Function Observer Based Event-triggered Control for Linear Systems with Guaranteed L∞-Gain
2015-08-09PeiJiaFeiHaoandHaoYu
Pei Jia,Fei Hao,and Hao Yu
Function Observer Based Event-triggered Control for Linear Systems with Guaranteed L∞-Gain
Pei Jia,Fei Hao,and Hao Yu
—This paper is devoted to event-triggered control design for linear systems based on function observer.More specifically,the main purpose is to design event-triggered mechanisms that trigger transmissions when the difference between the current value of the system and its previously transmitted value which includes the plant output or the function observer output exceeds an additional threshold.For such an eventtriggered mechanism,we derive conditions in terms of matrix inequality to guarantee the stability as well as longer inter-event time.We propose two approaches to investigate the closed-loop model,namely,reformulating the event-triggered control system as a hybrid system and interpreting the event-induced error as exogenous disturbance.Furthermore,the minimum inter-event time is guaranteed to be strictly positive.An example is presented to illustrate the feasibility and efficiency of the theoretic results.
Index Terms—Event-triggered control,output feedback,function observer,hybrid dynamical systems.
I.INTRODUCTION
A WIDE variety of today’s engineering applications are implemented on digital platforms.In such an implementation,the sampled-data control theory has shown its effectiveness and developed considerably well as shown[1-2].However, in these traditional sampled-data control frameworks,the control task is executed periodically regardless whether it is really required or not.Besides,the sampling period is chosen for a worst-case scenario,thus leading to conservatism.Moreover, these attributes arising from communication constraints of real networks lead to unnecessary utilization of channel and power consumption.Since the desired control specification cannot always be ensured using a fixed sampling period,the current trend is to adopt event-triggered control,see,e.g., [3-5].These papers highlighted the advantages of eventtriggered control and proposed systematic design methods, thus motivated the development of this theory.
Event-triggered control offers clear advantages with respect to traditional periodic control but at the same time introduces new practical problems,that is,it needs a special hardware as an event detector to decide the next sample time.Unfortunately,using this kind of hardware,such as field programmable gate array(FPGA),is not practical in many engineering applications.Therefore,an alternative approach called selftriggered control appears.Both the event-triggered control and self-triggered control have two basic components.A controller that computes the control input and a triggering mechanism that decides the control task release time.But the difference is that,in a self-triggered strategy[6],the next release time is computed using the current sampled data and dynamics of the plant.
Pei Jia,Fei Hao,and Hao Yu are with the Seventh Research Division, School of Automation Science and Electrical Engineering,Beihang University, Beijing 100191,China,and also with the Science and Technology on Aircraft Control Laboratory,Beijing 100191,China(e-mail:xdjiapei@163.com; fhao@buaa.edu.cn;yuhao1010@126.com).
Since[4]obtained results on event-triggered control under the assumption that feedback control law preserves input-tostate stability with respect to measurement error of the plant state,fruitful results appear,see,e.g.,[7-11].Self-triggered control of homogeneous control systems was investigated[7]and self-triggered scheme guaranteeing finite-gain L2stability was presented[8].
Most of the prior work on event-triggered and self-triggered control has a common assumption,that is,the full state information is available.However,in practice,the full state is often not available for measurement.Thus,it is important to extend to event-triggered output-based control with/without an observer.
A dynamic output-feedback controller based on eventtriggered control was implemented in[12],while an event condition based on the state error of the observer was proposed and the system with norm-bounded uncertainty was investigated in[13].A more recent work can be found in[14], which used the hybrid system method proposed in[15].In the work,the event-triggered systems is reformulated as a hybrid dynamical system and linear matrix inequalities are applied to study its stability and performance.In[16],observer-based event-triggered control was considered,and global uniform ultimate bounded stability of the event-triggered system was obtained.
Inspired by[14]and[16],we propose an event-triggered control strategy which is based on a function observer.Actually,in many engineering applications,the purpose of getting the estimate of state is to generate a feedback control law. Thus,in this situation,it is better to generate a linear combination of the state rather than to generate the estimate of the plant state.We will show that,in case we skip the intermediate procedure of generating estimate of the state,and directly transmit the estimate of the linear combination of state to the plant as control input,we will have better control performance and less numbers of sampling events.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:we first introduce some notations and background on hybrid systems in Section II;and then,the problem formulation is stated in Section III,besides,the event-triggered mechanism and closedloop model are presented in this section;two approaches are proposed to analyze the event-triggered control system in Section IV,with guaranteed positive minimum inter-event time;a numerical example is illustrated in Section V;finally, Section VI summarizes the main results.
II.NOTATIONS AND PRELIMINARIES
As usual,we shall use the notation‖·‖to denote the Eucli-dean norm of an element x∈Rn.Rndenotes the ndimensional Euclidean space and Rm×ndenotes the set of all m×n dimensional real matrices.R+denotes the set of positive real numbers.For real matrix X,XTand X-1are defined as the transpose and inverse of X.And λmin(X)and λmax(X)denotes the smallest and the largest eigenvalue of X,respectively.X≻Y(X≺Y)indicates that X-Y is a positive(negative)definite matrix.Besides,X≮Y denotes that X-Y is not negative definite.Finally,for a signal x,we denote the limit from above at time t∈R+by x+(t)=limh→0+x(t+h).
Definition 1[15].Consider a hybrid system H with the form
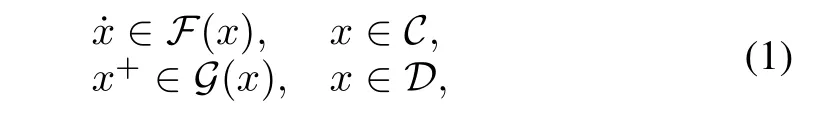
where C is called the flow set,F the flow map,D the jump set,and G the jump map.Besides,let A=C∨D,thus x∈A.
A compact set S⊆A is stable for H if for each ϵ>0 there exists δ>0 such that min{‖x(0)-y‖:y∈S}≤δ implies min{‖x(t)-y‖:y∈S}≤ϵ.
A compact set S is attractive if there exists a neighborhood of S from which each solution is bounded and converges to S,that is,limt→∞min{‖x(t)-y‖:y∈S}=0.
A compact S is asymptotically stable if it is stable and attractive.
Lemma 1[15].Consider the hybrid system H defined in Definition 1.The compact set S satisfies G(S∧D)⊂S.If there exists a Lyapunov function candidate V(x)for(H,S) such that
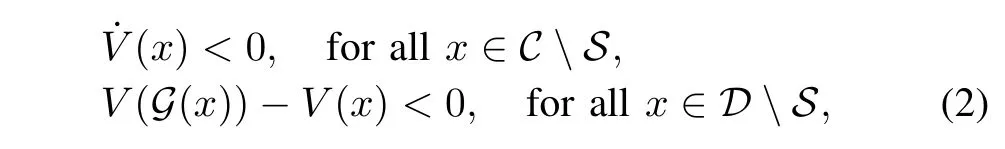
then the set S is asymptotically stable.
III.PROBLEM FORMULATION
Consider the following linear time-invariant system with the initial state x(t0)=x0that satisfies,for all t≥t0,‰
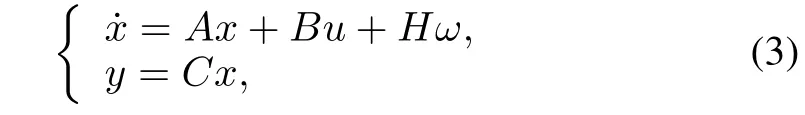
where x∈Rn,y∈Rq,u∈Rpand ω∈Rrdenote the state, output,control input and unknown disturbance,respectively. The pairs(A,B)and(A,C)are assumed to be controllable and observable,respectively.
In this paper,we focus on event-triggered control strategies that can be described with the help of Fig.1.In this setup,the plant output y is sampled only at the time instants tk,k∈N. This informationˆy(tk)is sent to a function observer(we can see a book on linear systems for more details,for example, see[17]),which is described by the following equation in the interval[tk,tk+1),

