小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒RT-PCR方法的建立及初步应用
2015-05-11李晓波王淑菁岳秉飞贺争鸣
李晓波,付 瑞,王 吉,卫 礼,王淑菁,岳秉飞,贺争鸣
(中国食品药品检定研究院实验动物资源研究所,北京 100050)
小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒RT-PCR方法的建立及初步应用
李晓波,付 瑞,王 吉,卫 礼,王淑菁,岳秉飞,贺争鸣
(中国食品药品检定研究院实验动物资源研究所,北京 100050)
目的 建立小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒RT-PCR方法并对方法进行初步应用。方法 根据NCBI发表的TMEV GD VII株(GI:62039)基因组序列设计特异引物,建立RT-PCR方法,验证方法的敏感性和特异性;脑腔接种方式感染9只BALB/c小鼠,感染后第6天采集动物的脑、心、肝、脾、肺、肾、盲肠内容物和血清等样本,用建立的方法进行检测;同时检测100份小鼠盲肠内容物样本,对方法进行初步应用。结果 以GD VIIRNA为模板,建立的RT-PCR方法能够扩增出约371bp的单一目的条带,敏感性验证显示能够检测到的最低GD VII cDNA量为0.69pg/μL;以脑心肌炎病毒、淋巴细胞脉络丛脑膜炎病毒、日本乙型脑炎病毒、小鼠诺如病毒及正常小鼠脑组织为对照进行方法特异性验证,均未出现目的条带。脑腔接种感染小鼠,所有小鼠在接种第3天均产生不同程度的精神萎靡后肢麻痹等症状,其中2只小鼠于第5天死亡;采集心、肝、脾、肺、肾、脑、盲肠内容物及血清等样本进行检测,所有小鼠的脑组织均检测到GD VIIRNA,而其他组织均未检测到;对100份小鼠盲肠内容物进行检测,结果均为阴性。结论 建立的TMEV GDVII株RT-PCR方法能够高效的检测小鼠组织中的病毒感染,可作为实验动物国家标准的有力补充。
Theiler氏脑脊髓炎病毒;GDVII;脑腔接种;逆转录-聚合酶链式反应
小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒(mouse encephalomyelitis virus,MEV)又称 Theiler氏小鼠脑脊髓炎病毒(theilerˊsmouse encephalomyelitis virus,TMEV),分类上属于小RNA病毒科,肠道病毒属,主要侵害小鼠中枢神经系统,多数呈隐性感染,有时表现脑脊髓炎和后肢麻痹等症状[1-3]。目前已从世界各地分离到多个毒株,根据其毒力的不同分为两个亚群:高毒力亚群以GDVII和FA株为代表,可引起急性致命性脑炎;低毒力亚群引起持续的中枢神经系统感染和炎性脱髓鞘[2,4]。实验动物国标将TMEV列为SPF小鼠检测项目之一。
本实验建立了TMEV的RT-PCR检测方法,通过对病毒感染动物组织样本的检测以及小鼠自然感染情况的监测,对方法进行了初步应用,试验结果表明该方法可以作为动物中TMEV检测的常规方法,是对实验动物国标检测技术的有力补充。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试剂
逆转录试剂为Sigma产品;PCR相关试剂购自Takara公司;RNA提取试剂盒为 QIAGEN产品;Trizol试剂为invitrogen公司产品;氯仿、异丙醇等其他化学试剂为北京化工。
1.2 病毒毒株
