Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011
2015-10-26WanqingChenRongshouZhengHongmeiZengSiweiZhangJieHe
Wanqing Chen, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng, Siwei Zhang, Jie He
National Office for Cancer Prevention and Control, National Cancer Center, Beijing 100021, China
Correspondence to: Jie He. National Office for Cancer Prevention and Control, National Cancer Center, Beijing 100021, China. Email: hejie@cicams.ac.cn.
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011
Wanqing Chen, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng, Siwei Zhang, Jie He
National Office for Cancer Prevention and Control, National Cancer Center, Beijing 100021, China
Correspondence to: Jie He. National Office for Cancer Prevention and Control, National Cancer Center, Beijing 100021, China. Email: hejie@cicams.ac.cn.
Objective: The National Central Cancer Registry (NCCR) collected population-based cancer registration data in 2011 from all cancer registries. National cancer incidence and mortality were compiled and cancer incident new cases and cancer deaths were estimated.
Methods: In 2014, there were 234 cancer registries submitted cancer incidence and deaths occurred in 2011. All datasets were checked and evaluated based on the criteria of data quality from NCCR. Total 177 registries’ data were qualified and compiled for cancer statistics in 2011. The pooled data were stratified by area (urban/rural), gender, age group (0, 1-4, 5-9, 10-14…85+) and cancer type. Cancer incident cases and deaths were estimated using age-specific rates and national population in 2011. All incidence and death rates are age-standardized to the 2000 Chinese standard population and Segi’s population expressed per 100,000 persons.
Results: All 177 cancer registries (77 in urban and 100 in rural areas) covered 175,310,169 populations(98,341,507 in urban and 76,968,662 in rural areas). The morphology verified cases (MV%) accounting for 70.14% and 2.44% of incident cases were identified through death certifications only (DCO%)with mortality to incidence ratio of 0.63. The estimates of new cancer incident cases and cancer deaths were 3,372,175 and 2,113,048 in 2011, respectively. The incidence rate was 250.28/100,000 (males 277.77/100,000, females 221.37/100,000), and the age-standardized incidence rates by Chinese standard population (ASIRC) and by world standard population (ASIRW) were 186.34/100,000 and 182.76/100,000 with the cumulative incidence rate (0-74 years old) of 21.20%. The cancer incidence and ASIRC in urban areas were 261.38/100,000 and 189.89/100,000 compared to 238.60/100,000 and 182.10/100,000 in rural areas, respectively. The cancer mortality was 156.83/100,000 (194.88/100,000 in males and 116.81/100,000 in females), the age-standardized mortality rates by Chinese standard population (ASMRC) and by world standard population (ASMRW) were 112.88/100,000 and 111.82/100,000, and the cumulative mortality rate(0-74 years old) was 12.69%. The cancer mortality and ASMRC were 154.37/100,000 and 108.20/100,000 in urban areas, and 159.42/100,000 and 117.97/100,000 in rural areas, respectively. Cancers of lung, female breast, stomach, liver, colon and rectum, esophageal, cervix, uterus, prostate and ovary were the most common cancers, accounting for about 75% of all cancer new cases. Lung cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer, esophageal cancer, colorectal cancer, female breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, brain tumor, cervical cancer and leukemia were the leading causes of cancer death, accounting for about 80% of all cancer deaths. The cancer incidence, mortality and spectrum showed difference between urban and rural areas, males and females.
Conclusions: The coverage of cancer registration population had a greater increase than that in the last year. The data quality and representativeness are gradually improved. As the basic work of cancer prevention and control, cancer registry is playing an irreplaceable role. The disease burden of cancer is increasing, and the health department has to take effective measures to contain the increased cancer burden in China.
Cancer registry; incidence; mortality; epidemiology; China
Introduction
Cancer is a major public health issue in China. It was the second leading cause of death, and the incidence and mortality keep increasing (1-3). In 2008, the national program of cancer registry was launched by the Ministry of Health of China. Since then, National Central Cancer Registry (NCCR) of China has been publishing cancer statistics annually based on registries’ data (4). In this article, we analyzed the cancer incidence and mortality in cancer registration areas in 2011 and estimated the numbers of new cancer cases and deaths nationally to provide an overview of current cancer statistics using data collected from local registries. The updated cancer burden results would be broadly used by government,researchers and clinicians for policy and research.
