image fusion. Typically,the relationships between image pairs are modeled by rigid or affine transformations. However,this cannot produce accurate alignments when the scenes are not planar,for example,face images. In this paper,we propose a regularized Gaussian fields criterion for non-rigid registration of visible and infrared face images. The key idea is to represent an image by its edge map and align the edge maps by a robust criterion with a non-rigid model. We model the transformation between images in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space and a sparse approximation is applied to the transformation to avoid high computational complexity. Moreover,a coarse-to-fine strategy by applying deterministic annealing is used to overcome local convergence problems. The qualitative and quantitative comparisons on two publicly available databases demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art method with an affine model. As a result,our method will be beneficial for fusion-based face recognition.
Keywords: registration; image fusion; infrared; non-rigid; face recognition; Gaussian fields
来源出版物:Pattern Recognition,2015,48(3): 772-784联系邮箱:Ma,JY; jiayima@whu.edu.cn
Fully automatic 3D facial expression recognition using polytypic multi-block local binary patterns
Li,XL; Ruan,QQ; Jin,Y; et al.
Abstract: 3D facial expression recognition has been greatly promoted for overcoming the inherent drawbacks of 2D facial expression recognition and has achieved superior recognition accuracy to the 2D. In this paper,a novel holistic,full-automatic approach for 3D facial expression recognition is proposed. First,3D face models are represented in 2D-image-like structure which makes it possible to take advantage of the wealth of 2D methods to analyze 3D models. Then an enhanced facial representation,namely polytypic multi-block local binary patterns(P-MLBP),is proposed. The P-MLBP involves both the feature-based irregular divisions to depict the facial expressions accurately and the fusion of depth and texture information of 3D models to enhance the facial feature. Based on the BU-3DFE database,three kinds of classifiers are employed to conduct 3D facial expression recognition for evaluation. Their experimental results outperform the state of the art and show the effectiveness of P-MLBP for 3D facial expression recognition. Therefore,the proposed strategy is validated for 3D facial expression recognition; and its simplicity opens a promising direction for fully automatic 3D facial expression recognition.
Keywords: 3D facial expression recognition; automatic data normalization; P-MLBP; feature-based irregular divisions; feature fusion
来源出版物:Signal Processing,2015,108: 297-308联系邮箱:Li XL; 09112087@bjtu.edu.cn
UGC-JU face database and its benchmarking using linear regression classifier
Seal,A; Bhattacharjee,D; Nasipuri,M; et al.
Abstract: In this paper,a new face database has been presented which will be freely available to academicians and research community for research purposes. The face database consists of both visual and thermal face images of 84 persons with varying poses,expressions and occlusions(39 different variations for each type,visual or thermal). A new thermal face image recognition technique based on Gappy Principal Component Analysis and Linear Regression Classifier has also been presented here. The recognition performance of this technique on the thermal face images of this database is found to be 98.61 %,which can be considered as the initial benchmark recognition performance this database.
Keywords: thermal face images; visual images; face database; GappyPCA; LRC classifier; decision level fusion
来源出版物:Multimedia Tools and Applications,2015,74(9): 2913-2937联系邮箱:Seal,A; ayanseal30@ieee.org
Learning face representation from scratch
Dong Yi; Zhen Lei; Shengcai Liao; Stan Z. Li
Abstract: Pushing by big data and deep convolutional neural network(CNN),the performance of face recognition is becoming comparable to human. Using private large scale training datasets,several groups achieve very high performance on LFW,i.e.,97% to 99%. While there are many open source implementations of CNN,none of large scale face dataset is publicly available. The current situation in the field of face recognition is that data is more important than algorithm. To solve this problem,this paper proposes a semi-automatical way to collect face images from Internet and builds a large scale dataset containing about 10000 subjects and 500000 images,called CASIAWebFace. Based on the database,we use a 11-layer CNN to learn discriminative representation and obtain state-of-theart accuracy on LFW and YTF. The publication of CASIAWebFace will attract more research groups entering this field and accelerate the development of face recognition in the wild.
来源出版物:preprint arXiv:1411.7923,2014
Joint sparse representation for robust multimodal biometrics recognitionl
Shekhar,S; Patel,VM; Nasrabadi,NM; et al.
Abstract: Traditional biometric recognition systems rely on a single biometric signature for authentication. While the advantage of using multiple sources of information for establishing the identity has been widely recognized,computational models for multimodal biometrics recognition have only recently received attention. We propose a multimodal sparse representation method,which represents the test data bya sparse linear combination of training data,while constraining the observations from different modalities of the test subject to share their sparse representations. Thus,we simultaneously take into account correlations as well as coupling information among biometric modalities. A multimodal quality measure is also proposed to weigh each modality as it gets fused. Furthermore,we also kernelize the algorithm to handle nonlinearity in data. The optimization problem is solved using an efficient alternative direction method. Various experiments show that the proposed method compares favorably with competing fusion-based methods.
