飞机载荷标定试验数据的多元回归选元方法*
2015-06-10段垚奇刘克格赵丽娜闫楚良
段垚奇, 刘克格, 赵丽娜, 闫楚良
(北京飞机强度研究所 北京,100083)
飞机载荷标定试验数据的多元回归选元方法*
段垚奇, 刘克格, 赵丽娜, 闫楚良
(北京飞机强度研究所 北京,100083)
进行飞机载荷标定试验时,由于载荷与应变参数之间存在耦合相关性,采用逐步回归法判断自变量是否显著时具有一定的主观性。针对飞机载荷标定试验数据处理提出了一种多元回归选元方法,将回归项的变异系数作为误差控制指标和选元的判据,逐步剔除变异系数最大的自变量,直至选出最优的自变量参数组合,以此得到较佳的回归结果。此方法已成功应用于多个型号飞机起落架航向、垂向、侧向载荷的飞行实测。
飞行载荷实测; 载荷标定试验; 多元回归; 选元
引言
飞机在研制和使用过程中需要进行载荷实测,以获得在真实使用条件下的载荷时间历程,这是进行强度设计、可靠性分析和全尺寸疲劳试验的前提。在采用应变计测量载荷时,需对结构部件进行载荷标定试验,建立输入载荷与应变电桥输出量值之间的定量关系。将这种确定的关系应用在飞机使用过程中实测到的应变量值上,可将应变时间历程转换为载荷时间历程[1]。
载荷标定试验记录的原始数据由两部分组成:a.载荷向量y为一个n维的向量(n为标定试验中记录数据的次数);b. 应变参数矩阵x为一个n×m的矩阵(m为应变参数的个数)。由于应变参数始终处于线弹性范围变化,因此多元线性回归方法适用于载荷标定数据的处理[2]。载荷标定方程中并非包含越多的自变量越好,引入不恰当的应变参数会降低实测载荷的精度。如何对应变参数进行优选,是载荷标定数据处理的关键问题。目前,常用的多元回归选元方法是逐步回归法[3],逐步回归法的方法步骤是按偏回归平方的大小次序将自变量逐个引入方程,对引入方程的每个自变量偏相关系数进行检验,效果显著的自变量保留在回归方程中,循环继续遴选下一个自变量,如果效应不显著,则停止引入新自变量。由于新自变量的引入,原已引入方程中的自变量由于变量之间的相互作用,其效应有可能变得不显著,经统计检验确认后要随时从方程中剔除,只保留效应显著的自变量,直至不再引入和剔除自变量为止,从而得到最优的回归方程。
逐步回归法在判断自变量是否显著时具有一定的主观性,而且由于载荷与应变参数之间有复杂的耦合相关性,往往会导致最终载荷标定精度的不稳定。以某型飞机起落架载荷实测试验采用逐步回归法得到的实测载荷-时间历程为例,在转弯时,左主起落架航向载荷有明显的变化趋势,而在刹车时,航向载荷却未表现出明显的变化趋势,这与理论分析及类似机型的测试结果相矛盾,因此认为逐步回归法不完全适用于载荷测量的所有情况。本研究建立了一种新的多元回归选元方法,能够有效控制实测载荷的误差。
1 理论模型
实测载荷的标定方程[1]可表示为
y=b1x1+b2x2+…+bmxm
(1)
其中:x1~xm为各实测应变参数;b1~bm为对应于各实测应变参数的真实系数;y为实测载荷参数。
对载荷应变参数进行回归选元的最终目的是控制实测载荷的误差。实测载荷的误差可用实测载荷变异系数的绝对值K来衡量,由于x1~xm为实测得到的应变值,可忽略其误差,K可表示为
(2)
其中:Sy为实测载荷的方差;Sb1~Sbm为各项系数b1~bm的方差。
因为Sb1~Sbm均为误差来源,而x1~xm为实测应变值,是尚未确定的变量,所以在标定数据处理时,无法根据式(2)直接对实测载荷的误差进行控制。
设
(3)
因为
(4)
所以有如下关系
(5)
将式(5)整理得到
K≤ZP
(6)

由于b1~bm为对应于各实测应变参数的真实系数,x1~xm为实测应变值,所以P中没有误差来源,因此可将Z作为实测载荷的误差指标来进行控制。
2 回归步骤
设有m个应变参数x1~xm可能与载荷参数y存在相关关系,设标定试验共进行了n次数据采集。方法流程如图1所示,步骤如下。

图1 方法流程图Fig.1 Flow chart
1) 计算式(7)~(9)
(7)
(8)
(9)

2) 计算各项系数及各项系数的标准差[4]
各项系数
b=Cl0
(10)
各项系数的标准差

(11)
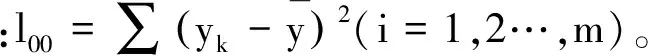
3) 按照式(9)计算各项系数的Z值(记为Zi),挑出Zi值最大的项,并记录最大的Zi值为A
(12)
4) 从第2次循环开始,如果第3步计算出的A大于上一次循环中计算出的A值,那么循环结束,上一步的回归结果为最优;否则,将Zi值最大的应变参数项删除,重新执行下一循环的第1~3步。需要注意的是,下一循环中的m应在当前m的基础上减1。
5) 将最终的回归结果代入实测应变曲线,得到实测载荷-时间历程,具体方法参考文献[5-8]。
3 实例验证
选取一段标定试验的数据进行测试,此数据来源于某型飞机水平尾翼载荷标定试验的数据,如表1所示。其中,y为载荷参数,在回归时y作为因变量。根据理论分析和对试验数据的观察结果,从众多应变参数中选出与载荷参数线性相关性较好的x1~x5作为回归自变量。

表1 测试数据
按照本研究方法进行处理,得到的结果如表2所示。第3次回归的结果为最终结果,最终结果的A值等于0.008 2。对x1~x5所有可能的组合情况分别进行回归处理,计算各种组合情况下的A值,如表3所示。
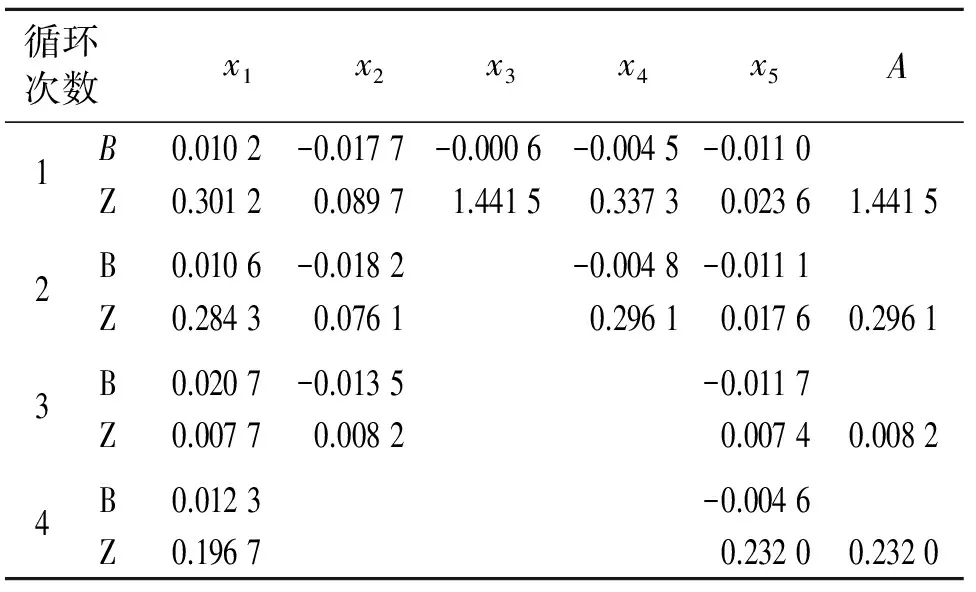
表2 基于本研究方法的处理结果

表3 所有组合情况分别回归的结果
为了比较本研究方法与逐步回归法的效果,用SPASS软件对表1中的数据进行逐步线性多元回归处理,结果如式(13)所示,A值等于0.019 5,大于用本研究方法得到选元结果的A值。从表2,3以及与SPASS处理结果的比较可以看出,利用本研究方法处理载荷-应变线性多元回归问题时,选出结果的A值小于用逐步回归法得到的结果和其他所有可能的组合情况。
y=-0.009 75x2-0.011 59x3-0.008 75x5
