蛇床子素对人肝癌细胞生长和TGF-β诱导侵袭转移的干预作用
2015-05-24王锦军
王锦军
蛇床子素对人肝癌细胞生长和TGF-β诱导侵袭转移的干预作用
王锦军
目的 观察蛇床子素对人肝癌细胞HepG2的杀伤及侵袭转移的影响。方法 将人肝癌细胞HepG2用不同浓度的蛇床子素干预后,采用MTT法检测蛇床子素对HepG2细胞增殖的抑制作用;PI染色流式细胞术检测细胞内DNA含量,测定蛇床子素对HepG2细胞周期的影响;采用transwell技术检测HepG2细胞在TGF-β培养体系中蛇床子素对细胞侵袭力的影响;Western blot检测肿瘤侵袭力相关蛋白MMP-9和vimentin的表达。结果 与对照组比较,蛇床子素对HepG2细胞有显著的抑制作用(P<0.05);蛇床子素各浓度组48h与24h比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素各浓度组72h与48h比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素100、150、200μM浓度组与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素150与100μM浓度组比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素200与150μM浓度组比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素加TGF-β各浓度组细胞个数明显低于对照组(P均<0.05);100、150、200μM蛇床子素加TGF-β组MMP-9表达量与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);100、150、200μM蛇床子素加TGF-β组vimentin表达量与对照组比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05);蛇床子素加TGF-β各浓度组间细胞个数、MMP-9、vimentin表达量比较,差异有统计学意义(P均<0.05)。结论 蛇床子素能抑制人肝癌细胞的生长和侵袭转移。
肝癌;肿瘤侵袭;蛇床子素;HepG2;TGF-β;MMP-9
肝细胞肝癌是世界上最常见的肝脏原发性恶性肿瘤,约占肿瘤总发病率的5.6%[1]。肝癌的不良预后和高侵袭转移性以及对常规治疗手段如化疗放疗的高抵抗性导致肝癌居癌症死亡率的第三位[2]。癌细胞属于上皮细胞来源,然而在肿瘤发展过程中肿瘤细胞逐渐失去上皮细胞特征并获得间充质细胞特性,这一过程称之为上皮细胞间质转型(EMT)[3]。EMT是肿瘤侵袭转移的关键过程,是肿瘤发展和致死的关键因素[4]。在EMT过程中,肿瘤微环境中的TGF-β是重要的调节因子,它通过信号转导通路上调间充质细胞骨架蛋白如波形蛋白(vimentin)及基质金属蛋白酶-9(MMP-9)等促进肿瘤细胞侵袭正常组织并发生肿瘤转移[5-7]。蛇床子素(osthole)是从中药蛇床子中提取的活性物质,研究发现蛇床子素具有抗湿疹、皮肤瘙痒,抗炎症,抗肝炎以及抗肿瘤作用[8-10]。