内质网应激反应触发肝硬化大鼠模型肝细胞凋亡及纤维化机制的探讨
2015-07-07蒋天鹏王黎洲李兴宋杰吴晓萍周石
蒋天鹏,王黎洲,李兴,宋杰,吴晓萍,周石
(贵阳医学院附属医院 放射科,贵州 贵阳 550004)
内质网应激反应触发肝硬化大鼠模型肝细胞凋亡及纤维化机制的探讨
蒋天鹏,王黎洲,李兴,宋杰,吴晓萍,周石Δ
(贵阳医学院附属医院 放射科,贵州 贵阳 550004)
目的 用动物实验的方法,探讨研究在肝硬化组织中形成肝纤维化的特殊机制。方法 将60只Wistar大鼠随机平均分为3组:肝硬化组(n=20)、假注射组(n=20)、对照组(n=20);在肝硬化组大鼠腹腔内注射二甲基亚硝胺建立肝硬化模型。大鼠肝组织经HE染色后观察肝纤维化及肝硬化,使用Western blot检测α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-smooth muscle actin,α-SMA)和结蛋白(desmin)的表达,使用流式细胞仪检测早期及晚期凋亡。内质网应激(ER stress)相关的未折叠蛋白反应(unfolded protein response,UPR)通道蛋白和凋亡蛋白(CHOP和caspase-12)均进行Western blot检测和/或 RT-PCR检测。结果 肝硬化组均成功建立肝硬化大鼠模型,并发现在肝硬化大鼠模型中出现了更多的肝纤维化。流式细胞学检测显示,在肝硬化模型中出现的早期和晚期细胞凋亡显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。肌醇激酶1(inositol requiring enzyme 1,IRE1)在肝硬化鼠模型中的表达均显著升高(P<0.05)。内质网应激蛋白(CHOP)在肝硬化大鼠模型中的表达与对照组比较也显著升高(P<0.05)。结论 在肝硬化大鼠模型的肝组织中可发现明显的细胞凋亡,这种细胞凋亡是通过激活内质网应激介导的IRE1和CHOP蛋白引起的。
肝硬化;细胞凋亡;内质网应激;肌醇激酶1;CHOP蛋白
肝硬化通常因肝炎病毒感染或酗酒对肝造成的长期破坏所致,其特点是肝内广泛纤维化和肝功能异常[1]。长期、晚期肝硬化通常不可逆,并常与静脉曲张出血或肝细胞肝癌的发生有关。因此,肝硬化是导致全球发病率和死亡率升高的主要疾病[2]。在肝组织中,休眠的肝星型细胞(hepatic stellate cells,HSC)和肝成纤维细胞是肝细胞外基质(extracellular matrix,ECM)的主要组成部分,而这2种细胞在肝硬化发病中起关键作用[3-4]。尽管HSC和成纤维细胞的增殖、迁移是肝纤维化的致病原因,但近期研究[5-6]显示,肝细胞凋亡也可能参与了肝纤维化和肝硬化的形成。
近年多项研究显示,内质网应激反应在诱导和调节细胞凋亡中起到了关键作用[7-8],内质网应激反应与多种通道有关,如内质网相关蛋白降解和未折叠蛋白反应(unfolded protein response,UPR)[9]。UPR通道也可激活数种蛋白,包括肌醇激酶1(inositol requiring enzyme-1,IRE1)、PKR样ER蛋白激酶(PKR-like ER kinase,PERK)和活化转录因子6(activating transcription factor 6,ATF6)[10],上述蛋白质可进一步激活细胞凋亡。本实验旨在研究和探讨肝硬化大鼠模型中肝纤维化的特殊发病机制,为寻求肝硬化患者治疗方法提供理论支持。