(13)
4 工程应用
某型飞机主起落架为四轮车架式,主起由四轮车架、主支柱、侧撑杆、前撑杆、扭力臂及收放作动筒等主要构件组成。为了测量其在实际使用过程中的受载情况,在主起落架上进行了应变计粘贴,共有应变参数39个。起落架倒装在试验台架上进行标定,其在试验台上的连接方式与在飞机上相同,起落架机轮用假轮代替。通过在假轮上的加载点进行航向、垂向、侧向载荷的加载,且载荷按单向加载、双向加载、三向加载多种工况分别进行,具体的标定技术可参考文献[5-9]。通过地面标定试验得到了载荷标定试验的原始数据。
根据本研究方法对载荷标定试验数据进行回归处理,得到了主起落架航向载荷、垂向载荷和侧向载荷的标定方程。为了验证标定载荷的正确性,在标定试验之后进行了验证加载,验证加载的理论和方法可参考文献[10-11]。表4为起落架验证加载时实际加载载荷与标定方程计算载荷分析。可以看出,标定方程计算载荷与实际加载载荷的误差均不超过5%,这满足顾客方提出的精度要求。
表4 起落架载荷标定结果验证
Tab.4 Verification of the load calibration result of landing gears
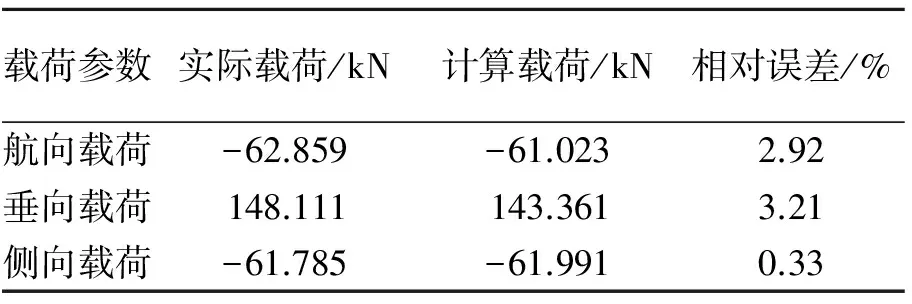
载荷参数实际载荷/kN计算载荷/kN相对误差/%航向载荷-62.859-61.0232.92垂向载荷148.111143.3613.21侧向载荷-61.785-61.9910.33
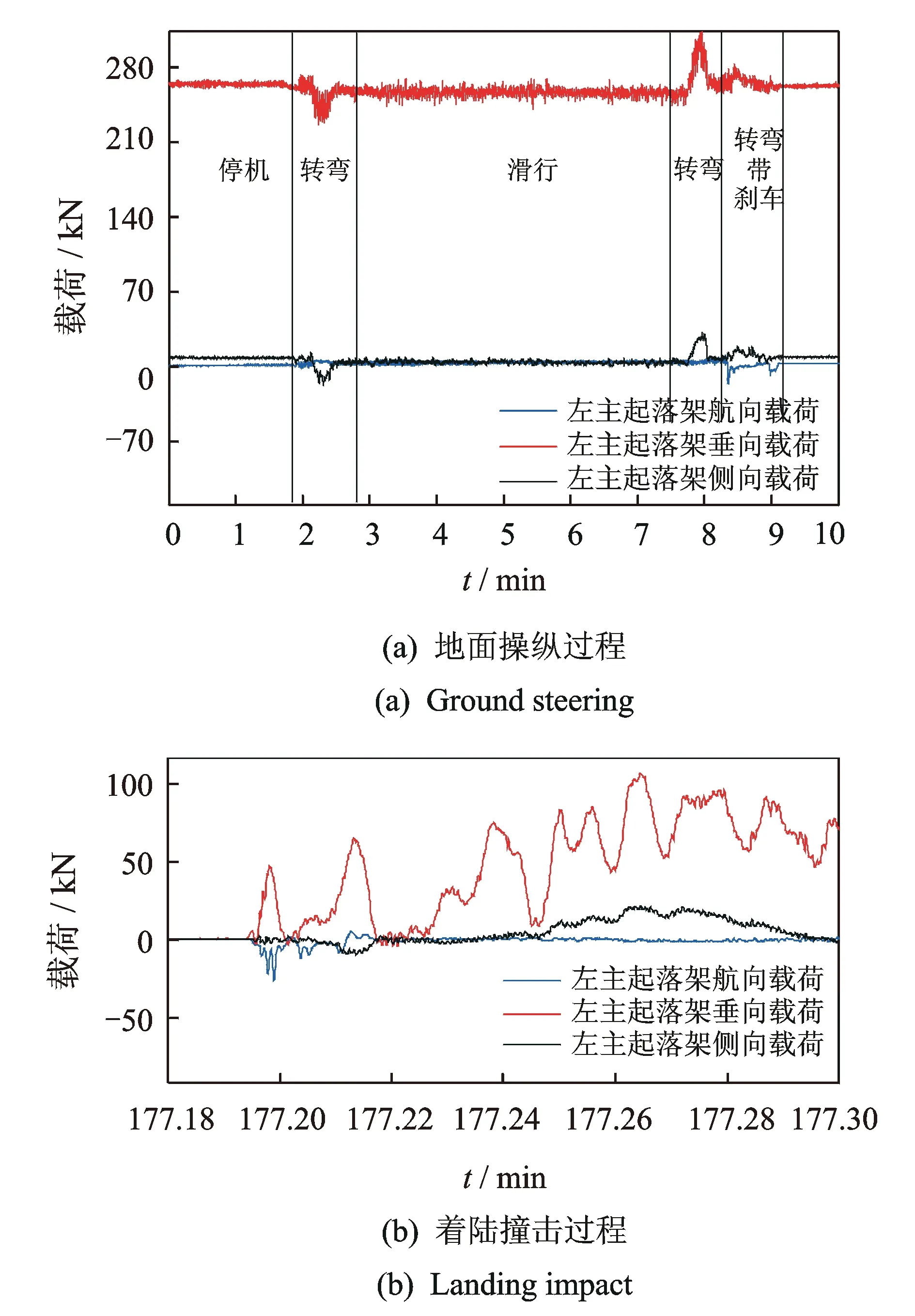
图2 利用本研究方法得到的某机型左主起落架实测载荷-时间历程Fig.2 Load of landing gears with the method proposed in this paper
如图2所示,将实测应变-时间历程代入标定方程得到实测载荷-时间历程。该机型主起落架为支柱式起落架,没有安装内束角,图2和图3的第1个转弯过程中没有刹车,因此航向载荷不应有明显的变化趋势(如图2),而图3中的航向载荷表现出明显的负向变化趋势,这是不符合事实的。在刹车过程中主起应受到逆航向的载荷,图2中可以明显看到这种趋势,但图3中的航向载荷在刹车时却没有明显的变化趋势,这也是不符合事实的。图2与图3相比,载荷变化规律能更好地符合理论分析结果及类似机型的经验。
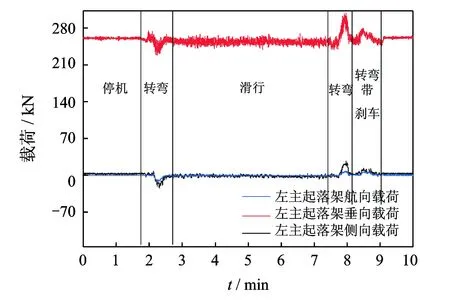
图3 利用逐步回归法得到的某机型左主起落架实测载荷-时间历程Fig.3 Load of landing gears with the stepwise regression
5 结束语
提出了一种基于回归项变异系数进行误差控制的多元回归选元方法。利用实测数据对此方法进行了验证。结果表明,该方法处理载荷-应变线性多元回归问题时,可以得到较佳的结果且计算量小,便于实际应用。此方法成功应用于某型飞机起落架的载荷实测试验,得到了起落架的实测载荷-时间历程。
[1] 闫楚良,苏开鑫.飞机起落架安全寿命与损伤容限设计[M].北京:航空工业出版社,2011:1-3.
[2] 张如一,沈观林,李朝第.应变电测与传感器[M].北京:清华大学出版社,1999:47-48.
[3] 方开泰. 实用多元分析[M]. 上海:华东师范大学出版社,1989:102-103.
[4] 韩於羹. 应用数理统计[M]. 北京:北京航空航天大学出版社,2004:65-70.
[5] 阎楚良,张书明,卓宁生. 飞机机翼结构载荷测量试验力学模型与数据处理[J]. 航空学报,2000,21(1):56-59.
Yan Chuliang, Zhang Shuming, Zhuo Ningsheng. Mechanical model and data processing of load measurement test for the airplane′s wing structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica ET Astronautica Sinica,2000,21(1):56-59.(in Chinese)
[6] 刘克格,阎楚良,张书明. 飞机主起落架载荷谱实测的台架标定[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2006,36(6):1024-1028.
Liu Kege,Yan Chuliang,Zhang Shuming. Bench calibration of load spectrum measurement for fighter airplane main undercarriage[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition,2006,36(6):1024-1028. (in Chinese)
[7] 闫楚良,刘克格.飞机结构经济寿命可靠性设计与评定[J].振动、测试与诊断,2012,32(3):355-363.
Yan Chuliang,Liu Kege. Design and evaluation of aircraft structure economic life reliability[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2012,32(3): 355-363. (in Chinese)
[8] 田兆锋,闫楚良. Web方式下飞机飞行实测数据可视化方法[J].振动、测试与诊断,2011,31(6):738-741.
