水安全保障与水资源可持续利用
2015-02-28
Bouhabila, E; Ben, Aim R; Buisson, H
Influence of the characteristics of natural organic matter on the fouling of microfiltration membranes
Fan, LH; Harris JL; Roddick FA; et al.
Fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes by natural waters
Howe, KJ; Clark, MM
Membrane fouling in pilot-scale membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater
Kimura, K; Yamato, N; Yamamura, H; et al.
气候变化视阈下的水安全现状及应对策略
侯立安,张林
(1. 第二炮兵工程大学3系,西安,710025;2. 浙江大学化学工程与生物工程学院,杭州,310027)
水与废水处理中的膜生物反应器技术
樊耀波,王菊思
热点追踪
水安全保障与水资源可持续利用
·编者按·
对于人类社会的发展而言,水既是必不可少的自然资源,也是重要的社会资源。中国的水资源总量约为2.8×1012m3,人均水资源量为2185 m3,仅为世界平均水平8800 m3的1/4,是世界上13个水资源贫乏的国家之一。由于过去工业的粗放发展模式,使得单位水资源产出水平较低,水环境污染较为严重;此外,中国自然的水资源还存在着时空分布不均、与生产力布局不相匹配,发展需求与水资源条件之间的矛盾突出等现象,中国水资源短缺形势不容乐观,水安全问题对社会发展的约束作用不断增强。
目前,中国工业、农业和生活废水的产生量大,而大部分的废水则是经过达标处理后排放到环境中,废水的回用率相对较低。对工业废水而言,其成分复杂,处理难度大,成本高,将多种处理技术相集成,提高废水处理效率,降低处理成本,甚至实现有价值物质的回收是近年来工业废水回用的发展新趋势。由于农业废水属于面源式污染,虽然有很多新技术已经被应用到农业废水的处理中,但目前收效并不理想。城镇生活污水在所有废水中所占比例最大,要想彻底解决生活废水问题,在发展新型的生化处理技术的同时,还需要提高民众的环保和节水意识。海绵城市,是新一代城市雨洪管理概念,是指城市在适应环境变化和应对雨水带来的自然灾害等方面具有良好的“弹性”,也可称之为“水弹性城市”。近年来,强降雨导致的城市雨洪问题既给城市安全带来困扰,又浪费了宝贵的水资源,加强雨洪储存和处理技术研究,有助于推进海绵城市的建设。
根据中国《中国水资源公报》统计数据,目前中国万元GDP用水量为109 m3,与世界平均水平相当,与发达国家相比仍有差距。而降低万元GDP用水量,提高水利用率,则需要提高节水型社会建设水平,实现水资源优化配置和建立高效利用的工程技术体系,近年来,随着材料和工程等相关科学的不断进步,以膜技术、吸附等为代表的水处理技术得到了快速发展,使其在非常规水源处理中得到了良好的应用,并发挥着越来越重要的作用。因此,绿色生产工艺的设计,高性能的水处理材料的制备,集成工艺的开发等将有助于从源头上解决水安全问题。
本专题得到了张林教授(浙江大学化学工程与生物工程学院)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年11月15日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“水处理(water treatment)、膜(membrane)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为987条与16696条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)
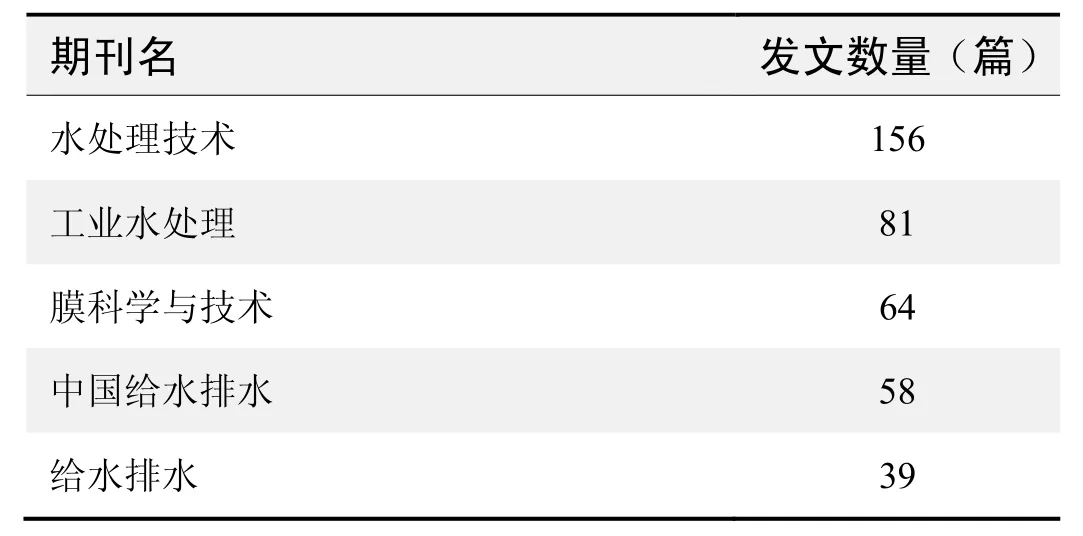
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
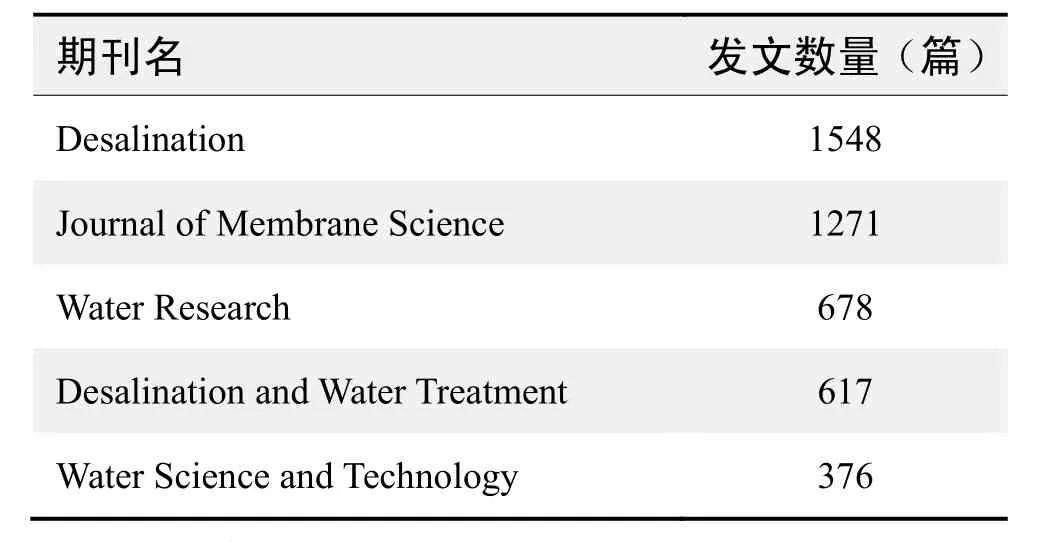
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“水处理(water treatment)、膜(membrane)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“水处理(water treatment)、膜(membrane)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 30文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物: Journal of Membrane Science 1997, 132 (2): 159-181