Keywords: Multimodal biometrics; feature fusion; sparse representation
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2014,36(1): 113-126
联系邮箱:Shekhar,S; sshekha@umiacs.umd.edu
Half-quadratic-based iterative minimization for robust sparse representation
He,R; Zheng,WS; Tan,TN; et al.
Abstract: Robust sparse representation has shown significant potential in solving challenging problems in computer vision such as biometrics and visual surveillance. Although several robust sparse models have been proposed and promising results have been obtained,they are either for error correction or for error detection,and learning a general framework that systematically unifies these two aspects and explores their relation is still an open problem. In this paper,we develop a half-quadratic( HQ)framework to solve the robust sparse representation problem. By defining different kinds of half-quadratic functions,the proposed HQ framework is applicable to performing both error correction and error detection. More specifically,by using the additive form of HQ,we propose an l(1)-regularized error correction method by iteratively recovering corrupted data from errors incurred by noises and outliers; by using the multiplicative form of HQ,we propose an l(1)-regularized error detection method by learning from uncorrupted data iteratively. We also show that the l(1)-regularization solved by soft-thresholding function has a dual relationship to Huber M-estimator,which theoretically guarantees the performance of robust sparse representation in terms of M-estimation. Experiments on robust face recognition under severe occlusion and corruption validate our framework and findings.
Keywords: I(1)-minimization; half-quadratic optimization; sparse representation; M-estimator; correntropy
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2014,36(2): 261-275
联系邮箱:He,R; rhe@nlpr.ia.ac.cn
Image Quality Assessment for Fake Biometric Detection: Application to Iris,Fingerprint,and Face Recognition
Galbally,Javier; Marcel,Sebastien; Fierrez,Julian
Abstract: To ensure the actual presence of a real legitimate trait in contrast to a fake self-manufactured synthetic or reconstructed sample is a significant problem in biometric authentication,which requires the development of new and efficient protection measures. In this paper,we present a novel software-based fake detection method that can be used in multiple biometric systems to detect different types of fraudulent access attempts. The objective of the proposed system is to enhance the security of biometric recognition frameworks,by adding liveness assessment in a fast,user-friendly,and non-intrusive manner,through the use of image quality assessment. The proposed approach presents a very low degree of complexity,which makes it suitable for real-time applications,using 25 general image quality features extracted from one image(i.e.,the same acquired for authentication purposes)to distinguish between legitimate and impostor samples. The experimental results,obtained on publicly available data sets of fingerprint,iris,and 2D face,show that the proposed method is highly competitive compared with other state-of-the-art approaches and that the analysis of the general image quality of real biometric samples reveals highly valuable information that may be very efficiently used to discriminate them from fake traits.
Keywords: image quality assessment; biometrics; security; attacks; countermeasures
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2014,23(2): 710-724
联系邮箱:Galbally,Javier; javier.galbally@jrc.ec.europa.es
Robust face recognition via occlusion dictionary learning
Ou,WH; You,XG; Tao,DC; et al.
Abstract: Sparse representation based classification(SRC)has recently been proposed for robust face recognition. To deal with occlusion,SRC introduces an identity matrix as an occlusion dictionary on the assumption that the occlusion has sparse representation in this dictionary. However,the results show that SRC's use of this occlusion dictionary is not nearly as robust to large occlusion as it is to random pixel corruption. In addition,the identity matrix renders the expanded dictionary large,which results in expensive computation. In this paper,we present a novel method,namely structured sparse representation based classification(SSRC),for face recognition with occlusion. A novel structured dictionary learning method is proposed to learn an occlusion dictionary from the data instead of an identity matrix. Specifically,a mutual incoherence of dictionaries regularization term is incorporated into the dictionary learning objective function which encourages the occlusion dictionary to be as independent as possible of the training sample dictionary. So that the occlusion can then besparsely represented by the linear combination of the atoms from the learned occlusion dictionary and effectively separated from the occluded face image. The classification can thus be efficiently carried out on the recovered non-occluded face images and the size of the expanded dictionary is also much smaller than that used in SRC. The extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves better results than the existing sparse representation based face recognition methods,especially in dealing with large region contiguous occlusion and severe illumination variation,while the computational cost is much lower.
