宁夏地区小震重定位①
2015-06-09李青梅张元生吕俊强李鸿庭赵卫东
李青梅, 张元生, 吕俊强, 谢 辉, 李鸿庭, 赵卫东
(1.宁夏回族自治区地震局,宁夏 银川 750001; 2.中国地震局兰州地震研究所,甘肃 兰州 730000)
宁夏地区小震重定位①
李青梅1, 张元生2, 吕俊强1, 谢 辉1, 李鸿庭1, 赵卫东1
(1.宁夏回族自治区地震局,宁夏 银川 750001; 2.中国地震局兰州地震研究所,甘肃 兰州 730000)
应用双差地震定位法与遗传算法进行定位计算,并对结果进行比较,发现其具有一致性和差异性。根据宁夏地区数据资料的实际情况,采用遗传算法收集整理1991年以来该区地震震相记录资料,获得至少具有3个S-P台站以上记录的地震事件共4 688个,重新定位结果基本勾画出地震在块体边界的空间展布特征;地震深度主要位于5~25 km的上、中和下地壳中上部,基本反映陆陆板块的活动边界形态。
宁夏地区; 双差定位; 遗传算法定位
0 引言
地震定位是指对震中位置、震源深度、发震时刻和震级等地震基本参数进行测定,对研究地下结构、震源机制、活动构造性质以及地震活动的空间分布等具有重要意义。目前,地震定位的方法有多种,每一种都有其适用的条件。总体上可分为绝对定位方法和相对定位方法,相对定位法有双差定位法[1-3]和主事件定位法[4];绝对定位方法有阻尼最小二乘法、遗传算法[5-10]以及独立事件定位方法。其中双差定位法适用于地震较密集或余震较多的地震序列;独立事件法的定位精度一般比双差定位法低,但在充分应用前人的研究成果、建立较好的速度模型的基础上,也能够获得较高精度的定位结果。
宁夏地区位于南北地震带的北段,属祁连地槽褶皱系与华北地台的过渡带区域,包含板块缝合地带,并有一系列规模较大的活动断裂带,地质状态不稳定。应用宁夏及邻省的地震台站记录,对宁夏地区多年的小震进行重定位,进一步了解该区的断裂活动以及断层的深部性质。
1 数据处理
1.1 数据收集及整理
利用宁夏地震台网提供的地震观测报告,研究35°~40°N、104°~108°E范围内1991年1月—2014年5月所发生的地震。经过理论走时计算,删除或修改误差大于10 s以上的地震事件记录,挑选出具有3个以上台站同时记录到S波和P波震相的地震事件共4 688个,S-P共27 999条,震相到时包括直达波Pg、Sg,首波Pn、Sn波。