Tian Zhaofeng, Yan Chuliang. Visualization method of airplane flight load measurement on Web[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2011,31(6):738-741. (in Chinese)
[9] 李五一,闫楚良,田兆锋,等. 基于VC++的飞机载荷谱数据可视化技术[J].振动、测试与诊断,2012, 32(3):458-461.
Li Wuyi, Yan Chuliang, Tian Zhaofeng, et al. Data visualization technique project based on VC++[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2012, 32(3):458-461. (in Chinese)
[10]Raymer D P. Aircraft design: a vonceptual approach-third edition[M]. Washington D C: AIAA,1999:7-10.
[11] Currey N S. Aircraft landing gear design: principles and practices[M]. Washington D C: AIAA,1988:1-20.

Abstract When an airplane load is calibrated, there is some subjectivity in judging whether an independent variable is significant due to coupled correlation between load and strain. A selection method of multiple regression elements for processing calibration test data in airplane structural load measurements is given that uses the coefficient of variation as a standard for selecting multiple regression elements. The biggest coefficient of variation is selected and excluded until optimal results are obtained. This method has been successfully applied to the loads measurement of landing gears.
Keywords flight load measurement; load calibration test; multiple regression; selected element
The Research for the Degradation of the Spindle of Machine Tool Based on Lempel-Ziv Index
DongXinfeng1,ZhangWeimin1,2,DengSong1
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering ,Tongji University Shanghai, 201804, China)(2.Chinese-German School for Postgraduate Studies, Tongji University Shanghai, 201804, China)
In order to estimate the states of the machine tool spindle system during the course of its operation, this paper proposes a deterioration method based on the complexity of the nonlinear system by monitoring the relative index. The vibration signals generated by the workpiece spindle when the grinder machine tool operation is idling were used as the objects of analysis, and the complexity relevant index is used to judge the states of the workpiece spindle of the grinding machine during several months of operation. The analysis results showed that the complexity of the vibration signals generated by the workpiece spindle system increased as the time in use increased. In order to verify the validity of the deterioration analysis, the complexity index is used to analyze the dates of the deterioration bearing published by CWRU. The results showed that the complexity is an effective method for deterioration analysis.