TMEV GDVII株购自ATCC,小鼠脑心肌炎病毒(mouse encephalomyocarditis virus,EMCV)、淋巴细胞脉络丛脑膜炎病毒(lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus,LCM)、乙型脑炎病毒(Japanese B encephalitis virus,JEV)及鼠诺如病毒(murine norovirus,MNV)均为本室保存。
1.3 BALB/c小鼠
SPF级,3周龄,雌性,共10只,来自本院动物供应室【SCXK(京)2014-0013】,使用许可证号【SYXK(京)2011-0008】。
1.4 动物样本
100份小鼠盲肠内容物样品来自2014年10月北京市实验动物会检各实验动物生产单位。
1.5 方法
1.5.1 引物的设计
根据NCBI发表的TMEV GDVII株(GI:62039)基因组序列,选取保守区域设计引物(表1)。

表1 GD VIIRT-PCR引物Tab.1 Primers for the GD VIIRT-PCR
1.5.2 病毒RNA的提取:TMEV GDVII株BHK21细胞培养物经三次冻融后,分别取200μL按试剂盒的操作说明提取RNA,其他对照病毒也按照该方法进行。
1.5.3 RT-PCR方法的建立及反应条件优化:首先逆转录提取的TMEV RNA,再进行PCR扩增,对PCR反应体系dNTP浓度、DNA聚合酶量、引物浓度及退火温度等进行优化,确定最佳反应条件。
1.5.4 敏感性测定:紫外分光光度法测定TMEV cDNA模板浓度,然后进行10-1~10-10系列稀释,用建立的PCR方法进行扩增,检测方法的灵敏度。
1.5.5 特异性测定:分别以 TEMV,EMCV,LCM,JEV,MNV及正常小鼠脑组织所提取的RNA为模板,用建立的RT-PCR方法进行扩增,验证方法的特异性。
1.5.6 初步应用
1.5.6.1 感染试验:10只BALB/c小鼠,9只脑腔注射30μL TMEV病毒液,另外1只作为PBS对照,逐日观察,于感染后第6天对所有动物施行安乐死,取心、肝、脾、肺、肾、脑、盲肠内容物和血清等样本,心、肝、脾、肺、肾、脑等组织用 Trizol试剂法提取RNA,盲肠内容物和血清参照1.5.2用RNA试剂盒提取RNA,随后用建立的RT-PCR方法进行扩增。
1.5.6.2 样本筛查:100份小鼠盲肠内容物,取100 mg加入900μL灭菌PBS,漩涡震荡后10000 r/min离心 5 min,取 200μL上清按试剂盒说明提取RNA,随后用建立的RT-PCR方法进行扩增。
2 结果
2.1 RT-PCR反应体系及条件
25μL逆转录体系包括5×RT buffer 5μL,dNTP 4μL,随机引物1μL,逆转录酶和RNA酶抑制剂各0.5μL,RNA模板8μL,无RNA酶水6μL;逆转录反应条件为37℃ 90 min,72℃ 15 min,4℃ 5 min各1个循环。优化后的PCR反应体系为10× PCR buffer 2.5μL,dNTP 2μL,上下游引物各1μL,DNA模板2μL,HSTaq酶0.5μL,最后加灭菌双蒸水补至25μL。反应条件为94℃ 30 s,56℃ 30 s,72℃ 1 min,共40个循环,最后72℃延伸7 min。
2.2 PCR产物测序
提取TMEV GDⅦ株细胞培养物RNA,用建立的双重PCR方法进行扩增,产物送上海生工进行测序,序列经NCBIBlast比对,符合率均为99%。
2.3 敏感性测定
紫外分光法测得TMEV cDNA模板浓度为690 ng/μL,由图1可见,建立的TMEV RT-PCR方法所能检测的最大稀释度为10-6,即该方法所能检测的最低cDNA浓度为0.69 pg/μL。
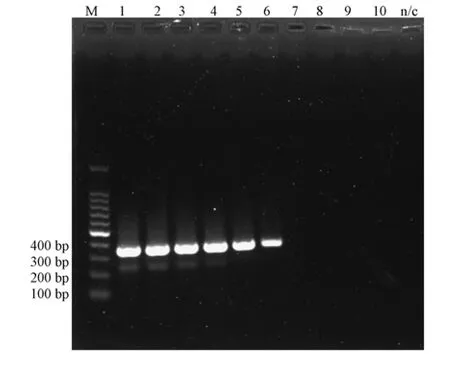
图1 TMEV RT-PCR方法敏感性Note:M:100 bp marker;1 to10:10-1 to 10-10 dilution of TMEV cDNA.Fig.1 Sensitivity of TMEV RT-PCR