蛇床子素对于多种肿瘤均具有良好抑制作用,然而其对人肝癌细胞生长和侵袭转移的抑制作用却很少报道。本研究观察蛇床子素对人肝癌细胞系HepG2的生物效应,探讨其对肝肿瘤细胞的生长和侵袭转移的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞培养 人肝癌细胞HepG2细胞系购于ATCC(American Type Culture Collection,美国模式培养物研究所),培养在RPMI-1640培养基中,含10%胎牛血清,100U/L青霉素和100mg/mL链霉素,培养环境为37℃恒温且通入5%的CO2。
1.2 试 剂 RPIM-1640培养基购于Gibco公司,胎牛血清购于杭州四季青生物工程有限公司,transwell小室购于美国康宁公司;蛇床子素、二甲亚砜、MTT、碘化丙啶(PI)购于美国Sigma公司;βactin、MMP-9、vimentin抗体购自美国Cell signal公司。
1.3 细胞增殖抑制试验 将HepG2细胞按2×103/孔接种于96孔板,加入 200μL含10%FBS的RPIM-1640培养,设置3个复孔,并分别加入0(对照组)、50、100、150和200μM的蛇床子素培养24、48及72h,加5mg/mL MTT 20μL,继续培养4h。弃上清,往孔中加150μL DMSO,震荡使紫色絮状物完全溶解,570nm波长下用酶标仪检测OD值,肿瘤细胞生长抑制率=(OD对照组-ODosthole)/OD对照组× 100%。
1.4 细胞周期检测 在HepG2细胞中分别加入0(对照组)、50、100、150和200μM的蛇床子素培养48h,收集细胞用生理盐水洗2次,用70%乙醇在4℃固定过夜后用生理盐水清洗,加入(50μg/mL)RNA酶,100μg/mL PI在暗处染色30min后立即用流式细胞仪检测细胞周期,G2期细胞所占比率可表示为肿瘤细胞进入G2/M阻滞[11]。
1.5 肿瘤细胞侵袭试验 在transwell小室中接种1×104个HepG2细胞置于24孔板中,上室培养基为无血清RPMI-1640培养基并加入2ng/mLTGF-β及各浓度蛇床子素,下室培养基为含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640。培养24h后取出transwell小室,用生理盐水洗去小室内的细胞,将transwell膜用3%多聚甲醛固定15min后用0.1%结晶紫染色20min,低倍镜(×100)观察4个随机选择的区域,计算细胞总数。
1.6 Western blot试验 在HepG2细胞中分别加入不同浓度的蛇床子素培养24h,然后将细胞裂解后做Western blot检测MMP-9和Vimentin的表达,蛋白表达量由它们在胶片上显色后的灰度与相应βactin的灰度比表示。
1.7 统计学方法 所有实验重复3次,实验数据用均值±标准差(±s)表示,应用SPSS10.0软件处理数据,采用非配对双边t检验以及单因素方差分析,P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 蛇床子素对人肝癌细胞系HepG2的抑制作用与对照组比较,蛇床子素各剂量组均呈现出抑制效应,呈剂量依赖性,且随着蛇床子素治疗时间的延长,对肿瘤细胞生长的抑制作用显著增加。见表1,图1。