1 材料与方法
1.1 大鼠肝硬化模型建立 选用4~6周龄的Wistar大鼠(贵阳医学院实验动物中心,许可证号:SYXK(黔)2012-0001)60只,雌雄不限,体质量0.18~0.2 kg。本实验遵循《实验动物保护条例》。本研究实验组为40只大鼠,其中注射组20只、假注射组20只;剩余20只在处死前未接受注射的正常大鼠作为对照组。使用溶于生理盐水的二甲基亚硝胺(日本国东京化成工业会社,LOTMA1041)对注射组大鼠进行了腹腔内注射,剂量为10 mg/kg,每周连续给药3天,持续5周;严格按照金树根等[11]的方法建立肝硬化模型及肝硬化判断标准参照其标准。同时,假注射组大鼠腹腔内仅注射与二甲基亚硝胺剂量相等的生理盐水。
1.2 组织学检查 10周后,所有动物全部处死并取肝组织行组织学检查。组织学检查由1名经验丰富且对本实验内容不知情的病理医师完成。肝组织使用10%福尔马林或70%乙醇溶液固定,并使用石蜡包埋。在结蛋白和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-smooth muscle actin,α-SMA)的免疫组化检查中,组织切片分别与单克隆抗鼠α-SMA抗体(圣克鲁兹生物技术公司,圣克鲁兹,美国)和单克隆抗鼠结蛋白抗体(圣克鲁兹生物技术公司,圣克鲁兹,美国)反应1 h。免疫组化操作程序按照Xu K等的报道[12]。
1.3 HE染色 将上述石蜡包埋肝组织切片,使用苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin-eosin,HE)和天狼星红染色以评定肝硬化。组织切片的分类根据Goldani等[13]的报道。
1.4 Western blot分析 使用Western blot分析来检测α-SMA和结蛋白(desmin)的表达,在缓冲液样品中将细胞裂解进行SDS-PAGE检测。蛋白质被电印到聚偏二氟乙烯膜上。在使用含有5%脱脂牛奶的PBS阻断后,将膜用兔抗大鼠单克隆或多克隆抗体培养(所有抗体均购自美国圣克鲁兹)。免疫反应性蛋白用增强的化学发光试剂显影。
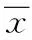
2 结果
2.1 在肝硬化大鼠模型中纤维化加重 本研究肝硬化组所有小鼠均能存活10周以上。正常肝、肝纤维化和肝硬化的组织学图片见(图1A)。肝组织被裂解并进行Western blot分析。结果表明,肝硬化组与假注射组、对照组相比α-SMA和结蛋白在肝脏的表达均有升高(P<0.05)(图1B)。这些发现明确提示肝硬化组20只小鼠均成功建模。
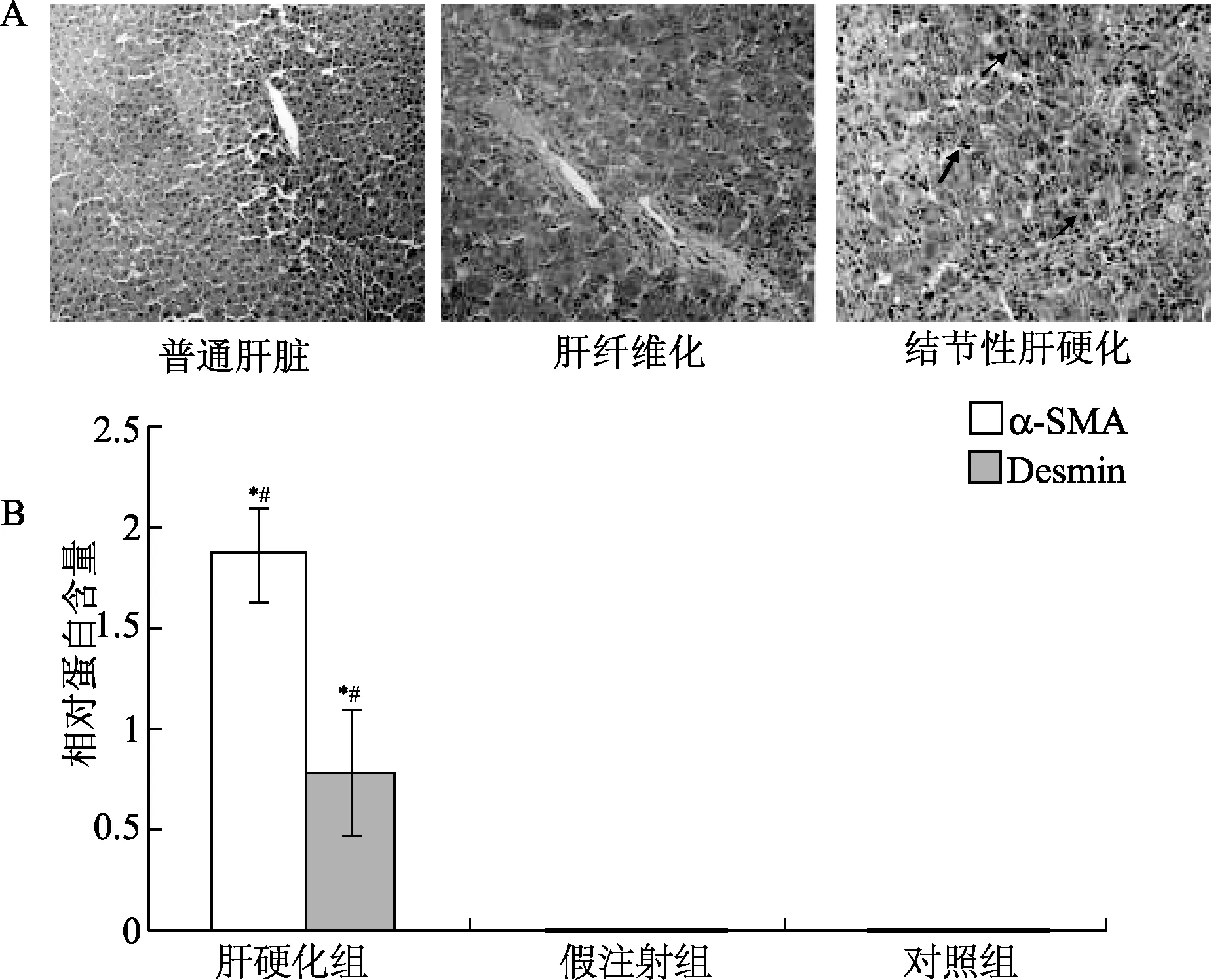