1.2 速度模型
通过研究区的4条人工地震测深剖面,即阿拉善左旗—定边剖面[11]、永登—平凉剖面[12]、兰州—靖边剖面[13]、西吉—中卫地震测深剖面[14],建立水平层状速度模型(表1)。波速比取1.73,莫霍面平均深度为43 km,莫霍下界面速度为8.00 km/s。
1.3 定位计算
1.3.1 双差定位与遗传算法定位结果对比
应用以上层状速度模型分别对4 688个地震事件进行定位,地震深度剖面表明这两种方法的计算结果基本一致(图1和图2),说明遗传算法地震定位结果是可信的。由于双差地震定位方法的条件所致,几乎75%的地震的不能用双差法进行重定位。基于此,我们采用遗传算法进行地震定位。
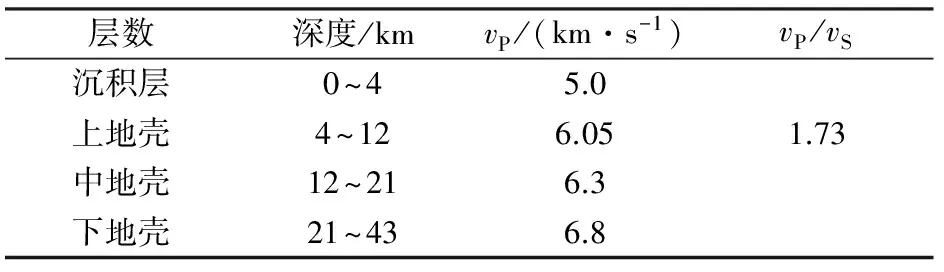
表1 地震定位速度模型
1.3.2 地震定位前后比较
从图3(a)可以清晰地看到,定位前地震深度分布呈现两个区域,即6 km深度左右密集区和10 km以下密集区。这种现象主要是定位软件不同或差异所致。地震重定位之后,地震条带分布更加明显(图3(b))。对地震定位的前后进行深度统计分析(图4),重新定位前地震震源深度集中在5~10 km、15~25 km,其他深度没有明显优势分布。重新定位后,5~30 km深度范围地震分布比较集中,平均深度为18 km。这与张国民、汪素云等中国大陆西部地震震源平均深度为(18±8) km的结果一致[15]。

图1 双差定位结果Fig.1 Results of double-difference location method
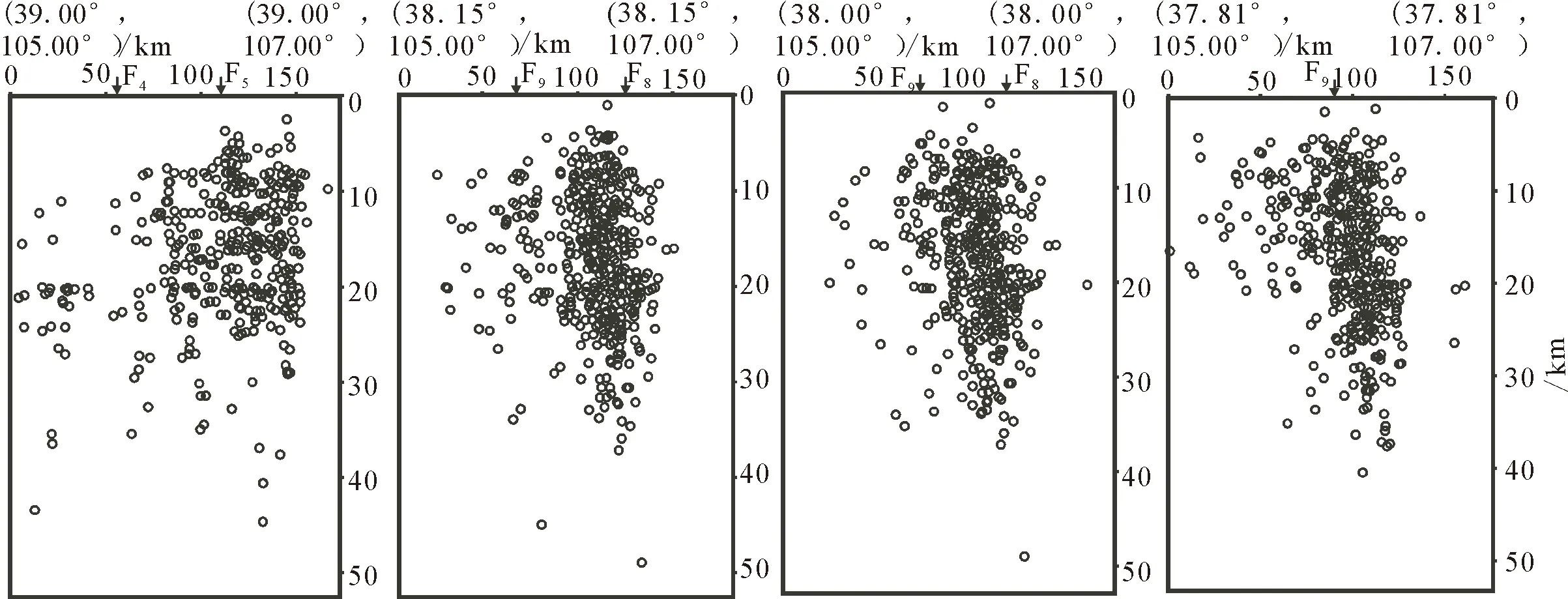
图2 遗传算法定位结果Fig.2 Results of genetic algorithm location method
2 定位结果分析