where z∈Rnand w∈Rpdenote the state and output of the function observer,respectively.Besides,all the eigenvalues of F have negative real part.
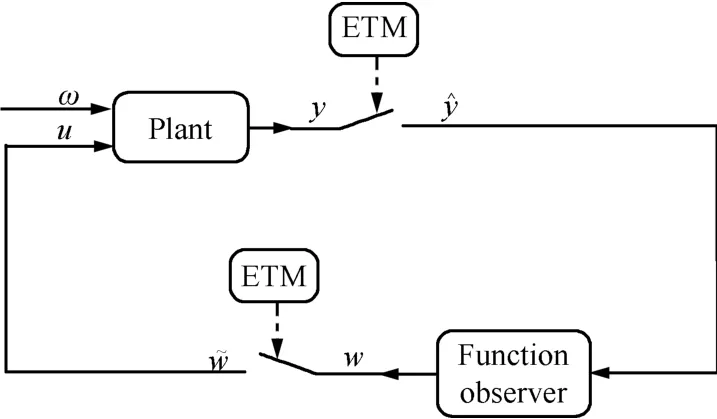
Fig.1.System structure.
If we have that limt→∞(P x(t)-z(t))=0,where P is chosen satisfying P A-F P=GC,K=E P+M C, N=P B,then we can get

The gain matrix K is designed using an emulation-based approach,that is,it is chosen such that asymptotical stability is guaranteed for a continuous-time controller with access to full state measurements.The function observer computes an estimate of the signal K x at the current sampling time.This estimated value will be sampled at tk,and then be sent to the plant as a control input.The control input is kept constant between sampling time by a zero-order hold,thus,

Here,tkis the time when the event happens.
Define the event-triggered-induced errors as

and select the event-triggering mechanism satisfying

for some σ,ϵ,ζ,δ≥0,and suppose t0=0.Let the observation error be defined as e(t)=P x(t)-z(t).Thus, the resulting closed-loop system becomes:

The problem addressed here aims at developing conditions on event-triggered control strategy in terms of linear matrix inequalities that renders the closed-loop system satisfying specified stability,which depends on the method employed. Actually,we will use two methods to analyze this system by deriving conditions such that the closed-loop system is asymptotically stable in a compact set and ultimate bounded stable,respectively.


