华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳的生长和变质演化*
2015-03-15刘贻灿王程程张品刚聂佳珍
刘贻灿 王程程 张品刚,2 聂佳珍
LIU YiCan1,WANG ChengCheng1,ZHANG PinGang1,2 and NIE JiaZhen1
1. 中国科学院壳幔物质与环境重点实验室,中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院,合肥 230026
2. 安徽省煤田地质局勘查研究院,合肥 230088
1. CAS Key Laboratory of Crust-Mantle Materials and Environments,School of Earth and Space Sciences,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230026,China
2. Exploration Institute of Anhui Coalfield Geology Bureau,Hefei 230088,China
2015-03-22 收稿,2015-05-28 改回.
1 引言
大陆地壳的形成与演化一直是前寒武纪地质学研究的重点(Windley,1973;Dewey and Windley,1981;Mclennan and Taylor,1982;Jahn et al.,1984;Taylor and McLennan,1985;Rogers and Santosh,2003;Griffin et al.,2004;Zhai,2014)。而大陆地壳的形成,一般归结于活动大陆边缘和板内两个典型的板块构造位置(Rudnick,1995)。其中,板内的大陆生长通常与地幔柱的岩浆板底垫托作用(Magmatic underplating)有关,而板缘的大陆生长则主要通过俯冲增生和弧-陆碰撞来实现的。而且,汇聚大陆边缘通常被认为是下地壳增生(包括幔源岩浆板底垫托作用和板块俯冲增生)的主要场所(Weber et al.,2002)。此外,幕式地壳生长已经被越来越多的研究者所认识(McCulloch and Bennett,1994;Condie,1998),而早前寒武纪被认为是大陆地壳生长的关键时期,并且主要集中于几个峰期如3.6Ga、2.7Ga、2.5Ga 和1.9 ~1.8Ga 等(McCulloch and Bennett,1994;Condie,1998,2000;Condie et al.,2011)。
麻粒岩包体和麻粒岩地体是透视下地壳形成与演化的重要窗口(Weber et al.,2002)。大多数麻粒岩被认为是在缺乏流体条件下变质形成的(Harley,1989;Pattison et al.,2003)。其中,高压麻粒岩以石榴子石+单斜辉石+斜长石+石英(变基性岩)和石榴子石+ 蓝晶石+ 钾长石+ 石英(变泥质岩和长英质岩石)等峰期矿物组合为主要特征(Yardley,1989;O’Brien and Rötzler,2003;Pattison,2003;Kotková and Harley,2010)。而石榴麻粒岩是高压麻粒岩中一种重要岩石类型,代表了高级的变基性岩,又称高压基性麻粒岩。但是,高压石榴麻粒岩不同于榴辉岩的是其矿物组合中含有斜长石和/或贫硬玉分子的单斜辉石,而中-低压麻粒岩不同于高压麻粒岩的主要特征是其矿物组合中常含有斜方辉石,但是高压麻粒岩在峰期之后减压过程中可能会形成以后成合晶冠状体形式存在的斜方辉石,表现为低压麻粒岩相退变质作用(Zhao et al.,2001)。高压麻粒岩出露相当广泛,从古元古代(如华北恒山杂岩;Zhao et al.,2001)到新生代(如喜马拉雅山脉;Liu and Zhong,1997)的诸多大陆碰撞造山带中均有报道。在特定地带鉴定出高压麻粒岩有助于增强对涉及大陆碰撞及有关下地壳演化过程的认识,而对高压麻粒岩相变质作用的岩石学观察和年代学测定对进一步理解变质作用和下地壳演化之间的关系至关重要。但是,获得精确的前寒武纪高压麻粒岩相变质作用的时代往往比较困难。这种困难主要来自于后期多阶段变质作用叠加与改造以及相关过程导致的矿物间同位素体系(尤其是Sm-Nd和Rb-Sr)的重置或不平衡,因此影响了人们对岩石的形成过程和构造背景的认识。然而,锆石是一种十分常见的难熔矿物,具有很低的Pb 扩散速率和很好的保存放射性成因Pb 的能力(Cherniak and Watson,2003),能够保存多期岩浆和变质年龄记录,特别是对于涉及复杂变质过程的高级变质岩来说,是U-Pb 定年的理想矿物(Gebauer et al.,1997;Hermann et al.,2001;Rubatto et al.,2001;Möller et al.,2002;Corfu et al.,2003;Hermann and Rubatto,2003;Liu et al.,2006,2011b),从而为揭示前寒武纪变质基底的形成和演化过程提供了重要年代学手段(Griffin et al.,2004;Liu et al.,2009,2013b)。此外,锆石的Lu-Hf 同位素体系,优于U-Pb 同位素体系,具有很强的抗蚀变等有关地质过程的干扰和影响(Amelin et al.,2000;Cherniak and Watson,2003;Gerdes and Zeh,2009;Zeh et al.,2010),因而保留了初始的Hf 同位素比值并且可以用来示踪源区性质和岩石成因(Griffin et al.,2004;Woodhead et al.,2004)。因此,根据锆石U-Pb 年龄和Hf 同位素分析数据就可以有效地提供可靠的、很详细的有关前寒武纪地壳形成和变质演化过程的时代及岩石成因方面信息或制约(Vervoort and Blichert-Toft,1999;Amelin et al.,2000;Griffin et al.,2000,2004;Andersen et al.,2002;Condie et al.,2005;Iizuka et al.,2005;Hawkesworth and Kemp,2006;Wu et al.,2006;Gerdes and Zeh,2009;Kemp et al.,2009;Zeh et al.,2009)。
近三十年来,众多研究者对华北陆块前寒武纪变质地体(或麻粒岩地体)和下地壳包体岩石开展了大量的岩石学、大地构造学、地球化学和地质年代学等诸方面研究,并在其形成和演化上获得了一些重要进展。其中,Zhao et al. (2000,2005)将华北陆块变质基底划分为东部陆块、西部陆块及分割东、西部陆块的中部造山带。而且,东、西部陆块被认为是沿中部造山带在~1.85Ga 完成克拉通拼合(Zhao et al.,2000,2005;Guo et al.,2002,2005;Wilde et al.,2002;Kröner et al.,2005;Wilde and Zhao,2005;Hou et al.,2006;Wan et al.,2006)。拼合完成之后,在1.85 ~1.6Ga 期间,克拉通内部和边缘经历了一系列的伸展和裂解事件(Zhai et al.,2000;Zhai and Liu,2003;Peng et al.,2005,2008;Hou et al.,2006,2008;Lu et al.,2008)。值得注意的是,已报道的古元古代高压麻粒岩相变质作用主要来自于中部造山带(Zhai et al.,1993,2000;Zhao et al.,2000,2001,2005;Guo et al.,2002,2005;Zhai and Liu,2003;Kröner et al.,2005),而东部陆块已在胶东/胶北(刘文军等,1998;Zhou et al.,2004;Tang et al.,2007;刘平华等,2010,2012;Tam et al.,2011;Li et al.,2012;刘福来等,2012)、信阳(Zheng et al.,2003,2004a,b)和蚌埠-宿州(Liu et al.,2009,2013b)等地区有陆续报道。但是,对华北陆块古元古代高压麻粒岩相变质作用的构造背景还存在两种不同的解释:一种观点认为这些高压麻粒岩形成于东、西部陆块拼合(Zhao et al.,2000,2005;Guo et al.,2002,2005;Wilde et al.,2002)或“胶-辽-吉古元古代构造带”(Zhao et al.,2001,2012;Luo et al.,2004;Li and Zhao,2007;Liu et al.,2014a)的碰撞-造山环境中;另一种观点则认为它们是与哥伦比亚超大陆裂解有关的、古元古代地幔柱活动的产物(Zhai et al.,2000;Zhai and Liu,2003;Zheng et al.,2003;Peng et al.,2005,2008;Liu et al.,2009,2013b)。也许是不同地点或构造带高压麻粒岩具有不同的成因过程与机制。此外,根据华北陆块内部和北部的麻粒岩包体和变质地体岩石研究表明,华北陆块在前寒武纪发生过幕式地壳生长,主要峰期集中在2.7Ga 和2.5Ga(Jahn et al.,2008;Zheng et al.,2009;Jiang et al.,2010,2013;Diwu et al.,2011;Liu et al.,2011a,2012a,2013a;Wan et al.,2011,2013;Zhai and Santosh,2011;Zhang,2012;Zhang et al.,2012;Zhao and Zhai,2013)。此外,已发表的Pb 同位素研究结果(Zhu,1991;涂湘林等,1993;张理刚,1995;张国辉等,1998;张本仁等,2002)表明,华北陆块前寒武纪变质基底/下地壳岩石通常具有特征性的低放射成因Pb 同位素组成,一方面指示其形成于古老的太古代(-古元古代?),另一方面明显区别于扬子/华南前寒武纪变质基底/下地壳岩石的高放射成因Pb 同位素组成。
关于华北陆块的形成与演化,虽然受到广泛关注并日益引起国内外研究者的兴趣,但是大部分研究都集中于华北内部、北部和东、西陆块结合带或中部造山带,而东南缘前寒武纪地壳的形成与演化方面研究尚显得较薄弱。华北东南缘霍邱、蚌埠及相邻地区出露的变质基底(五河杂岩和霍邱杂岩)和深源下地壳包体岩石无疑为这一研究提供了极好的天然实验室。
最近的研究结果显示,五河杂岩中的变基性岩经历了1.80 ~1.90Ga 的高压麻粒岩相变质作用(Guo and Li,2009;Liu et al.,2009;Wang et al.,2013a)。徐州-宿州一带中生代闪长斑岩中深源包体的岩石学、年代学和岩石地球化学研究(Xu et al.,2002,2004,2006,2009;Guo and Li,2009;Liu et al.,2009,2013b;Wang et al.,2012)表明,它们包括前寒武纪下地壳包体和古生代幔源包体,而下地壳包体大部分形成于2.5 ~2.6Ga 和部分形成于~2.1Ga 并经过~1.8Ga 高压麻粒岩相变质作用,少数晚太古代下地壳包体还经历了~2.5Ga 或~2.1Ga 麻粒岩相变质作用。此外,五河杂岩中变基性岩表现为两类高、低放射成因Pb 同位素组成(Wang et al.,2013a),而高放射成因Pb 同位素成分的成因解释仍存在争议(刘贻灿和王安东等,2012;刘贻灿等,2015;Wang et al.,2012)、尚需要更多的证据和数据加以查明。而且,研究区前寒武纪变质基底和下地壳包体岩石是否都经历了部分熔融作用以及部分熔融与变质交代的过程和期次等是亟待解决的重要科学问题。