图1 肝纤维化在3组中的形成情况A:接受二甲基亚硝胺腹腔注射的大鼠肝脏切片的镜下图片(箭头提示阳性细胞,HE,×200);B:Western blot检测分析α-SMA和结蛋白(desmin)在肝硬化组、假注射组和对照组大鼠肝脏中的表达*P<0.05,与假手术组比较;#P<0.05,与对照组比较Fig.1 Fibrosis formation in the cirrhotic group, sham group and control groupA:photomicrographs of liver sections stained from the rats receiving dimethylnitrosamine intraperitoneally (the positive staining cells represented by arrows, HE,×200); B:changes in expression of hepatic α-SMA and desmin in cirrhotic group, sham group and control group
2.2 肝硬化大鼠的肝细胞凋亡分析 流式细胞学检测表明,在肝硬化模型中,早期凋亡细胞率、晚期凋亡细胞率显著高于假注射组和对照组(P<0.01),死亡细胞率显著高于假注射组和对照组(P<0.05,见图2)。
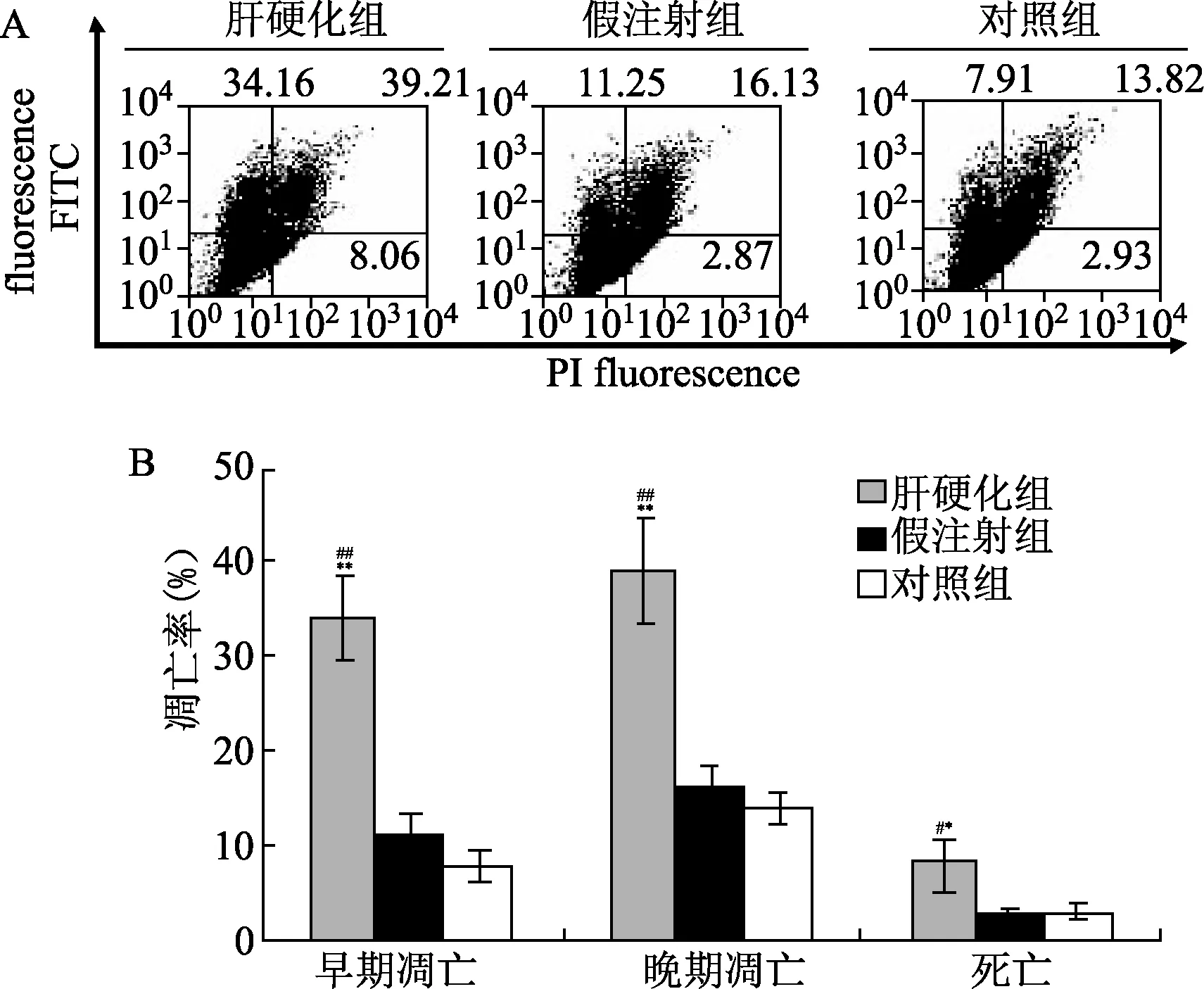
图2 肝硬化模型中大鼠的肝细胞凋亡结果A:3组大鼠膜联蛋白V/PI双染检测(X轴表示经PI染色的细胞数目,Y轴表示膜联蛋白V-FITC染色细胞的数量);B:统计分析[膜联蛋白V标记的细胞(Q1区域)百分比]*P<0.05,**P<0.01,与假手术组比较;#P<0.05,##P<0.01,与对照组比较Fig.2 Apoptosis results in the cirrhosis modelA:Annexin V/PI double staining assays of cells in three groups(X axis indicates the number of PI stained cells; Y axis indicates the number of Annexin VFITC stained cells);B:statistical analysis[the percentages of the cells labeled with only Annexin V (counted in Q1 region)]**P<0.01,*P<0.05,compared with sham group;##P<0.01,#P<0.05,compared with control group
2.3 内质网应激UPR通道参与肝硬化介导的细胞凋亡 在本研究中,内质网应激UPR的3个主要因素,包括IRE1,PERK和ATF6,通过Western blot法(图3)和RT-PCR分析(图4)分别进行了分析。结果显示,与假注射组和对照组比较,注射组IRE1的表达显著增加(图3A,P<0.05)。此外,上述UPR蛋白的mRNA表达用半定量RT-PCR分析,如图4所示,假注射组和对照组IRE1的mRNA水平较注射组升高(图4A,P<0.01)。3组中ATF6和p-PERK没有显著差异(见图4B、C)。

