2014年8月3日云南鲁甸6.5级地震序列破裂过程研究
2015-04-17李艳娥陈学忠陈丽娟郭祥云
李艳娥, 陈学忠, 陈丽娟, 郭祥云
中国地震局地球物理研究所, 北京 100081
2014年8月3日云南鲁甸6.5级地震序列破裂过程研究
李艳娥, 陈学忠*, 陈丽娟, 郭祥云
中国地震局地球物理研究所, 北京 100081
本文利用主地震相对定位法,对2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震序列中的8月3日—9月30日地震进行了重新定位,借助于时空图像分析方法,对本次地震破裂过程进行了分析,得到如下结果:(1)2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震主要沿NW向破裂,存在沿NE向破裂的成分,但是NE向破裂并不明显;(2)地震破裂时,主要从主震震中处往ES方向传播,破裂带长度大约为10 km,破裂面近乎直立;(3)余震活动主要集中于主震上方区域,震源深度大于主震的余震稀少.根据上述结果,结合当地的地震构造情况和本次地震的震源机制解,分析表明,本次地震的破裂面为NW向,其发震断层为包谷垴—小河断裂的可能性很大.
鲁甸MS6.5地震; 主地震; 相对定位; 破裂过程
1 引言
地震破裂过程的研究不仅与地震发生的成因有关,而且还涉及到地震趋势判定的研究内容,一直受到国内外地震学家们的重视.地震破裂过程的研究主要包括两个方面:一是利用波形反演技术研究主震破裂的时空过程(Chen et al., 1996; 许力生和陈运泰, 1997, 1999);另一是基于余震通常沿主破裂展布,利用地震序列的精确定位结果,分析地震破裂过程(Hurukawa,1998; Ohnaka and Kuwahara, 1990; Ohnaka,1992; 陈学忠等, 2001a, b, 2008).
2014年8月3日16点30分,在云南鲁甸县发生MS6.5级强烈地震,根据中国地震台网测定的结果,震中位置为27.1°N,103.3°E.鲁甸6.5级地震附近分布的主要断裂有三条NE向的断裂:西鱼河—昭通断裂、昭通—鲁甸断裂和莲峰断裂,还有一条NW向断裂,即包谷垴—小河断裂,在其西面有NNW向小江断裂.附近地区自公元624年以来发生了多次MS≥5.7地震,如图1所示.鲁甸6.5级地震附近地区有三个强震活动地区:一个是位于其西北部的冕宁—西昌一带,另一个是在其北部的峨边—马边—大关一带,还有一个是其南部的巧家—东川一带,也就是说,在鲁甸6.5级地震发生地附近西北部、北部和南部都是强震活动区,而在其本地,据历史地震记载,却没有发生过强震.
刘超等(2014)给出这次地震的震源机制解显示其断层节面为NE和NW两组节面,错动性质为近纯走滑型.鲁甸地震发生的地方十分靠近NE向的西鱼河—昭通断裂和NW向的包谷垴—小河断裂.由区域台网给出的余震震中分布显示出SSE和近EW向的“L”型分布,用双差定位方法给出的余震定位结果与此基本上一致(王未来等, 2014; 张广伟等,2014),无论是将西鱼河—昭通断裂,还是将包谷垴—小河断裂作为发震断层,都不能很好地解释余震的震中分布图像.许力生等(2014)对此次地震的视震源时间函数进行分析之后,认为这次地震发生于两个走向分别为NE向和NW向的相互交叉的断层,破裂开始于NE向的断层,但很快触动了NW向的断层,两条断层同时参与了这次地震.徐锡伟等(2014)认为此次地震的发震断层为NW向的包谷垴—小河断裂,呈左旋走滑性质,属大凉山断裂南端部组成部分.张勇等(2014)认为鲁甸地震的发震断层走向为162°.从上述研究结果看来,关于鲁甸地震的发震断层面是NE向的断层还是NW向的断层仍存争议.