Fouling characterisation in membrane bioreactors
Bouhabila, E; Ben, Aim R; Buisson, H
Abstract:Compared with conventional wastewater treatment processes, membrane bioreactors offer several advantages, e.g. high biodegradation efficiency, smaller sludge production and compactness. However, membrane fouling is the main limitation to faster development of this process. An experimental study has been performed using hollow fibers (pore size 0.1 mum) immersed in an aerated tank for treating synthetic wastewater representative of dairy effluent. For the same organic load (5.7 kg COD/m3per day) the COD removal efficiency, the sludge production and fouling ability were compared in three reactors operated at different sludge ages (10, 20 and 30 days). COD removal was high: 95%-97.5%. The sludge production decreased from 0.31 to 0.16 kg MLSS/kg COD removed when the sludge age increased from 10 to 30 days. Concerning the fouling ability of the sludge, a specific experiment (measurement of the specific resistance and hydraulic resistance during filtration) was designed to determine the influence on membrane fouling of the three fractions of the sludge: suspended solids, colloids and solutes. All the experiments confirm the importance of the interstitial matter-colloids and solutesin membrane fouling. Consecluently, bubbling can be expected to be only partially efficient, as bubbles are efficient for limiting particle deposition and polarisation phenomena, but not for internal fouling. Increasing the air flow rate from 1.2 to 3.6 m3/m2membrane area) per hour, it was possible to decrease the total resistance-thus increasing the filtrate flux-by a ratio of 3. However, for given conditions of aeration, periodic backwashing rave an additional efficiency by decreasing internal fouling. In optimal conditions of backwashing (15 severy 5 min) the resistance could be decreased by 3.5-fold.