图3 内质网应激UPR通道蛋白检测*P<0.05,与假手术组比较;#P<0.05,与对照组比较Fig.3 Examination of unfolded protein response pathway proteins*P<0.05,compared with sham group;#P<0.05,compared with control group

图4 内质网应激UPR相关基因的mRNA水平检测A:IRE1的mRNA;B:裂解ATF6的mRNA;C:p-PerK的mRNA**P<0.01,与假手术组比较;##P<0.01,与对照组比较Fig.4 Examination of mRNA levels of ER stress associated UPR genes**P<0.01, compared with sham group;##P<0.01,compared with control group
2.4 肝硬化大鼠中CHOP在介导内质网应激相关凋亡中的作用分析 探讨在肝组织中导致细胞凋亡的具体途径,对经裂解的半胱氨酸蛋白酶12和CHOP蛋白的细胞水平使用Western blot检测法进行了评价。结果显示,与对照组相比,CHOP蛋白含量水平在肝硬化组中显著升高(P<0.05)。与假注射组和对照组比较,裂解的半胱氨酸蛋白酶12在肝硬化模型中无显著差异(图5)。
图5 细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达*P<0.05,与假手术组比较;#P<0.05,与对照组比较Fig.5 Apoptosisrelated protein expression*P<0.05,compared with sham group; #P<0.05,compared with control group
3 讨论
因肝外伤和/或炎症的影响,激活态的肝星形细胞和成纤维细胞使外基质沉积在肝脏中,是肝硬化和肝纤维化形成过程中的主要来源。另一方面,在肝纤维化自我修复过程中,活化的肝星形细胞和成纤维细胞可激发细胞凋亡[14]。因此,肝细胞和成纤维细胞密切参与了肝纤维化/肝硬化的修复过程。虽然有探索肝硬化和细胞凋亡关系的研究[15-16],但本课题是最先研究肝组织中导致肝硬化具体机制的课题之一。
肝纤维化的形成可在肝硬化大鼠模型中被观测到。结果表明,与正常对照组相比,肝纤维化在肝硬化模型中表现显著。现在所知的肝纤维化直至肝硬化的形成过程中,需要细胞进行纤维化相关蛋白的表达。因此,本研究检测了肝组织中的α-SMA和结蛋白[17]。显著增加的纤维组织扩张、α-SMA和结蛋白在肝内表达提示肝纤维化和肝硬化的形成。我们推测,肝细胞凋亡时有一种潜在机制导致α-SMA和结蛋白的强化表达。
为了探讨肝硬化与凋亡相关的具体机制,对内质网应激(UPR通路)相关蛋白,包括p-PERK,IRE1,ATF6水平进行了检测[18]。本研究发现IRE1蛋白和mRNA在肝硬化模型的肝组织中均被激活。所以IRE1 UPR通路可能参与了肝硬化相关凋亡的过程,肝硬化相关凋亡可能有助于进一步阐明纤维化在肝纤维化或肝硬化发展中的作用。既往研究表明,IRE1活化可激活内质网相关的细胞凋亡和细胞死亡[19]。这些数据有力证明了内质网应激出现在肝硬化大鼠模型中。因此本研究推测,内质网应激可能参与了肝纤维化、肝硬化形成的病理过程。