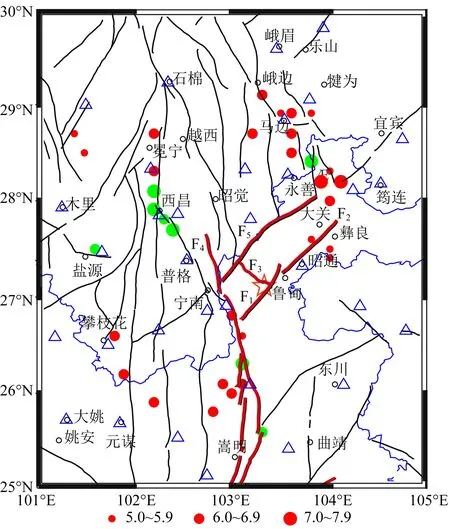
图1 鲁甸MS6.5地震附近地区公元624年以来发生的MS≥5.7地震、地震构造和地震观测台站分布绿色实心圆为624年—1899年地震,红色实心圆为1900年—2014年地震,黄色五角星为2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震,兰色空心三角形为本文用于重新定位的地震观测台站.F1:西鱼河—昭通断裂,F2:昭通—鲁甸断裂,F3:包谷垴—小河断裂,F4:小江断裂;F5:莲峰断裂.Fig.1 The tectonic background and the distribution of epicenters of earthquakes with MS≥5.7 occurring after 624 around the epicenter of the Ludian earthquake and the distribution of regional seismic stationsThe green solid circles indicate earthquakes occurring from 624 to 1899; The red solid circles indicate earthquakes occurring from 1900 to 2014; The yellow star denotes the Ludian MS6.5 earthquake. The bule triangles indicate the regional seismic stations used in this paper. F1 is Xiyuhe-Zhaotong fault, F2 is Zhaotong-Ludian fault, F3 is Baogunao-Xiaohe fault, F4 is Xiaojiang fault, F5 is Lianfeng fault.
主地震相对定位法的基本原理是选定一个震源位置较为精确的主地震(或叫参考地震),计算待定地震相对于它的位置,进而确定这些待定地震的震源位置.由于相对定位法对所假设的地壳模型依赖较小,因此与通常的绝对定位法相比,所得到的震源位置受地壳模型的影响较小.对于震源破裂过程的研究,只要知道相对位置变化即可,因此,由这种方法得到的结果,适合于地震序列的破裂过程的研究.
为了揭示鲁甸地震破裂面与断裂的关系,本文将利用主地震相对定位法,对2014年8月3日—2014年9月30日鲁甸地震序列中的地震进行重新定位.根据定位结果,借助于时空图象分析方法,分析序列发展过程中各次地震震源位置的相对变化,进而揭示该序列的破裂过程.
2 资料和定位结果
本文收集了中国地震台网中心2014年8月3日—2014年9月30日的震相观测报告资料,对发生在经纬度范围在(26.7°N—27.5°N,102.8°E—103.8°)之内的ML≥0.8级共698次地震进行重新定位,使用的台站分布如图1所示.
定位时取6.5级主震为参考地震,即主地震,其震中位置为(27.11°N,103.33°E),震源深度为10 km.重新定位前后的地震空间分布如图2,图3为重新定位地震的M-t图.
重新定位的经度误差平均约为0.07 km,最大为0.27 km,最小为0.06 km.纬度误差平均为0.07 km,最大0.55 km,最小为0.054 km.定位时使用的观测报告中只有直达波震相资料,缺乏首波资料,这种情况下主地震相对定位法给出的震源深度的定位误差为2.0 km,考虑到有近台资料,震源深度的误差不会太大.
图2为重新定位前后的地震震中分布图,对比图2a和图2b可以看出,重新定位的地震震中空间分布比重新定位前地震的空间分布更加向主震集中,重新定位前余震活动已经穿过西鱼河—昭通断裂,重新定位的结果显示余震主要分布在西鱼河—昭通断裂以西,似乎并未穿过它.