IV.EVENT-TRIGGERED CONTROL DESIGN
A.Hybrid Dynamical System Method
In this section,we reformulate the event-triggered control system using the method in[15],thus get a hybrid system model satisfying the following set of state equations,



The flow set is

and the jump set is

Let us now define the notion of L∞-gain of a system,and for which we introduce a performance output zp∈Rmgiven by
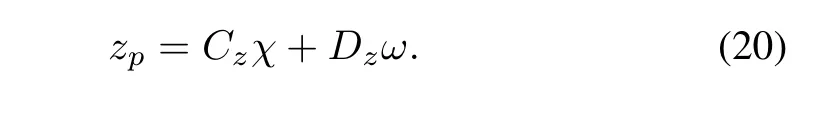
Definition 2.The L∞-gain of the system(10),with(20)is defined as

where zpis given by(20),in which χ is a solution to(10), with initial condition χ(0)∈A and disturbance ω∈L∞.

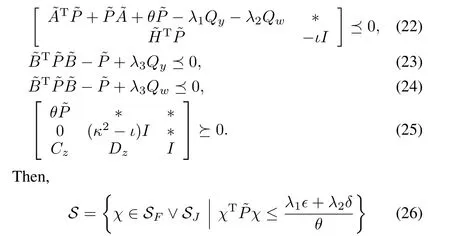



Using the comparison lemma,we can observe that the inequality above implies that

From(23)and(24),we can get
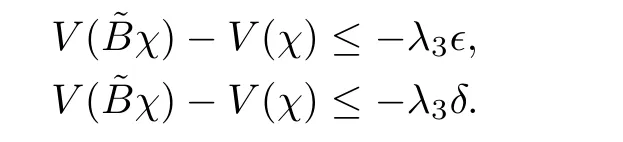

And thus,
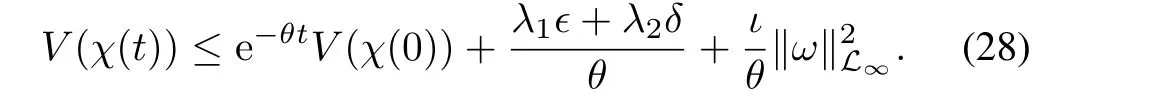
Observe that(25)implies that

and that κ2≥ι.We substitute(28)into(29)and observe that‖ω(t)‖≤‖ω‖L∞for all t∈R+,yielding

Taking now the supremum of the left and the right-hand side of(30)over all time t∈R+,we have that

with δ(χ(0))as defined in the hypothesis of the theorem.This shows that the L∞-gain is smaller than κ.□
As a specific example,let us consider the case in which the disturbance equals zero,that is ω=0.Therefore,we can obtain the next corollary.


Remark 1.In Theorem 1,we assume that there exists a minimum inter-event time τ>0,and its proof is given in the next theorem.From the expression of S,we can see that ϵ and δ are parameters influencing the asymptotically stable set. Small ϵ and δ will lead to better performance,with the cost of stricter event-triggered mechanism and more transmissions.
Theorem 2.Consider the event-triggered control system (10),with(11),(12),(13),(15),(16)and(20).For every initial condition χ(0)satisfying‖χ(0)‖≤a and every disturbance ω∈Rrsatisfying‖ω‖≤b,there exists a nonzero minimum inter-event time τ,i.e.,tk+1-tk≥τ>0,for all k∈N.An explicit expression for a lower bound on τ is given by
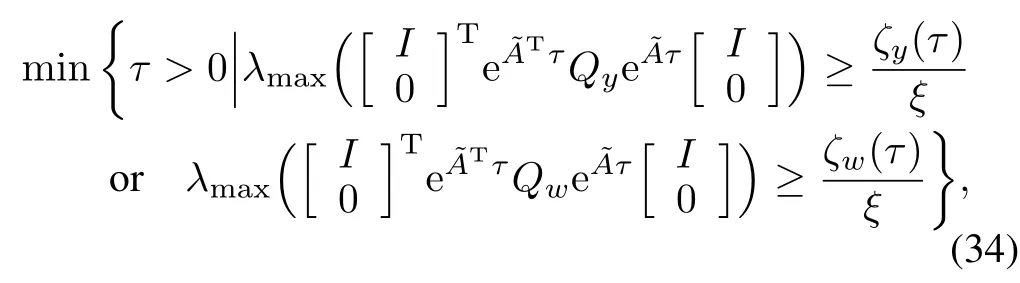
in which
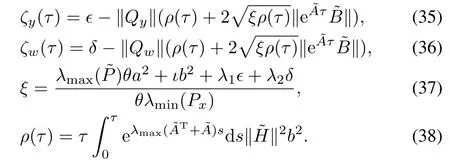
Proof.In the proof of this theorem,we will temporarily introduce notations Qi,ζiand ϵi,in which i=y,w.That means ϵy=ϵ and ϵw=δ.At the start of computing a guaranteed τ>0,we compute the event time tk+1given by(8),which can be expressed as