根据已发表的文献[20],内质网应激相关因子(裂解的半胱氨酸蛋白酶-12和CHOP蛋白)可被检测用以确定参与肝硬化发病机制中的特定细胞凋亡因子。一些学者发现,裂解的半胱氨酸蛋白酶-12可以激活半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3和触发细胞凋亡,同时CHOP可以直接诱导内质网应激相关的细胞凋亡[21-22]。在本研究中,我们发现裂解的半胱氨酸蛋白酶12蛋白(激活态)在所有分组中均无显著差异。然而,注射组大鼠的CHOP水平显著高于假注射组和对照组。从这些结果我们发现,内质网应激相关的CHOP蛋白被激活,从而诱导细胞凋亡进入下一步。因此,我们研究发现内质网应激诱导活化的CHOP可导致纤维化发生。
总之,细胞凋亡可在肝硬化大鼠的肝组织中被发现,而细胞凋亡是通过激活内质网应激介导的IRE1和CHOP蛋白引起的。
[1] Zhang C,Wang Y,Chen H,et al.Protective effect of the herbal medicine Gan-fu-kang against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats[J].Mol Med Rep,2013,8(3):954-962.
[2] Kim WH,Matsumoto K,Bessho K,et al.Growth inhibition and apoptosis in liver myofibroblasts promoted by hepatocyte growth factor leads to resolution from liver cirrhosis[J].Am J Pathol,2005,166(4):1017-1028.
[3] Alcolado R,Arther MJP,Iredale JP.Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis[J].ClinSci,1997,92(2): 103-112.
[4] Yoshiji H,Noguchi R,Ikenaka Y,et al, Uemura M and Fukui H: Combination of branched-chain amino acid and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor improves liver fibrosis progression in patients with cirrhosis[J].Mol Med Rep,2012,5(2): 539-544.
[5] Ramadori G and Saile B: Mesenchymal cells in the liver—one cell type or two?[J].Liver,2002,22(4): 283-294.
[6] Cha JH,Bae SH,Kim HL,et al.Branched-chain amino acids ameliorate fibrosis and suppress tumor growth in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma with liver-cirrhosis[J].PLoS One,2013,8(11): e77899.