complexity; degradation; machine tool spindle system; bearing; fault
Selection of Regularization Matrixes for Moving Force Identification Based on Truncated Generalized Singular Value Decomposition
ChenZhen1,2,YuLing2
(1.School of Civil Engineering and Communication, North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power Zhengzhou, 450045, China)(2.Key Laboratory of Disaster Forecast and Control in Engineering of Ministry of Education, Jinan University Guangzhou, 510632, China)
Abstract Based on the time domain method (TDM) theory, a truncated generalized singular value decomposition(TGSVD) method for moving force identification has been developed by introducing a regularization matrix. The influence of TGSVD identification can be identified by comparing it with different regularization matrixes. Then, when comparing the TGSVD method with the TDM method, the numerical simulation of two-axle moving force loads shows that regularization matrixes have great influence on such properties as identification accuracy, robustness, etc. With appropriate regularization matrixes, the proposed TGSVD method has many good properties compared with TDM, such as better identification accuracy and robust noise with bending moment responses or acceleration responses. TGSVD has prominent advantages with single responses type or less responses number, which is beneficial for the application of TGSVD in the field identification of dynamic axle loads on bridges.
Keywords bridge; moving force; identification; ill-posed problem; time domain method; truncated generalized singular value decomposition; regularization matrixes
Defect,Improvement and Verification of Seismic Multi-supported Response Spectrum Model
LiuGuohuan1, 2,LianJijian1, 2,GuoWei3,GengChen4,TianLi5
(1.State Key Laboratory Hydraulic Engineering Simulation and Safety, Tianjin University Tianjin, 300072, China) (2.School of Civil Engineering, Tianjin University Tianjin, 300072, China)(3.School of Civil Engineering, Central South University Changsha, 410075, China)(4.School of Civil Engineering, Tianjin Chengjian University Tianjin, 300384, China)(5.School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Shandong University Jinan, 250100, China)
Abstract The multiple support response spectrum (MSRS) theory formula based on displacement and the displacement-velocity model are induced and given. Then, the irrationality and unconvergency of the responses, which are calculated from the displacement-multiple support response spectrum (D-MSRS) model and derived from the current displacement input model, are explained. This paper also addresses the accidence in deducing processing, and necessity in calculation results of MSRS deduced from the acceleration model. The deriving processing and numerical results show that the displacement velocity-multiple support response spectrum (DV-MSRS) is strict and logical. The D-MSRS can induce the unreasonable and unconvergent internal force of the bottom element. The reasonability of A-MSRS (acceleration-multiple support response spectrum) derived from the two negligible terms can be counteracted, but is suitable for a classic damping system.
Keywords seismic ground motion; multi-support response spectrum(MSRS); acceleration input model; displacement input model; displacement-velocity input model; classical damping
Dynamic Performance of a Solar Array Deployable Mechanism with Multiple Clearances
GuYongxia1,YangTianfu2,GuoFeng2
(1.School of Material and Mechanical Engineering, Beijing Technology and Business University Beijing, 100048, China)(2.State Key Laboratory of Tribology, Tsinghua University Beijing, 100084, China)
Abstract All large spacecrafts have deployable structures like solar arrays, which are folded during launch and deployed in orbit. The clearances between the deployable joints greatly impact the system′s dynamics. A multi-body model consisting of a satellite, solar panels, clearance revolute joints and flexible panels is established with ADAMS software. The deployment progress of multiple clearances is numerically simulated, and the comparison between models with different numbers of clearance joints is analyzed by calculating the impact force and relative trail of the shaft mass centroid in the joint. The results show that increasing the clearance number brings in more complexity, and that the joint near the spacecraft base has a stronger influence.
Keywords spacecraft; deployable mechanism; joint clearance; impact
Separation of Real-Time Dynamic Deflection Signals for Long-Span Bridges
YangHong1,LiuXiaping2,CuiHaixia3,PengJun1,SunZhuo2
(1.School of Physics & Electronic Engineering, Guangzhou University Guangzhou, 510006, China)(2.School of Civil Engineering, Guangzhou University Guangzhou, 510006, China)(3.School of Physics and Telecommunication Engineering, South China Normal University Guangzhou, 510006, China)
Abstract The real-time dynamic deflection signal separation of the long-span bridge is an effective new method for the long-span bridge fault diagnosis. Because empirical mode decomposition (EMD) can decompose nonlinear and non-stationary signals into a set of linear and stationary intrinsic mode functions, a blind source separation (BSS) method based on EMD is proposed that combines the respective advantages of BSS and EMD for single-channel long-span bridge deflection signal separation, while EMD can decompose the nonlinear and non-stationary signals into a set of linear and stationary intrinsic mode functions. The source number is estimated using singular value decomposition (SVD), and then to composes the multi-channel input signals with the single-channel deflection signal and its intrinsic mode functions according to the source number. Finally, the method separates the source signals using the fast independent component analysis (Fast ICA) algorithm and obtains the separation value of each component of the bridge deflection signal. Simulation research indicates that this is a good solution for estimating the quantity of source number estimation for the independent component analysis (ICA) model and single-channel deflection signal BSS problem.
Keywords filtering; empirical mode decomposition; independent component analysis; singular value decomposition; deflection signal separation
Prediction and Optimization Method for the Longitudinal Stiffness of V-type Thrust Rod
KeJun1,ShiWenku1,TengTeng2,ZhouYufei2,LiuTianyun3,WuZhiyong3
(1.State Key Laboratory of Automobile Simulation and Control, Jilin University Changchun, 130022, China)(2.China Faw Group Corporation R&D Center Changchun, 130011, China)(3.Changchun Cheng Yun Auto Parts Limited Company Changchun, 130114, China)
Abstract In order to forecast and optimize the longitudinal stiffness of the V-type thrust rod applied to heavy-duty commercial vehicles, the hyperelastic constitutive model of rubber material in the V-type thrust rod is built based on uniaxial tension and compression experiment for rubber specimens. Then the dynamic finite element simulation for the work process of the V-type thrust rods are carried out using Abaqus software. The longitudinal stiffness of the V-type thrust rods is predicted using the post processor module of Abaqus software. The relationship between the V-type thrust rod's longitudinal stiffness and the structure of the spherical hinge is studied according to the strain contours of the rubber layer. The simulation results demonstrates that increasing the width of the plastic layer in the spherical hinge can improve the V-type thrust rod's longitudinal stiffness, because this structure can change the volume and vulcanization area of the rubber layer and block rubber layer extend to end covers. Bench tests for the samples of the primary structure and optimized structure are carried out, and the results show that the prediction and optimization method is valid. This method can shorten the R&D period of the V-type thrust rod and dramatically improve its longitudinal stiffness.