Materials and methods
Data source
The NCCR is responsible for cancer data collection, evaluation and publication from local population-based cancer registries. The cancer information was reported to the cancer registries from local hospitals, and community health centers, including the Basic Medical Insurances for Urban Residents and the New-Rural Cooperative Medical System. The Vital Statistical Database was linked with the cancer incidence database for identifying cases with death certificate only (DCO) and follow-up. By 1 June 2014, 234 cancer registries (98 cities and 136 counties) from 31 provinces submitted 2011 data to the NCCR. Data covered about 221,390,275 people, accounting for about 16.43% of the national population. All cancer cases were classified according to the International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, 3rdedition (ICD-O-3) and the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10thRevision (ICD-10). Invasive cases of lung cancer (ICD10: C33-C34) were extracted and analyzed from the overall cancer database. Incidence and mortality [2011] were based on data from 177 population-based cancer registries which distributed in 28 provinces (77 in urban and 100 in rural areas)and covered a total of 175,310,169 populations (98,341,507 in urban and 76,968,662 in rural areas) including 88,655,668 males and 86,654,501 females, accounting for 13.01% of the national population (Figure 1).
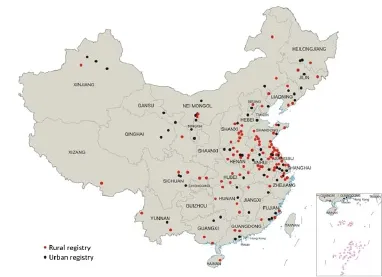
Figure 1 Map of the 177 contributing cancer registries and geographic regions in China (the dots are location of the cancer registries).
National population estimates
The national population in 2011 was estimated based on the 5thNational Population Census data [2000] provided by the National Statistics Bureau of China, taking into account of the changes of age composition, gender ratio and the proportion of urban and rural transformation released by the National Bureau of Statistics (http://data.stats.gov.cn/). The national population in 2011 was stratified by area (urban/ rural), gender (male/female) and age groups (0-, 1-4, 5-84 by 5 years, 85+ years). The changes of age-specific death probability were also adjusted when calculating population. Linear changes were assumed in each age group between the fifth and sixth Population Censuses.
Quality control