为了揭示华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳(尤其是变质基底)的形成和演化过程,本文根据作者等近年来对蚌埠地区出露的五河杂岩和宿州夹沟中生代闪长斑岩中深源下地壳包体岩石的研究成果和进展,结合已发表的、来自钻孔岩芯或矿区的有关霍邱杂岩及相关岩石的研究成果,系统总结了华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳岩石的高压麻粒岩相变质、部分熔融以及幕式地壳生长与多期改造方面的证据,并提出了目前存在的相关科学问题和未来拟开展的研究工作设想与展望。
2 区域地质背景
华北陆块是世界上最古老、最大的克拉通地块之一,保存有>3.6Ga 的古老地壳物质(Liu et al.,1992;Zheng et al.,2004a,b;Wu et al.,2008;Zhang et al.,2012)。地质位置上,西接早古生代祁连造山带,北邻晚古生代-三叠纪天山-内蒙-大兴安岭造山带;在南部,秦岭-大别-苏鲁造山带把华北和华南(扬子)板块分开(图1)。基于年代学、岩石组合、构造演化和P-T-t 轨迹的不同,华北克拉通被划分为东部陆块、西部陆块及夹于其中的中部造山带(Zhao et al.,2000,2001;Kusky and Li,2003;Zhai and Liu,2003)。本文研究区位于华北东南缘,距苏鲁造山带西端的郯-庐断裂带以西约100km,距大别造山带北端大约300km (图1)。区内变形的新元古代和古生代盖层,以及前寒武纪变质基底岩石中分布一些中生代闪长斑岩(如夹沟等)和花岗岩(如荆山、涂山等)。涉及的前寒武纪变质基底主要零星分布于霍邱、蚌埠及相邻地区,包括“五河杂岩”和“霍邱杂岩”,并且“五河杂岩”常被中生代含石榴子石花岗岩所侵入(图2a);而中生代闪长斑岩中含有大量下地壳和地幔包体/捕虏体(Xu et al.,2002,2004,2006;Guo and Li,2009;Liu et al.,2009,2013b;Wang et al.,2012)的徐州-宿州地区则无变质基底出露。目前,中生代花岗岩类已经被广泛深入研究并取得了一些重要进展(Xu et al.,2005;徐祥等,2005;杨德彬等,2005,2008;王安东等,2009;Yang et al.,2010;Liu et al.,2012b;Wang et al.,2013b;Li et al.,2014)。其中,怀远-凤阳地区的荆山、涂山和老山等地发育的含石榴子石花岗岩体已经被证明是由华南三叠纪俯冲陆壳岩石在160Ma 左右发生部分熔融形成的(Xu et al.,2005;王安东等,2009;Wang et al.,2013b;Li et al.,2014),而另一部分花岗闪长岩/闪长斑岩则是由华北加厚镁铁质下地壳岩石在110 ~130Ma 发生部分熔融形成的(杨德彬等,2005,2008;Yang et al.,2010;Liu et al.,2012b)。

图1 华北东南缘五河杂岩及相邻地区地质简图Fig.1 Simplified geological map of the Wuhe Complex and adjacent parts of the southeastern margin of the North China Block
3 岩石产状与类型

图2 华北东南缘前寒武纪变质岩的野外产出形式(据刘贻灿和王安东,2012)(a)变质地体中变基性岩与中生代含石榴花岗岩的侵入接触关系;(b)中生代闪长斑岩中的下地壳包体Fig. 2 Photographs showing the field occurrence of the Precambrian metamorphic rocks at the southeastern margin of the North China Block (after Liu and Wang,2012)

图3 华北东南缘五河杂岩的野外照片(a)变基性岩的部分熔融与混合岩化作用(据刘贻灿等,2015);(b)糜棱岩化花岗片麻岩Fig. 3 Photographs showing the field occurrence of the Wuhe complex at the southeastern margin of the North China Block
华北陆块东南缘前寒武纪下地壳变质岩,以高级变质地体(或麻粒岩地体)和(麻粒岩)捕虏体或包体形式存在(图2)。变质地体/基底主要分布于霍邱和蚌埠地区,包括原“霍邱群”(或霍邱杂岩)及“五河群”和“凤阳群”(或五河杂岩)等。其中,霍邱杂岩主要由白云斜长片麻岩/TTG 片麻岩、石英岩、云母片岩、大理岩、条带状铁建造(BIF)和斜长角闪岩等,但地表大多已被第四纪覆盖;五河杂岩中主要含有石榴斜长角闪岩/榴闪岩、石榴麻粒岩、异剥钙榴岩、石榴斜长角闪片麻岩与花岗片麻岩/TTG 片麻岩、云母片岩、大理岩和变质砂岩等不同类型的变质岩。五河杂岩与中生代花岗岩类的侵入接触关系(图2a)常常可以在野外露头上看见。下地壳包体主要产于夹沟(图2b)、班井和利国等中生代闪长斑岩中,岩石类型丰富、多样,主要有含石榴斜长角闪岩、榴闪岩、石榴角闪石岩、石榴麻粒岩、含石榴角闪斜长片麻岩和花岗片麻岩等。有限的早期区调资料显示五河杂岩的形成时代为晚太古代-早元古代(安徽省地质局区域地质调查队,1979①安徽省地质局区域地质调查队. 1979. 1∶20 万蚌埠幅区域地质调查报告;安徽省地质矿产局,1987,1997)。深变质的麻粒岩相岩石(麻粒岩相地体)主要出露于蚌埠一带。也就是说,研究区前寒武纪变质基底岩石主要出露于蚌埠及相邻地区(即五河杂岩分布区)(图1),由变质的镁铁质和长英质火成岩以及表壳岩系所组成,并伴生有古元古代片麻状钾长花岗岩和中生代花岗岩类,因此常被称为“蚌埠隆起”。该区变质基底的主要岩石类型有黑云斜长片麻岩、黑云二长片麻岩、角闪斜长片麻岩、石榴斜长角闪岩、榴闪岩、石榴麻粒岩、灰色TTG 片麻岩、石英/云母片岩类、变质砂岩、不纯大理岩类和变形变质侵入体(变质钾长花岗岩)等。
野外调查表明,五河杂岩中变基性岩(石榴斜长角闪岩)已发生明显部分熔融(这已被岩相学研究所证实,见后文)、甚至混合岩化作用,表现为强烈的面理化和含有浅色体(leucosome)(图3a),并有时呈构造透镜体或岩块产于不纯的大理岩中(刘贻灿等,2015),两者之间为构造接触关系,反映了它们原岩性质的不同以及可能具有不同的形成与演化历史,它们的原岩分别为基性岩和不纯灰岩。而且,不同类型的变质岩都经历了强烈的构造变形、甚至糜棱岩化(刘贻灿等,2015)(图3b)。
4 高压麻粒岩相变质与部分熔融
最近,杨晓勇等(2012)认为“霍邱群”的最高变质相为高角闪岩相;王娟等(2014)根据蒙城钻孔中石榴斜长角闪岩的岩石学研究,认为五河杂岩经历了“高压角闪岩相变质作用(T =671 ~700℃和P =0.82 ~0.95GPa)”。然而,Liu et al. (2009)根据凤阳一带石榴斜长角闪岩以及夹沟变基性岩包体的岩石学研究,证明它们的峰期变质矿物组合为石榴子石+单斜辉石+斜长石+金红石+石英等,结合传统的矿物对温压计估算结果,认为它们形成于高压麻粒岩相变质条件下(T=800 ~860℃和P=1.1 ~1.2GPa)。因此,研究区前寒武纪变质基底岩石的峰期变质条件和P-T-t 轨迹方面研究尚显得不足或缺乏。但是,已有研究结果表明,至少一部分前寒武纪变质岩经历了高压麻粒岩相变质作用。
五河杂岩中变基性岩的代表性显微照片,如图4 所示。石榴斜长角闪岩主要由石榴子石、斜长石和角闪石,以及少量单斜辉石、石英、榍石和微量金红石等矿物组成。石榴子石在成分上是均一的,为铁铝榴石-镁铝榴石-钙铝榴石固溶体,锰含量较低。斜长石有三种产出形式(Liu et al.,2009):以包裹体形式产于石榴子石中(An =49%);以后成合晶形式与绿色角闪石共生(An =22%);以基质形式产出(An =47% ~51%)。富钛的、棕色角闪石通常以包裹体形式产于斜长石或基质中,TiO2含量高达3.82%;而产于基质中或与斜长石共生产于后成合晶中的绿角闪石(图4a)几乎不含Ti。基质中残留的单斜辉石为透辉石。石榴麻粒岩的主要矿物组合为石榴子石+单斜辉石+斜长石+石英+Ti-角闪石(金红石(图4b),这种矿物组合指示其经历了高压麻粒岩相变质作用(Yardley,1989;O’Brien and Rötzler,2003;Pattison,2003)。榴闪岩主要由石榴子石、角闪石、斜长石和石英等组成,石榴子石在成分上相对均一,类似于石榴斜长角闪岩中石榴子石组成;角闪石有两期,分别为早期的棕色高钛角闪石和晚期的绿色低钛角闪石(图4c,d),这些特征暗示榴闪岩也经历了类似的高压麻粒岩相变质作用及后期角闪岩相和绿片岩相变质作用叠加(Liu et al.,2009)。
近期的岩石学研究还表明,凤阳一带不纯大理岩中主要矿物有方解石、石英、单斜辉石、角闪石、榍石、磷灰石、不透明矿物(钛铁矿/磁铁矿),以及少量黑云母、斜长石和钾长石(刘贻灿等,2015)。其中,钾长石主要为微斜长石,而且有些颗粒的核、边部有熔蚀形成的蠕虫状石英集合体或者表现为微斜长石和石英的交生体,说明岩石曾经历部分熔融(Zhou et al.,2004)或代表早期熔体的结晶产物(Vernon and Collins,1988;Holness and Sawyer,2008),因而证明大理岩经历了部分熔融作用(这也与其共生的石榴斜长角闪岩中发现有部分熔融证据相吻合,见后文)。结合大理岩中1.83 ~1.85Ga 变质锆石区的石英+单斜辉石+斜长石+金红石等矿物包体组合(刘贻灿等待发表资料),由此证明大理岩类似于石榴斜长角闪岩(Liu et al.,2009)和石榴麻粒岩(Wang et al.,2013a)等变基性岩,同样经历了古元古代高压麻粒岩相变质作用。

图4 华北东南缘五河杂岩中变基性岩的显微照片(据刘贻灿等,2015)(a)石榴子石中石英包裹体以及斜长石+角闪石交生体,石榴斜长角闪岩;(b)石榴子石+单斜辉石+斜长石,石榴麻粒岩;(c)石榴子石中的斜长石包体及早期富Ti 角闪石(Hbl1)和晚期角闪石(Hbl2),榴闪岩;(d)早期富Ti 角闪石(Hbl1)和晚期角闪石(Hbl2)以及斜长石的绿帘石化,石榴斜长角闪岩. Grt-石榴子石;Cpx-单斜辉石;Rt-金红石;Ttn-榍石;Hbl-角闪石;Pl-斜长石;Ilm-钛铁矿;Ep-绿帘石Fig.4 Photomicrographs of the meta-basic rocks in the Wuhe complex at the southeastern margin of the North China Block (after Liu et al.,2015)