Keywords:submerged membrane bioreactor; aeration; membrane fouling; wastewater treatment; backwashing
来源出版物: Separation and Purification Technology, 2001, 22-23 (1-3): 123-132
Influence of the characteristics of natural organic matter on the fouling of microfiltration membranes
Fan, LH; Harris JL; Roddick FA; et al.
Abstract:Natural organic matter (NOM) plays a significant role in fouling microfiltration membranes in drinking water treatment processes even though the NOM is retained only to a small extent. The aim of this study was to obtain a better understanding of the interactions between the fractional components of NOM and microfiltration membranes. Filtration experiments were performed using 0.22 mum hydrophobic and hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes in a stirred-cell system on the NOM isolated from three Australian surface waters. As expected, the fouling rate for the hydrophobic membrane was considerably greater than for the hydrophilic membrane. Focusing on the hydrophobic membrane, it was shown that the high molecular weight fraction of NOM (>30 kDa) was responsible for the major flux decline. Filtration tests on the four fractions of NOM isolated on the basis of hydrophobicity and charge using non-functionalised and anionic resins revealed that the fouling potential for the three waters was hydrophilic neutral > hydrophobic acids > transphilic acids >hydrophilic charged. The low-aromatic hydrophilic neutral compounds were the main determinant of the rate and extent of flux decline. This was linked to the colloidal size fraction (>30 kDa) and to the selective concentration of calcium in the fraction leading to organics-Ca2+bridging. It was also shown that the higher the aromaticity of the NOM the greater the flux decline, and the aromatics mainly resided in the hydrophobic acids fraction. Overall, the fouling mechanism controlling the flux decline involved the combined effects of adsorptive and colloidal fouling by the hydrophilic neutral fraction in the internal pore structure of the membrane.
Keywords:drinking water treatment; fouling; microfiltration; natural organic matter
来源出版物: Water Research, 2001, 35 (18): 4455-4463
Fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes by natural waters
Howe, KJ; Clark, MM
Abstract:Membrane filtration (microfiltration and ultrafiltration) has become an accepted process for drinking water treatment, but membrane fouling remains a significant problem. The objective of this study was to systematically investigate the mechanisms and components in natural waters that contribute to fouling. Natural waters from five sources were filtered in a bench top filtration system: A sequential filtration process was used in most experiments. The first filtration steps removed specific components from the water, and the latter filtration steps investigated membrane fouling by the remaining components. Particulate matter (larger than 0.45 mum) was relatively unimportant in fouling as compared to dissolved matter. Very small colloids, ranging from about 3-20 nm in diameter, appeared to be important membrane foulants based on this experimental protocol. The colloidal foulants included both: inorganic and organic matter, but the greatest fraction of material was organic. When the colloidal fraction of material was removed, the remaining dissolved organic matter (DOM); which was smaller than about 3 nm band included about 85%-90% of the total DOM, caused very little fouling. Thus, although other studies have identified DOM, as a major foulant during filtration of natural waters, this work shows that a small fraction of DOM may be responsible for fouling. Adsorption was demonstrated to be an important-mechanism for fouling by colloids.
来源出版物: Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36 (16): 3571-3576
Membrane fouling in pilot-scale membrane Bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater
Kimura, K; Yamato, N; Yamamura, H; et al.
Abstract:The main obstacle for wider use of membrane bioreactors (MBRs) for wastewater treatment is membrane fouling (i.e., deterioration of membrane permeability), which increases operating costs. For more efficient control of membrane fouling in MBRs, an understanding of the mechanisms of membrane fouling is important. However, there is a lack of information on membrane fouling in MBRs, especially information on features of components that are responsible for the fouling. We conducted a pilot-scale experiment using real municipal wastewater with three identical MBRs under different operating conditions. The results obtained in this study suggested that the food-microorganisms ratio (F/M) and membrane filtration flux were the important operating parameters that significantly influenced membrane fouling in MBRs. Neither concentrations of dissolved organic matter in the reactors nor viscosity of mixed liquor, which have been thought to have influences on fouling in MBRs, showed clear relationships with membrane fouling in this study. Organic substances that had caused the membrane fouling were desorbed from fouled membranes of the MBRs at the termination of the operation and were subjected to Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses. These analyses revealed that the nature of the membrane foulant changes depending on F/M. It was shown that high F/M would make the foulant more proteinaceous. Carbohydrates were dominant in membrane foulants in this study, while features of humic substances were not apparent.