Keywords: face recognition; occlusion dictionary learning; mutual incoherence; structured sparse representation
来源出版物:Pattern Recognition,2014,47(4): 1559-1572联系邮箱:You,XG; you1231cncn@gmail.com
Discriminative multimanifold analysis for face recognition from a single training sample per person
Lu ,JW; Tan,YP; Wang,G
Abstract: Conventional appearance-based face recognition methods usually assume that there are multiple samples per person(MSPP)available for discriminative feature extraction during the training phase. In many practical face recognition applications such as law enhancement,e-passport,and ID card identification,this assumption,however,may not hold as there is only a single sample per person(SSPP)enrolled or recorded in these systems. Many popular face recognition methods fail to work well in this scenario because there are not enough samples for discriminant learning. To address this problem,we propose in this paper a novel discriminative multimanifold analysis(DMMA)method by learning discriminative features from image patches. First,we partition each enrolled face image into several nonoverlapping patches to form an image set for each sample per person. Then,we formulate the SSPP face recognition as a manifold-manifold matching problem and learn multiple DMMA feature spaces to maximize the manifold margins of different persons. Finally,we present a reconstruction-based manifold-manifold distance to identify the unlabeled subjects. Experimental results on three widely used face databases are presented to demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed approach.
Keywords: face recognition; manifold learning; subspace learning; single training sample per person
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,35(1): 39-51
联系邮箱:Lu ,JW; jiwen.lu@adsc.com.sg
Fast l(1)-minimization algorithms for robust face recognition
Yang,AY; Zhou,ZH; Balasubramanian,AG; et al.
Abstract: l(1)-minimization refers to finding the minimum l(1)-norm solution to an underdetermined linear system b = Ax. Under certain conditions as described in compressive sensing theory,the minimum l(1)-norm solution is also the sparsest solution. In this paper,we study the speed and scalability of its algorithms. In particular,we focus on the numerical implementation of a sparsity-based classification framework in robust face recognition,where sparse representation is sought to recover human identities from high-dimensional facial images that may be corrupted by illumination,facial disguise,and pose variation. Although the underlying numerical problem is a linear program,traditional algorithms are known to suffer poor scalability for large-scale applications. We investigate a new solution based on a classical convex optimization framework,known as augmented Lagrangian methods. We conduct extensive experiments to validate and compare its performance against several popular l(1)-minimization solvers,including interior-point method,Homotopy,FISTA,SESOPCD,approximate message passing,and TFOCS. To aid peer evaluation,the code for all the algorithms has been made publicly available.
Keywords: l(1)-minimization; augmented Lagrangian methods; face recognition
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2013,22(8): 3234-3246联系邮箱:Yang,AY;yang@eecs.berkeley.edu
Hybrid Deep Learning for Face Verification
Yi Sun; Xiaogang Wang; Xiaoou Tang
Abstract: his paper proposes a hybrid convolutional network(ConvNet)-Restricted Boltzmann Machine(RBM)model for face verification in wild conditions. A key contribution of this work is to directly learn relational visual features,which indicate identity similarities,from raw pixels of face pairs with a hybrid deep network. The deep ConvNets in our model mimic the primary visual cortex to jointly extract local relational visual features from two face images compared with the learned filter pairs. These relational features are further processed through multiple layers to extract high-level and global features. Multiple groups of ConvNets are constructed in order to achieve robustness and characterize face similarities from different aspects. The top-layer RBM performs inference from complementary high-level features extracted from different ConvNet groups with a two-level average pooling hierarchy. The entire hybrid deep network is jointly fine-tuned to optimize for the task of face verification. Our model achieves competitive face verification performance on the LFW dataset.
来源出版物: 2013 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE,2013: 1489-1496.
编辑:王微
We have developed a near-real-time computer system that can locate and track a subject's head,and then recognize the person by comparing characteristics of the face to those of known individuals. The computational approach taken in this system is motivated by both physiology and information theory,as well as by the practical requirements of near-real-time performance and accuracy. Our approach treats the face recognition problem as an intrinsically two-dimensional(2-D)recognition problem rather than requiring recovery of three-dimensional geometry,taking advantage of the fact that faces are normally upright and thus may be described by a small set of 2-D characterstic views. The system functions by projecting face images onto a feature space that spans the significant variations among known face images. The significant features are known as "eigenfaces," because they are the eigenvectors(principal components)of the set of faces; they do not necessarily correspond to features such as eyes,ears,and noses. The projection operation characterizes an individual face by a weighted sum of the eigenface features,and so to recognize a particular face it is necessary only to compare these weights to those of known individuals. Some particular advantages of our approach are that it provides for the ability to learn and later recognize new faces in an unsupervised manner,and that it is easy to implement using a neural network architecture.
superior temporal sulcus; human faces; neurons; macaque; monkey; cortex
典
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1Eigenfaces for RecognitionTurk,MJournal of Cognitive Neuroscience,1991,3(1):71-86 2 Pattern Recognition,1996,29(1): 51-59 3Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using class A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on feature distributions Ojala,T specific linear projectionBelhumeur,PNIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,1997,19(7): 711-720 4 2004,57(2): 137-154 5PCA versus LDAMartinez,AMIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2001,23(2): 228-233 Robust real-time face detection Viola,P International Journal of Computer Vision,
Eigenfaces for Recognition
Turk,M; Pentland,A