图2c和图2d分别是重新定位前和重新定位后ML≥3.0地震的空间分布.重新定位前,ML≥3.0地震似乎显示出NW(AA′)和NE(BB′)两个方向的分布,但NW向更为明显.经重新定位之后,ML≥3.0地震似乎更加集中于NW(AA′)方向分布,NE(BB′)向分布几乎辨认不出来.各家得到的震源机制解中,NW向截面的走向分布在150°~167°内(许力生等, 2014; 徐锡伟等, 2014),本文结果NW方向分布走向大约为146°,与震源机制解结果基本一致.
图4和图5分别为重新定位前后地震沿震源深度方向的剖面图.图4a和图5a为图2中AA′截面的,图4b和图5b为BB′截面的深度剖面.重新定位前的地震,其深度的分布显示余震在4~25 km的深度范围内,余震不光发生在主震上方,在主震下方,也发生了一定数量的余震,有的余震已经达到20 km深处的下方.重新定位之后,余震分布在9~10 km的深度范围内,主要位于主震上方,主震位于余震分布区下方边缘.图5b显示,破裂面倾角较陡,近乎直立.张勇等(2014)利用全球范围内震中距介于10°~90°范围内的28个宽频带垂直向P波波形资料对鲁甸地震破裂过程进行反演,得到的结果表明此次地震破裂方向是朝地表扩展,这可能是导致余震分布在主震上方的原因.
3 破裂过程分析
一次强震发生之后,通常都会发生许多的余震,形成一个地震序列.地震序列可以分成三种基本类型,即主余震型序列、前主余震型序列和双震型或震群型序列.鲁甸地震属于主余震型序列.对于主余震型地震序列,主震发生时形成了破裂面的绝大部分,余震发生时破裂面继续扩展,余震沿主震形成的破裂面分布.所以,余震的空间分布可以勾画出破裂面的概貌.我们利用重新定位的地震,进行地震频次空间扫描,结果如图6所示.
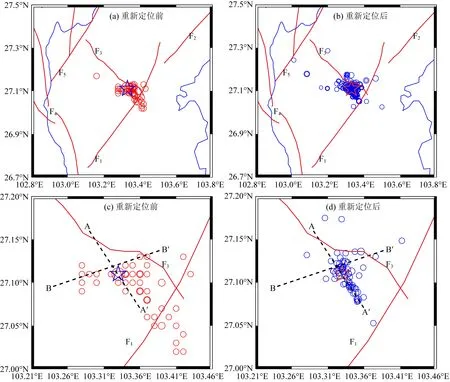
图2 鲁甸MS6.5地震及其余震震中分布(2014年8月3日—9月30日)(a)重新定位前ML≥0.8;(b) 重新定位后ML≥0.8;(c)重新定位前ML≥3.0;(d) 重新定位后ML≥3.0.Fig.2 The distribution of Ludian MS6.5 earthquake sequence(3 August 2014 to 30 September )(a) Before relocated earthquakes with ML≥0.8; (b) After relocated earthquakes with ML≥0.8;(c) Before relocated earthquakes with ML≥3.0; (d) After relocated earthquakes with ML≥3.0.
图3 重新定位地震的M-t图Fig.3 The M-t diagram of the relocated earthquakes
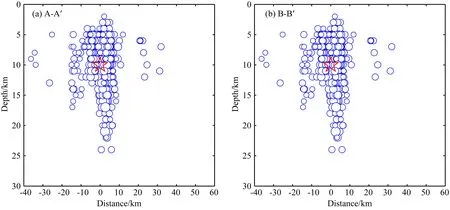
图4 重新定位前地震沿A-A′、B-B′截面的深度剖面Fig.4 Focal depth profiles of the before relocation earthquakes along profiles A-A′、B-B′

图5 重新定位后地震沿A-A′、B-B′截面深度剖面Fig.5 Focal depth profiles of the after relocated earthquakes along profiles A-A′、B-B′

图6 地震频次空间扫描结果(空间窗:0.01°×0.01°的矩形区域,滑动步长:0.001°)(a) 2014年8月3日—9月30日; (b) 8月3—4日; (c) 8月5—7日; (d) 8月8—14日; (e) 8月15—20日; (f) 8月21日—9月30日.Fig.6 The spatial distribution of the earthquake number (spatial window: 0.01°×0.01°, slip step: 0.001°)(a) 3 August 2014 to 30 September ; (b) 3 August 2014 to 4 August 2014;(c) 5 August to 7 August ; (d) 8 August to 14 August; (e) 15 August to 20 August ; (f) 21August 2014 to 30 September.