与不纯大理岩共生的石榴斜长角闪岩的石榴子石中发现有多相固体包裹体(刘贻灿等,2015),主要由钾长石、斜长石、石英和黑云母的交生体构成,表现为“纳米花岗岩(nanogranite)”(Cesare et al.,2009;Sawyer et al.,2011;Ferrero et al.,2012;Groppo et al.,2012)。这种位于石榴子石变斑晶核部的“纳米花岗岩(nanogranite)”常被解释为石榴子石在峰期变质生长期间伴随有部分熔融作用产生的熔体并结晶形成的(Groppo et al.,2012;Bartoli et al.,2013)。结合该石榴斜长角闪岩的峰期变质时代为1.83Ga(Liu et al.,2009),因此,证明了研究区变质基底岩石经历了古元古代部分熔融作用,并且可能接近于峰期高压麻粒岩相变质时代,至于确切时代有待于进一步限定。但是,古元古代晚期(~1.8Ga)部分熔融作用是否引起混合岩化作用,以及研究区变质基底岩石是否经历了更早期(晚太古代末期)和稍晚的部分熔融与混合岩化作用,尚需要进一步岩石学和年代学方面研究。如果发生过混合岩化作用,必定能找到对应的岩石学和年代学证据即同期的浅色体和暗色体,否则,仅表现为局部的部分熔融作用。结合野外观察(图3a)和前文所述,至少在局部发生了混合岩化作用,至于混合岩化时代和过程即是与~1.8Ga 部分熔融作用有关、还是与燕山期岩浆作用有关,尚需进一步深入研究与限定。
因此,五河杂岩中不同类型的变质岩,它们大多数都含有石榴子石、单斜辉石、金红石、斜长石和石英等峰期矿物组合,指示形成于高压麻粒岩相条件下(Liu et al.,2009)。而且,基于岩相学和矿物之间相互关系观察,至少可以区分出峰期高压麻粒岩相(石榴子石+斜长石+单斜辉石+石英+金红石±富Ti 角闪石)变质矿物组合,以及后期角闪岩相(斜长石+绿角闪石+钛铁矿+榍石)和绿片岩相(绿泥石+方解石+ 磁铁矿)等退变质矿物组合(Liu et al.,2009,2013b)(图4)。矿物组合与初步的温压计算结果表明,高压麻粒岩相变质阶段温度、压力分别为800 ~860℃和1.0 ~1.2GPa(Liu et al.,2009),这也与夹沟中生代闪长斑岩中下地壳包体岩石及其变质锆石的温压估算(Liu et al.,2009;Wang et al.,2012)一致。
华北东南缘前寒武纪变质岩经历了复杂的多阶段变质演化与改造。除了高压麻粒岩相、角闪岩相和绿片岩相变质作用以及部分熔融和绿帘石化作用外,还遭受了碳酸盐交代作用、含水熔/流体交代作用和绿泥石化作用等。岩相学观察(Liu et al.,2009;刘贻灿等,2015)表明,凤阳一带与大理岩相共生的石榴斜长角闪岩经历了多期交代作用,其中:(1)石榴子石中多相矿物包裹体指示了碳酸盐交代、角闪岩相变质和绿泥石化,即石英和方解石位于中心、而边部有角闪石和绿泥石等蚀变矿物,也就是说,前者指示早期存在含碳酸盐的熔体或者近于峰期变质之后即发生含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用,而后者则指示晚期的角闪岩相变质和绿泥石蚀变;(2)石榴子石斑晶的裂隙中分布有钾长石+石英+斜长石+角闪石+黑云母等矿物,指示了峰期之后的熔/流体活动和交代作用。此外,研究区异剥钙榴岩的成因也与钙质交代作用有关(Coleman,1977;Li et al.,2004;Ferrando et al.,2010)。
很显然,凤阳一带石榴斜长角闪岩在高温条件下经历了含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用,并且可能发生在1.83 ~1.85Ga,这为其高放射成因Pb 同位素成分的成因解释提供了新的重要证据(刘贻灿等,2015):因为不纯大理岩与其共生的石榴斜长角闪岩具有一致的峰期高压麻粒岩相变质时代、共同经历了古元古代高温变质、部分熔融与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用,而含碳酸盐的熔/流体通常具有高的Pb含量和高放射成因Pb 同位素组成(Othman et al.,1989);相比较,那些未发现含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用的变基性岩则仍显示华北前寒武纪变质地体或下地壳岩石的低放射成因Pb 成分。这不同于作者等(刘贻灿和王安东,2012;Wang et al.,2012,2013a)的以前解释即“因为2.1Ga 大洋俯冲与变质作用的强烈影响而造成靠近俯冲带的下地壳底部岩石发生Pb 同位素均一化并形成高放射成因Pb 同位素组成”。但是,无论何种解释,高放射成因Pb 同位素成分的成因都与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用有关。显然,仍需要更多的数据和证据加以查证。另外,我们不仅在五河杂岩变质岩中观察到峰期高压麻粒岩相变质及稍后期间的熔/流体活动,而且在夹沟下地壳包体岩石中也同样观察到峰期变质之后的熔/流体活动与交代作用(Liu et al.,2013b;图5)。
然而,部分熔融以及多期变质交代作用常导致矿物之间的Fe-Mg 交换或重置(Frost and Chacko,1989;Pattison et al.,2003),这为研究区前寒武纪变质岩的温度、压力计算与确定带来了巨大困难和挑战。而且矿物之间Fe-Mg 交换的封闭温度(Closure temperature)低于麻粒岩相峰期变质温度(Frost and Chacko,1989;Harley,1989;Spear and Florence,1992;Pattison et al.,2003)。因此,已获得的高压麻粒岩相阶段的变质温度范围较大(660 ~894℃)(Liu et al.,2009;Wang et al.,2012,2013a;王娟等,2014),而最高变质温度仍可能代表峰期变质温度的最小估计值(Davis et al.,2003;Kotková and Harley,2010;Liu et al.,2015)。这也与变基性岩的锆石学研究结果一致(Liu et al.,2009,2013b;Wang et al.,2012,2013a),即已定年的变基性岩中锆石主要为变质锆石、很少有岩浆锆石残留。前人研究也表明,高温(特别是>900℃)部分熔融作用有可能使难熔的矿物相(如锆石)完全溶解,因而造成大陆碰撞造山带和麻粒岩地体高级变质岩(特别是变基性岩)中常很少保留有早期岩浆锆石、而大多数表现为近于圆形的变质锆石(Hermann and Rubatto,2003;Klavera et al.,2015)。据此推断,研究区前寒武纪变质基底岩石有可能经历了超高温变质作用。实际上,宿州夹沟变基性下地壳包体岩石的石榴子石中针状金红石出溶体(Liu et al.,2009;图6)也指示其可能发生过超高温变质作用(Gou et al.,2014)。因此,超高温变质作用也许比目前认识的更普遍(Ague et al.,2013),但是,由于大多数经历过复杂变质演化的下地壳岩石都遭受了强烈的退变质作用和糜棱岩化作用的影响并使早期超高温条件下形成的矿物(组合)及有关证据消失,而不易于被识别(De Roever et al.,2003)。

图5 华北东南缘夹沟下地壳包体中石榴斜长角闪岩的背散射图像(据Liu et al.,2013b)钾长石和斜长石沿单斜辉石的裂隙分布. Cpx-单斜辉石;Pl-斜长石;Hbl-角闪石;Kfs-钾长石Fig.5 A back scattered electron (BSE)image of garnetbearing amphibolite from lower-crust xenoliths at Jiagou in the southeastern margin of the North China Block (after Liu et al.,2013b)
5 岩石成因与时代
正如前文所述,华北陆块是一个古老的克拉通并经历了复杂的演化过程,为此,我们根据作者等的最新研究进展以及已发表的有关华北东南缘前寒武纪变质地体和下地壳包体岩石的锆石U-Pb 年代学和Lu-Hf 同位素与Sr-Nd-Pb 同位素分析数据,探讨了华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳变质岩及相关岩石的成因和时代。
5.1 岩石成因
五河杂岩和霍邱杂岩以及下地壳包体的岩石类型多样,因而涉及的过程和岩石成因都很复杂。现根据有限的已发表资料,对它们的岩石成因综述如下。

图6 华北东南缘夹沟变基性下地壳包体的显微照片(据Liu et al.,2009)(a)具有针状金红石出溶体的石榴子石含有透辉石及其退变的角闪石包体;(b)具有针状金红石出溶体的石榴子石及金红石退变为榍石;(c)具有针状金红石出溶体的石榴子石含有透辉石+石英包体. Grt-石榴子石;Di-透辉石;Rt-金红石;Hbl-角闪石;Qz-石英;Ttn-榍石Fig.6 Photomicrographs of meta-basic lower-crust xenoliths from Jiagou at the southeastern margin of the North China Block (after Liu et al.,2009)
霍邱杂岩 根据来自矿区和钻孔含铁变质岩系和有关岩石样品的元素和Hf 同位素地球化学研究(邢凤鸣和任思明,1984;Wan et al.,2010;杨晓勇等,2012;刘磊和杨晓勇,2013;Wang et al.,2014;Liu and Yang,2015;Liu et al.,2014b)表明,霍邱杂岩包括原岩属于晚太古代海相-火山沉积型复理石-碧玉铁质建造以及2.75Ga 和2.56Ga 的两期花岗岩类,伴生有古元古代混合岩化花岗岩,而且:(1)霍邱地区BIF 铁矿及相关的斜长角闪岩和大理岩形成于晚太古代弧后盆地;(2)晚太古代变质岩还经历了1.8 ~1.9Ga 构造-热事件和变质作用与混合岩化作用,并形成混合岩和高钾花岗岩;(3)一部分TTG 片麻岩是由2.71 ~2.76Ga 加厚的镁铁质下地壳岩石发生部分熔融形成的。但是,霍邱杂岩中不同成因和不同类型变质岩石的具体变质演化过程、不同阶段的P-T 条件(特别是峰期变质条件)以及部分熔融与混合岩化作用的期次和时代等尚缺乏系统研究和限定。
五河杂岩 主要出露于蚌埠、怀远、凤阳及五河一带(图1)。岩石类型主要有含石榴斜长角闪岩、榴闪岩、石榴麻粒岩、异剥钙榴岩和片麻岩(石榴斜长角闪片麻岩、花岗片麻岩/TTG 片麻岩)以及云母片岩、大理岩和变质砂岩以及古元古代片麻状钾长花岗岩等。至于其具体的岩石成因,报道的资料较少。涂荫玖(1994)根据微量元素和Sr 同位素研究认为,TTG 片麻岩是由斜长角闪岩在晚太古代(~2.5Ga)发生部分熔融作用形成的。杨德彬等(2009)根据锆石U-Pb 定年以及元素和Hf-Nd 同位素研究,认为五河杂岩分布区出露的片麻状钾长花岗岩是在~2.1Ga 由原始岩浆起源于有少量古老(古元古代-晚太古代)地壳物质涉入的新生下地壳的部分熔融形成的,属于A 型花岗岩,形成于伸展的构造背景下。Liu et al. (2013b)根据石榴斜长角闪岩的Hf 同位素研究,认为该变基性岩的原岩起源于与大洋板块俯冲有关的岛弧成因。Wang et al. (2013a)根据石榴麻粒岩和石榴斜长角闪岩的Sr-Nd-Pb 同位素分析,认为它们是形成于~2.5Ga 的镁铁质下地壳并遭受了1.83 ~1.88Ga 高压麻粒岩相变质作用,而且,这些变基性岩表现为两类高、低放射成因Pb 同位素组成。其中,低放射成因Pb 同位素成分类似于典型的华北前寒武纪下地壳岩石特点,而高放射成因Pb 同位素成分与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用有关(刘贻灿等,2015)。但是,这些不同类型、不同形成时代的前寒武纪变质岩仍缺乏系统的元素和同位素地球化学方面研究,至于它们的岩石成因尚需更多的数据和证据给予查明和限定。