采用遗传算法定位方法,对1991年1月至2014年5月宁夏及邻区4 688个小地震全部重新定位,获得宁夏地区小地震在空间上的展布特征。根据该区构造资料[16-17]和小震的密集特点,将研究区划分为4个区域(图5),分别是A:石嘴山—内蒙古乌海地区、B:灵武-吴忠地区、C:同心—中宁地区以及D:海原-固原地区。各个区域作垂直断层方向的地震剖面,共计10条(图6),基本说明了断层在深部的性质。
A区地处二级大地构造单元,属中朝准地台(Ⅰ)的次级单元阿拉善台隆(Ⅰ1)、鄂尔多斯台缘褶带(Ⅰ2)和鄂尔多斯台拗(Ⅰ3),该区主要断裂有贺兰山西麓断裂(F4:左旋-逆走滑,走向NS)、贺兰山东麓断裂(F5:右旋-正断,走向NE)、黄河断裂(F8:断层走向NE)等。地震和断裂主要分布于台缘褶带区域,1738年发生过平罗8.0级大地震,台缘褶带区域两侧构造单元相对较稳定,地震活动明显减弱。3条地震深度剖面基本给出了断层的深部性质(主要横切F4、F5、F6、F7、F8),地震集中分布在5~25 km深度范围,宽度分布约50~60 km(图6(a)、(b)、(c)),倾向SE或SEE,倾角约50°。地震主要位于中上地壳和下地壳的顶部,说明断层至少错断了中地壳或下地壳顶部,可能还没错断到莫霍面。
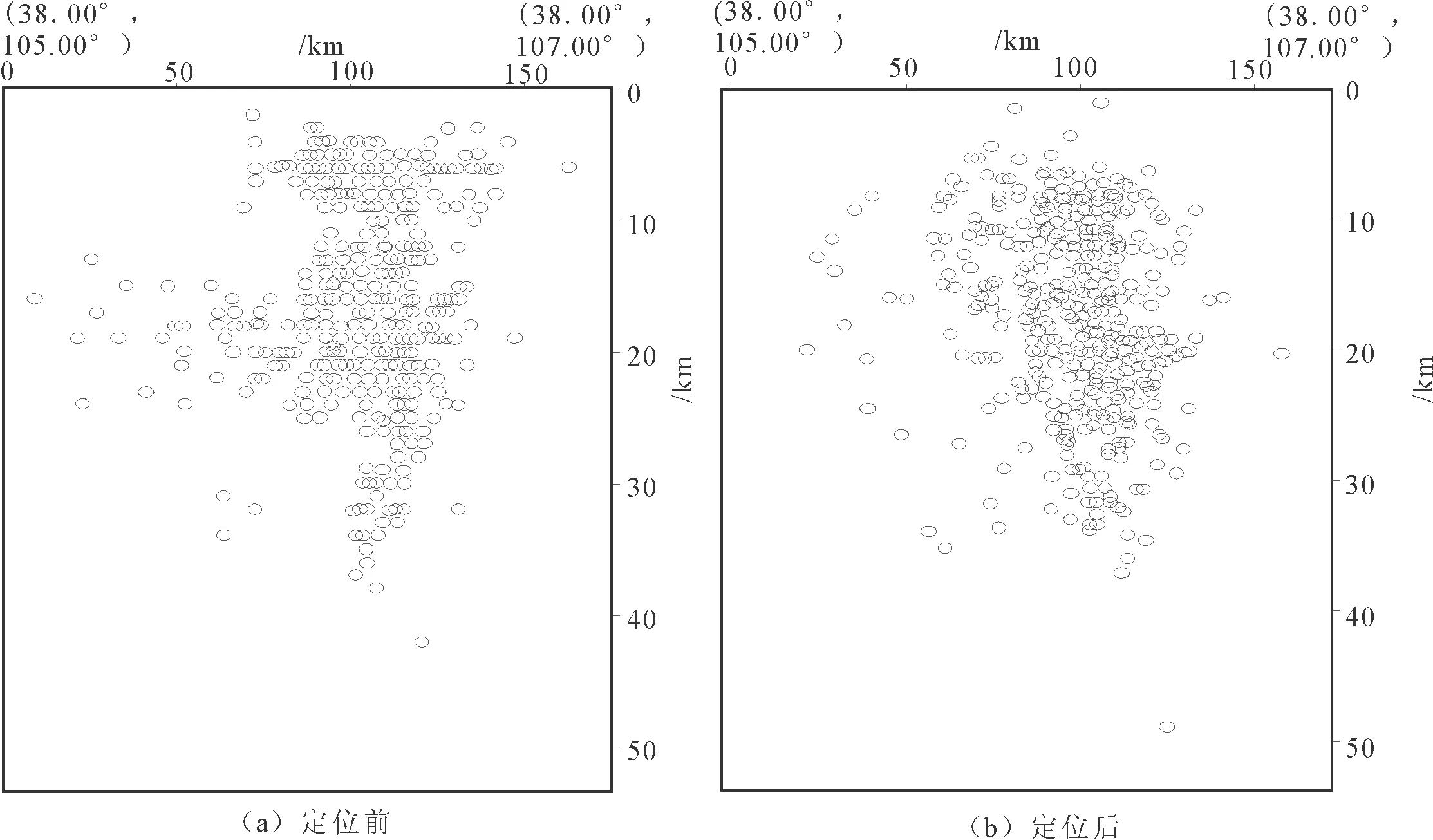
图3 定位前后震源深度剖面图Fig.3 Sectional view of the focal depths of before and after location

图4 震源深度柱状分布图Fig.4 Histogram of the focal depths

C区所处构造单元与B区基本相同,即鄂尔多斯台缘褶带(Ⅰ2)、走廊过渡带(Ⅲ1)和北祁连优地槽褶皱系(Ⅲ2)。主要活动断层有三关口—牛首山—固原断裂带(F9逆-走滑,走向SN)、烟筒山断裂带(F10:逆-走滑,走向NW)、中卫—同心断裂带(F11:左旋-逆走滑断层,走向NW)、海原断裂(F13:逆-左旋走滑,走向NW)。该区小地震主要沿活动断层F10和F11走向分布。地震深度剖面主要横切F9、F10、F11断层,地震带宽度约70 km(图6(g)),震源深度主要集中分布在22 km以上,地震条带倾向NE,倾角约40°,断层错断到中地壳。