表1 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞的抑制作用(±s)
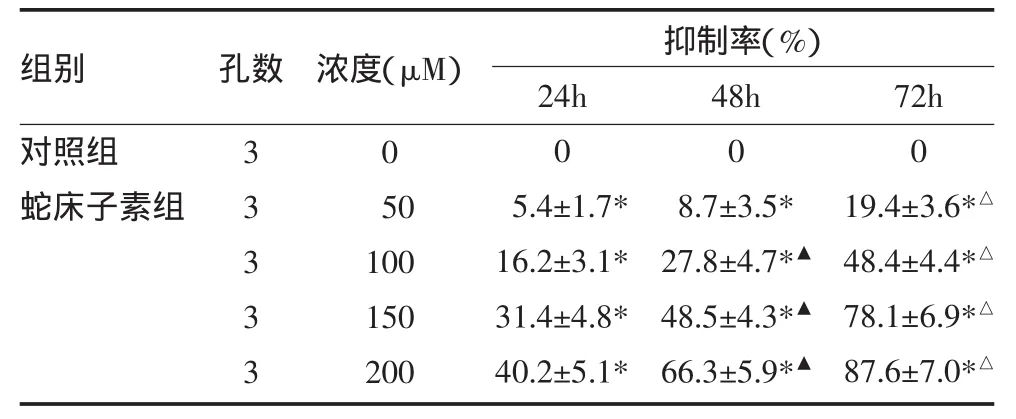
表1 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞的抑制作用(±s)
注:与对照组比较,*P<0.05;与24h比较,▲P<0.05;与48h比较,△P<0.05
组别对照组蛇床子素组孔数 抑制率(%)33333浓度(μM)0 50 100 150 200 24h 0 5.4±1.7* 16.2±3.1* 31.4±4.8* 40.2±5.1* 48h 0 8.7±3.5* 27.8±4.7*▲48.5±4.3*▲66.3±5.9*▲72h 0 19.4±3.6*△48.4±4.4*△78.1±6.9*△87.6±7.0*△
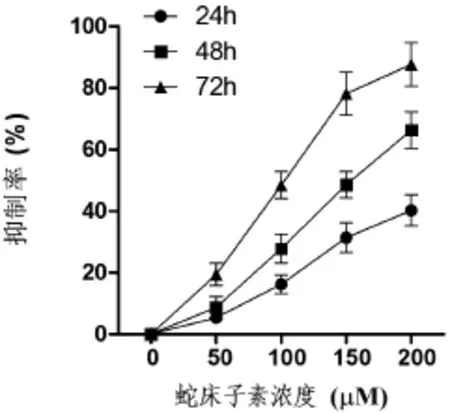
图1 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞抑制作用
2.2 蛇床子素通过G2/M阻滞抑制HepG2细胞周期
流式细胞术检测结果显示,当蛇床子素浓度达到150μM时,进入G2期的HepG2细胞从对照组的1.9%增加到15.4%,表明蛇床子素对HepG2细胞有G2/M阻滞作用,使肿瘤细胞的增殖周期停滞,从而抑制和杀伤肝肿瘤细胞。见表2。
表2 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞周期的阻滞效应(±s)
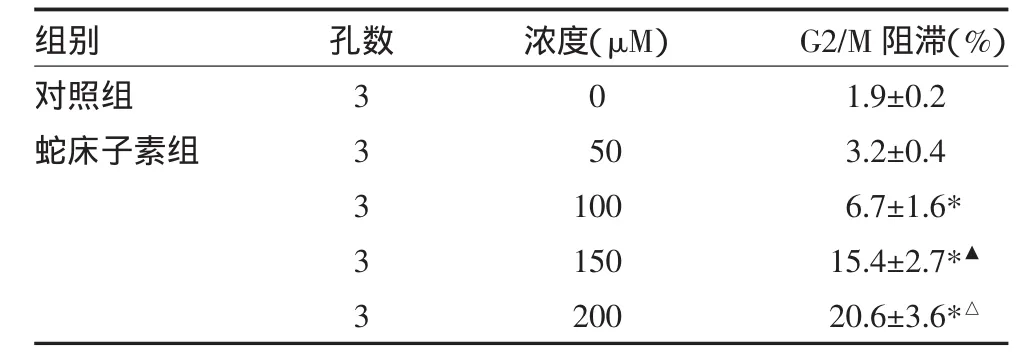
表2 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞周期的阻滞效应(±s)
注:与对照组比较,*P<0.05;与100μM组比较,▲P<0.05;与150μM组比较,△P<0.05
组别对照组蛇床子素组孔数33333浓度(μM)0 50 100 150 200 G2/M阻滞(%)1.9±0.2 3.2±0.4 6.7±1.6* 15.4±2.7*▲20.6±3.6*△
2.3 蛇床子素抑制TGF-β诱导的肿瘤侵袭转移将HepG2细胞用不同浓度的蛇床子素处理48h,显微镜计数transwell膜上的细胞数测定HepG2细胞的侵袭能力。结果发现随着蛇床子素剂量的增加,transwell膜上的细胞数显著减少(见表3),表明蛇床子素能抑制肝肿瘤的侵袭和转移。为了在蛋白水平上进一步研究蛇床子素对HepG2细胞侵袭能力的影响,采用Western blot法检测TGF-β诱导的侵袭相关蛋白MMP-9和Vimentin表达,发现随着蛇床子素剂量的增加,MMP-9和Vimentin表达降低,表明蛇床子素通过下调HepG2细胞MMP-9和Vimentin表达抑制TGF-β依赖的肿瘤侵袭能力。见表3,图2。
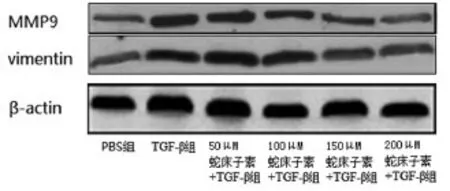