下地壳包体 夹沟中生代闪长斑岩中不同类型下地壳包体的变质岩石学、元素和Hf 同位素地球化学等方面研究(Xu et al.,2006;Wang et al.,2012;Liu et al.,2013b)表明:(1)前寒武纪变质岩主要包括原岩晚太古代(2.5 ~2.6Ga)岛弧或弧后成因的基性岩(玄武岩/辉长岩)和酸性岩石(花岗岩)以及古元古代(~2.1Ga)岛弧成因的中酸性岩石(如安山岩等),证明至少在晚太古代(2.5 ~2.6Ga)即存在板块构造作用以及存在2.5 ~2.6Ga 和~2.1Ga 两期与大洋板块俯冲有关的岛弧岩浆作用;(2)不同时代的前寒武纪变质岩分别经历了不同程度的2.48 ~2.49Ga、~2.1Ga 和1.8 ~1.9Ga 麻粒岩相变质作用以及390Ma 和176Ma 的变质改造。其中,390Ma 和176Ma 分别与古生代(393 ±7Ma)岩浆热事件和角闪岩相退变质作用有关(Liu et al.,2009,2013b)。而且,不同类型前寒武纪下地壳包体岩石类似于前文所述的五河杂岩,也表现为两类高、低放射成因Pb 同位素组成(Xu et al.,2009;Wang et al.,2012;刘贻灿和王安东,2012),其高放射成因Pb 同位素成分同样与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用有关(刘贻灿等,2015),这也与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代证据以及元素地球化学特点(Liu et al.,2013b,及未发表资料)相吻合。
因此,华北东南缘前寒武纪变质岩涉及到不同形成时代和多种成因以及多阶段演化与改造,包括2.7 ~2.8Ga 的镁铁质和中酸性岩浆成因,但是其中主要还是与2.5 ~2.6Ga和~2.1Ga 两期与大洋板块俯冲有关的岛弧岩浆作用及弧后盆地火山-沉积作用有关,而且,经历了1.8 ~1.9Ga 高压麻粒岩相变质作用以及390Ma 和176Ma 的变质改造或热事件的影响。研究区前寒武纪下地壳岩石中的高放射成因Pb同位素成分的成因可能与含碳酸盐的熔/流体交代作用有关。
5.2 时代
最早,邢凤鸣和任思明(1984)根据含铁变质岩系的Rb-Sr 全岩等时线年龄,认为“霍邱群”的形成时代为2.75Ga。同时,营俊龙等(1984)根据变质岩的锆石U-Pb 和全岩的Rb-Sr 定年结果,认为“霍邱群”的形成时代为2.7 ~2.8Ga;而角闪石和黑云母的K-Ar 年龄为~1.75Ga,指示变质时代。之后,涂萌玖(1994)根据五河杂岩中TTG 片麻岩的单颗粒锆石逐层蒸发法获得的U-Pb 年龄为2.41 ~2.46Ga,并解释为形成时代;庄子里、磨盘山和石门山一带变形的变质钾长花岗岩的形成时代为~2.1Ga(Guo and Li,2009;杨德彬等,2009),而沿面理分布的白云母的Ar-Ar 年龄为1734 ±3Ma并被解释为韧性变形时代(徐祥等,2005);许文良等(2006)根据蚌埠隆起区独山石榴斜长辉石岩中锆石LA-ICPMS UPb 年龄为1833 ±8Ma,认为五河杂岩的形成时代为古元古代;Liu et al. (2009)对凤阳石榴斜长角闪岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 定年和矿物包体研究表明,高压麻粒岩相变质时代为1839 ±31Ma,然而,其锆石的Hf 模式年龄为2137 ±31Ma 以及εHf(t)为正值(Liu et al.,2013b)。Wan et al. (2010)根据锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 定年结果,认为“霍邱群”的形成时代为2.75 ~1.84Ga(包括2.75 和2.56Ga 形成的花岗岩类)并经历了~1.84Ga 的构造热事件和变质作用;杨晓勇等(2012)根据“霍邱群”中斜长角闪岩的锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年结果,认为其形成时代为~2.8Ga;Wang et al.(2014)认为霍邱杂岩中存在三期太古代的岩浆事件即~3.02Ga、~2.77Ga 和~2.71Ga,也就是说至少包括三种原岩为太古代形成的变质火成岩,而且,眼球状钾长花岗岩中3262 ±35Ma(上交点年龄)继承锆石可能指示霍邱地区存在更早期的古太古代结晶基底。作者等的最新研究表明,五河杂岩中花岗片麻岩的最老原岩形成时代为2.83Ga。Xu et al. (2004,2006)、Liu et al. (2009,2013b)和Wang et al. (2012)根据夹沟中生代闪长斑岩中大量下地壳和地幔包体的岩石学和锆石U-Pb 年代学研究表明,前寒武纪下地壳包体至少包括形成时代为2.5 ~2.6Ga 和~2.1Ga 两类并分别经历了2.48~2.49Ga、~2.1Ga 和1.8 ~1.83Ga 麻粒岩相变质作用。

图7 华北东南缘前寒武纪变质岩和花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄累计曲线统计数据来自文献Xu et al. (2006)、Guo and Li (2009)、Liu et al. (2009,2013b,2014b)、Wang et al. (2012,2013a)和杨晓勇等(2012),其中红色曲线代表岩浆锆石年龄,黑色曲线代表变质锆石年龄Fig.7 Accumulative curves of zircon U-Pb ages for the Precambrian metamorphic rocks and granites in the southeastern margin of the North China Block
根据锆石阴极发光图像可以看出,华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳包体岩石经历了复杂的岩浆热事件和多期变质作用,大多数锆石显示核-幔-边结构,包括典型的岩浆锆石核和具有石榴子石+单斜辉石+金红石+斜长石等高压麻粒岩相矿物组合的1.8 ~1.9Ga 变质锆石(Liu et al.,2009,2013b)以及具有高的(>800℃)Ti 温度的2.48 ~2.49Ga 麻粒岩相变质锆石(Wang et al.,2012)。综合不同类型前寒武纪变质岩和花岗岩的锆石U-Pb 年龄结果统计显示(图7),研究区前寒武纪下地壳经历了多期构造-热事件和多阶段变质演化,至少包括2.7 ~2.8Ga、2.5 ~2.6Ga、2.1Ga、1.92Ga、1.82Ga 的岩浆热事件以及2.5Ga、2.1Ga、1.84Ga、390Ma 和176Ma 的变质事件。其中,强烈的1.83 ~1.85Ga 高压麻粒岩相变质作用可能是由于~1.9Ga 幔源岩浆底侵于下地壳底部而导致大规模地壳加热和增厚引起的,这也与该时期华北克拉通存在广泛的伸展、裂解(rifting)以及相关的镁铁质岩浆侵位等相吻合(Zhai et al.,2000;Hou et al.,2006,2008;Peng et al.,2008;Liu et al.,2009,2013b)。至于该期麻粒岩相变质作用是否与古元古代碰撞造山作用有关(Zhao et al.,2001,2012;Luo et al.,2004;Li and Zhao,2007;Zhao and Zhai,2013),还有待于详细的岩石学和P-T轨迹研究而给予查明。但是,无论何种成因机制,也许正是由于1.83 ~1.85Ga 高温(-超高温?)高压麻粒岩相变质作用,引起部分熔融和混合岩化作用(图3a;及前文所述),并形成了~1.82Ga 的花岗岩(Liu et al.,2014b)。
6 前寒武纪下地壳的幕式生长
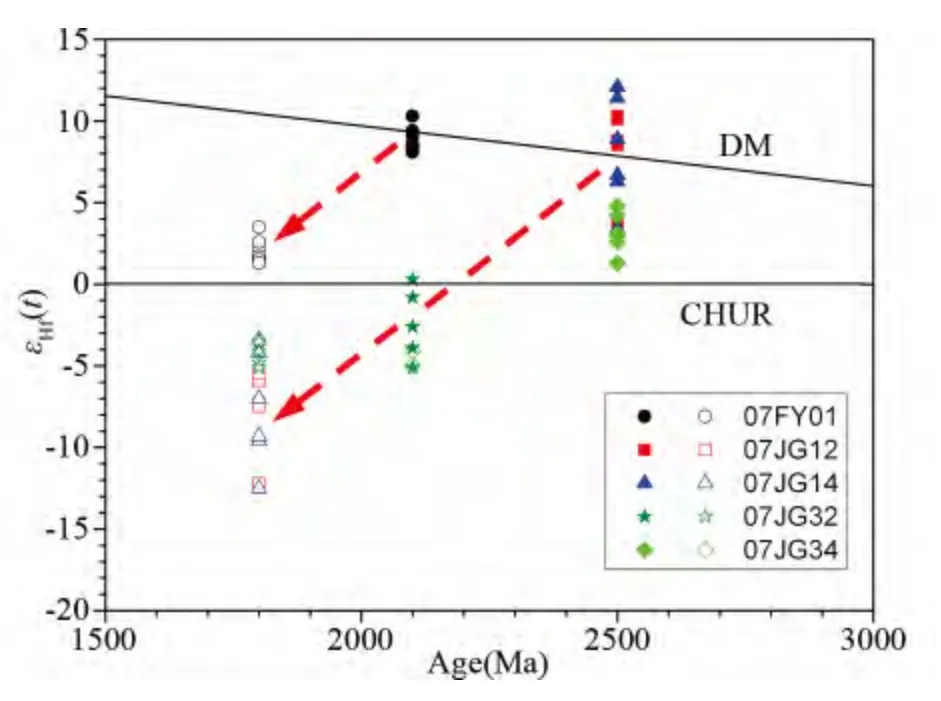
图8 华北陆块东南缘前寒武纪下地壳岩石的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 年龄和εHf(t)值(据Liu et al.,2013b)DM 和CHUR 分别代表亏损地幔和球粒陨石. 实心和空心符号分别代表不同样品所对应的原岩和变质时代的εHf(t)值Fig.8 The relationship between SHRIMP U-Pb ages and εHf(t)values for the igneous core and metamorphic rim of zircons as identified by the cathodoluminescene (CL)images for the Precambrian lower-crustal rocks from the southeastern margin of the North China Block (after Liu et al.,2013b)
锆石的U-Pb 年龄和Hf 同位素分析统计结果(图8)表明,研究区前寒武纪下地壳经历了2.5Ga 和2.1Ga 的岩浆-热事件。鉴于这两期岩浆锆石的εHf(t)值中有明显的正值(+ 5 ~ + 12)以及Hf 模式年龄分别为2.7 ~2.8Ga 和~2.5Ga,反映它们的原岩来自于新生地壳,结合其原岩性质和地球化学特点,指示它们的岩石成因与两期俯冲增生事件有关,而且大多数都经历了1.83 ~1.85Ga 高压麻粒岩相变质作用(Liu et al.,2009,2013b)。因此,前寒武纪下地壳的形成时间≥2.1Ga,而1.8 ~1.9Ga 代表了一期垂向地壳增生时间,可能与哥伦比亚超大陆裂解引起的地幔柱活动有关(Liu et al.,2009,2013b;Zhai and Santosh,2011)。此外,夹沟下地壳包体中2.7 ~2.8Ga 的继承锆石U-Pb 年龄(Wang et al.,2012;Liu et al.,2013b)、霍邱BIF 铁矿建造中2.7 ~2.9Ga 的碎屑锆石年龄(Liu and Yang,2015)以及来自霍邱杂岩中有形成时代为2.7 ~2.8Ga、锆石Hf 模式年龄为~3.0Ga 和εHf(t)值中有+4 ~+6 的斜长角闪岩(Wan et al.,2010;杨晓勇等,2012)和石榴黑云斜长片麻岩(Wang et al.,2014),而且,霍邱杂岩中还存在原岩形成时代为2.7 ~2.8Ga 的变质花岗岩类岩石(Wan et al.,2010;Wang et al.,2014),结合作者等近期获得的五河杂岩中花岗片麻岩锆石U-Pb 年龄(形成时代为2.83Ga),因此,这些资料都暗示研究区还存在2.7 ~2.8Ga 的地壳生长时期,这也是前人认为的华北陆块重要地壳生长时期(见前文)。因此,华北东南缘前寒武纪下地壳经历了幕式地壳生长(刘贻灿和王安东,2012;Liu et al.,2013b),这可能与其早前寒武纪一直位于华北陆块的边缘有关。
7 存在的问题与展望
华北陆块东南缘前寒武纪下地壳的形成与变质演化过程方面的研究,尚存在一些分歧与问题,有待于进一步解决或查明的一些关键科学问题列举如下:
(1)前寒武纪变质基底岩石的深熔/部分熔融作用期次及其时代与地球化学和岩石学效应?