Keywords thrust rod; constitutive model; finite element analysis; stiffness optimize; tandem suspension
Order Selection for Wavelet Series Decomposition in Dynamic Load Identification
YangFan,ZhangFang
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract Based on orthogonal wavelet series decomposition, there is often inaccuracy or huge amounts of calculation when identifying the load due to improper choice of wavelet series order. The envelope line of the wavelet series coefficient amplitude is proposed, which tends to converge with the increasing order through the matrix spectral decomposition and Parseval theorem of which represents that the total energy in the time-domain and frequency-domain is equivalent. The non-analytical wavelet coefficient is analyzed, and the function between the wavelet series order and the relative error of the identified load is obtained. The wavelet series order is thus chosen according to the error level of the engineering requirements. The theoretical basis of the order selection when using the series decomposition in the dynamic load to be identified is proposed. Both the computer simulation in the form of the single-frequency and multi-frequency, real signal as well as the lab test in the form of the impact signal confirm that the proposed approach is feasible and effective. The results show that the proposed approach is applicable to all forms of the loads.
Keywords load identification; series order determination; wavelet series; orthogonal wavelet basis; structural dynamics
High-Rise Structure Damage Identification Based on Pseudo-Transfer Function
LiWanrun1,2,3,DuYongfeng1,2,NiYiqing3,LiHui1,2
(1.Key Laboratory of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation in Civil Engineering of Gansu Province, Lanzhou University of Technology Lanzhou, 730050, China)(2.Institute of Earthquake Protection and Disaster Mitigation, Lanzhou University of Technology Lanzhou, 730050, China)(3.Shenzhen Research Institute of Hong Kong Polytechnic University Shenzhen, 518057, China)
Abstract A novel damage location method, which is based on the pseudo-transfer function (PTF) established by the ARX model (autoregressive model with eXogenous input), is proposed based on the conception of the transform function reflected the relationship of the input-output (structural characteristics). According to the correlation with the degree of freedom (DOF), the DOF is grouped, the response of one DOF is chosen as a reference channel (which is the ARX model output), and the response of the other DOF correlating with the reference channel is taken as the input of the ARX model. The reference PTF is established using the responses of the health structure. After creating the reference PTF, these models are used to predict the data from the damaged structure. The difference between the fit ratios is used as the damage feature. The methodology is applied to the reduced finite element model of the Canton Tower, and the threshold of damage is established using the change of the fit ratios of the responses with Gaussian white noise of the health structure. The results show that this methodology is successful in damage identification and localization, and can also determine the severity of damage under noise effects.
Keywords pseudo-transform function; ARX model(autoregressive model with exogenous input); damage identification; fit ratio; high-rise structure
Dynamics Modeling Method and Test of Sliding Crawler Travel System
ZhangHong1,KangPeng2,SongYang2,ZhangXiaokun2
(1.School of Mechanical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Science and Technology Taiyuan, 030024,China)(2.Taiyuan Institute of China Coal Technology & Engineering Group Corp Taiyuan, 030006, China)
Abstract In this paper, the operational status of the sliding crawler is studied under special conditions in the underground mine. With the continuous miner as the research object, the interaction between the sliding crawler in a continuous miner coal cutter and the underground as well as the contact characteristics of the various components within the crawler system are analyzed. The contact characteristics of the various components within the crawler system are established. Then, the multi-body interaction mechanics model of the sliding crawler is established to simulate the coal-rock road and running state of the track sliding friction. The crawler system operating parameters of the tractive force and support force at different tensioning displacements, as well as the simulation feature data extraction and conversion are obtained. Then, the machine's total travel power is indirectly calculated by the characteristic data of the machine's total travel power. On this basis, the power-time history curve of the actual real time operating state of the continuous miner is drew according to the underground field test to obtain the power time history curve of actual operating state. The order of magnitude of the conversion power of the simulation results is shown to be within a permissible range of the measured power of the experimental results. The study provides a reliable basis and valid path for the structure optimization and power matching of the crawler system.
Keywords sliding crawler; internal and external friction resistance; physical simulation; underground test
Research on Parameters Identification Method for Local Boundary of Rotor-Bearing System
TanZhen1,2,LiChaofeng2,TaiXingyu2,WenBangchun2
(1.School of Technology, Shen Yang Radio & TV University Shenyang, 110003, China)(2.School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Northeastern University Shenyang, 110819, China)
Abstract A whole dynamical model is often built to analyze the dynamic characteristics of exactly one part, because the rotor system has a complex structure and a strong coupling effect between its parts. For example, in a plate or blade, the degrees of freedom of the complete machine finite element model are enormous, and the computational efficiency is low. A constrained parameters identification method for the local restriction is proposed to increase the computational efficiency and make it easier to analyze the part's vibration. A constrained parameters identification method for local restriction is present, considering the subsystem coupling effects in a complex system. The rotor system is resolved and decomposed into the axis and plate and the subsystem and main system are established. Considering the subsystem coupling effects in the complex system, the restrain stiffness and dampness of the boundary unit can be identified by deducing the dynamical equation. The nodes response of the finite element model can be computed and compared with the corresponding nodes of the whole model. The results show that the equations are correct. This method can be used in the vibration analysis modeling of the rotating structure to save computing resources.
Keywords rotor system; parameter identification; dynamical model; stiffness; damp
Method for On-Line Forecasting of Gyro's Drift Based on Wavelet-Strong Tracking Filter Algorithm
ZhangWei1,DuDangbo2,HuChanghua2,ZhouZhijie2,ZhangJianxun2
(1.Department of Information, Xi′an Institute of Hi-Tech Xi′an, 710025, China)(2.Department of Automation, Xi′an Institute of Hi-Tech Xi′an, 710025, China)
Abstract An on-line forecasting method based on the wavelet-suboptimal multiple fading kalman filtering algorithm is proposed in order to advance the forecasting precision of the gyro′s drift coefficients for its data mutation and strong trend according to the characteristics of the gyro′s drift coefficients non-stationary time series. The experimental results indicate that the gyro′s drift can be precisely forecasted, which can effectively improve the problem of inaccurate results brought by the data mutation and the strong trend.
Keywords wavelet analysis; strong tracking filter; gyro′s drift; suboptimal multiple fading factor
Numerical Characteristic and Theory Modeling for Parameter Uncertainty Propagation in Complex System
TangBingsong1,HanXiaolin2,YangHuifeng3
(1.The State Key Laboratory of Structure Analysis of Industrial Equipment, Dalian University of Technology Dalian, 116024, China)(2.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Engineering Mechanics, Southeast University Nanjing, 210096, China)(3.The State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract Parameter uncertainty of measurements is nominally an experimental value fluctuating around a true value in the condition of a definite confidence level. This is a very important tool for describing the accuracy of parameters besides error measures. The concept of uncertainty measurements is developed that multivariable parameters uncertainty is proposed. The basic property of generalized uncertainty is discussed later. Both the propagating characteristic of generalized uncertainty in the complex system and the classification of the propagating characteristic are investigated. The property and mode of parameter uncertainty propagation in one single subsystem are very important research contents. There is significant influence on the calculating result and the absolute value of the elements in the propagation matrix. The comparison between all the subsystems′ parameters uncertainty propagation is discussed, and the corresponding criterion is simultaneously achieved. The examples show the effectiveness and feasibility of this theory when it is applied in the parameter uncertainty propagation problem for a complex system.