图2 蛇床子素对TGF-β处理的HepG2细胞转移相关蛋白表达的抑制作用
表3 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞侵袭能力的抑制作用(±s)
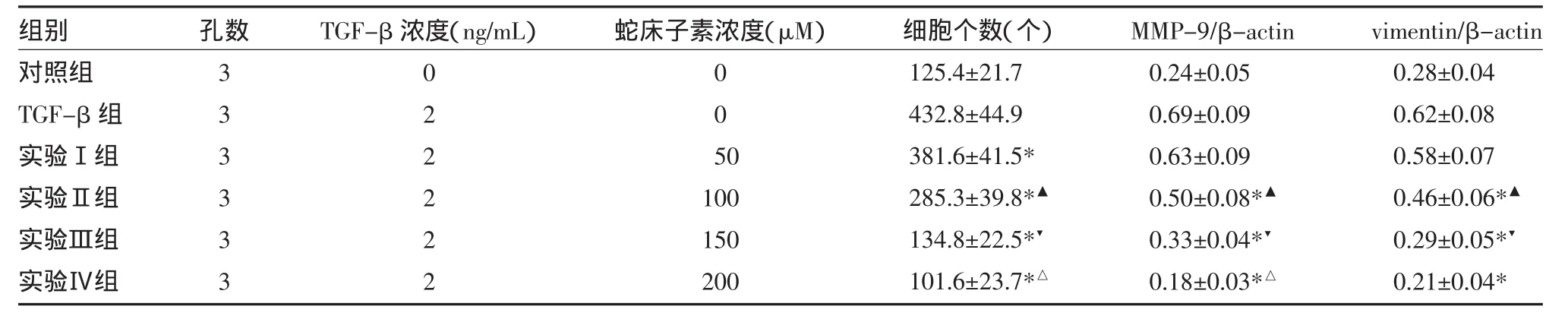
表3 蛇床子素对HepG2细胞侵袭能力的抑制作用(±s)
注:实验Ⅰ组:50μM蛇床子素+TGF-β;实验Ⅱ组:100μM蛇床子素+TGF-β;实验Ⅲ组:150μM蛇床子素+TGF-β;实验Ⅳ组:200μM蛇床子素+ TGF-β;与对照组比较,*P<0.05;与实验Ⅰ组比较,▲P<0.05;与实验Ⅱ组比较,▼P<0.05;与实验Ⅲ组比较,△P<0.05
组别对照组TGF-β组实验Ⅰ组实验Ⅱ组实验Ⅲ组实验Ⅳ组孔数333333 TGF-β浓度(ng/mL)022222蛇床子素浓度(μM)005 0 100 150 200细胞个数(个)125.4±21.7 432.8±44.9 381.6±41.5* 285.3±39.8*▲134.8±22.5*▼101.6±23.7*△MMP-9/β-actin 0.24±0.05 0.69±0.09 0.63±0.09 0.50±0.08*▲0.33±0.04*▼0.18±0.03*△vimentin/β-actin 0.28±0.04 0.62±0.08 0.58±0.07 0.46±0.06*▲0.29±0.05*▼0.21±0.04*
3 讨论
肿瘤生长微环境中的TGF-β与肿瘤发生EMT有密切的联系,肿瘤的侵袭能力依赖于TGF-β的信号转导通路,当TGF-β与Ⅱ型TGF-β受体结合后激活Ⅰ型TGF-β受体,Ⅰ型TGF-β受体是一种跨膜丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,它能进一步使转录因子Smads2和Smads3发生磷酸化激活,从而上调侵袭相关蛋白如MMP-9和vimentin的表达促进EMT的发生[12-13]。
文献报道很多天然药物具有十分显著的抗肝肿瘤作用,并且有高效、低毒、高肿瘤选择性的特点,有很大的研究价值[14-15]。蛇床子素是一种天然药物,在临床上已经大量应用,证实了它的低毒低副作用特性。本研究发现蛇床子素还具有十分良好的抗肝肿瘤细胞增殖的生物活性。此外,蛇床子素还能显著抑制TGF-β诱导的肿瘤侵袭效应,表明蛇床子素能减少肝癌细胞的侵袭和转移,对肝肿瘤患者的预后起到十分积极的作用。本研究结果提示蛇床子素可能在人肝癌治疗中有广阔的应用前景。
[1]Sherman M.Hepatocellular Carcinoma:Epidemiology,Surveillance,and Diagnosis[J].Semin Liver Dis,2010,30(1):3-16.
[2]Enguita-Germán M,Fortes P.Targeting the insulin-like growth factor pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].World J Hepatol,2014,6(10):716-737.