尽管已发现前寒武纪变质基底岩石中存在部分熔融作用的岩相学证据,但是,部分熔融的发生时代和条件以及效应方面,尚需要锆石学、变质岩石学和地球化学等方面的综合研究与查明。而且,如果发生了部分熔融作用,往往在锆石上都有不同程度的记录和表现(包括年龄、阴极发光图像和微量元素等)(如,刘福来等,2012)。
(2)不同地点花岗片麻岩或TTG 片麻岩是否具有相同的时代和成因以及它们与古元古代片麻状钾长花岗岩的成因联系又如何?
TTG(Tonalite-Trondhjemite-Granodiorite)片麻岩是前寒武纪变质地体或下地壳包体中常见的岩石类型,通常被认为是由玄武质下地壳岩石部分熔融形成的(Reichardt and Weinberg,2012,及所引参考文献)。蚌埠、凤阳及五河一带零星出露有不同类型的TTG 片麻岩,那么,这些不同地点片麻岩是否都是晚太古代形成、还是古元古代形成的?如果有不同形成时代的花岗片麻岩(原岩为花岗岩类),结合岩石学研究,将有助于确定部分熔融作用的期次与条件,进而查明这些花岗片麻岩与古元古代片麻状钾长花岗岩(图1)的成因联系。
(3)华北东南缘古元古代高压麻粒岩相变质作用的地球动力学背景?以及前寒武纪下地壳岩石是否发生过超高温变质作用?
华北东南缘古元古代高压麻粒岩相变质作用的地球动力学背景,也就是说是与大陆裂解引起的幔源岩浆作用有关、还是与碰撞造山有关,需要深入的变质岩石学方面研究而予以查明。该问题的探明,将有助于问题(6)的解决。此外,根据前寒武纪下地壳捕虏体岩石中发现的石榴子石中针状金红石出溶体以及变基性岩中变质锆石特点以及不同类型岩石中存在的部分熔融与混合岩化证据(图3a)(刘贻灿等,2015)等(见前文),推断研究区发生过超高温变质作用,但是,仍需要更多的岩石学证据(特别是寻找典型的超高温矿物组合)和P-T 条件等方面来限定。
(4)霍邱杂岩的最高变质作用是高压麻粒岩相、还是高角闪岩相?以及变质演化过程?
霍邱杂岩的变质岩石学方面研究,目前还很少有文章涉及,尚需进一步深入研究与探讨,以查明其峰期变质条件与最高变质作用及P-T-t 轨迹。
(5)五河杂岩的岩石组成和确切形成时代及其形成和演化过程?
正如前文所述,五河杂岩的岩石类型比较复杂,除了大量变基性岩外,还存在TTG 花岗片麻岩和大理岩等变质表壳岩系,那么,它们的形成时代以及变质演化过程(包括P-T-t轨迹),都是前期未解决的科学问题。
(6)霍邱杂岩和五河杂岩与胶-辽-吉古元古代构造带的关系如何?
霍邱杂岩和五河杂岩是否属于“胶-辽-吉古元古代构造带”(Zhao et al.,2001,2012;Luo et al.,2004;Li and Zhao,2007;Zhao and Zhai,2013;Liu et al.,2014a),主要还是取决于霍邱杂岩和五河杂岩的变质P-T-t 轨迹的构建以及不同变质岩的原岩性质和成因的查明。其中,关键是查明二者是否具有类似的P-T-t 轨迹,以及华北东南缘前寒武纪变质岩是否经历了古元古代高压麻粒岩相峰期变质之后的等温减压过程。
上述问题的存在,显然与该区研究程度较低有关,它们的进一步系统研究与解决,除了涉及前寒武纪下地壳变质岩的原岩性质、岩石成因与具体变质演化过程的确定外,还将有助于查明研究区板块构造作用的最早发生时代与特点。因此,为了更好地理解华北陆块东南缘前寒武纪下地壳的形成和演化过程,以及前寒武纪变质作用和部分熔融过程中的元素和同位素行为,拟开展变质岩石学、岩石地球化学和同位素年代学等方面综合研究。在岩石学研究方面,除了采用常规的方法外,还需要应用现代岩石学分析方法,包括相平衡和P-T 视剖面图(P-T pseudosection)以及锆石中Ti 和金红石中Zr 温度计等方法来限定不同变质阶段的P-T 条件;在年代学方面,因前寒武纪变质岩的多阶段演化与多期改造的复杂性,重点需要加强锆石学及U-Pb 年代学方面研究,对于不同成因、不同阶段形成的变质锆石以及与部分熔融作用有关的锆石,还需要结合其中矿物包裹体成分以及锆石微量元素分析来帮助查明岩石的年代学意义;在元素和同位素地球化学方面,除了常规的元素分析外,还需要开展Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-Mg-Fe 等同位素分析,以便联合示踪与查明岩石成因以及不同变质条件下的元素和同位素行为。
致谢 感谢两位匿名审稿人提出的建设性修改意见!
Ague JJ,Eckert JO Jr,Chu X,Baxter EF and Chamberlain CP. 2013.Discovery of ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in the Acadian orogen,Connecticut,USA. Geology,41(2):271 -274
Amelin Y,Lee DC and Halliday AN. 2000. Early-Middle Archaean crustal evolution deduced from Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotopic studies of single zircon grains. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,64(24):4205 -4225
Andersen T,Griffin WL and Pearson NJ. 2002. Crustal evolution in the SW part of the Baltic Shield:The Hf isotope evidence. Journal of Petrology,43(9):1725 -1747
Bartoli O,Tajcˇmanová L,Cesare B and Acosta-Vigil A. 2013. Phase equilibria constraints on melting of stromatic migmatites from Ronda(S. Spain):Insights on the formation of peritectic garnet. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,31(7):775 -789
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Anhui Province. 1987.Regional Geology of Anhui Province. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1 -721 (in Chinese)
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Anhui Province. 1997.Stratigraphy (Lithostratic) of Anhui Province. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences Press,1 -271 (in Chinese)
Cesare B,Ferrero S,Salvioli-Mariani E,Pedron D and Cavallo A. 2009.“Nanogranite” and glassy inclusions: The anatectic melt in migmatites and granulites. Geology,37(7):627 -630
Cherniak DJ and Watson EB. 2003. Diffusion in zircon. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,53(1):113 -143
Coleman RG. 1977. Ophiolites, Minerals and Rocks. Berlin/Heidelberg,Germany:Springer-Verlag
Condie KC. 1998. Episodic continental growth and supercontinents:A mantle avalanche connection?Earth and Planetary Science Letters,163(1 -4):97 -108
Condie KC. 2000. Episodic continental growth models:After thoughts and extensions. Tectonophysics,322(1 -2):153 -162
Condie KC,Beyer EE,Belousova E,Griffin WL and O’Reillyal SY.2005. U-Pb isotopic ages and Hf isotopic composition of single zircons:The search for juvenile Precambrian continental crust.Precambrian Research,139(1):42 -100
Condie KC,Bickford ME,Aster RC,Belousova E and Scholl DW.2011. Episodic zircon ages,Hf isotopic composition,and the preservation rate of continental crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin,123(5 -6):951 -957
Corfu G,Hancher JM,Hoskin PWO and Kinny P. 2003. Altas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,53(1):469-500
Davis WJ,Canil D,MacKenzie JM and Carbno GB. 2003. Petrology and U-Pb geochronology of lower crustal xenoliths and the development of a craton,Slave Province,Canada. Lithos,71(2 -4):541 -573
De Roever EWF,Lafon JM,Delor C,Cocherie A,Rossi P,Guerrrot C and Potrel A. 2003. The Bakhuis ultrahigh-temperature granulite belt (Suriname):I. Petrological and geochronological evidence for a counterclockwise P-T path at 2. 07 ~2. 05Ga. Géollogie de la France,2-3-4:175 -205
Dewey JF and Windley BF. 1981. Growth and differentiation of the continental crust. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London,Series A,301(1461):189 -206
Diwu CR,Sun Y,Guo AL,Wang HL and Liu XM. 2011. Crustal growth in the North China Craton at ~2.5Ga:Evidence from in situ zircon U-Pb ages,Hf isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry of the Dengfeng complex. Gondwana Research,20(1):149 -170
Ferrando S,Frezzotti ML,Orione P,Conte RC and Compagnoni R.2010. Late-Alpine rodingitization in the Bellecombe meta-ophiolites(Aosta Valley,Italian Western Alps):Evidence from mineral assemblages and serpentinization-derived H2-bearing brine.International Geology Review,52(10 -12):1220 -1243
Ferrero S,Bartoli O,Cesare B,Salviol-Mariani E,Acosta-Vigil A,Cavallo A,Groppo C and Battiston S. 2012. Microstructures of melt inclusions in anatectic metasedimentary rocks. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,30(3):303 -322
Frost BR and Chacko T. 1989. The granulite uncertainty principle:Limitations on thermobarometry in granulites. The Journal of Geology,97(4):435 -450
Gebauer D,Schertl HP,Brix M and Schreyer W. 1997. 35Ma old ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and evidence for very rapid exhumation in the Dora Maira Massif,Western Alps. Lithos,41(1-3):5 -24
Gerdes A and Zeh A. 2009. Zircon formation versus zircon alteration:New insights from combined U-Pb and Lu-Hf in-situ LA-ICP-MS analyses,and consequences for the interpretation of Archean zircon from the Central Zone of the Limpopo Belt. Chemical Geology,261(3 -4):230 -243
Gou LL,Zhang CL,Zhang LF and Wang Q. 2014. Precipitation of rutile needles in garnet from sillimanite-bearing pelitic granulite from the Khondalite Belt,North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin,59(32):4359 -4366
Griffin WL,Peason NJ,Belousova E,Jackson SE,van Achterbergh E,O’Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,64(1):133 -147
Griffin WL,Belousova EA,Shee SR,Pearson NJ and O’Reilly SY.2004. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton:UPb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons. Precambrian Research,131(3 -4):231 -282
Groppo C,Rolfo F and Indares A. 2012. Partial melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines of Eastern Nepal:The effect of decompression and implications for the‘channel flow’model. Journal of Petrology,53(5):1057 -1088
Guo JH,O’Brien PJ and Zhai MG. 2002. High-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area,North China Craton:Metamorphic evolution,P-T paths and geotectonic significance. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,20(8):741 -756
Guo JH,Sun M,Chen FK and Zhai MG. 2005. Sm-Nd and SHRIMP UPb zircon geochronology of high-pressure granulites in the Sanggan area,North China Craton:Timing of Paleoproterozoic continental collision. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,24(5):629 -642
Guo SS and Li SG. 2009. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages for the Paleoproterozoic metamorphic-magmatic events in the southeast margin of the North China Craton. Science in China (Series D),52(8):1039 -1045
Harley SL. 1989. The origins of granulites:A metamorphic perspective.Geological Magazine,126(3):215 -247
Hawkesworth CJ and Kemp AIS. 2006. Using hafnium and oxygen isotopes in zircons to unravel the record of crustal evolution.Chemical Geology,226(3 -4):144 -162
Hermann J,Rubatto D,Korsakov A and Shatsky VS. 2001. Multiple zircon growth during fast exhumation of diamondiferous,deeply subducted continental crust (Kokchetav massif,Kazakhstan).Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,141(1):66 -82
Hermann J and Rubatto D. 2003. Relating zircon and monazite domains to garnet growth zones:Age and duration of granulite facies metamorphism in the Val Malenco lower crust. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(9):833 -852
Holness MB and Sawyer EW. 2008. On the pseudomorphing of melt-filled pores during the crystallization of migmatites. Journal of Petrology,49(7):1343 -1363
Hou GT,Liu YL and Li JH. 2006. Evidence for 1.8Ga extension of the Eastern Block of the North China Craton from SHRIMP U-Pb dating of mafic dyke swarms in Shandong Province. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,27(4):392 -401