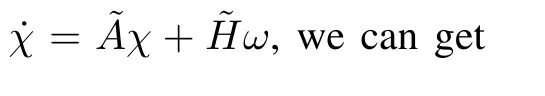
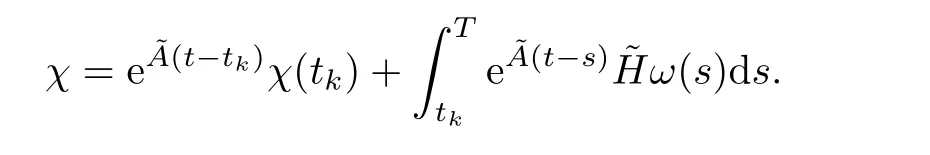
Substitute it into χTQiχ<ϵi,yielding

which is equivalent to
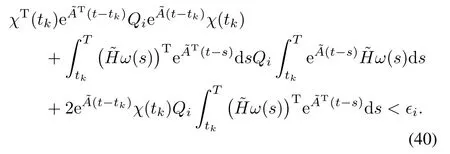
Now using Holder’s inequality and Wazewski’s inequality,we can get

Hence,the left-hand side of(41)can be upper bounded by ρ(t-tk),with ρ(·)defined in(38).Therefore,
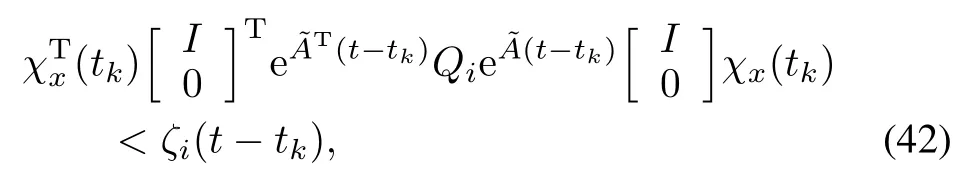
for t>tk,implying satisfaction of(40).Namely,no events are triggered as long as(42)is satisfied.From(28)in Theorem 1,we can get
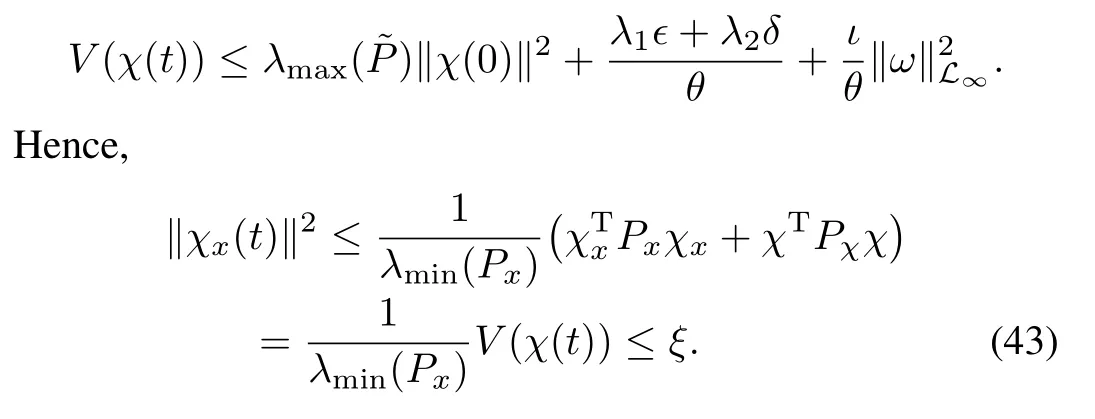
Now the solution to(34)is the smallest value τmin:=t-tk, such that

Thus,by using(43)and(44),we can get the conclusion that (42)is satisfied as long as t<tk+τmin,or equivalently,no events are triggered under these conditions.□
Theorem 3.Consider the event-triggered control system given by(10),with(11),(13),(15)and(16).For every initial condition χ(0)satisfying‖χ(0)‖≤a,there exists a time τ∈R+such that the inter-event time implicitly defined by the event-triggering mechanism(8)are lower bounded by τ, i.e.,tk+1-tk≥τ>0,for all k∈N.And the lower bound can be described as
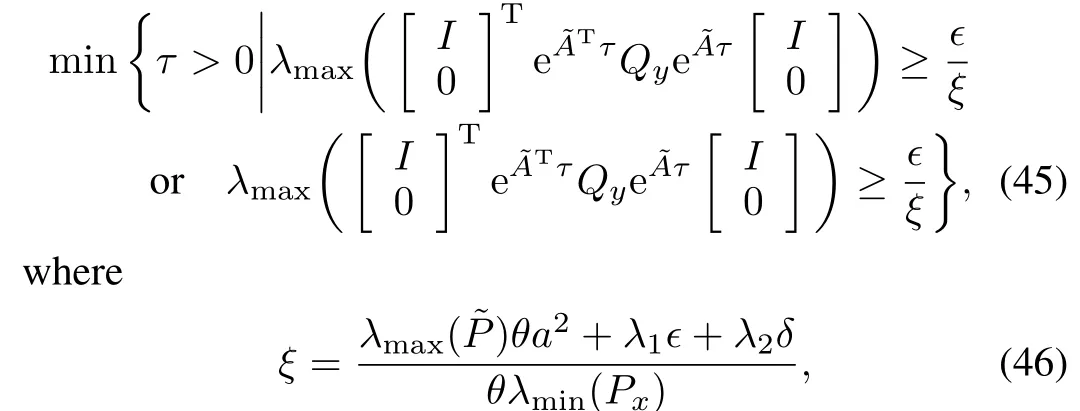
Proof.By Theorem 1,we know that

holds for t∈(tk,tk+1],k∈N.Using comparison lemma,we have
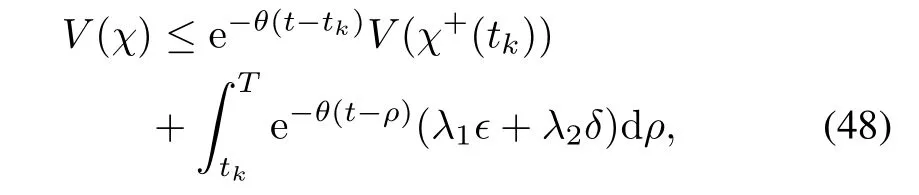