D区位于祁连优地槽褶皱系(Ⅲ2)、祁连中间隆起带(Ⅲ3)和南祁连褶皱带(Ⅲ4)。主要断层有三关口—牛首山—固原断裂带(F9:逆-走滑,走向SN)、海原断裂(F13逆-左旋走滑,走向NW)、六盘山东麓断裂(F14左旋走滑,走向NNW)和月亮山—六盘山西麓断裂(F15逆断层,走向NW)。该区构造复杂,断裂活动强烈,1920年曾发生震惊世界的海原8.5级大地震。地震深度剖面主要横切F9、F13、F14和F15断层,地震主要集中分布在0~25 km深度范围。D1剖面经过海原断裂(F13)处,该断裂倾向为WS,倾角较缓。受断层带的控制,地震分布宽度由北向南逐渐变窄(图6(i)、(j)),地震带倾向NEE,倾角约50°。断裂F9和F14至少错断了中地壳。

图5 活动断裂与地震震中分布图Fig.5 Distribution of active faults and epicenters

图6 震源深度剖面图Fig.6 Sectional view of the focal depths
3 结论与讨论
采用双差定位方法与遗传定位方法对1991年1月-2014年5月宁夏地区的小地震进行重新定位,虽多数地震不满足双差定位条件,但两者方法定位结果基本一致,说明重定位结果可信。应用遗传定位方法对具有3个S-P台站的4 688个地震进行重定位,精度总体上有较好的提高。地震在空间上更加集中分布或沿断裂带分布,绝大多数断裂延伸到中、下地壳,与已有地质资料和前人研究结果较为一致[18]。除海原断裂(F13)倾向WS,倾角较缓外,其他断裂倾向SE或NE,倾角较陡。
同时存在台站分布不均匀、台间距较大和三维速度结构不精细等原因,产生地震深度定位的误差根源。随着地震台站的密度越来越大,地震定位精度将不断提高。
References)
[1] Walhauser F,Ellsworth W.A Double-difference Earthquake Location Algorithm:Method and Application to the Northern Hayward Fault,California[J].Bull Seism Sos Am,2000,90(6):1353-1368.