Keywords complex system; uncertainty of measurement; propagation matrix; propagation mode
Aero-Engine Fault Diagnosis Based on Dynamic PCA and Improved SVM
CuiJianguo1,YanXue1,PuXueping2,QiYiwen1,JiangLiying1,ShiJianqiang2
(1.School of Automatization, Shenyang Aerospace University Shenyang, 110136, China)(2.China Gas Turbine Establishment Chengdu, 610500, China )
Abstract In order to effectively diagnose aero-engine faults and ensure safety in aircraft flights, a method based on dynamic principal component analysis (PCA) and the improved support vector machine is put forth. It combines the advantages of dynamic PCA in the feature extraction and improves the support vector machine (SVM) in the fault diagnosis. The dynamic PCA method can complete the pre-treatment through de-noising, dimension reduction, and eliminating correlation on the processing variables. The improved SVM method can diagnose faults with the eigenvector. The proposed method can solve such problems as the lubrication system like, low accuracy of the aero-engine model, and limited measurement parameters, all of which are problems that can lead to low efficiency, ease of misdiagnosis, and other issues. A certain type of lubrication system of the aero-engine is taken as an example to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results show that using the dynamic PCA and improved SVM fault diagnosis method can effectively improve accuracy and realize the fault diagnosis performance of the lubrication system of the aero-engine. Furthermore, it has good prospects for future application.
Keywords aero-engine; lubrication system; dynamic principal component analysis; improved support vector machine; fault diagnosis
A Fault Diagnostic Rules Gaining Method for Aviation Electronic Equipment under Incomplete Information Condition
ZhaoLiangliang1,XiaoMingqing1,ShengSheng1,ZhiHuilai2,ZhangLei1
(1.College of Aeronautics and Astronautics Engineering, Air Force Engineering University Xi′an, 710038, China)(2.School of Computer Science and Technology, Henan Polytechnic University Jiaozuo, 454000, China)
Abstract Uncertainty caused by incomplete information brings great challenges to fault diagnostic rules gaining method for aviation electronic equipment. In order to solve the problem, by defining the incompleteness from the two angles of narrow sense and broad sense respectively, the consistency first completer algorithm is designed to solve the inconsistency problem caused by incomplete information based on maximal confidence and attribute value expectation, which exists in indirect completing algorithms. The symptom attributes concept lattice and diagnostic decision-making attributes concept lattice are constructed, and the equivalent relationship on the symptom attributes concept is introduced. Based on this, the disjunctive normal form discernibility function of the maximum inconsistent symptom attributes concept set is computed, then the optimal reduced attribute set is obtained based on which diagnostic rules are gained. Taking the weapon launching system as an example, the approach is validated with a precision of 83.3%. It can be concluded that the approach is better than the existing representative approach in dealing with incomplete information, accuracy and intuitionism of the diagnosis knowledge display.
Keywords incompleteness; discernibility matrix; concept lattice; reduction; diagnostic rules
A Mode-Control-Decoupling Linear Ultrasonic Motor with a Tower-Type Stator
ChenQianwei1,JuQuanyong1,HuangWeiqing2,ShiYunlai2
(1.School of Mechatronic Engineering, Jinling Institute of Technology Nanjing, 211169, China)(2.State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract In order to solve the problem that the existing tower-type ultrasonic motors(USMs) cannot control the stator′s normal vibration or tangential vibration separately, a mode-control-decoupling linear ultrasonic motor(LUSM) with a tower-type stator is presented. The LUSM is designed to have two non-coplanar, orthogonal working modes: one is the symmetric vibration mode in thex-zplane that independently excites the driving tip′s normal vibration, while the other is the bending vibration mode in they-zplane that independently excites the driving tip′s tangential vibration. Further, the scheme of piezoelectric ceramics (PZTs) polarization and arrangement location is correspondingly designed as follows: The PZTs are divided into two phases, A and B, in which phase A is used to excite the symmetric vibration mode in thex-zplane, and phase B is used to excite the bending vibration mode in they-zplane. So the two working modes can be controlled in a decoupling way by controlling the phases separately. The experimental results show that under the mode-control-decoupling condition, when the driving voltage of phase A is equal to 400 Vp-pand the driving voltage of phase B is varied between 0 and 400 Vp-p, the motor offers a maximum velocity of 420 mm/s and a minimum velocity of 23 mm/s.
Keywords working mode; control-decoupling; ultrasonic motors(USMs); piezoelectric
Nonlinear Eddy Current Testing Method for Nondestructive Evaluation of Plastic Damage in Structural Materials
LiYunfei1,ChenZhenmao2
(1.Institute of Systems Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics Mianyang, 621900, China) (2.School of Aerospace, Xi′an Jiaotong University Xi′an, 710049, China )
Abstract An experimental system is built based on the nonlinear eddy current (NEC) detection method. Quantitative nondestructive evaluation of the plastic damage degree of structural materials, such as Q195 carbon steel and 304 stainless steel, is studied. It is found that structural materials′ plastic damage degree has a certain linear correlation with the fundamental frequency′s amplitude and the third harmonic component′s amplitude in the nonlinear eddy current detection signal spectrum. The linear correlation is different from each other. The detection signal of Q195 carbon steel decreases with increasing damage degree, while the detection signal of 304 stainless steel does the opposite. By developing this experimental system, importing plastic deformation, nonlinear eddy current testing experiment and analysis of detection signal, it is found that the amplitudes of the fundamental and third harmonic components of detection signals show good correlation with the degree of plastic damage. The feasibility and efficiency of the proposed method for quantitative nondestructive evaluation of structural materials′ plastic damage are also investigated.
Keywords nonlinear eddy current; structural materials; plastic deformation; non-destructive evaluation
Numerical Empirical Study on Structural Approximation Analysis of Neural Network for Blade of Wind Turbine
WangLei,LuJingui,ZhangJiande,HuaQi
(Computer Aided Design Center, Nanjing University of Technology Nanjing, 210009, China)
Abstract Structural approximation analysis is important for the design optimization of wind turbine blades. First, the method of structural approximation analysis of the neural network for the wind turbine blade is introduced, and the neural network for the blade is briefed. The empirical and relevant practical studies on the structural approximation analysis of the neural network is introduced, and the influence of the patterns of the wind turbine blade′s performance on the analysis is investigated. The numerical experiments of different learning rates to construct the model of the neural network for the structural approximation analysis are made. According to the experimental results, the number of patterns of the blade should be enough to describe the relationship between the performance and the blade′s parameters. It is concluded that the accuracy of the structural approximation analysis of the neural network is higher with a greater number of patterns of the blades. Based on the experiments, the large learning rate is helpful for obtaining a better model of the neural network. The empirical study is helpful for reducing the expensive cost of the design optimization of the wind turbine blade using the structural approximation analysis of the neural network.