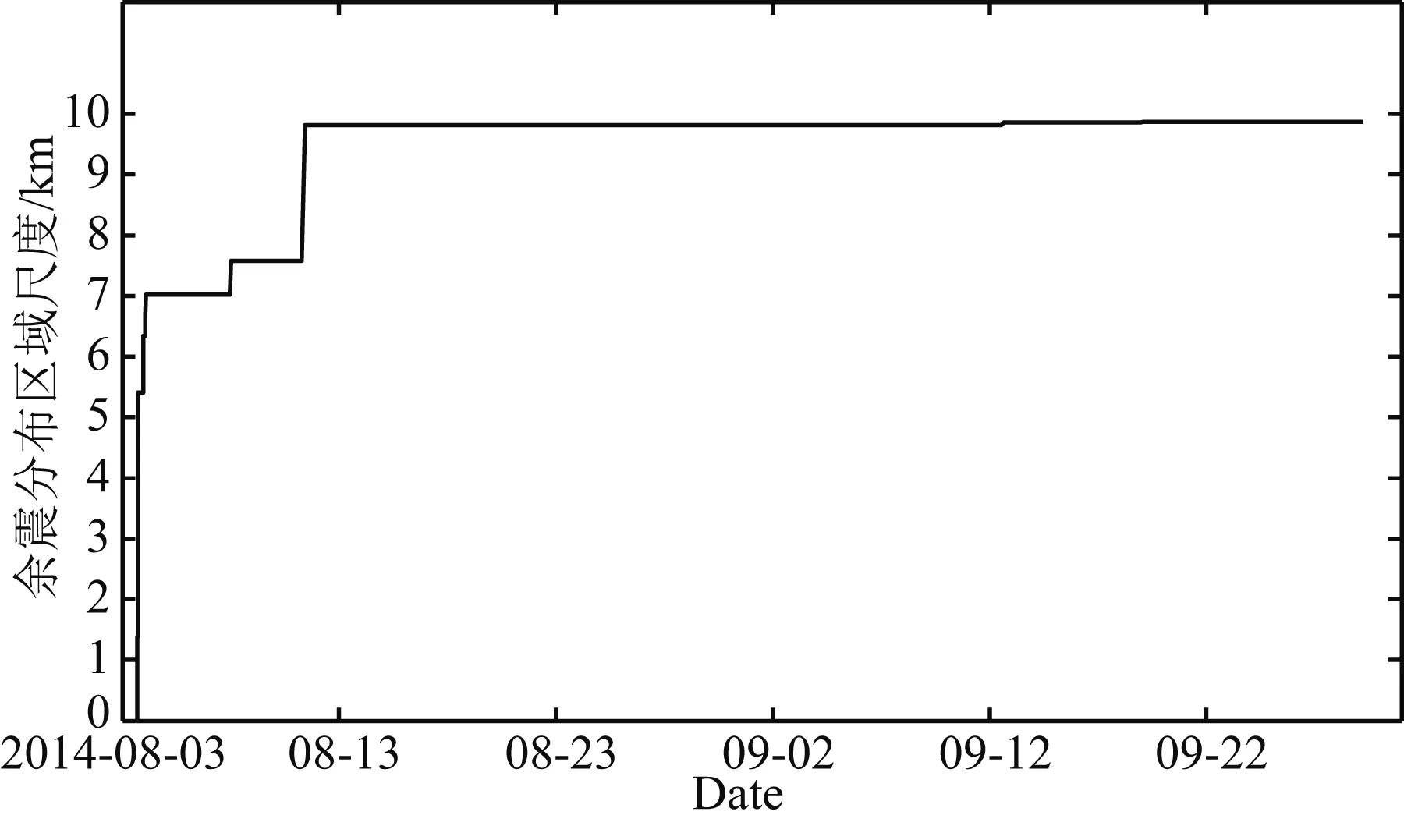
图7 余震分布区域尺度随时间的变化Fig.7 The aftershock distribution scale changes with time
重新定位的地震频次空间扫描图像显示地震频次相对高值区呈一NW走向的带状区域,长轴走向约为156°,长度大约10 km,主震位于地震频次高值区北端附近(图6a).为了了解破裂过程细节,我们分析了地震序列不同时间段的地震频次空间分布.从序列开始的2天即8月3—4日地震频次空间分布可以看出,地震频次呈明显的NW向带状分布,余震往主震两侧扩展,余震分布区域展布尺度大约7 km(图6b).8月5—7日,余震频次分布变成NE向带状分布,NW向的余震活动稀少(图6c).8月8—14日,余震呈现出非常清晰的NW向带状分布,并继续往主震东南方向扩展了大约3 km的距离(图6d).8月15日以后,余震局限在已经形成的破裂带及附近的局部区域内活动,破裂带不再扩展(图6e—6f).
从上述余震频次空间分布可以得到如下认识:此次地震以NW向破裂为主,兼有NE向的破裂,主破裂面为NW向,其长度大约为10 km,与刘成利等(2014)利用区域宽频带数据反演得到的破裂长度一致.
图7为余震分布区域尺度随时间的变化,可以看出余震分布区域的尺度于8月4日凌晨4点左右就达到7 km,之后再没有大的变化,大约仅仅扩展了3 km,最终破裂尺度约为10 km.
4 结论
根据上述对重新定位的鲁甸MS6.5地震序列的破裂过程的分析,得到以下结论.