Notice that,
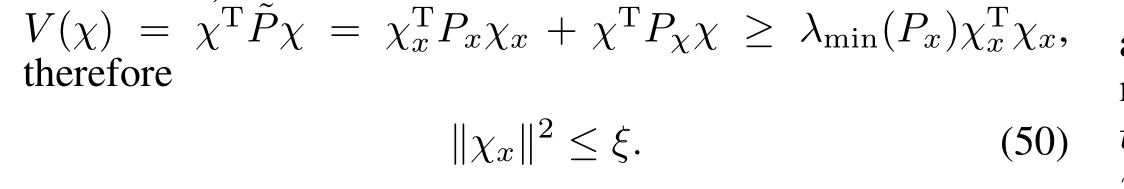


no events are triggered.We know that τ is the smallest value satisfying(45),which is equivalent to

hence,for tk<t<tk+τ,
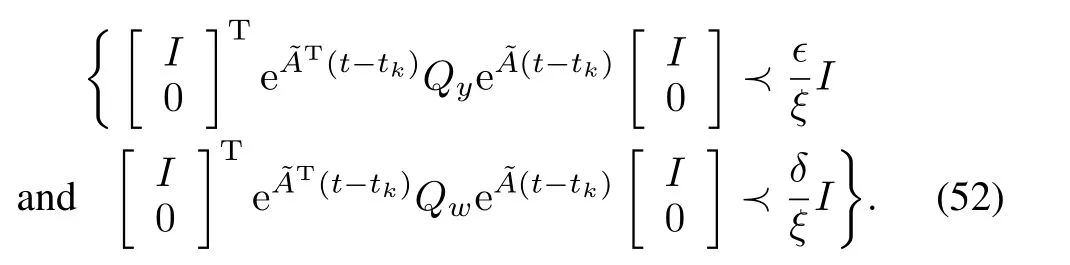
This together with(50)implies

Hence,we have that(15)is guaranteed to be satisfied and thus no events are triggered under these conditions.This provides a lower bound on the inter-event time.□
B.Interpreting the Event-induced Error as a Disturbance
The purpose of this subsection is to show that the methods proposed in[16]for the case of state observers can be generalized to a function observer scenario.We begin by briefly introducing the principle(further details may be found in the corresponding references)and then proceed to describe their stability properties when the control input directly uses the sampled value of the output K x of the function observer.
It is shown in[16]that if the typical event is defined as the error signals exceeding a given threshold,and the observer along with controller are updated only at the event-triggered sampling instants,then the closed-loop system is globally uniformly ultimately bounded stable.

In this subsection,we assume the practical external disturbance is equal to zero,i.e.,ω=0.Thus the closed-loop system (9)can be written as

We have the following theorem.
Theorem 4.Consider the closed-loop system(55)with event-triggered mechanism determined by


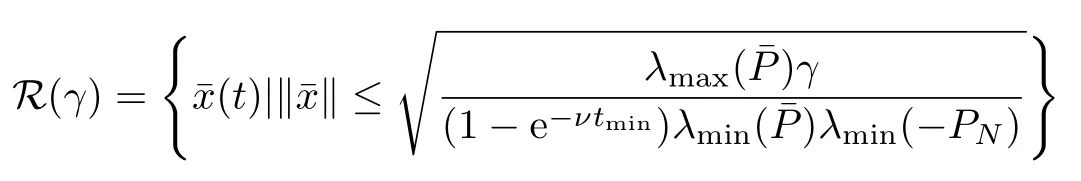


V.NUMERICAL EXAMPLE
In this section,we borrow the ball and beam model from [18],with state space description