Hou GT,Li JH,Yang MH,Yao WH,Wang CC and Wang YX. 2008.Geochemical constraints on the tectonic environment of the Late Paleoproterozoic mafic dyke swarms in the North China Craton.Gondwana Research,13(1):103 -116
Iizuka T,Hirata T,Komiya T,Rino S,Katayama I,Motoki A and Maruyama S. 2005. U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotope systematics of zircons from the Mississippi River sand:Implications for reworking and growth of continental crust. Geology,33(6):485 -488
Jahn BM,Vidal P and Kröner A. 1984. Multi-chronometric ages and origin of Archaean tonalitic gneisses in Finnish Lapland:A case for long crustal residence time. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,86(4):398 -408
Jahn BM,Liu DY,Wan YS,Song B and Wu JS. 2008. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula,China,as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology,elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry.American Journal of Science,308(3):232 -269
Jiang N,Guo JH,Zhai MG and Zhang SQ. 2010. ~2.7Ga crust growth in the North China craton. Precambrian Research,179(1 -4):37-49
Jiang N,Guo JH and Chang GH. 2013. Nature and evolution of the lower crust in the eastern North China craton:A review. Earth-Science Reviews,122:1 -9
Kemp AIS,Foster GL,Scherstén A,Whitehouse MJ,Darling J and Storey C. 2009. Concurrent Pb-Hf isotope analysis of zircon by laser ablation multi-collector ICP-MS,with implications for the crustal evolution of Greenland and the Himalayas. Chemical Geology,261(3 -4):244 -260
Klavera M,De Roever EWF,Nanne JAM,Mason PRD and Davies GR.2015. Charnockites and UHT metamorphism in the Bakhuis Granulite Belt,western Suriname:Evidence for two separate UHT events. Precambrian Research,262:1 -19
Kotková J and Harley SL. 2010. Anatexis during high-pressure crustal metamorphism:Evidence from garnet-whole-rock REE relationships and zircon-rutile Ti-Zr thermometry in leucogranulites from the Bohemian Massif. Journal of Petrology,51(10):1967 -2001
Kröner A,Wilde SA,Li JH and Wang KY. 2005. Age and evolution of a Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic upper to lower crustal section in the Wutaishan/Hengshan/Fuping terrain of northern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,24(5):577 -595
Kusky TM and Li JH. 2003. Paleoproterozoic tectonic evolution of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,22(4):383-397
Li SG,Wang SJ,Guo SS,Xiao YL,Liu YC,Liu SA,He YS and Liu JL. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of leucogranites from the southeast margin of the North China Block:Origin and migration.Gondwana Research,26(3 -4):1111 -1128
Li SZ and Zhao GC. 2007. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Liaoji granitoids:Constraints on the evolution of the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji belt in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,158(1 -2):1 -16
Li SZ,Zhao GC,Santosh M,Liu X,Dai LM,Suo YH,Song MC and Wang PC. 2012. Paleoproterozoic structural evolution of the southern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton. Precambrian Research,200 -203:59 -73
Li XP,Rahn M and Bucher K. 2004. Metamorphic processes in rodingites of the Zermatt-Saas ophiolites. International Geology Review,46(1):28 -51
Liu DY,Nutman AP,Compston W,Wu JS and Shen QH. 1992.Remnants of 3800Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology,20(4):339 -342
Liu F,Guo JH,Peng P and Qian Q. 2012a. Zircon U-Pb ages and geochemistry of the Huai’an TTG gneisses terrane:Petrogenesis and implications for ~2.5Ga crustal growth in the North China Craton.Precambrian Research,212 -213:225 -244
Liu FL,Gerdes A,Liou JG,Xue HM and Liang FH. 2006. SHRIMP UPb zircon dating from Sulu-Dabie dolomitic marble,eastern China:Constraints on prograde, ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,24(7):569-589
Liu FL,Liu PH,Ding ZJ,Liu JH,Yang H and Hu WH. 2012. Genetic mechanism of granitic leucosome within high-pressure granulite from the Early Precambrian metamorphic basement of Shandong Peninsula,SE North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(9):2686 -2696 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu FL,Wang F,Liou JG,Meng E,Liu JH,Yang H,Xiao LL,Cai J and Shi JR. 2014a. Mid-Late Triassic metamorphic event for Changhai meta-sedimentary rocks from the SE Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt,North China Craton:Evidence from monazite U-Th-Pb and muscovite Ar-Ar dating. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,94:205 -225
Liu JH,Liu FL,Ding ZJ,Liu CH,Yang H,Liu PH,Wang F and Meng E. 2013a. The growth,reworking and metamorphism of Early Precambrian crust in the Jiaobei terrane,the North China Craton:Constraints from U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics,and REE concentrations of zircon from Archean granitoid gneisses.Precambrian Research,224:287 -303
Liu L and Yang XY. 2013. Geochemical characteristics of the Huoqiu BIF ore deposit in Anhui Province and their metallogenic significance:Taking the Bantaizi and Zhouyoufang deposits as examples. Acta Petrologica Sinica,29 (7):2551 - 2566 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu L,Yang XY,Santosh M and Aulbach S. 2014b. Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic continental growth in the southeastern margin of the North China Craton:Geochemical,zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope evidence from the Huoqiu complex. Gondwana Research,doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.08.011
Liu L and Yang XY. 2015. Temporal,environmental and tectonic significance of the Huoqiu BIF,southeastern North China Craton:Geochemical and geochronological constraints. Precambrian Research,261:217 -233
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F and Liu JH. 2010. Genetic mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of mafic high-pressure (HP)granulites from the Shandong Peninsula,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,26(7):2039 -2056 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu PH,Liu FL,Wang F,Liu JH,Yang H and Shi JR. 2012.Geochemical characteristics and genesis of the high-pressure mafic granulite in the Jiaobei high-grade metamorphic basement,eastern Shandong,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(9):2705 - 2720(in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu SA,Li SG,Guo SS,Hou ZH and He YS. 2012b. The Cretaceous adakitic-basaltic-granitic magma sequence on south-eastern margin of the North China Craton:Implications for lithospheric thinning mechanism. Lithos,134 -135:163 -178
Liu SW,Santosh M,Wang W,Bai X and Yang PT. 2011a. Zircon U-Pb chronology of the Jianping Complex:Implications for the Precambrian crustal evolution history of the northern margin of North China Craton. Gondwana Research,20(1):48 -63
Liu WJ,Zhai MG and Li YG. 1998. Metamorphism of the high-pressure basic granulites in Laixi,eastern Shandong,China. Acta Petrologica Sinica,14(4):449 -459 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu Y and Zhong D. 1997. Petrology of high-pressure granulites from the eastern Himalayan syntaxis. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,15(4):451 -466
Liu YC,Wang AD,Rolfo F,Groppo C,Gu XF and Song B. 2009.Geochronological and petrological constraints on Palaeoproterozoic granulite facies metamorphism in southeastern margin of the North China Craton. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,27(2):125 -138
Liu YC,Gu XF,Li SG,Hou ZH and Song B. 2011b. Multistage metamorphic events in granulitized eclogites from the North Dabie complex zone,central China:Evidence from zircon U-Pb age,trace element and mineral inclusion. Lithos,122(1 -2):107 -121
Liu YC and Wang AD. 2012. Episodic growth and multiple modification of Precambrian lower crust in the southeastern margin of the North China China Craton:Petrologic,geochronological and Hf-isotope evidences. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,34(4):1 -11 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu YC,Wang AD,Li SG,Rolfo F,Li Y,Groppo C,Gu XF and Hou ZH. 2013b. Composition and geochronology of the deep-seated xenoliths from the southeastern margin of the North China Craton.Gondwana Research,23(3):1021 -1039
Liu YC,Deng LP,Gu XF,Groppo C and Rolfo F. 2015. Application of Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers to constrain hightemperature metamorphism in eclogites from the Dabie orogen,central China. Gondwana Research,27(1):410 -423
Liu YC,Wang CC,Zhang PG,Groppo C,Rolfo F and Wang AD. 2015.Granulite facies metamorphism,partial melting and metasomatism in the Wuhe Complex at the southeastern margin of the North China Block. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,37(1):1 -11(in Chinese with English abstract)
Lu SN,Zhao GC,Wang HC and Hao GJ. 2008. Precambrian metamorphic basement and sedimentary cover of the North China Craton:A review. Precambrian Research,160(1 -2):77 -93
Luo Y,Sun M,Zhao GC,Li SZ,Xu P,Ye K and Xia XP. 2004. LAICP-MS U-Pb zircon ages of the Liaohe Group in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton:Constraints on the evolution of the Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt. Precambrian Research,134(3 -4):349 -371