2.4 特异性测定
用建立的 RT-PCR方法分别扩增 TEMV,EMCV,LCM,JEV,MNV及正常小鼠脑组织,结果以TMEV为模板产生371 bp的特异条带,以其他对照病毒及正常小鼠脑组织为模板均不产生特异条带(图2)。
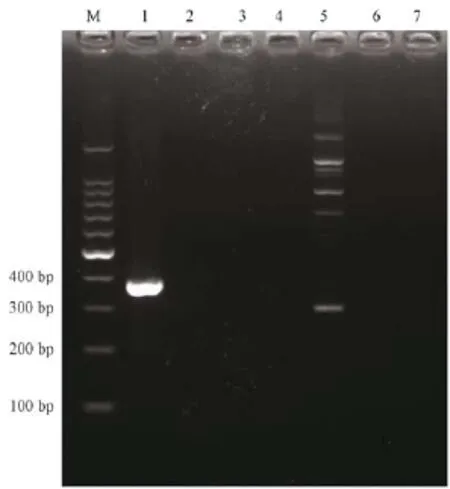
图2 TMEV RT-PCR方法特异性Note:M:100 bp marker;1 to 7:TMEV,EMCV,LCM,JEV,MNV,normalmouse brain tissue,sterile ddH2O.Fig.2 Specificity of TMEV RT-PCR
2.5 初步应用
2.5.1 感染实验
感染小鼠于感染第3天产生不同程度的临床症状,比较对照小鼠表现为明显发育不良,后肢麻痹、精神萎靡(图3),其中2只小鼠于感染后第5天死亡。对感染小鼠心、肝、脾、肺、肾、脑、盲肠内容物及血清等组织样本进行RT-PCR检测,结果显示,所有小鼠脑组织均产生371bp的目的条带,其他组织均未出现目的条带(部分结果见图4)。对脑组织PCR产物测序,结果经NCBI比对,与TMEV(GI:62039)的符合率为100%。
2.5.2 样本筛查:对会检的100份小鼠盲肠内容物进行TMEV RT-PCR扩增,结果均为阴性。
3 讨论
脑脊髓炎病毒在动物中的感染时有报道,不仅能够感染小鼠,也可以感染大鼠,且感染率较高[5-10]。实验动物国标中TMEV的检测方法主要为血清学方法,本实验建立了TMEV的RT-PCR方法,与以往报道的分子生物学方法相比[11],不需要进行后续的探针检测,用时短,且敏感性更高,特异性更好。
报道[12],本实验在脑腔注射感染小鼠的过程中采用眼角斜上方浅进针(2 mm)的方式进行注射,减少了对动物脑部的损伤。实验用的TMEV毒株为强毒株GDVII,感染动物在第3天均出现明显的临床症状,变现为后肢瘫痪、震颤等,其中2只于感染第5天死亡。用建立的RT-PCR方法对感染小鼠的组织进行检测,所有感染动物的脑组织均检测到GDVII核酸,在肺组织产生约400 bp的非特异条带,经测序排除了TMEV,其他组织均未检测到,这与之前的报道结果一致[13-14],可能病毒未通过血脑屏障,因而未感染到其他器官。
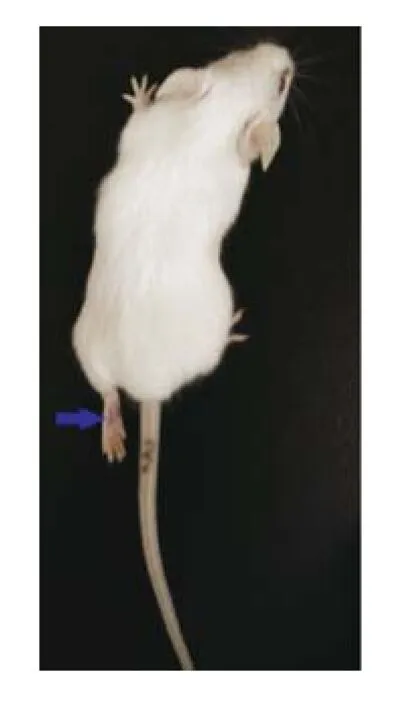
图3 感染小鼠后肢瘫痪
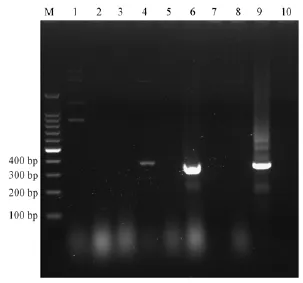
图4 感染小鼠组织RT-PCR扩增结果Note:M:100 bp marker;1 to 8:Heart,liver,spleen,lung,kidney,brain,serum,cecal contents;9:Positive control;10:Sterile ddH2O.Fig.4 The results of RT-PCR for tissues of infected mice
对100份小鼠的盲肠内容物样本进行TMEV的筛查,结果均为阴性,初步表明近年北京地区实验动物中TMEV的控制情况良好。
综上所述,我们建立的TMEV RT-PCR方法具有良好的敏感性和特异性,可以作为实验动物国标的补充检测方法。
参考文献:
[1] 田克恭.实验动物病毒性疾病[M].农业出版社,1992:99-104.
[2] Downs WG.Mouse encephalomyelitis virus.In:Foster HL,Small JD,Fox JG ed.Themouse in biomedical research,vol.II[M].New York:Academic Press,1982.341-352.