Keywords blade of wind turbine; structural approximation analysis; neural network; approximation model
Method on Rotor Health Monitoring Signal Evolution Analysis and Damage Tracking
ZhuXucheng
(Department of Aircraft Engineering, Naval Aeronautical and Astronautical University Yantai, 264001, China)
Abstract To address helicopter rotor health monitoring issues and get a kind of the damage sensitivity but disturbance insensitive metrics, the evolving properties of damaged rotor behaviors are investigated in the reconstructed phase space, then a new damage tracking method is developed. First, an aeroelastic model of the rotor system is derived using the finite element method, and the simulated measurements are reconstructed in a higher state space according to the embedding theory. A globally nonlinear reference model to predict the rotor state is formulated using the Volterra series. The difference between the model-estimated state and measured results is used as the state prediction error, the average value of which is evaluated in some disjoint regions of the reconstructed phase space and combined into a damage tracking feature vector. Next, the time series of the damage tracking feature vectors are used directly to extract the dimension fact and trending information about the blade damage by solving an eigenvalue problem. In the case of fault to failure time prediction, the double exponential smoothing method is employed to establish damage trending prognosis models. The feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified using the data from the blade damage model and the rotor aeroelastic model simulations. The results show that this method can provide fault pattern auto-recognition capabilities and is suitable for tracking the hidden damage in situations in which no pre-knowledge about damage dimension or evolution models is available. The method can also reconstruct the dynamic nature of the underlying system in the phase space using the nonlinear property of the single monitoring signal, which provides a new way to study the system degeneration process in different dimensional spaces with a proper time scale.
Keywords helicopter; rotor; health monitoring; fault diagnosis; phase space
Pattern Recognition of Bearing Defect Severity Based on Multiwavelet Packet Sample Entropy Method
ZhangJianyu1,ZhangSuizheng1,GuanLei2,YangYang1
(1.Beijing Key Laboratory of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, Beijing University of Technology Beijing, 100124, China)(2.Jiangsu Myande Food Machinery Co., Ltd. Yangzhou, 225127, China)
Abstract In order to automatically recognize different scales of bearing faults, a method of pattern recognition based on the multiwavelet packet sample entropy method and BP neural network is put forth. First, the vibration signals of rolling bearings with five different scaled outer race defects are decomposed into three layers using the GHM multiwavelet packet. The signal sample entropy of 16 decomposed frequency bands are then used as the neural network′s input vector, so that the complete information of the multiwavelet packet decomposition can be thoroughly utilized. Based on the learning and training of a three-layer BP neural network, and in comparison with the dB10 wavelet packet, it can be concluded that the convergence speed and identification accuracy of the multiwavelet packet sample entropy method is much better than those of the traditional wavelet neural network classification. As a result, the multiwavelet packet sample entropy method is effective in automatically recognizing different scales of bearing faults.
Keywords fault severity; multiwavelet packet, sample entropy; back propagation; automatic identification
Research of Active Structural Acoustic Control in a Rectangle Enclosure with Two Flexible Plates
ChenDalin,ChenNan
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Southeast University Nanjing, 211189, China)
Abstract This paper studies the active structural acoustic control (ASAC) in a rectangular enclosure by applying different control forces to the elastic plate. The acoustic cavity model of a rectangular enclosure consisting of two simply supported flexible plates is developed to analyze the structural-acoustic coupled system of the enclosure. The formula is derived to calculate the sound pressure in the enclosure when some point forces are applied to the flexible plate. The optimal control model of ASAC is established and analyzed. Then the simulation of the sound pressure level (SPL) in the local cavity sound field when some of the second forces with different parameters are applied to the flexible plate is analyzed. Then, a simulated model to analyze the control effect on the partial acoustic field is developed. The results indicate that the parameters of the second forces to be given are more important to the control effect; but it is not better with an infinitely increasing number of parameters. Meanwhile, the number of second control forces isn′t better.
Keywords enclosure sound field; structural-acoustic coupling; structure acoustic radiation; active structural acoustic control (ASAC); sound pressure level (SPL)
Trend Prediction of Civil Aircraft Engine Vibration Signal Using Ensemble Process Neural Networks
LeiDa,ZhongShisheng
(School of Mechatronics Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology Harbin, 150001, China)
Abstract An ensemble prediction model based on boosting process neural networks (PNN) is proposed to predict vibration signal trends of civil aircraft engines. First, the error functions of the AdaBoost.RT algorithm are improved, and an adaptive adjustment strategy is adopted to adjust the classification threshold during the training process. Then, the improved AdaBoost.RT is utilized as the ensemble framework so as to build the ensemble PNN prediction model. The performance of the proposed model is evaluated through the prediction of two actual civil aircraft engine vibration signal series. The results show that the ensemble model performs better than the single PNN model while with simpler structures. The proposed modification version of AdaBoost.RT is superior to the original AdaBoost.RT and a contrast modification version with only improved threshold adjustment strategy. Therefore, the proposed model is suitable for the prediction of civil aircraft engine vibration signal trends.
Keywords aircraft engine; vibration signal; trend prediction; ensemble learning; AdaBoost.RT; process neural networks
Virtual Axis Machine Tool Positioning Method
JiaYuqin,HuXiaoxiong
(School of Mechanical Engineering, Taiyuan University of Science and Technology Taiyuan, 030024, China)
Abstract To solve the dynamic virtual axis machine tool spindle positioning on the platform, a method is presented based on the improved consistency of multi-sensor data fusion virtual axis machine tool positioning, visual technology and electronic compass used in the measurement of the position and orientation of the virtual axis machine tool moving platform. This method is the virtual axis machine tools of each rod of the encoder information, visual information and the dynamic inertial measurement data fusion, obtained by dynamic calculation of the confidence distance relationship matrix, the position and attitude of the virtual axis machine tool moving platform (pose) the precise positioning of a good guarantee. After a simplified test of the direction of movement of a single axle measurement, the measurement of the virtual axis machine tool 6 degrees of freedom of the moving platform pose as the object of study, and its simulation test. The test results show that the proposed positioning method is feasible, effective, and practically significant.