(1) 2014年鲁甸MS6.5地震主要沿NW向破裂,存在沿NE向破裂的成分,但是NE向破裂并不明显.无论是ML≥3.0地震震中分布,还是地震频次空间扫描结果,都清楚地显示出余震沿NW向分布的特征,似乎余震沿NE向分布的迹象并不明显.
(2) 地震破裂时,主要从主震震中沿ES方向传播,破裂带长度大约为10 km,破裂面近乎直立.
(3) 余震活动主要集中于主震上方区域,震源深度大于主震的余震稀少.
在鲁甸MS6.5地震震中附近的西鱼河—昭通断裂、昭通—鲁甸断裂和莲峰断裂等三条NE向断裂,他们都是逆冲兼右旋走滑型断裂,而震源机制解给出的鲁甸MS6.5地震的发震断层却是几乎纯走滑型,这显然与当地存在的NE向断裂的运动性质是不一致的.因此,根据上述结果,本次地震的破裂面为NW向,其发震断层为包谷垴—小河断裂的可能性很大.
致谢 感谢中国地震台网中心提供的震相报告数据,感谢许力生研究员、严川博士的有益讨论,感谢两位审稿专家提出的评审意见.
Chen X Z, Guo T S, Zhu L R. 2001a. An example of earthquake nucleation of the strong continental earthquakes.ActaSeismologicaSinica(in Chinese), 23(2): 213-216.Chen X Z, Gai Z X, Zhou S Y, et al. 2001b. The investigation of rupture process of the Xiuyan 5.4 earthquake on November 29, 1999.ActaSeismologicaSinica(in Chinese), 23(6): 659-662.