Submitted data were checked and evaluated by NCCR based on “Guideline for Chinese Cancer Registration”and referring to relevant data quality criterion of “Cancer Incidence in Five Continents Volume IX” by IARC/IACR (5). Software such as MS-FoxPro, MS-Excel and ICRC/IACR tools IARC-crgTools was used for data collection, sorting,checking and evaluation. Proportion of morphological verification (MV%), percentage of cancer cases identified with death certification only (DCO%), mortality to incidence ratio (M/I), percentage of uncertified cancer (UB%) and percentage of cancer with undefined or unknown primary site (secondary) (O&U%) were used to evaluate the completeness, validity and reliability of cancer statistics.
Statistical analysis
Incidence and mortality rates were calculated by area,gender and age groups. The numbers of new cases and deaths were estimated using the 5-year age-specific cancer incidence/mortality rates and the corresponding populations. The Chinese population in 2000 and World Segi’s population were used for age-standardized rates. The cumulative risk of developing or dying from cancer before 75 years of age(in the absence of competing causes of death) was calculated and presented as a percentage. Software including MS-Excel,IARCcrgTools2.05 issued by IARC and IACR was used for data checking and evaluation (6). SAS software (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, USA) was used to calculate the incidence and mortality rates.
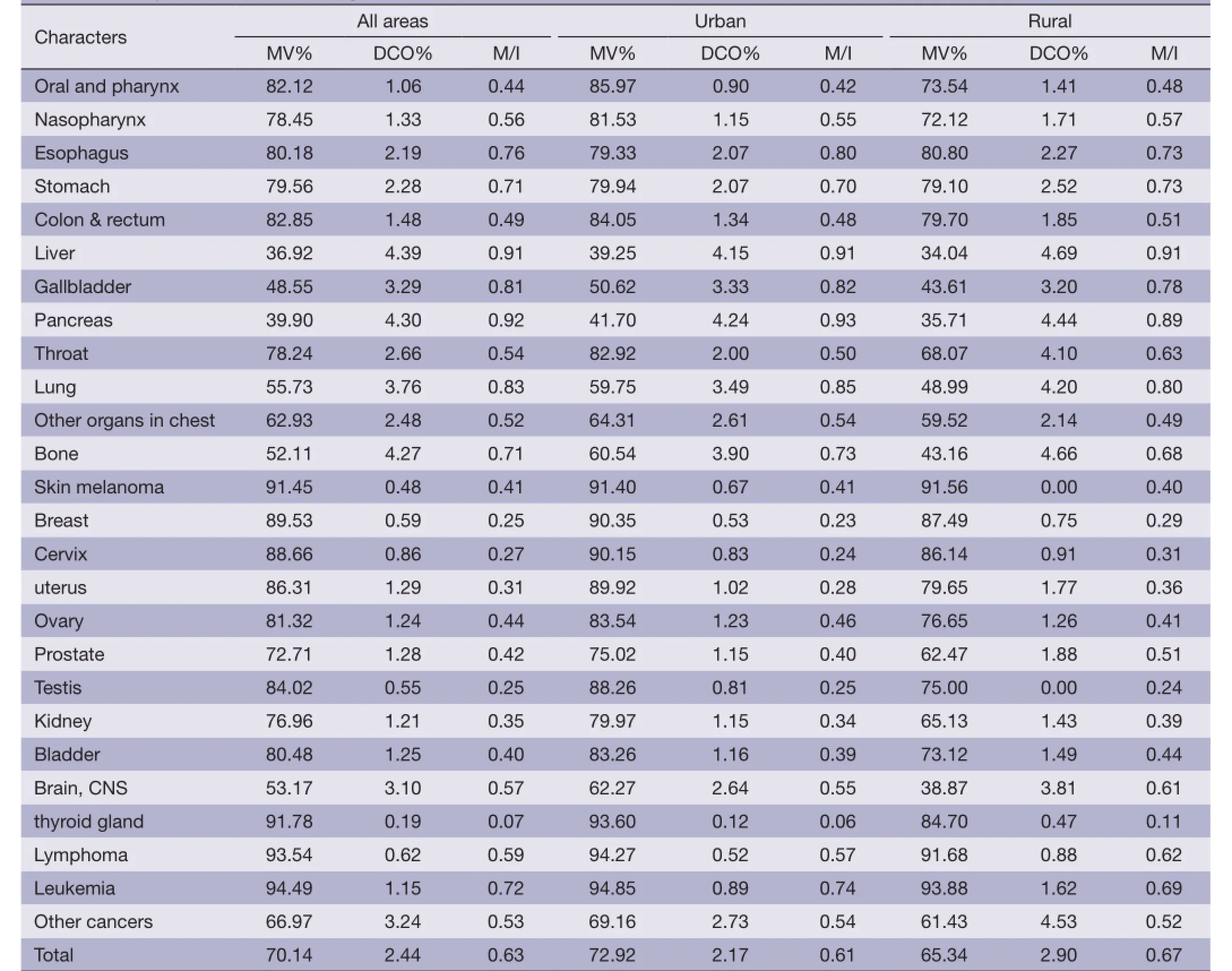
Table 1 Quality evaluation of cancer registration data, 2011
Results
Data quality
There were 177 registries accepted by this annual report distributed in 28 provinces, including 77 cities and 100 counties covering 175,310,169 of populations, including 88,655,668 males and 86,654,501 females, accounting for 13.01%.
The overall indicators of MV%, DCO%, and M/I ratio were 70.14%, 2.44% and 0.63, respectively. They were 72.92%, 2.17% and 0.61 in urban registries, compared to 65.34%, 2.90% and 0.67 in rural areas. The quality evaluation for major cancers is presented in Table 1.
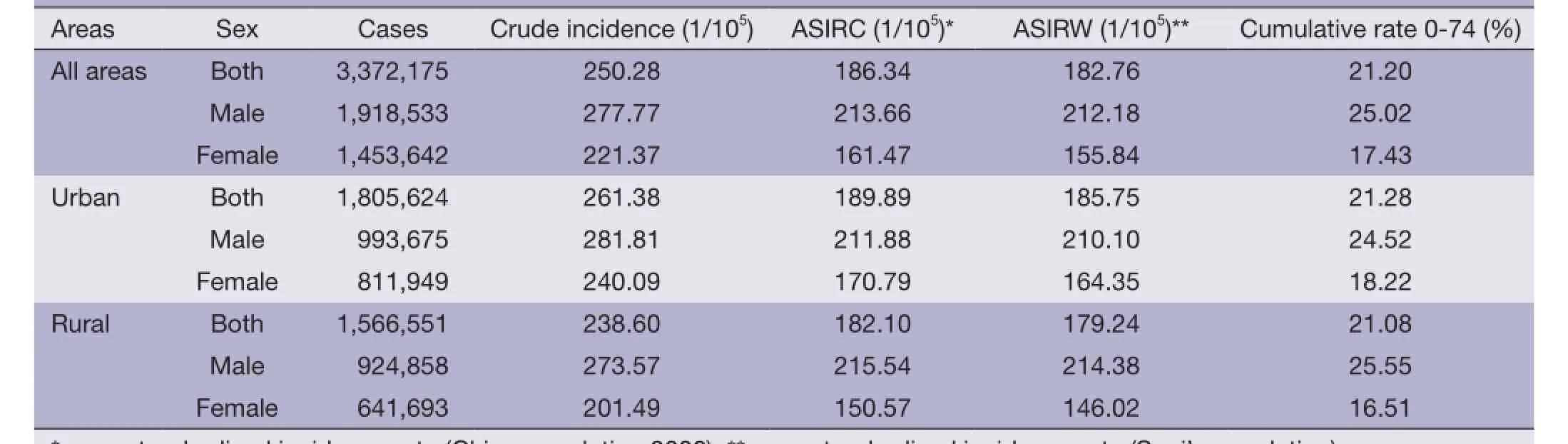
Table 2 Cancer incidence in China, 2011
Incidence and mortality of overall cancers
Incidence
It was estimated there were 3,372,175 new cases diagnosed as cancer in 2011. The crude incidence rate of all cancers was 250.28/100,000 (277.77/100,000 in males and 221.37/100,000 in females). The age-standardized incidence rates were 186.34/100,000 and 181.49/100,000 by Chinese population(ASIRC) and World population (ASIRW), respectively. Among the patients aged 0-74 years, the cumulative incidence rate was 21.28%. The crude cancer incidences rate