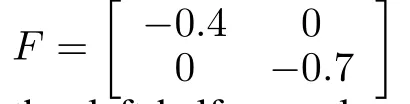
A.Hybrid Dynamical Systems Method with Disturbance
The initial condition is set to bex0=[-0.1 0.2]T.Besides, the disturbance is chosen as white noise,with mean equal to zero and variance equal to one.
With event-triggered mechanism(8),by solving the LMIs (22)-(25),we get a feasible valueσ=ζ=0.001.If we takeϵ=δ=0.005,then practical stability of the event-triggered control system(3),(5)can be guaranteed using the hybrid system formulation.
The evolution of the plant state and the function observer state as a function of time are illustrated in Figs.2 and 3. Moreover,the plots depicted in Fig.4 show the behavior of the observation error.The evolution of the inter-event time is shown in Fig.5.In Fig.6,we can observe that the performance outputzpis relatively good withL∞-gainκ=0.0739.
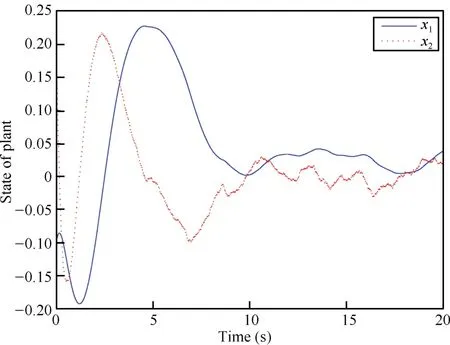
Fig.2.The trajectories of plant state as a function of time using hybrid system method with disturbance.
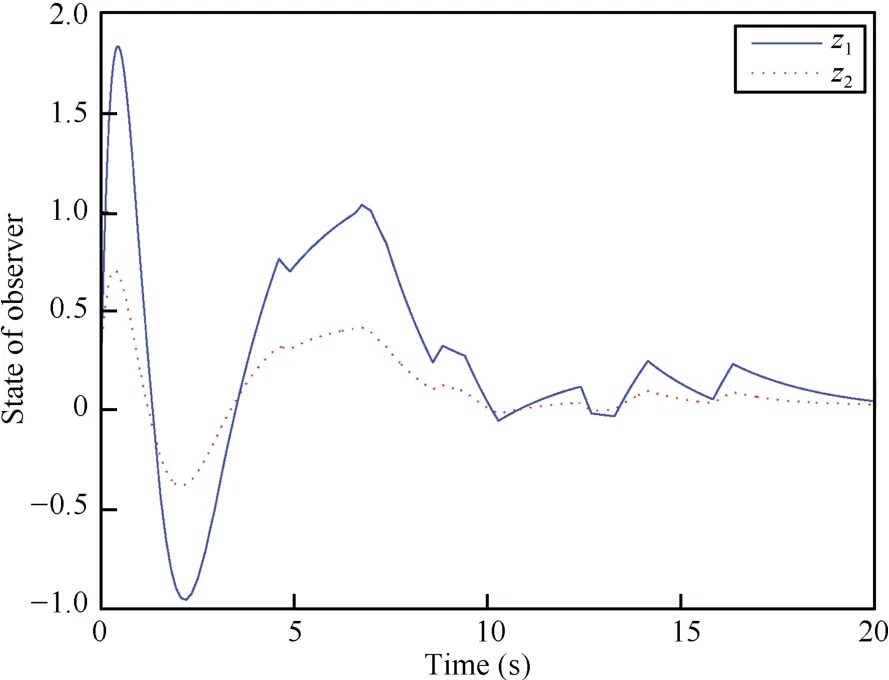
Fig.3.The trajectories of function observer state as a function of time using hybrid system method with disturbance.

Fig.4.The trajectories of observation error as a function of time using hybrid system method with disturbance.
We can see that the system converges gently,requiring a period of time of about 10 s.During this time,the sampling is executed frequently and the minimum inter-event time is 0.0180 s.Whent>10 s,all the trajectories of the plant and the observer are bounded to an area around the zero equilibrium. And this means asymptotic stability of a compact set.Besides, the average task period is 0.3255 s.What is important to notehere is the continuous slight fluctuation of the observation error,as is shown in Fig.4.This suggests there should be a persistent disturbance imposed on the system.To some extent, this method provides a first step at developing hybrid-systembased event-triggered mechanism when there is disturbance. With the findings from this simulation in hand,one can identify an important issue that future research into observerbased event-triggered control with persistent disturbance may confront.And one might,for instance,implement an eventtriggered disturbance decoupled observer.
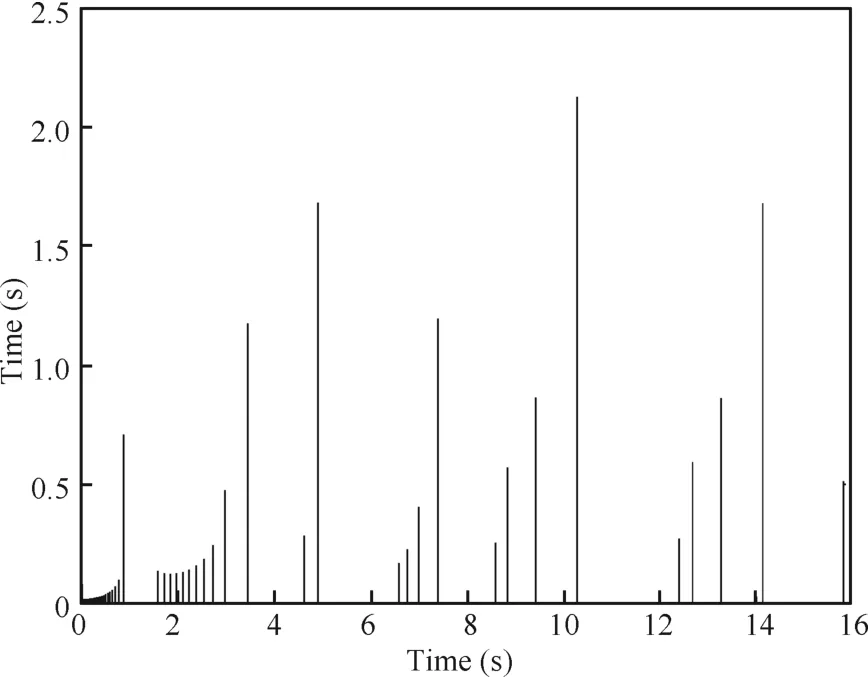
Fig.5.Evolution of inter-event time using hybrid system method with disturbance.