Keywords virtual axis machine tool; multi-sensor; locating; data fusion
Correlated Jointly Frequency Rotor Fault Sources Number Estimation and Sub-band Blind Separation
LiJiyong1,LiShunming1,TianGuocheng2,ChenXiaohong3
(1.College of Energy and Power Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)(2.Shandong Zhongshi Yitong Group Co., Ltd. Jinan, 250000, China)(3.College of Science, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract Crosscover frequency response is produced by the rotor under abnormal vibration, so rotor jointly frequency fault sources cannot be satisfied statically independent request. The traditional source number estimation such as singular value decomposition method and standard independent standard analysis cannot extract fault sources. This paper estimates fault sources number with a non-negative method in the frequency domain, source and mixture system characteristics not in consider, and then to extract fault signals with wavelet packet, and separate recovered signals with small mutual information, to eliminate jointly frequency signal, to obtain independent non-correlated sources. The feasibility is verified by practical and theoretical methods.
Keywords correlated sources; non-negative matrix factorization; mutual information; sub-band decomposition; blind source separation
Dynamic Performance Analysis and Kinetic Parameters Optimization of High-Speed Elevator Based on VPT
LinYao1,2,LiuYanbin1,WuHui1,HuangYaozhi1
(1.College of Mechanical Engineering,Fuzhou University Fuzhou, 350106, China)(2.Fujian Province Special Equipment Inspection & Research Institute Fuzhou, 350008, China)
Abstract The main factors that affect comfort in speed elevators are horizontal and vertical vibrations. To improve comfort and mitigate the effects of vibration and shock inside elevator equipment, the kinetic parameters of the elevator vibrations are optimized. The process of running the speed and acceleration of the high-speed elevator in the virtual prototype simulation by virtual prototype technology (VPT) technology is completed, a sensitivity analysis method is used, and the kinetic parameters of vibrations that affect the vertical and horizontal directions of the elevator system are optimized. The simulation results show that the vertical vibration acceleration of the optimized elevator system dropped from 1.12 m/s2to 1.04 m/s2, and the horizontal vibration acceleration of the lift car is less than 0.1 m/s2.This ensures that the maximum amplitude of the vertical and horizontal vibration acceleration is reduced, the ride comfort of the elevator is improved, and an effective way to optimize the research and design of the high-speed elevator system is provided.
Keywords virtual prototype technology(VPT); high-speed elevator; dynamic performance; kinetic parameters; simulation
Study on Modeling and Vibration Transmission Characteristics of Distributed Parameter Two-Stage Isolation Systems
YangMingyue,SunLingling,WangXiaole
(Key Laboratory of High-Efficiency and Clean Mechanical Manufacture, Shandong University Jinan, 250061, China)
Abstract Two analytical models of a typical two-stage vibration isolation system are established from the point of view of vibration power transmission and engineering practices. Considering the distributed parameter characteristics of the elastic raft, isolators and flexible foundation, dynamic equations of each subsystem are derived using the mobility matrix approach. The mechanism of the vibration transmission is revealed using the concept of power flow. Meanwhile, general rules which should be followed when designing the two-stage isolation systems are discussed. It is shown that the moment excitations play an important role in the vibration transmission process. Hence, the injection of power caused by the moment excitations should be reduced. In the permitting condition of the energy efficiency and installation spaces, a better isolation effect will be obtained when appropriately enlarging the intermediate mass. The distribution parameter characteristics of the elastic raft, isolators, and non-rigid foundation can lead to a deterioration of performance in the high-frequency domain. Using the scheme of the dispersion intermediate mass can effectively avoid the impact of the flexible raft, and can also significantly inhibit the interaction between the wave effects caused by the isolators and modals of the flexible raft, which may input more power to the installed foundation.
Keywords two-stage vibration isolation; intermediate mass; mobility matrix; distribution parameters; wave effects
A New Type of Large-Thrust Linear Piezoelectric Actuator
ZhuPengju,ShiYunlai,ZhaoChunsheng
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures,Nanjing University of Aeronautics And Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract A new type of large-thrust linear piezoelectric actuator is proposed. It achieves the goal of large-thrust and large-displacement output by accumulating the micro-amplitude of the piezoelectric stack through a kind of screw clamp mechanism. The driving mechanisms of the actuator and the key technology during the designing process are discussed in detail, including the design of the torque motor speed, the torsional stiffness of the flexible coupling, the design of the relationship between the nut and screw, and the best frequency phase of the stack after testing its performance. The length of the actuator is 140 mm, and the maximum diameter is 45 mm. The actuator weighs 0.7 kg with a stroke of 40 mm. The actuator exhibits a 130 N blocked force when the speed of the torque motor is 300 r/min and the frequency of the piezoelectric stack is 100 Hz.
Keywords piezoelectric actuator; feed-screw; inchworm; large-thrust
Contact and Friction Behavior of Piezoelectric Vibrator for Driving Track
HuangChong,WangLiang,ShuChengyou,ZhangHongxuan,JinJiamei
(State Key Laboratory of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Nanjing, 210016, China)
Abstract In order to enhance the efficiency and velocity of the traditional piezoelectric vibrators for driving tracks, the operating mode of the piezoelectric vibrator is improved. The new operating mode uses the torsional vibration of the annular part of the piezoelectric vibrator instead of the bending vibration. Then, two torsional standing waves synthesize a torsional traveling wave. The new mode is more suitable for the piezoelectric vibrator to drive the track, and enhances the piezoelectric vibrator′s driving efficiency, which increases the contact area between the piezoelectric and track and reduces energy waste generated by the contact between the troughs of the traveling waves in the annular parts and track. The piezoelectric vibrator is designed using FEM analysis, and the prototype is manufactured. After that, experiments on contact and friction behavior are conducted. Based on the study of the velocity of the piezoelectric vibrator with different pre-pressures under track material surfaces with different levels of hardness and roughness, it can be found that the hardness of the material is greater, and the load capacity of the piezoelectric vibrator is stronger. There is an optimized collocation between hardness, roughness and pre-pressure, which will make the piezoelectric vibrator arrive at maximum velocity. The research results subsequently lay a foundation for the design of the track and the integral optimization of the driving system.
Keywords track; planetary exploration; piezoelectric vibrator; friction behavior; experimental research
Selection Method of Multiple Regression Elements for Load Calibration Test Data
DuanYaoqi,LiuKege,ZhaoLina,YanChuliang
(Beijing Aircraft Strength Institute Beijing, 100083, China)
*国家自然科学基金资助项目(50135010)
2014-09-03;
2014-12-09
10.16450/j.cnki.issn.1004-6801.2015.01.030
V217+.32; TH13
段垚奇,男,1986年4月生,工程师。主要研究方向为飞机结构可靠性。曾发表《基于最小航道法的实测数字信号奇异值剔除算法》(《农业机械学报》2012年第43卷第5期)等论文。 E-mail:dyq319@126.com