and age-standardized rates in urban areas were higher than that of rural areas. The crude incidences in males and females were higher in urban than in rural. However, after adjusted by age, cancer incidences for males in urban and rural areas were conversed. More new cancer cases occurred in eastern areas than middle areas and western areas, however, crude incidence rates in three areas were not great different (Table 2).
Age-specific incidence rate
Cancer incidence was relatively lower before 40 years old,then increased dramatically after 40 years old and finally peaked after 80 years and then slightly decreased after 85 years(Table 3, Figure 2). The pattern was similar between urban and rural areas. Comparing the age-specific incidence rate between urban and rural areas, except age from 55-64,urban had higher incidence rates in most of age groups. The incidence at 80 years old was higher in urban areas than in rural areas, but lower in the age group of 40-74 years. Before age of 70 years, most age groups of males in rural areas had higher incidence rate than that in urban. However, in females, the incidences were higher in urban than in rural areas in every age group after 25 years (Table 3, Figure 2).
Mortality
It was estimated there were 2,113,048 died from cancer in 2011. The crude mortality of all cancers in China was 156.83/100,000 (194.88/100,000 in males and 116.81/100,000 in females). The age-standardized mortalities were 112.88/100,000 and 111.82/100,000 by Chinese population (ASMRC) and World population(ASMRW), respectively. Among the patients aged 0-74 years,the cumulative incidence rate was 12.69%. The crude cancer mortality rate and age-standardized rates in urban areas was higher than that in rural areas. The crude cancer mortalities were higher in urban than in rural, however,after adjusted by age, the mortalities were conversed both in male and female. More cancer deaths occurred in eastern areas than middle areas and western areas, however, western areas had higher mortalities than eastern and middle areas(Table 4).
Age-specific mortality
The cancer mortality was relatively lower before 45 years and then dramatically increased reaching peak after 85 years(Table 5, Figure 3). The mortality in rural areas was highest in the age group of 80-84 years. The age-specific mortality in urban males was lowered than that in rural in most of age-groups before 80 years old. In females, the mortality in urban was higher than that in rural only for age group over 75 years.