[7] Yung HW,Korolchuk S,Tolkovsdy AM,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress exacerbates ischemia-reperfusion-induced apoptosis through attenuation of Akt protein synthesis in human choriocarcinoma cells[J].FASEB,2007,21(3): 872-884.
[8] Moenner M,Pluquet O,Bouchecareilh M,et al.Integrated endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in cancer[J].Cancer Res,2007,67(22): 10631-10634.
[9] Banjerdpongchai R,Punyati P,Nakrob A,et al .4’-Hydroxycinnamaldehyde from Alpinia galangal (Linn.) induces human leukemic cell apoptosis via mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways[J].Asian Pac J Cancer Prev,2011,12(3):593-598.
[10] Hung JY,Hsu YL,Ni WC.Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling are involved in dehydrocostuslactone -mediated apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cells[J].Lung Cancer,2010,68(3): 355-265.
[11] 金树根,王灵台,任家潍,等.二甲基亚硝胺致大鼠肝纤维化的造模研究[J].中西医结合肝病杂志,1994,4(1),28-32.
[12] Xu K,Liu XN,Zhang HB,et al.Replication-defective HSV-1 effectively targets trigeminal ganglion and inhibits viral pathopoiesis by mediating interferon gamma expression in SH-SY5Y cells[J].J MolNeurosci,2014,53(1):78-86.
[13] Goldani HAS,Matte US,Ramos ARL,et al.The role of food restriction on CC4-induced cirrhosis model in rats[J].ExpToxicolPathol,2007, 58(5): 331-337.