Fig.6.Evolution of the performance output and the disturbance along with time.
B.Hybrid Dynamical Systems Method Without Disturbance
The initial condition is chosen asx0=[-0.3 0.2]T. Besides,the disturbance is set to be zero.
With event-triggered mechanism(8),by solving the LMIs (31)-(33),we get a feasible valueσ=ζ=0.019.If we takeϵ=δ=0.001,then practical stability of the event-triggered control system(3),(4)can be guaranteed using the hybrid system formulation.
The evolution of the plant state,function observer state and observation error as a function of time are illustrated in Fig.7. The evolution of the inter-event time is shown in Fig.8.To more clearly illustrate the samples,Fig.9 presents the zoom-in version of the first two seconds.
We can see that the system converges gently,requiring a period of time of about 10 s.During this time,the sampling is executed frequently as the observation error is relatively large and the minimum inter-event time is 0.0120 s.Whent>10 s,all the trajectories of the plant and the observer are bounded to an area around the zero equilibrium.And this means asymptotic stability of a compact set.Besides,the average task period is 0.2061 s.
Comparing both Figs.7 and 8,we notice that samplings occur less often when the system is close to its steady state, although there are slight fluctuations of the plant and observer state.This also demonstrates the tradeoff between the number of samples and system performance.

Fig.7.The trajectories of plant state,function observer state and observation error as a function of time using hybrid system method withϵ=δ=0.001.
Takingϵ=δ=0.0001,we will get Fig.10.The minimum inter-event time is 0.0040 s and average task period is 0.1234 s. Interestingly,for a smallerϵandδ,the fluctuations of the plant state whent>10 s also become smaller,given by 0.2524%.Whereas this is 0.6427%if we takeϵ=δ=0.001. However,the number of transmissions that are needed is 161 withϵ=δ=0.0001 and only 94 withϵ=δ=0.001, which is a reduction of 41.61%.This fact is in accordance with Remark 2.
From these results,we can formally prove that a globally asymptotically stable compact set does exist and the minimum inter-event time is positive.Furthermore,we can conclude that hybrid dynamical system method truly describes the dynamic characteristics of the event-triggered control system.
C.Interpreting the Event-induced Error as a Disturbance
Takingγ=0.02,the event-triggered condition istk+1= inf{t>tk|‖¯e(t)‖2>0.02},then it can be verified that conditions in Theorem 4 are satisfied.The state trajectories in Fig.11 demonstrate the ultimately bounded stability of the system.
The inter-event time illustrated in Fig.12 have an average value of 0.4376 s.The guaranteed minimum inter-event time is 0.0200 s.We observe that samples are executed significantly frequently at the first second.And indeed 46.67%of them take place whent<0.9030 s.
VI.CONCLUSION
In this paper,the issue of event-triggered control based on function observer was explored.An event-triggering mechan-ism was proposed.To analyze the resulting event-triggered control systems,we used two methods,that is,reformulating it as a hybrid dynamical system and interpreting the eventinduced error as disturbance.Conditions of the two methods in terms of matrix inequality were established to guarantee theasymptotic stability of a compact set and ultimately bounded stability,respectively.A numerical example was worked out to show the feasibility of the proposed event-triggered mechanism.

Fig.8.Evolution of inter-event time using hybrid system method withϵ=δ=0.001.

Fig.9.Zoom-in evolution of inter-event time in the beginning 2 s using hybrid system method.

Fig.10.The trajectories of plant state,function observer state and observation error as a function of time and the evolution of inter-event time using hybrid system method withϵ=δ=0.0001.