Incidence and mortality for major cancers
Cancer incidence for the 10 most common cancers
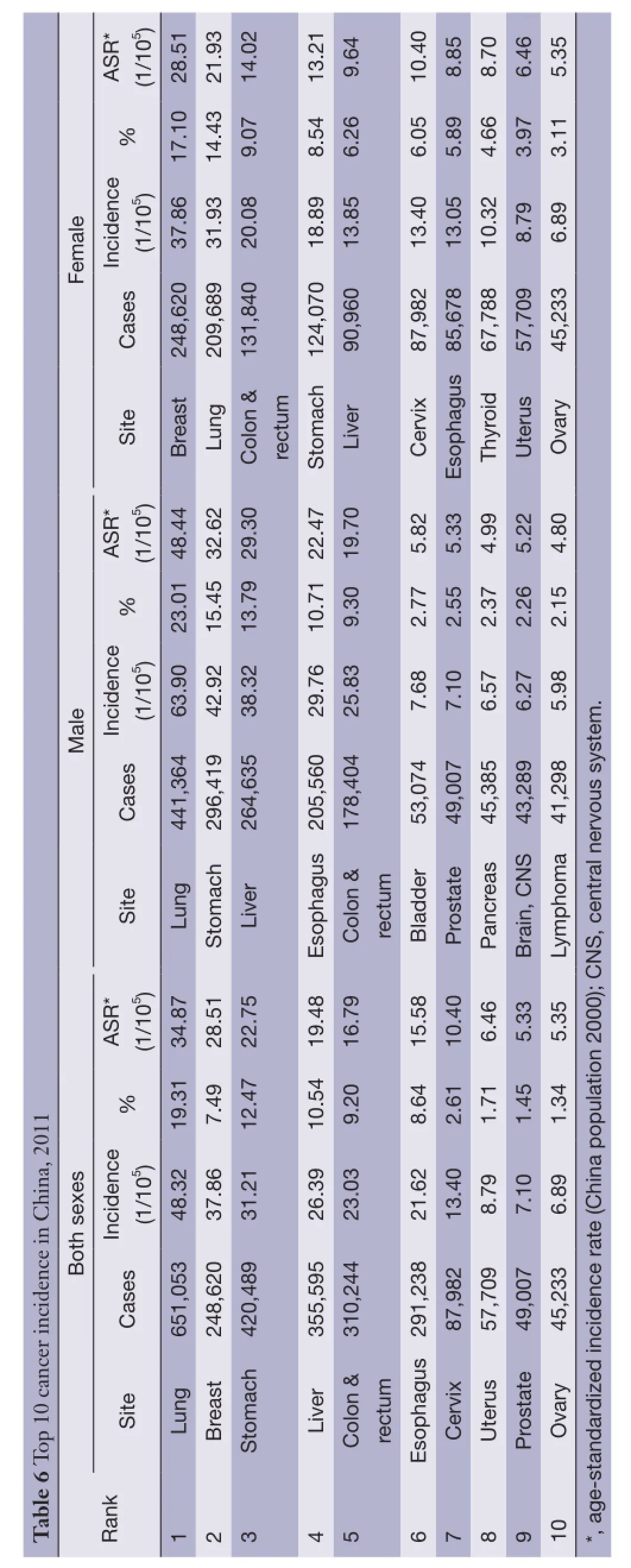
Lung cancer was the most common cancer in all areas,followed by female breast cancer, stomach cancer, livercancer and colorectal cancer with estimated new cases of 651,053, 248,620, 420,489, 355,595 and 310,244, respectively. Lung cancer was the most frequently diagnosed cancers in males followed by stomach cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer. Breast cancer was the most common cancers in females followed by lung cancer, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer and liver cancer (Table 6).

Table 3 Age-specific incidence rates of overall cancers, 2011 (1/105)
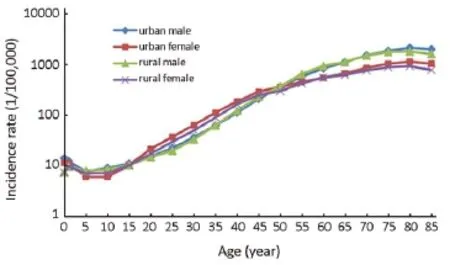
Figure 2 Age-specific cancer incidence rates in urban and rural areas, 2011.
Cancer death of top 10 cancers
Lung cancer was the leading cause of death in China followed by liver cancer, stomach cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer with estimated deaths of 529, 153,322,417, 297,496, 218,957 and 149,722, respectively. In males, lung cancer was the leading cause followed by liver cancer, stomach cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer; while in females, lung cancer was still the leading cause followed by stomach cancer, liver cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer (Table 7).
