原发性肾病综合征患者外周血Th9及IL—9的变化及临床意义
2015-08-29任金来等
任金来等

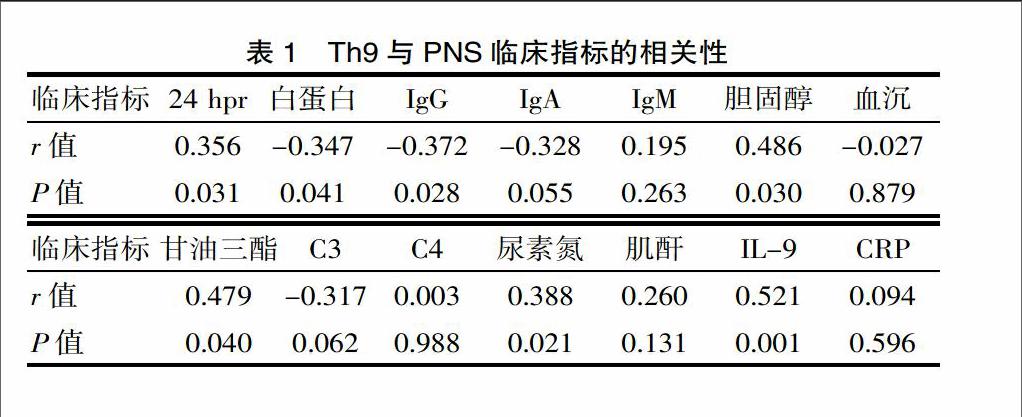
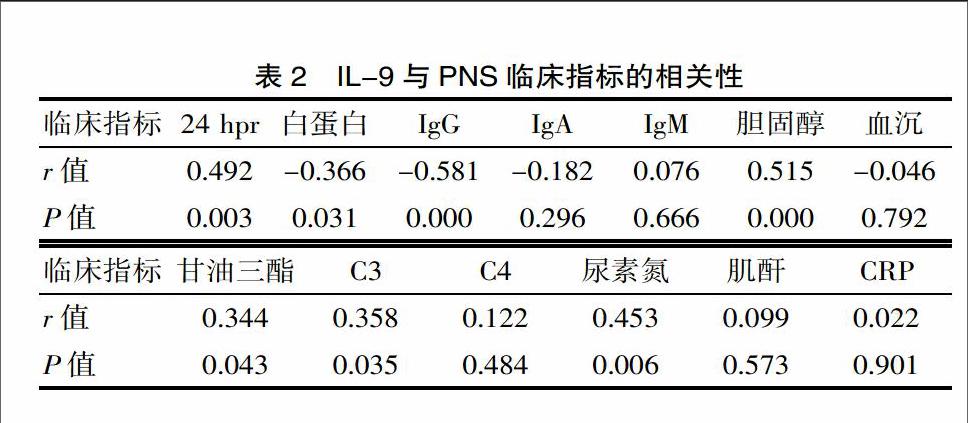
[摘要] 目的 研究原发性肾病综合征(primary nephrotic syndrome,PNS)患者外周血中辅助性T细胞9(Th9)的含量及其效应分子白细胞介素(IL-9)的表达情况,探讨Th9及IL-9与PNS临床指标的相关性及可能的免疫学机制。 方法 收集35例PNS患者和30名健康对照者。用流式细胞仪检测PNS患者和健康对照者外周血中的Th9细胞在CD4+T细胞中的比例;酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测PNS患者及健康对照者血浆中IL-9的水平。采用t检验和Spearman秩相关分析进行统计学分析。结果 PNS患者外周血中Th9细胞的比例明显高于健康对照组差异有统计学意义[分别为(1.06±0.20)%,(0.26±0.07)%,P<0.05]。PNS患者外周血IL-9水平高于健康对照组差异有统计学意义[分别为(70.02±13.66) pg/mL,(18.77±5.35) pg/ml,P<0.05]。PNS患者外周血Th9细胞的表达与24 h尿蛋白、胆固醇、甘油三酯、尿素氮及IL-9的水平呈正相关,与血清白蛋白、IgG水平呈负相关;PNS患者IL-9的水平与24 h尿蛋白、胆固醇、甘油三酯、尿素氮的水平呈正相关,与血清白蛋白、IgG、C3水平呈负相关。结论 PNS患者外周血Th9细胞比例及血浆中lL-9水平显著升高,且与相关临床指标明显相关,提示Th9及IL-9可能在PNS的发病过程中发挥重要作用。
[关键词] 原发性肾病综合征;辅助性T细胞9;白细胞介素9
[中图分类号] R392.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2015)06(c)-0006-04
[Abstract] Objective To detect the concentration of T helper cells 9(Th9) and the expression of its effector molecule interleukin(IL-9) in the peripheral blood of primary nephrotic syndrome(PNS) patients, and analyze the relationship of Th9 and IL-9 with the clinical indexes of PNS and their possible role in the immunological pathogenesis of PNS. Methods Thirty-five patients with PNS and 30 healthy controls were included. Th9 cells were obtained from PNS patients and healthy controls and detected by flow cytometry. The levels of IL-9 in PNS patients and healthy controls were detected by ELISA tests. T-test and Spearmans correlation were used for statistical analysis. Results The expression of Th9 in the peripheral blood of PNS patients was significantly higher than normal controls [(1.06±0.20)% vs (0.26±0.07)%], P<0.05. Meanwhile, the level of IL-9 in the peripheral blood of PNS patients was significantly higher than normal controls [(70.02±13.66) vs (18.77±5.35)]pg/ml, P<0.05. The expression of Th9 was positively correlated with 24-hour urinary protein, cholesterol, triglyceride, blood urea nitrogen, the level of IL-9 respectively, while that of Th9 cells was inversely proportional to serum albumin, immunoglobulin G respectively. The level of IL-9 was positively correlated with 24-hour urinary protein, cholesterol, triglyceride, blood urea nitrogen respectively, and the level of IL-9 was inversely proportional to serum albumin, immunoglobulin G, C3 respectively. Conclusion The expression of Th9 and level of IL-9 in the peripheral blood of PNS patients increase significantly, and which are related with the relative clinical indicators, these indicate that the abnormality of Th9 and IL-9 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of PNS.