Chen X Z, Lü J, Wang H M. 2008. Investigation on rupture process of the Jiujiang-Ruichang earthquake sequence of November 26, 2005.Earthquake(in Chinese), 28(1):100-106.
Chen Y T, Xu L S, Li X, et al. 1996. Source process of the 1990 Gonghe, China, earthquake and tectonic stress field in the Northeastern Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau.PureandAppliedGeophysics, 146(3-4): 697-715.
Hurukawa N. 1998. The 1995 Off-Etorofu earthquake: joint relocation of foreshocks, the mainshock, and aftershocks and implication for the earthquake nucleation process.Bull.Seism.Soc.Am., 88(5): 1112-1126.Liu C L, Zheng Y, Xiong X, et al. 2014. Rupture process ofMS6.5 Ludian earthquake constrained by regional broadband seismograms.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3028-3037, doi: 10.6038/cig20140927.Ohnaka M, Kuwahara Y. 1990. Characteristic features of local breakdown near a crack-tip in the transition zone from nucleation to unstable rupture during stick-slip shear failure.Tectonophysics, 175(1-3): 197-220.
Ohnaka M. 1992. Earthquake source nucleation: a physical model for short-term precursors.Tectonophysics, 211(1-4): 149-178.Wang W L, Wu J P, Fang L H, et al. 2014. Double difference location of the LudianMS6.5 earthquake sequences in Yunnan province in 2014.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3042-3051, doi: 10.6038/cig20140929.
Xu L S, Chen Y T. 1997. Inversion of source parameters of Gonghe earthquake by using broadband digital seismic wave data.ActaSeismologicaSinica(in Chinese), 19(2): 113-128.
Xu L S, Chen Y T. 1999. Temporal-spatial rupture process of the 1997 Mani, Tibet earthquake.ActaSeismologicaSinica(in Chinese), 21(5): 449-459.
Xu L S, Zhang X, Yan C, et al. 2014. Analysis of the Love waves for the source complexity of the LudianMS6.5 earthquake.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3006-3017, doi: 10.6038/cig20140925.Xu X W, Jiang G Y, Yu G H, et al. 2014. Discussion on seismogenic fault of the LudianMS6.5 earthquake and its tectonic attribution.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3060-3068. doi: 10.6038/cig20140931.Zhang G W, Lei J S, Liang S S, et al. 2014. Relocations and focal mechanism solutions of the 3th August 2014 Ludian, YunnanMS6.5 earthquake sequence.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3018-3027, doi: 10. 6038/cig20140926.Zhang Y, Xu L S, Chen Y T, et al. 2014. Rupture process of the 3 August 2014 Ludian Yunnan,Mw6.1 (MS6.5) earthquake.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese), 57(9): 3052-3059, doi: 10.6038/cig20140930.
附中文参考文献
陈学忠, 郭铁栓, 朱令人. 2001a. 一次大陆强震前震成核的实例. 地震学报, 23(2): 213-216.
陈学忠, 盖增喜, 周仕勇等. 2001b. 1999年11月29日辽宁岫岩5.4级地震序列的破裂过程研究. 地震学报, 23(6): 659-662.
陈学忠, 吕坚, 王慧敏. 2008. 2005年11月26日江西九江—瑞昌MS5.7地震序列的破裂过程研究. 地震, 28(1): 100-106.
刘超, 许力生, 陈运泰. 2014. 2014年8月3日云南鲁甸6.5级地震. http:∥www.cea-igp.ac.cn/tpxw/270724.shtml.
刘成利, 郑勇 熊熊等. 2014. 利用区域宽频带数据反演鲁甸MS6.5级地震震源破裂过程. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3028-3037, doi: 10.6038/cig20140927.
王未来, 吴建平, 房立华等. 2014. 2014年云南鲁甸MS6.5地震序列的双差定位. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3042-3051, doi: 10.6038/cig20140929.
许力生, 陈运泰. 1997. 用数字化宽频带波形资料反演共和地震的震源参数. 地震学报, 19(2): 113-128.