Cancer incidence of the 10 most common cancers in urban areas
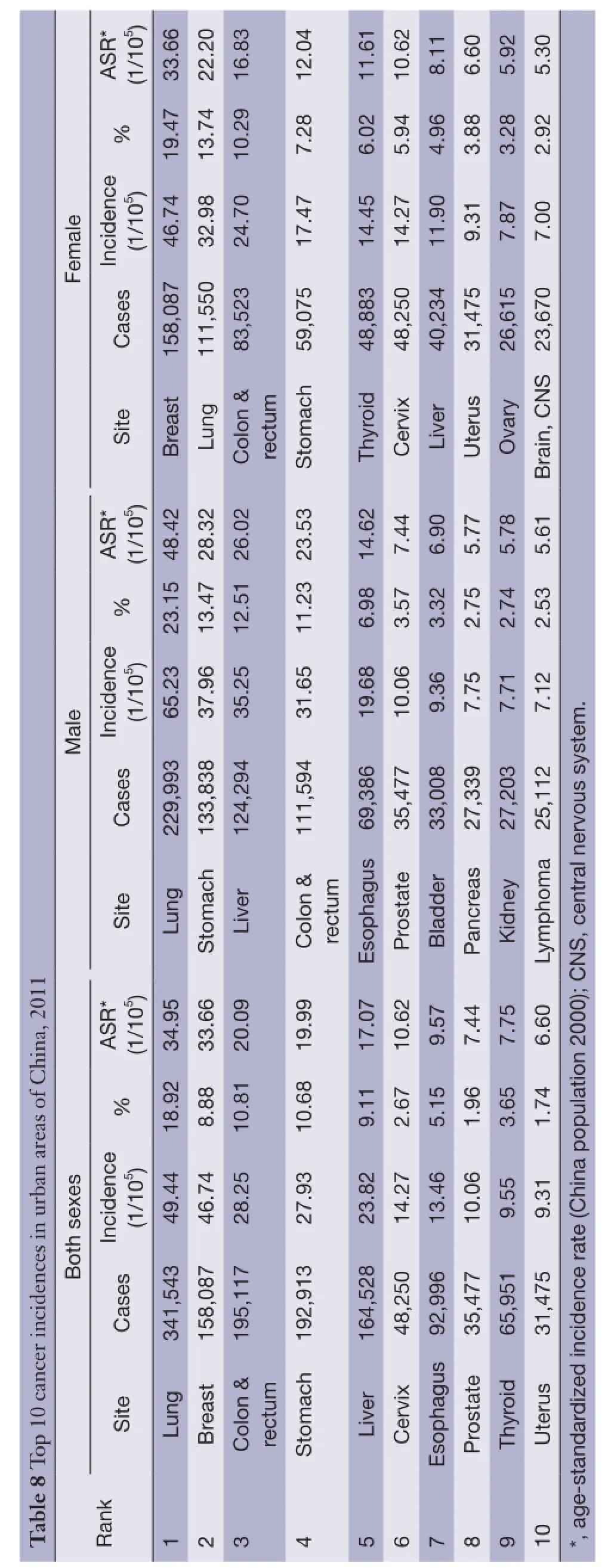
In urban areas, lung cancer was the most frequently diagnosed cancers, followed by female breast cancer,colorectal cancer, stomach cancer and liver cancer with the estimated new cases of 341,543, 158,087, 195,117, 192,913 and 164,528, respectively. The most common sites of cancer were lung, stomach, liver, colon-rectum and esophagusin males, while in females, cancers of breast, lung, colonrectum, stomach and thyroid were the most common (Table 8).

Table 4 Cancer mortality in China, 2011

Table 5 Age-specific mortality of overall cancers, 2011 (1/105)
Cancer death of top 10 cancers in urban areas
Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death in urban areas for both males and females with number of deaths and mortalities of 192,074, 52.47/100,000 and 88,927,26.29/100,000, respectively. Other cancer types with high mortality in males were liver cancer, stomach cancer,esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer. In females, stomach cancer was the second cause of cancer death, followed by colorectal cancer, liver cancer and breast cancer (Table 9).
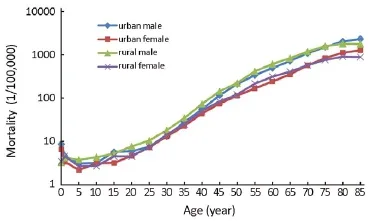
Figure 3 Age-specific cancer mortality in urban and rural areas, 2011.