McCulloch MT and Bennett VC. 1994. Progressive growth of the Earth’s continental crust and depleted mantle:Geochemical constraints.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,58(21):4717 -4738
Mclennan SM and Taylor SR. 1982. Geochemical constraints on the growth of the continental crust. The Journal of Geology,90(4):347-361
Möller A,O’Brien PJ,Kennedy A and Kröner A. 2002. Polyphase zircon in ultrahigh-temperature granulites (Rogaland,SW Norway):Constraints for Pb diffusion in zircon. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,20(8):727 -740
O’Brien PJ and Rötzler J. 2003. High-pressure granulites:Formation,recovery of peak conditions and implications for tectonics. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(1):3 -20
Othman DB,White WM and Patchett J. 1989. The geochemistry of marine sediments,island arc magma genesis,and crust-mantle recycling. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,94(1 -2):1 -21
Pattison DRM. 2003. Petrogenetic significance of orthopyroxene-free garnet+clinopyroxene+plagioclase±quartz-bearing metabasites with respect to the amphibolite and granulite facies. Journal of Metamorphic Geology,21(1):21 -34
Pattison DRM,Chacko T,Farquhar J and Mcfarlane CRM. 2003.Temperatures of granulite-facies metamorphism:Constraints from experimental phase equilibria and thermobarometry corrected for retrograde exchange. Journal of Petrology,44(5):867 -900
Peng P,Zhai MG,Zhang HF and Guo JH. 2005. Geochronological constraints on the Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:SHRIMP zircon ages of different types of mafic dikes.International Geology Review,47(5):492 -508
Peng P,Zhai MG,Ernst RE,Guo JH,Liu F and Hu B. 2008. A 1.78Ga large igneous province in the North China craton:The Xiong’er volcanic province and the North China dyke swarm.Lithos,101(3 -4):260 -280
Reichardt H and Weinberg RF. 2012. Hornblende chemistry in meta-and diatexites and its retention in the source of leucogranites:An example from the Karakoram shear zone,NW India. Journal of Petrology,53(6):1287 -1318
Rogers JJW and Santosh M. 2003. Supercontinents in Earth history.Gondwana Research,6(3):357 -368
Rubatto D,Williams IS and Buick IS. 2001. Zircon and monazite response to prograde metamorphism in the Reynolds Range,central Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,140(4):458-468
Rudnick RL. 1995. Making continental crust. Nature,378(6557):571-578
Sawyer EW,Cesare B and Brown M. 2011. When the continental crust melts. Elements,7(4):229 -234
Spear FS and Florence FP. 1992. Thermobarometry in granulites:Pitfalls and new approaches. Precambrian Research,55(1 -4):209 -241
Tam PK,Zhao GC,Liu FL,Zhou XW,Sun M and Li SZ. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt:New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites,gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research,19(1):150 -162
Tang J,Zheng YF,Wu YB,Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane:Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research,152(1 -2):48 -82
Taylor SR and McLennan SM. 1985. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution. London: Blackwell Scientific Publications,1 -312
Tu XL,Zhu BQ,Fan SK and Hu AQ. 1993. Pb isotopes of the granulites from the North China and the comparison with other places over the world. Science in China (Series B),23(5):537 - 544 (in Chinese)
Tu YJ. 1994. On the Late Archean TTG-gneiss in the northern Jianghuai area. Geology of Anhui,4(4):15 -23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Vernon RH and Collins WJ. 1988. Igneous microstructures in migmatites. Geology,16(12):1126 -1129
Vervoort JD and Blichert-Toft J. 1999. Evolution of the depleted mantle:Hf isotope evidence from juvenile rocks through time. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,63(3 -4):533 -556
Wan YS,Wilde SA,Liu DY,Yang CX,Song B and Yin XY. 2006.Further evidence for ~1.85Ga metamorphism in the Central Zone of the North China Craton:SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from metamorphic rocks in the Lushan area,Henan Province. Gondwana Research,9(1 -2):189 -197
Wan YS,Dong CY,Wang W,Xie HQ and Liu DY. 2010. Archean basement and a Paleoproterozoic collision orogen in the Huoqiu area at the Southeastern margin of North China Craton:Evidence from sensitive high resolution Ion Micro-Probe U-Pb zircon geochronology.Acta Geologica Sinica,84(1):91 -104
Wan YS,Liu DY,Wang SJ,Yang EX,Wang W,Dong CY,Zhou HY,Du LL,Yang YH and Diwu CR. 2011. ~2.7Ga juvenile crust formation in the North China Craton (Taishan-Xintai area,western Shandong Province):Further evidence of an understated event from U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic composition of zircon. Precambrian Research,186(1 -4):169 -180
Wan YS,Xu ZY,Dong CY,Nutman AP,Ma MZ,Xie HQ,Liu SJ,Liu DY,Wang HC and Cu H. 2013. Episodic Paleoproterozoic(~2.45,~1.95 and ~1.85Ga)mafic magmatism and associated high temperature metamorphism in the Daqingshan area,North China Craton:SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating and whole-rock geochemistry.Precambrian Research,224:71 -93
Wang AD,Liu YC,Gu XF,Li SG and Xie HQ. 2009. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating for garnet-bearing gneissic granite at Laoshan,Bengbu:Implications for recycling of the subducted continental crust of the South China Block. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,29(2):38-43 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang AD,Liu YC,Gu XF,Hou ZH and Song B. 2012. Late-Neoarchean magmatism and metamorphism at the southeastern margin of the North China Craton and their tectonic implications.Precambrian Research,220 -221:65 -79
Wang AD,Liu YC,Santosh M and Gu XF. 2013a. Zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes from the metamorphic basement in the Wuhe Complex:Implications for Neoarchean active continental margin along the southeastern North China Craton and constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids. Geoscience Frontiers,4(1):57 -71
Wang J,Sheng Y,Pu XP,Kang T and Shi YH. 2014. The investigation on metamorphic petrology and P-T conditions of Wuhe complex rocks:Evidences from drill ZK02 in the South of Mengcheng area.Chinese Journal of Geology,49(2):556 -575 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang QY,Zheng JP,Pan YM,Dong YJ,Liao FX,Zhang Y,Zhang L,Zhao G and Tu ZB. 2014. Archean crustal evolution in the southeastern North China Craton:New data from the Huoqiu Complex. Precambrian Research,255(Part 1):294 -315
Wang SJ,Li SG and Liu SA. 2013b. The origin and evolution of lowδ18O magma recorded by multi-growth zircons in granite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,373:233 -241
Weber MBI,Tarney J,Kempton PD and Kent RW. 2002. Crustal makeup of the northern Andes,evidence based on deep crustal xenolith suites,Mercaderes,SW Colombia. Tectonophysics,345(1):49-82
Wilde SA,Zhao GC and Sun M. 2002. Development of the North China Craton during the Late Archaean and its final amalgamation at 1.8Ga: Some speculations on its position within a global Palaeoproterozoic supercontinent. Gondwana Research,5(1):85 -94
Wilde SA and Zhao GC. 2005. Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,24(5):519 -522
Windley BF. 1973. Crustal development in the Precambrian.Philosophical Transactions Royal Society of London A,273(1235):421 -441
Woodhead J,Hergt J,Shelley M,Eggins S and Kemp R. 2004. Zircon Hf-isotope analysis with an excimer laser,depth profiling,ablation of complex geometries,and concomitant age estimation. Chemical Geology,209(1 -2):121 -135
Wu FY,Yang YH,Xie LW,Yang JH and Xu P. 2006. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology,234(1 -2):105 -126
Wu FY,Zhang YB,Yang JH,Xie LW and Yang YH. 2008. Zircon UPb and Hf isotopic constraints on the Early Archean crustal evolution in Anshan of the North China Craton. Precambrian Research,167(3):339 -362
Xing FM and Ren SM. 1984. The preliminary study on origin of the banded and striped silico-iron formation of Houqiu Group in western Anhui. Acta Geologica Sinica,58(1):35 -48 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu WL,Wang DY,Liu XC,Wang QH and Lin JQ. 2002. Discovery of eclogite inclusions and its geological significance in Early Jurassic intrusive complex in Xuzhou-northern Anhui, eastern China.Chinese Science Bulletin,47(14):1212 -1216
Xu WL,Wang QH,Liu XC,Wang DY and Guo JH. 2004. Chronology and sources of Mesozoic intrusive complexes in the Xuzhou-Huainan region,central China:Constraints from SHRIMP U-Pb dating. Acta Geologica Sinica,78(1):96 -106
Xu WL,Wang QH,Yang DB,Liu XC and Guo JH. 2005. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating in Jingshan“migmatitic granite”,Bengbu and its geological significance. Science in China (Series D),48(2):185-191
Xu WL,Gao S,Wang QH,Wang DY and Liu YS. 2006. Mesozoic crustal thickening of the eastern North China craton:Evidence from eclogite xenoliths and petrologic implications. Geology,34(9):721-724