Fig.11.The trajectories of plant state,function observer state and observation error as a function of time using the disturbance model method.
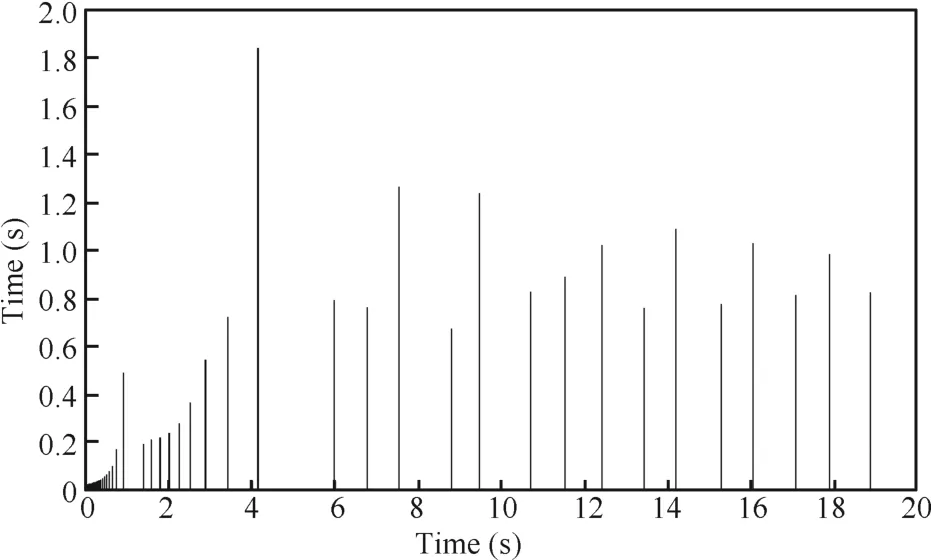
Fig.12.Evolution of inter-event time using using the disturbance model method.
REFERENCES
[1]Chen T W,Francis B A.Optimal Sampled-Data Control Systems. London,U.K.:Springer,1995.
[2]AAstr¨om K J,Wittenmark B.Computer-Controlled Systems(Third edition).London,U.K.:Prentice Hall,1997.
[3]AAstr¨om K J,Bernhardsson B.Comparison of periodic and event based sampling for first-order stochastic systems.In:Proceedings of the 1999 IFAC World Conference.Beijing,China:IFAC,1999.301-306
[4]Tabuada P.Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2007,52(9): 1680-1685
[5]Henningsson T,Johannesson E,Cervin A.Sporadic event-based control of first-order linear stochastic systems.Automatica,2008,44(11): 2890-2895
[6]Velasco M,Mart´ı P,Fuertes J M.The self triggered task model for real-time control systems.In:Proceedings of the 24th IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium(RTSS WIP 2003).Cancun,Mexico:IEEE,2003. 67-70
[7]Anta A,Tabuada P.To sample or not to sample:self-triggered control for nonlinear systems.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2010, 55(9):2030-2042
[8]Wang X F,Lemmon M D.Self-triggered feedback control systems with if nite-gain L2stability.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2009, 54(3):452-467
[9]Lunze J,Lehmann D.A state-feedback approach to event-based control. Automatica,2010,46(1):211-215
[10]Mazo M J,Anta A,Tabuada P.An ISS self-triggered implementation of linear controllers.Automatica,2010,46(8):1310-1314
[11]Liu D,Hao F.Decentralized event-triggered control strategy in distributed networked systems with delays.International Journal of Control, Automation,and Systems,2013,11(1):33-40
[12]Kofman E,Braslavsky J H.Level crossing sampling in feedback stabilization under data-rate constraints.In:Proceedings of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.San Diego,CA:IEEE,2009. 4423-4428
[13]Chen X,Hao F.Observer-based event-triggered control for certain and uncertain linear systems.IMA Journal of Mathematical Control and Information,2013,30(4):527-542
[14]Donkers M C F,Heemels W P M H.Output-based event-triggered control with guaranteed L∞-gain and improved and decentralized event-triggering.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2012,57(6): 1362-1376
[15]Goebel R,Sanfelice R G,Teel A R.Hybrid dynamical systems.IEEE Control Systems Magazine,2009,29(2):28-93
[16]Zhang J H,Zhao D Y,Wang D K.Observer-based control for linear system with event-triggered sensor.In:Proceedings of the 31st Chinese Control Conference.Hefei,China:IEEE,2012.5747-5752
[17]Zheng D Z.Linear System Theory.Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2002.(in Chinese)
[18]Velasco M,Marti P,Bini E.Control-driven tasks:modeling and analysis. In:Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Barcelona,Spain:IEEE,2008.280-290

Pei Jia received the B.S.degree in automation from Xidian University in 2011.He received the M.S. degree at the School of Automation and Electrical Engineering,Beihang University in 2014.His research interests include dynamical output feedback and event-driven control.

Fei Hao received the M.S.degree in mathematics from Inner Mongolia University and the Ph.D.degree in dynamics and control from Peking University in 1999 and 2002,respectively.From 2002 to 2004, he was a post-doctoral researcher at the Center for Systems and Control,Peking University.Since 2004, he has been with the Seventh Research Division, Beihang University.He is currently a professor of Beihang University.His research interests include robust and optimal control,event-triggered control, and networked control systems.Corresponding author of this paper.

Hao Yu received the B.S.degree at Beihang University in 2013.Currently he is a master student at the School of Automation and Electrical Engineering, Beihang University.His research interests include linear systems and event-driven control.
t
June 11,2014;accepted October 27,2014.This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(61174057, 61573036)and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing(4112034).Recommended by Associate Editor Zhiyong Geng.
:Pei Jia,Fei Hao,Hao Yu.Function observer based event-triggered control for linear systems with guaranteed L∞-gain.IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica,2015,2(4):394-402
杂志排行
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Logic-based Reset Adaptation Design for Improving Transient Performance of Nonlinear Systems
- Security Risk Assessment of Cyber Physical Power System Based on Rough Set and Gene Expression Programming
- Security-aware Signal Packing Algorithm for CAN-based Automotive Cyber-physical Systems
- A Priority-aware Frequency Domain Polling MAC Protocol for OFDMA-based Networks in Cyber-physical Systems
- Review Expert Collaborative Recommendation Algorithm Based on Topic Relationship
- A Systematic Approach for Designing Analytical Dynamics and Servo Control of Constrained Mechanical Systems