[2] 杨智娴,陈永泰,郑月军,等.双差地震定位法在我国中西部地区地震精确定位中的应用[J].中国科学:D辑,2003,33(增刊) :129-134.YANG Zhi-xian,CHEN Yong-tai,ZHENG Yue-jun,et al.Accurate Relocation of Earthquakes in Central-western China Using the Double Difference Earthquake Location Algorithm[J].Secience in China:Series D,2003,33(Suppl):129-134.(in Chinese)
[3] 莘海亮,方盛明,李稳.豫北及邻区地震双差法重新定位研究[J].大地测量与地球动力学,2011,31(6):63-68.XIN Hai-liang,FANG Sheng-ming,LI wen.Use the Double Difference Method to Study on the Relocation of Earthquakes in North of Henan Province[J].Geodesy and Geodynamics,2011,31(6).63-68.(in Chinese)
[4] 周仕勇,许忠淮,韩京,等.主地震定位法的改进及1997年新疆伽师强震群地震的高精度定位[C]//中国地震学会成立20周年纪念文集.北京:地震出版社,1999.ZHOU Shi-yong,XU Zhong-huai,HAN Jing,et al.Improvement of Main Seismic Location Method and High Precision Positioning of Jiashi Strong Earthquake Swarm of Xinjiang,1997[C]//The 20 Anniversary Memorial Collection of the Seismological Society of China.Beijing:Seismological Press,1999.(in Chinese)
[5] 张元生,李清河,徐果明,联合利用走时与波形反演技术研究地壳三维速度结构(Ⅰ)——理论与方法[J].西北地震学报,1998,20(2):8-15.ZHANG Yuan-sheng,LI Qing-he,XU Guo-ming.The Combined Use of Travel Time and Waveform Inversion Technique on the 3-D Velocity Structure of the Crust (Ⅰ)——The Theory and the Method[J].Northwestern Seismological Journal,1998,20(2):8-15.(in Chinese)
[6] 周民都,张元生,张树勋.遗传算法在地震定位中的应用[J].西北地震学报,1999,21(2):167-171.ZHOU Ming-du,ZHANG Yuan-sheng,ZHANG Shu-xun.Application of the Genetic Algorithm to Seismic Location[J].Northwestern Seismological Journal,1999,21(2):167-171.(in Chinese)
[7] 张元生,李清河,徐果明.联合利用走时与波形反演技术研究地壳三维速度结构 (Ⅱ)——应用[J].西北地震学报,1998,20(3):44-51.ZHANG Yuan-sheng,LI Qing-he,XU Guo-ming.The Combined Use of Travel Time and Waveform Inversion Technique on the 3-D Velocity Structure of the Crust (Ⅱ)——Application[J].Northwestern Seismological Journal,1998,20(3):44-51.(in Chinese)
[8] 莘海亮,刘明军,张元生,等.甘东南地区地震重新定位研究[J].地震研究,2010,33(3).292-299.XIN Hai-liang,LIU Ming-jun,ZHANG Yuan-sheng,et al.Study on the Repositioning of Earthquake of the Southeast Area of Gansu[J].Earthquake Research,2010,33(3):292-299.(in Chinese)
[9] 黄耘,李清河,张元生,等.江苏及邻区地震重新定位和构造特征分析[J].地球物理学报,2008,51(1):175-185.HUANG Yun,LI Qing-he,ZhANG Yuan-sheng,et al.Analysis of Earthquake Repositioning and Tectonic Characteristics in Jiangsu and its Adjacent Area[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2008,51(1):175-185.(in Chinese)
[10] Kennet B L N,Sambridge M S.Earthpuake Hypocenter Location Using Genetic Algorithrns[J].Bull Seism Soc Am,1993,83(5):1467-1491.