[3]Zhu QC,Gao RY,Qin HL,et al.Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its role in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer[J].Asian Pasific J Cancer Pre,2013,14(5):2689-2698.
[4]Xu J,Lamouille S,Derynck R.TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition[J].Cell Res,2009,19(2):156-172.
[5]Munger JS,Sheppard D.Cross talk among TGF-b signaling pathways,integrins,and the extracellular matrix[J].Cold SpringHarb PerspectBiol,2011,3(11):a005017.
[6]Sipos F,Galamb O.Epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-toepithelial transitions in the colon[J].World J Gastroenterol,2012,18(7):601-608.
[7]Zhang B,Halder SK,Kashikar ND,et al.Antimetastatic role of Smad4 signaling in colorectal cancer[J].Gastroenterology,2010,138(3):969-980.
[8]Balayssac S,Gilard V,Malet-Martino M,et al.Analysis of herbal dietary supplements for sexual performance enhancement:first characterization of propoxyphenyl-thiohydroxyhomosildenafil and identification of sildenafil,thiosildenafil,phentolamine and tetrahydropalmatine as adulterants[J].J Pharm Biomed Anal,2012,63:135-150..
[9]Lin YC,Lin JC,Way TD,et al.Osthole inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human brain cancer cells[J].J Agric Food Chem,2014,62(22):5061-5071
[1 0]Gao Z,Wen Q,Zou S.Osthole augments therapeutic efficiency of neural stem cells-based therapy in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis[J].J Pharmacol Sci,2014,124(1):54-65.
[1 1]Kong Y,Chen J,Chen C,et al.Cucurbitacin e induces cell cycle g2/m phase arrest and apoptosis in triple negative breast cancer[J].PLoS One,2014,9(7):e103760.
[1 2]Lampropoulos P,Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A,Papavassiliou AG,et al.TGF-beta signalling in colon carcinogenesis[J].Cancer Lett,2012,314(1):1-7.
[1 3]Sipos F,Galamb O.Epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-toepithelial transitions in the colon[J].World J Gastroenterol,2012,18(7):601-608.
[1 4]Lachenmayer A,Alsinet C,Llovet JM,et al.Molecular approaches to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma[J].Digestive and Liver Disease,2010,3:S264-S272.
[1 5]Song G,Luo Q,Shi Y,et al.Effects of oxymatrine on proliferation and apoptosis in human hepatoma cells[J].Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,2006,48(1):1-5.
(收稿:2014-08-07 修回:2014-11-03)
Osthole Inhibited The Growth and TGF-β-induced Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
WANGJinjun.The Central Hospital of Jinhua City,Jinhua(321000),China
Objective To investigate the effects of osthole on proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.Methods HepG2 cells were treated with various concentrations(50,100,150,200μM)of osthole.The proliferation of osthole-treating HepG2 cells was measured by using MTT assay.Cell cycle of the HepG2 cells treated with osthole was evaluated by flow cytometry with PI staining.The effect of osthole on invasion induced by TGF-β was measured by transwell method.The expressions of invasion related proteins MMP9 and vimentin were detected by Western blot.Results Compared with control group,osthole significantly inhibited the growth of HepG2 cells(P<0.05).The growth of HepG2 cells in all osthole groups was different between 24h treatment and 48h treatment and between 72h treatment and 48h treatment(all P<0.05).Significant difference in HepG2 cell growth was found between 100,150,200μM of osthole group and control group(all P<0.05),between 150μM and 100μM of osthole groups(P<0.05),and between 200μM and 150μM of osthole groups(P<0.05).Compared with control group,the HepG2 cell growth,the expression of MMP-9 and vimentin in all osthole plus TGF-β groups was significantly different(all P<0.05).The cell count and the expression of MMP9 and vimentin were statistically different among different concentration of osthole plus TGF-β groups(all P<0.05).Conclusion Osthole can inhibit the growth and invasion in hepatocellula carcinoma.
hepatocellular carcinoma;tumor invasion;osthole;HepG2;TGF-β;MMP-9
浙江省金华市中心医院儿一科(金华 321000)