Cancer incidence of the 10 most common cancers in rural areas
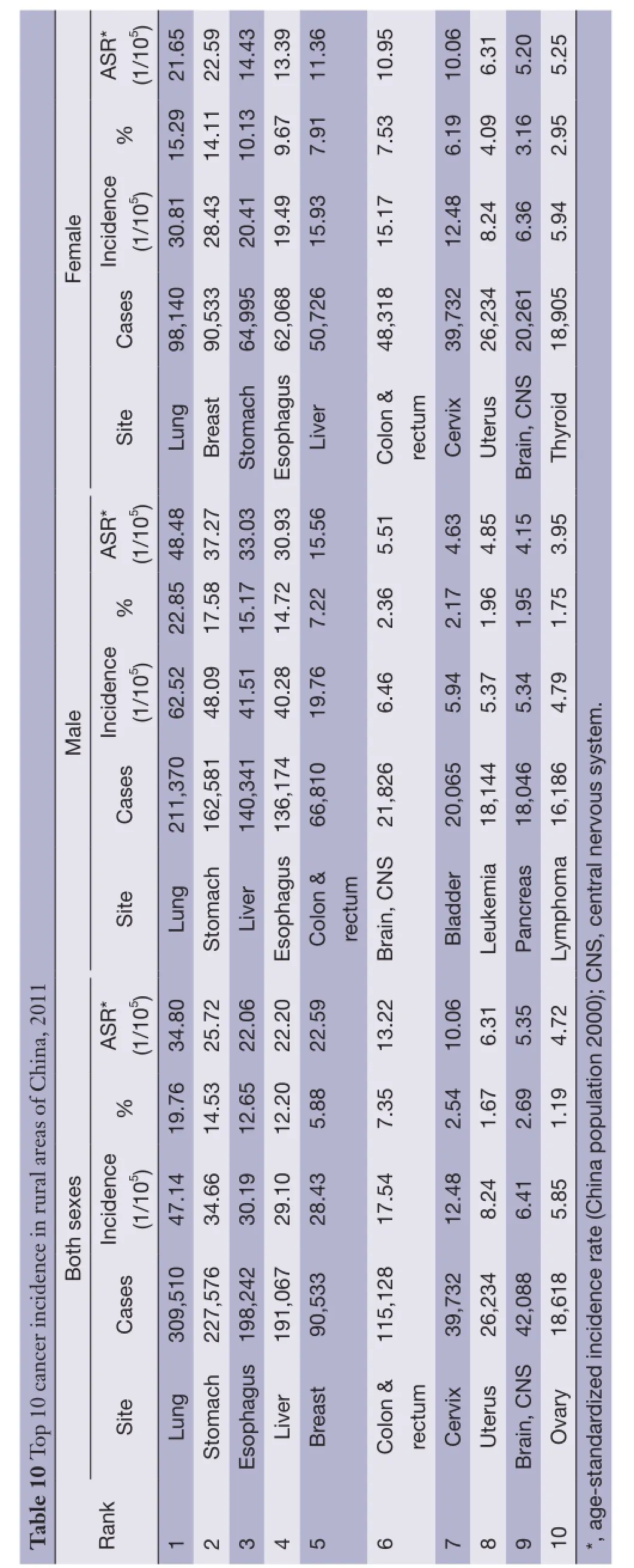
Table 10 shows the 10 most common cancer incidence rates in rural areas. Lung cancer has been becoming the most frequently diagnosed cancers (309,510 new cases with incidence rate of 47.14/100,000), followed by stomach cancer, esophagus cancer, liver cancer and female breast cancer. The most common sites of cancer in males were lung, stomach, liver, esophagus, and colon-rectum, while in females, they were cancers of lung, breast, stomach,esophagus and liver (Table 10).
Cancer death of top 10 cancers in rural areas
Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death in rural areas for both males and females. The number of deaths on lung cancer in rural was 248,152 with mortality of 37.80/100,000. The other cancer types with high mortality were liver cancer, stomach cancer, esophageal cancer and colorectal cancer in males; stomach cancer, liver cancer,esophageal cancer and breast cancer in females (Table 11).
Discussion
Population-based cancer registry in China collects the information on cancer incident cases and cancer deaths from covered population to surveillance the cancer epidemics in certain areas. The cancer registration data are not only applied for cancer control planning, implementation and evaluation on cancer prevention and control, but also for scientific research (7).
In mid of 2014, the NCCR called for data submission in 2011 from all registries supported by national program of cancer registry. Total 234 registries reported registration data including national registries and some provincial registries. The population coverage of all registries was over 221 million, accounting for 16.4% of national populations. Stringent quality control is essential based on the national criteria issued in program protocol to ensure the data reliability. The incidence, mortality and population from a same registry have to keep reasonable levels compared to past data. The indicators of completeness, comparability and invalidity, such as MV%, DCO%, M/I ratio, UB% and O&U%, were evaluated for every registry’s data to judge if submitted data is valid or not. If any logical errors,inexplicable incidence, or mortality, the data would be sent back to registries to check and correct. Through the double evaluations in provincial and national level, 177 registries were qualified and accepted for final pooled database, which was used for cancer statistics in 2011. The population was estimated based on the fifth National Population Census data in 2000 released by the National Bureau of Statistics,and the changes of age construction, gender ratio, the extent of urbanization level and age specific death probability were taken into account (http://data.stats.gov.cn/). The national population and registries’ data in 2011 stratified by area (urban/rural), gender (male/female) and age groups were used for estimates of national cancer new cases and cancer deaths. In the annual report of 2010, the national population from the sixth Population Census was used for estimation, which residential population was registered (4). However, the household population is considered to be more suitable because the cancer data are based on the household registration.