[3] Lipton HL,Rozhon EJ.The Theiler’smurine encephalomyelitis viruses.In:Bhatt PN,Jacoby RO,Morse HC,et al.Viral and mycoplasmal infections of laboratory rodents: effects on biomedical research[M].London:Academic Press Inc,1986.253-275.
[4] Lipton HL.Theiler’s virus infection in mice:an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination[J].Infect.Immun,1975,11:1147-1155.
[5] Roble GS,Gillespie V,Lipman NS.Infectious disease survey of Musmusculus from pet stores in New York City[J].Journal of the Amecican Association for Laboratory Animal Science,2012,51:37-41.
[6] Hansen AK,Thomsen P,Jensen HS.A serological indication of the existence of a guineapig poliovirus[J].Laboratory Animals,1997,31:212-218.
[7] Hayashimoto N,Morita H,Ishida T,et al.Microbiological survey ofmice(Musmusculus)purchased from commercial pet shops in Kanagawa and Tokyo, Japan[J]. Experimental Animals,2014,Advance Publication:1-15.
[8] Lipton HL,Kim BS,Yahikozawa H,et al.Serological evidence that Mus musculus is the natural host of Theilerˊs murine encephalomyelitis virus[J].Virus Research,2001,76:79-87.
[9] Rodrigues DM,Martins SS,Gilioli R,et al.Theilerˊs murine encephalomyelitis virus in nonbarrier rat colonies[J].Comparative Medicine,2005,55(5):459-464.
[10] Dammann P, Hilken G, Hueber B, et al. Infectious microorganisms in mice(Mus musculus) purchased from commercial pet shops in Germany[J].Laboratory Animals,2011,45:271-275.
[11] Zoll J,Galama J,Melchers W.Molecular identification of cardioviruses by enzymatic amplification[J].Molecular and Cellular Probes,1993,7:447-452.
[12] 李慧,王春华,罗姗,等.关于小鼠脑内不同注射手法的探讨[J].实验动物科学,2013,30(2):48-50.
[13] Trottier M,Schlitt BP, Lipton HL.Enhanced detection of Theiler’s virus RNA copy equivalents in the mouse central nervous system by real-time RT-PCR[J].Journal of Virological Methods,2002,103:89-99.
[14] Shaw-Jackson C,Michiel T.Absence of internal ribosome entry site-mediated tissue specificity in the translation of a bicistronic transgene[J].JVirol,1999,73(4):2729–2738.
Development and application of RT-PCR for detection of TMEV
LIXiao-bo,FU Rui,WANG Ji,WEILi,WANG Shu-jing,YUE Bing-fei,HE Zheng-ming
(Laboratory Animal Institute,National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,Beijing 100050,China)
Objective To develop RT-PCR for detection of TMEV and apply the method.M ethods To design specific primers on the basis ofGD VII(GI:62039)genome sequences published in NCBIand establish RT-PCR.To verify the sensitivity and specificity ofmethod after optimizing PCR.We infected 9 BALB/c mice intracerebrally and collected brain,heart,liver,spleen,lung,kidnet,cecal contents and serum samples the 6thday postinfection.The samples were tested by the TMEV RT-PCR.100 mouse cecal contents samples were also detected to apply the established method.Results The 371bp single band was amplified using GDVIIas template.Sensitivity test showed that the RT-PCR method can detect as low as 0.69 pg/μLGDVII cDNA.There were no objective band amplified when encephalomyocarditis virus,lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus,Japanese B encephalitis virus,murine norovirus and normalmouse brain tissue were used as case-control.All infectedmice showed symptom of different degrees such as depression and hind limb paralysis the 3th day postinoculation and two of infected mice died the 5th day postinoculation.Tissues such as heart,liver,spleen,lung,kidney,brain,cecal contents and serum were collected and tested for TMEV.All the brain samples were detected positive for GDVIIand other tissues were all negative;The 100 cecal contents samples were tested and all were negative.Conclusions RT-PCR for TMEV GDVIIstrain can detect virus infection inmouse tissues efficiently and can be used as a powerful supplement for the national standard of lab animal.
TMEV;GDVII;Intracerebral inoculation;RT-PCR
R-332
A
1671-7856(2015﹞10-0017-04
10.3969.j.issn.1671.7856.2015.010.004
国家科技支撑计划“实验动物质量监测体系的完善与检测关键技术研究”(2013BAK11B00)。
李晓波(1980-),助理研究员,研究方向:实验动物病毒学.E-mail:lxb8493059@163.com。
贺争鸣(1957-),研究员,研究方向:实验动物微生物学。E-mail:zhengminghe57@163.com。
﹞2015-08-31
研究报告