[11] 国家地震局地学断面编委会.上海奉贤至内蒙古阿拉善左旗地学断面(说明书)[M].北京:地震出版社,1992.Gelogical Transect Editorial Committee of State Seismological Bureau.Georaverse form shanghai to Alashan Zuoqi of Inner Mongolia(Instruction)[M].Beijing:Seismological Press,1992.(in Chinese)
[12] 国家地震局地学断面编委会.青海门源至福建宁德地学断面(说明书)[M].北京:地震出版社,1992.Gelogical Transect Editorial Committee of State Seismological Bureau.Georaverse form Qinhai Menyuan to Fujian Ningde(Instruction)[M].Beijing:Seismological Press,1992.(in Chinese)
[13] 李松林,张先康,张成科,等.玛沁—兰州—靖边地震测深剖面地壳速度结构的初步研究[J].地球物理学报,2002,45(2):210-217.LI Song-lin,ZHANG Xian-kang,ZHANG Cheng-ke,et al.A Preliminary Study on The Crustal Velocity Structure of Maqin—Lanzhou—Jinbian by Means of Deep Seismic Sounding Profile[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2002,45(2):210-217.(in Chinese)
[14] 李松林,张先科,任青芳,等.西吉—中卫地震测深剖面及其解释[J].地震地质,2001,23(1):86-92.LI Song-lin,ZhANG Xian-ke,REN qing-fang, et al.Seismic Sounding Profile and Its Interpretation of Xiji-Zhongwei[J].Seismic Geology,2001,23(1):86-92.(in Chinese)
[15] 张国民,汪素云,李丽,等.中国大陆地震震源深度及其构造含义[J].科学通报,2002,47(9):663-668.ZHANG Guo-min,WANG Su-yun,LI Li,et al.China Continental Earthquake Focal Depth and Its Tectonic Implications[J].Science Bulletin,47(9):663-668.(in Chinese)
[16] 孟广魁,王增光,廖玉华,等.银川平原地震区划研究[M].宁夏:人民出版社,1994.MENG Guang-kui,WANG Zeng-guang,LIAO Yu-hua,et al.Study on Seismic Zoning of Yinchuan Plain[M].Ningxia:People’s Publishing House,1994.(in Chinese)
[17] 谢晓峰,王伟涛,崔瑾,等.宁夏及邻区地壳上地幔结构特征分析[J].地震工程学报,2014,36(2):309-313,337.XIE Xiao-feng,WANG Wei-tao,CUI Jin,et al.Analysis of Crust and Upper Mantle Structure in Ningxia and its Adjacent Area[J].China Earthquake Engineering Joural,2014,36(2):309-313,337.(in Chinese)
[18] 杨明芝,马禾青,廖玉华.宁夏地震活动与研究[M].北京:地震出版社,2007.YANG Ming-zhi,MA He-qing,LIAO Yu-hua.Seismic Activity and Research of Ningxia[M].Beijing:Seismological Press,2007.(in Chinese)
Relocation of Small Earthquakes in the Ningxia Area
LI Qing-mei1, ZHANG Yuan-sheng2, LV Jun-qiang1, XIE Hui1, LI Hong-ting1, ZHAO Wei-dong1
(1.EarthquakeAdministrationofNingxiaHuiAutonomousRegion,Yinchuan,Ningxia750001,China;2.LanzhouInstituteofSeismology,CEA,Lanzhou,Gansu730000,China)
Ningxia and its neighboring area are located in two blocks of the northeastern margin of the Qingzang-Tibet plateau:the Erdos block and the Alashan block.The geological structure in this area of the plateau is known to be unstable.Over recorded time,many large or great earthquakes have occurred in this area.Based on previous research results,we employed two different earthquake location methods,i.e.,double-difference and genetic algorithm,to recompute the location of small earthquakes that were recorded by the Ningxia Regional Earthquake Monitoring Network from 1991 to May 2014.This process consisted of first employing the theoretical travel time method to delete or modify the seismic events whose arrival time error exceeded 10 s.Next,we selected seismic events that contained S and P waves recorded by at least three stations.In addition,Pg,Sg,Pn,and Sn seismic phases are included in each earthquake event.The velocity model was obtained from four seismic sounding profiles that crossed the research area.In addition,a horizontally layered velocity model was