It was estimated that cancer incident new cases were 3.37 million and 2.11 million died in cancer all over the country in 2011 with the incidence rate of 250.28/100,000 and mortality of 156.83/100,000. Compared to the figures in 2010, there were 280 thousands and 150 thousands more on cancer new cases and deaths with 6.4% and 5.4% increases of incidence rate and mortality due to the different population mentioned before. After adjusted by age, the incidence and mortality were kept stable. Therefore, the cancer statistics in 2011 were reasonable and creditable. There are still few registries in the west due to the low population density. The western region would be the emphasis for building new cancer registries to meet the requirement of the national and regional representativeness of cancer registry (8).
?

?
?

?
?

?
Urban areas in China had a higher cancer incidence and lower mortality than those in rural areas and the cancer patterns are quite different (2,3). Recent study showed the differences narrowed (9,10). Lung cancer becomes themost common cancer in rural areas instead of stomach cancer. The reason might be high prevalence of tobacco smoking (11) and the air pollution due to the rapid development of urbanization and industrialization (12). A population-based cancer survival study displayed that rural China had a much low relative 5-year survival rate compared with urban China (13,14). This could be explained by limited medical resources, low level of cancer cares and more patients with late stage of cancers. The government should notice the differences between urban and rural areas and implement effective measurement to bridge the gap.
Cancers from upper digestive organ are still the more common cancers and cancer deaths in China, and the incidences of lung cancer, breast cancer and colorectal cancer are increasing. Thyroid cancer had ranked the eighth frequent cancer in China and fifth in urban females that needs to be noticed. The improvement of diagnosis might be the key reason, but the further etiological study is necessary.
In 2014, the number of registries has been increased to 308, covering 300 millions of population. An extra budget was settled to support follow-up and survival analysis from 2014. The registration data would be getting more valuable and play an important role on cancer control. The National Cancer Center launched a project of cancer atlas,which would provide useful information about geographic distribution of cancer to make national cancer control program more efficient.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledged the cooperation of all the population-based cancer registries in providing cancer statistics, data collection, sorting, verification and database creation. The authors assumed full responsibility for analyses and interpretation of these data.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
1 Chen JG, Zhang SW, Chen WQ. Analysis of liver cancer mortality in the national retrospective sampling survey of death causes in China, 2004-2005. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine (in Chinese) 2010;44:383-9.
2 Zeng HM, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, et al. Trend analysis of cancer mortality in China between 1989 and 2008. Chinese Journal of Oncology (in Chinese) 2012;34:525-31.
3 Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zeng HM, et al. Trend analysis and projection of cancer incidence in China between 1989 and 2008. Chinese Journal of Oncology (in Chinese)2012;34:517-24.
4 Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, et al. Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010. Chin J Cancer Res 2014;26:48-58.
5 Curade MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, et al. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents. Vol. IX. Lyon: IARC Scientific Publications, 2008:1-837.
6 Ferlay J. The IARC crgTools Programs. Lyon: IARC,2006. Available online: http://www.iacr.com.fr/index. php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=blog&i d=68&Itemid=445
7 Parkin DM. The evolution of the population-based cancer registry. Nat Rev Cancer 2006;6:603-12.
8 Li GL, Chen WQ. Representativeness of populationbased cancer registration in China--comparison of urban and rural areas. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2009;10:559-64.
9 Wang N, Yuan YN, Zheng RS. An analysis on difference of cancer incidence between urban and rural areas in China, 2009. China Cancer (in Chinese) 2013;22:168-73.
10 Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, et al. Trend analysis of the changes of male/female, urban/rural incidences and average age of cancer patients in China, 1989-2008. Chinese Journal of Oncology (in Chinese) 2014;36:796-800.
11 Yang T, Abdullah AS, Mustafa J, et al. Factors associated with smoking cessation among Chinese adults in rural China. Am J Health Behav, 2009;33:125-34.
12 Zhao Y, Wang S, Aunan K, et al. Air pollution and lung cancer risks in China--a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 2006;366:500-13.
13 Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, et al. Cancer survival in China,2003-2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer 2015;136:1921-30.
14 Allemani C, Weir HK, Carreira H, et al. Global surveillance of cancer survival 1995-2009: analysis of individual data for 25 676 887 patients from 279 population-based registries in 67 countries(CONCORD-2). Lancet 2014. [Epub ahead of print].
Cite this article as: Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S, He J. Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer Res 2015;27(1):2-12. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.01.06
10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.01.06
Submitted Dec 15, 2014. Accepted for publication Jan 08, 2015.
View this article at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2015.01.06
杂志排行
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Cancer statistics: updated cancer burden in China
- Population-based cancer incidence analysis in Beijing, 2008-2012
- Incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer in China, 2011
- Pancreatic cancer incidence and mortality patterns in China, 2011
- Ovary cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2011
- Oral cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2011