[14] Saile B,Matthes N,Neubauer K,et al.Rat liver myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells differ in CD95-mediated apoptosis and response to TNF-alpha[J].Am J Physiol,2002, 283(2): G435-G444.
[15] Foster CR,Daniel LL,Daniels CR,et al.Deficiency of ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase modulates cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction: involvement in fibrosis and apoptosis[J].PLoS One,2013, 8(12): e83513.
[16] Puche JE,Saiman Y,Friedman SL.Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis[J].ComprPhysiol,2013, 3(4): 1473-1492.
[17] Sheng L,Jiao B,Shao L,et al.Probucol inhibits hydrogen peroxide to induce apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells[J].Mol Med Rep,2013,7(4):1185-1190.
[18] Xiao B,Han F,Wang HT,et al.Single-prolonged stress induces increased phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder[J].Mol Med Rep,2011,4(3): 445-449.
[19] Lee JH,Kwon EJ,Kim DH.Calumenin has a role in the alleviation of ER stress in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes[J].BiochemBiophy Res Comm,2013,439(3):327-332.
[20] Zhao XH,Xu ZR,Zhang Q,et al.Simvastatin protects human osteosarcoma cells from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through mitochondrial-mediated signaling[J].Mol Med Rep,2011,5(2): 483-488.
[21] Wang X,Shi Q,Xu K,et al.Familial CJD associated PrP mutants within transmembrane region induced Ctm-PrP retention in ER and triggered apoptosis by ER stress in SH-SY5Y cells[J].PLoS One,2011,6(1): e14602.
[22] Xu K,Wang X,Shi Q,et al.Human prion protein mutants with deleted and inserted octarepeats undergo in different pathways to trigger cell apoptosis[J].J MolNeurosci,2011,43(3): 225-234.
(编校:王俨俨,谭玲)
Mechanism of liver cell apoptosis and fibrosis triggered by ER stress in liver cirrhosis rat model
JIANG Tian-peng,WANG Li-zhou,LI Xing,SONG Jie,WU Xiao-ping,ZHOU ShiΔ
(Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guiyang Medical College, Guiyang 550004, China)
ObjectiveTo investigate specific mechanism of the forming of fibrosis or cirrhosis in hepatic cirrhosis tissues.Methods60 Wistar rats were randomly divided into three groups equally: cirrhotic group (n=20), sham group(n=20) and control group(n=20); The cirrhosis model was established by intraperitoneally administered dimethylnitrosamine.The HE staining was performed on the hepatic tissues of the rats to observe the fibrosis or cirrhosis.Western blot was employed to detect the α-smooth muscle actin(α-SMA) and desmin protein expression.Flow cytometry analysis was used to examine the early and late apoptosis.The ER stress associated unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway proteins and the apoptotic proteins (CHOP and caspase-12) were also detected by Western blot and/or RT-PCR.ResultsThe cirrosis model was established successfully in cirrhotic group and more fibrosis was formed in the cirrhosis rat model.Flow cytometry analysis showed that early and late apoptosis in cirrhosis model were significantly higher compared with control group (P<0.05).The expression of UPR pathway protein and inositol requiring enzyme 1(IRE1) were increased significantly in the cirrhosis rat tissues(P<0.05).The expression of CHOP protein in cirrhosis model was significantly increased compared with the control group (P<0.05). ConclusionThe obvious apoptosis is observed in the hepatic tissue of cirrhosis rats, and the apoptosis was caused by activating the ER stress mediated IRE1 and CHOP protein.
liver cirrhosis; apoptosis; ER stress; IRE1; CHOP protein
贵州省科技厅社会发展基金(黔科合SY字【2012】3145号)
蒋天鹏,男,硕士,副主任医师,研究方向:外周介入的治疗与临床研究,E -mail:wlz_wlz@163.com;周石,通信作者,学士,男,主任医师,研究方向:外周及神经介入的治疗与临床研究,E-mail:156722229@qq.com。
R364
A
1005-1678(2015)02-0092-04