used.The double-difference method results showed that the seismic source depth was not so different from that obtained using the genetic algorithm method.But only a few earthquake events (approximately 25% of the total 4 688 seismic events) can meet the relocation requirement in the double-difference method.Therefore,the genetic algorithm method can be used to recalculate and reanalyze the depth characteristics of small earthquakes and their relation to the deep fault in the research area.Relocation results showed that the seismic zone distribution by depth is more apparent.Statistical analysis,taking the relocation calculation into account,showed that more earthquakes happened from 5 to 30 km.The average depth was 18 km.The space distribution of small earthquakes in this area was obtained.To facilitate the analysis of the relationship between the occurrence of earthquakes and faults in this region,we divided the geographic research region into four districts on the basis of their tectonic characteristics and concentration region of small earthquakes.These districts were named A,B,C,and D.In each district,the seismic profile perpendicular to fault was obtained.In district A,the results showed that the seismic depth was mainly distributed from 5 to 25 km.The earthquake distribution width was 50 to 60 km.In district A,earthquakes occurred primarily in the upper and middle crust or in the top of the lower crust.It was postulated that fractures parted only the upper or middle crust while not the Moho.In district B,the small earthquake distribution was primarily in the north-south direction.In this district,the earthquakes were primarily distributed from 5 to 35 km.The width of the epicenter was approximately 50 km.The dip of the seismic zone was from SE or NE,with an angle of approximately 50°.The fault fracture was primarily in the middle or lower crust.In district C,small earthquakes occurred along fault F10and F11.The epicenter width was approximately 70 km.The seismic source was mainly ≤22 km.The dip of the seismic zone was to the NE,and the dip angle was approximately 40°.The fault fracture was confined to the middle crust.In district D,the depth range of the seismic source was primarily from 0 to 25 km.The dip of the seismic zone was to the NEE,and the dip angle was approximately 50°.But the dip of the Haiyuan fault was to the SW,which is different from the results reported in previous studies.The geologic structure and the fault activity of this district are more complex.These results imply that the fracture depth of fault F9and F14is deep to at least the middle crust.The genetic algorithm calculation results revealed that the depth distribution of a large number of reported earthquakes is denser and that the epicenter of the seismic distribution is along the faults that resulted in the great earthquakes.The depths of the deep faults extended to the middle or lower crust.
the Ningxia area; double-difference algorithm; genetic algorithm
2014-10-30
测震台网青年骨干项目(20150428)
李青梅(1976-),女(汉族),甘肃兰州人,工程师,主要从事地震监测工作.E-mail:nxlqm_2008@163.com
通迅作者:张元生(1965-),男(汉族),贵州湄潭人,研究员,主要从事地震学与卫星遥感方面的研究工作.
P315
A
1000-0844(2015)02-0518-07
10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2015.02.0518