许力生, 陈运泰. 1999. 1997年中国西藏玛尼MS7.9地震的时空破裂过程. 地震学报, 21(5): 449-459.
许力生, 张旭, 严川等. 2014. 基于勒夫波的鲁甸MS6.5地震震源复杂性分析. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3006- 3017, doi: 10.6038/cig20140925.
徐锡伟, 江国焰, 于贵华等. 2014. 鲁甸6.5级地震发震断层判定及其构造属性讨论. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3060-3068, doi: 10.6038/cig20140931.
张广伟, 雷建设, 梁姗姗等. 2014. 2014年8月3日云南鲁甸MS6.5级地震序列重定位与震源机制研究. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3018-3027, doi: 10.6038/cig20140926.
张勇, 许力生, 陈运泰等. 2014. 2014年8月3日云南鲁甸Mw6.1 (MS6.5) 地震破裂过程. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3052-3059, doi: 10.6038/cig20140930.
(本文编辑 胡素芳)
Investigation on the rupture process of the LudianMS6.5 earthquake sequence on 3 August, 2014 in Yunnan province
LI Yan-E, CHEN Xue-Zhong*, CHEN Li-Juan, GUO Xiang-Yun
InstituteofGeophysics,ChinaEarthquakeAdministration,Beijing100081,China
AnMS6.5 earthquake occurred in Ludian, Yunnan province. The rupture process has been analyzed by different researchers. From existing research results, it remains controversial that the seismogenic fault plane is NE or NW fault. Investigation of the aftershock distribution along the main fault is one of the important methods for analysis of earthquake rupture process. In this paper we use the master event relative location method. We select an earthquake with more accurate location than other earthquakes as the main earthquake or reference earthquake, then calculated aftershocks relative to the main location. Compared with absolute location method, this method is more suitable for analyzing the rupture process of earthquake sequence. To investigate the rupture process and seismogenic fault of LudianMS6.5 earthquake, we have selected the earthquake phase data recorded by Yunnan, Sichuan and nearby Digital Seismic Networks from 3 August 2014 to 30 September 2014. We use master event relative location method and have relocated the LudianMS6.5 sequence. We take the mainshock as the master event,and then obtain the aftershock′s relative location. We analyzed the relocated result with the aid of spatial-temporal pattern analyzing method, the following result is obtained. (1) The rupture process for the LudianMS6.5 earthquake contains mainly the rupture in the direction of NW and a little one in the direction of NE; (2) The main shock ruptures from the epicenter of the main shock towards the southeast, and the rupture surface is nearly vertical with a rupture length of about 10 km; (3) Most of aftershocks are located in the upper region of the main shock, the aftershocks with the focal depth greater than that of the main shock are very few.According to the above results, combining with tectonic conditions and focal mechanism, we can infer that the rupture surface of the Ludian earthquake is along NW, and the possibility that Baogunao-Xiaohe fault could be the seismogenic fault is very large.
LudianMS6.5 earthquake; Master event; Relative location; Rupture process
李艳娥, 陈学忠, 陈丽娟等. 2015. 2014年8月3日云南鲁甸6.5级地震序列破裂过程研究.地球物理学报,58(9):3232-3238,
10.6038/cjg20150918.
Li Y E, Chen X Z, Chen L J, et al. 2015. Investigation on the rupture process of the LudianMS6.5 earthquake sequence on 3 August, 2014 in Yunnan province.ChineseJ.Geophys. (in Chinese),58(9):3232-3238,doi:10.6038/cjg20150918.
10.6038/cjg20150918
P315
2015-01-15,2015-06-09收修定稿
地震行业科研专项(201508020)资助.
李艳娥,女,1983年生,助理研究员,主要从事数字地震学及地震预测预报等研究.E-mail:liyane05@cea-igp.ac.cn
*通讯作者 陈学忠,教授,主要从事地震成因与地震预测研究. E-mail:cxz8675@163.com