Xu WL,Yang DB,Pei FP,Yang CH,Liu XM and Hu ZC. 2006. Age of the Wuhe complex in the Bengbu uplift:Evidence from LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating. Geology in China,33(1):132 -137 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu WL,Gao S,Yang DB,Pei FP and Wang QH. 2009. Geochemistry of eclogite xenoliths in Mesozoic adakitic rocks from Xuzhou-Suzhou area in central China and their tectonic implications. Lithos,107(3-4):269 -280
Xu X,Hou MJ,Qiu RL,Wu LB and Li JS. 2005.40Ar-39Ar dating of granites and related dikes in the Bengbu area on the southeastern margin of the North China block. Geology in China,32(4):588 -595 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang DB,Xu WL,Pei FP,Wang QH and Liu XM. 2005. Formation time and magma source of granites in Bengbu uplift:Evidence from LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating and tracing. Geochimica,34(5):443 -454 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang DB,Xu WL,Pei FP,Wang QH and Gao S. 2008. Chronology and Pb isotope compositions of Early Cretaceous adakitic rocks in Xuzhou-Huaibei area,central China:Constraints on magma sources and tectonic evolution in the eastern North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica,24(8):1745 -1458 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang DB,Xu WL,Pei FP and Wang QH. 2009. Petrogenesis of the Paleoproterozoic K-Feldspar granites in Bengbu Uplift:Constraints from petro-geochemistry,zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotope. Earth Science,34(1):148 -164 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang DB,Xu WL,Wang QH and Pei FP. 2010. Chronology and geochemistry of Mesozoic granitoids in the Bengbu area,central China:Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the eastern North China Craton. Lithos,114(1 -2):200 -216
Yang XY,Wang BH,Du ZB,Wang QC,Wang YX,Tu ZB,Zhang WL and Sun WD. 2012. On the metamorphism of the Huoqiu Group,forming ages and mechanism of BIF and iron deposit in the Huoqiu region,southern margin of North China carton. Acta Petrologica Sinica,28(11):3476 -3496 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yardley BWD. 1989. An introduction to Metamorphic Petrology.Longman Group,Harlow,UK:Prentice Hall,49 -51
Ying JL,Wang YD,Zhao PY,Lin XL,Sang BL,Xing FM and Chen YZ. 1984. Geochronological studies of Precambrian metamorphic rocks from western Anhui Province. Geochimica,13(2):145 -152(in Chinese with English abstract)
Zeh A,Gerdes A and Barton Jr JM. 2009. Archean accretion and crustal evolution of the Kalahari Craton:The zircon age and Hf isotope record of granitic rocks from Barberton/Swaziland to the Francistown arc. Journal of Petrology,50(5):933 -966
Zeh A,Gerdes A,Will TM and Frimmela HE. 2010. Hafnium isotope homogenization during metamorphic zircon growth in amphibolitefacies rocks:Examples from the Shackleton Range (Antarctica).Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,74(16):4740 -4758
Zhai MG,Guo JH,Yan YH,Li YG and Han XL. 1993. Discovery of high-pressure basic granulite terrain in North China Archaean craton and preliminary study. Science in China (Series B),36(11):1402-1408
Zhai MG,Bian AG and Zhao TP. 2000. The amalgamation of the supercontinent of North China craton at the end of Neo-Archaean and its breakup during the Late Palaeoproterozoic and Mesoproterozoic.Science in China (Series D),43(Suppl.1):219 -232
Zhai MG and Liu WJ. 2003. Palaeoproterozoic tectonic history of the North China Craton:A review. Precambrian Research,122(1 -4):183 -99
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2011. The Early Precambrian odyssey of the North China Craton:A synoptic overview. Gondwana Research,20(1):6 -25
Zhai MG. 2014. Multi-stage crustal growth and cratonization of the North China Craton. Geoscience Frontiers,5(4):457 -469
Zhang BR,Gao S,Zhang HF and Han YW. 2002. Geochemistry of the Qinling Orogenic Belt. Beijing:Science Press,1 - 187 (in Chinese)
Zhang HF. 2012. Destruction of ancient lower crust through magma underplating beneath Jiaodong Peninsula,North China Craton:U-Pb and Hf isotopic evidence from granulite xenoliths. Gondwana Research,21(1):281 -292
Zhang GH,Zhou XH,Sun M,Chen SH and Feng JL. 1998. Sr,Nd and Pb isotopic characteristics of granulite and pyroxenite xenoliths in Hannuoba basalts,Hebei Province,and their implications for geologic processes. Acta Petrologica Sinica,14(2):190 -197 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HF,Ying JF,Santosh M and Zhao GC. 2012. Episodic growth of Precambrian lower crust beneath the North China Craton:A synthesis. Precambrian Research,222 -223:255 -264
Zhang LG. 1995. Block-Geology of Eastern Asia Lithosphere:Isotope Geochemistry and Dynamics of Upper Mantle, Basement and Granite. Beijing:Science Press,1 -252 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao GC,Cawood PA,Wilde SA,Sun M and Lu LZ. 2000.Metamorphism of basement rocks in the Central Zone of the North China craton:Implications for Palaeoproterozoic tectonic evolution.Precambrian Research,103(1 -2):55 -88
Zhao GC,Wilde SA,Cawood PA and Sun M. 2001. Archean blocks and their boundaries in the North China craton: Lithological,geochemical,structural,and P-T path constraints and tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research,107(1 -2):45 -73
Zhao GC,Sun M,Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research,136(2):177 -202
Zhao GC,Cawood PA,Li SZ,Wilded SA,Sun M,Zhang J,He YH and Yin CQ. 2012. Amalgamation of the North China Craton:Key issues and discussion. Precambrian Research,222 -223:55 -76
Zhao GC and Zhai MG. 2013. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton: Review and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research,23(4):1207 -1240
Zheng JP,Sun M,Lu FX and Pearson N. 2003. Mesozoic lower crustal xenoliths and their significance in lithospheric evolution beneath the Sino-Korean Craton. Tectonophysics,361(1 -2):37 -60
Zheng JP,Griffin WL,O’Reilly SY,Lu FX,Yu CM,Zhang M and Li HM. 2004a. U-Pb and Hf-Isotope analysis of zircons in mafic xenoliths from Fuxian kimberlites:Evolution of the lower crust beneath the North China Craton. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,148(1):79 -103
Zheng JP,Griffin WL,O’Reilly SY,Lu FX,Wang CY,Zhang M,Wang FZ and Li HM. 2004b. 3.6Ga lower crust in central China:New evidence on the assembly of the North China Craton. Geology,32(3):229 -232
Zheng JP,Griffin WL,O’Reilly SY,Zhao JH,Wu YB,Liu GL,Pearson N,Zhang M,Ma CQ,Zhang CQ,Yu CM,Su YP and Tang HY. 2009. Neoarchean (2.7 ~2.8Ga)accretion beneath the North China Craton:U-Pb age,trace elements and Hf isotopes of zircons in diamondiferous kimberlites. Lithos,112(3 -4):188 -202
Zhou XW,Wei CJ,Geng YS and Zhang LF. 2004. Discovery and implications of the high-pressure pelitic granulite from the Jiaobei massif. Chinese Science Bulletin,49(18):1942 -1948
Zhu BQ. 1991. Evidence of isotopic systematics from crust and mantle for chemical heterogeneities of terranes. Chinese Science Bulletin,36(15):1279 -1282
附中文参考文献
安徽省地质矿产局. 1987. 安徽省区域地质志. 北京:地质出版社,1 -721
安徽省地质矿产局. 1997. 安徽省岩石地层. 武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1 -271
刘福来,刘平华,丁正江,刘建辉,杨红,胡伟华. 2012. 山东半岛高压麻粒岩中花岗质浅色脉体的成因. 岩石学报,28(9):2686-2696
刘磊,杨晓勇. 2013. 安徽霍邱BIF 铁矿地球化学特征及其成矿意义:以班台子和周油坊矿床为例. 岩石学报,29(7):2551-2566
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉. 2010. 山东半岛基性高压麻粒岩的成因矿物学及变质演化. 岩石学报,26(7):2039 -2056
刘平华,刘福来,王舫,刘建辉,杨红,施建荣. 2012. 胶北高级变质基底中高压基性麻粒岩的地球化学特征及其成因. 岩石学报,28(9):2705 -2720
刘文军,翟明国,李永刚. 1998. 胶东莱西地区基性高压麻粒岩的变质作用. 岩石学报,14(4):449 -459
刘贻灿,王安东. 2012. 华北克拉通东南缘前寒武纪下地壳的幕式生长与多期改造:岩石学、年代学和Hf 同位素证据. 地球科学与环境学报,34(4):1 -11
刘贻灿,王程程,张品刚,Groppo C,Rolfo F,王安东. 2015. 华北板块东南缘五河杂岩的麻粒岩相变质、部分熔融与交代作用. 地球科学与环境学报,37(1):1 -11
涂湘林,朱炳泉,范嗣昆,胡霭琴. 1993. 华北麻粒岩相带铅同位素组成特征及其与全球对比. 中国科学(B 辑),23(5):537 -544
涂荫玖. 1994. 江淮地区北部晚太古宙TTG 质片麻岩. 安徽地质,4(4):15 -23
王安东,刘贻灿,古晓锋,李曙光,颉颃强. 2009. 蚌埠老山含石榴子石片麻状花岗岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb 年龄及其对华南俯冲陆壳再循环的意义. 矿物岩石,29(2):38 -43
王娟,盛勇,卜香萍,康涛,石永红. 2014. 五河杂岩的变质岩石学及P-T 条件分析——来自蒙城南ZK02 钻孔的研究. 地质科学,49(2):556 -575
邢凤鸣,任思明. 1984. 皖西霍邱群条带状硅铁建造成因雏议. 地质学报,58(1):35 -48
许文良,杨德彬,裴福萍,杨承海,柳小明,胡兆初. 2006. 蚌埠隆起区五河杂岩的形成时代:锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb 定年证据. 中国地质,33(1):132 -137
徐祥,侯明金,邱瑞龙,吴礼彬,李建设. 2005. 华北陆块东南缘蚌埠地区花岗岩与相关脉岩40Ar-39Ar 定年. 中国地质,32(4):588 -595
杨德彬,许文良,裴福萍,王清海,柳小明. 2005. 蚌埠隆起区花岗岩形成时代及岩浆源区性质:锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb 定年与示踪. 地球化学,34(5):443 -454
杨德彬,许文良,裴福萍,王清海,高山. 2008. 徐淮地区早白垩世adakitic 岩石的年代学和Pb 同位素组成:对岩浆源区与华北克拉通东部构造演化的制约. 岩石学报,24(8):1745 -1458
杨德彬,许文良,裴福萍,王清海. 2009. 蚌埠隆起区古元古代钾长花岗岩的成因:岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb 年代学与Hf 同位素的制约. 地球科学,34(1):148 -164
杨晓勇,王波华,杜贞保,王启才,王玉贤,涂政标,张文利,孙卫东. 2012. 论华北克拉通南缘霍邱群变质作用、形成时代及霍邱BIF 铁矿成矿机制. 岩石学报,28(11):3476 -3496
营俊龙,王扬德,赵溥云,林秀兰,桑宝梁,邢凤鸣,陈跃志. 1984.皖西前寒武纪变质岩系地质年代学研究. 地球化学,13(2):145 -152
张本仁,高山,张宏飞,韩吟文. 2002. 秦岭造山带地球化学. 北京:科学出版社,1 -187
张国辉,周新华,孙敏,陈绍海,冯家麟. 1998. 河北汉诺坝玄武岩中麻粒岩类和辉石岩类捕虏体Sr、Nd、Pb 同位素特征及其地质意义. 岩石学报,14(2):190 -197
张理刚. 1995. 东亚岩石圈块体地质——上地幔、基底和花岗岩同位素地球化学及其动力学. 北京:科学出版社,1 -252