来源出版物: Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39 (16): 6293-6299
·推荐综述·
气候变化视阈下的水安全现状及应对策略
侯立安,张林
(1. 第二炮兵工程大学3系,西安,710025;2. 浙江大学化学工程与生物工程学院,杭州,310027)
近年来,全球气候变化越来越显著,引起全社会的普遍关注。气候变化指气候系统随时间发生的变化,是自然变化和人类社会活动共同作用的结果。导致气候变化的直接原因是大气中温室气体和气溶胶的浓度及太阳辐射和地表性质的改变,这些因素综合影响了地球气候系统的能量平衡,从而导致了全球范围的气候变化。
全球变暖是气候变化的主要特征,它由人为排放的超量温室气体所致。温室气体包括化石燃料大量燃烧所释放的二氧化碳及甲烷、氧化亚氮和一些消耗臭氧的物质等。温室气体通过吸收大地反射回来的能量并重新辐射这部分热量来影响地球的气候。气候变化将会改变全球水文循环,引起水资源在时空上的重新分配,并对降水、蒸发等气候因素造成直接影响,引发一系列的水安全问题。
水安全,指一个国家或地区可以保质保量、及时持续、稳定可靠、经济合理地获取所需的水资源、水资源性产品及维护良好生态环境的状态或能力。
水安全问题不仅是一个资源问题,也是一个生态环境问题、经济问题、社会问题和政治问题,直接关系到国家的安全。水安全的内涵包括5个方面:1)水资源安全,包括水量充裕和结构均衡;2)水环境安全,包括饮用水安全、环境容量内的纳污能力和良好的环境服务功能;3)水生态安全,即拥有良性水循环和水生生物多样性,能够实现自我修复和维持整个生态系统的保育;4)水工程安全,即在江河、湖泊和地下水源开发、利用、控制、调配和保护水资源各类工程的安全,包括防洪、灌溉、供水、发电、防洪、发电、水土保持、水资源保护等工程的合理建设与良性运行等;5)供水安全,包括结构供水安全和城乡供水安全,结构供水安全包括生产、生活和生态供水安全。
根据联合国政府间气候变化专业委员会(IPCC)最近两次的统计数据,气候变化在近几十年来对全球范围内自然生态系统和人类社会都产生了深远影响,对于气候变化可能引发的水安全问题必须引起足够重视。因此,本文阐述全球气候变化背景下水安全所面临的挑战并初步探讨应对策略。
1 气候变化的现状
气候变化对水安全的影响,主要来自于全球变暖及降雨量和降雨时空分布发生的变化。IPCC 2014年发布的气候变化评估报告给出了关于全球变暖的最新统计和预测数据。
由图1可知,除去少部分数据不足和气温变化不明显的区域外,全球绝大部分区域的气温均呈现上升趋势。由图2可见,全球的平均气温虽然在短期内有所波动,但长期来看平均气温上升明显;并且两种不同气候模型的模拟结果表明,在将来很长一段时间内,全球的平均气温仍呈现上升趋势。这些数据充分说明全球变暖已是不争的事实。
全球变暖会直接导致高纬度、高海拔地区永冻土层和冰川升温融化、海平面上升,气旋、热浪等自然灾害发生的可能性增加,从而引发次生的水生态问题,如水体富营养化污染等。
根据IPCC报道,由于北极冻土层顶部温度上升,自20世纪初以来北半球季节冻土覆盖面积已减少了约7%;从1978年以来,北极海冰面积以2.7%/10年的平均速率退缩。冰川对气候变化则表现得更为敏感,自20世纪80年代以来,高原冰川末端在近几十年间出现了快速退缩,且在边缘山区比中腹地区更为明显。中国拥有46377座冰川,覆盖面积达59425 km2。有研究指出,由于全球气候变暖,中国的西部有超过80%的冰川处于衰退中。有学者通过气温重建技术证实,过去的50年是青藏高原近500年以来最热的半个世纪,直接导致了过去40年中,青藏高原的冰川衰退了7%(3790 km2),并且厚度每年以200 mm的速度衰退。
全球变暖引起的海平面上升,主要是由海水吸热膨胀、陆地冰川融化、格陵兰冰盖融化及南极冰盖融化等的综合作用所致。IPCC 2007年的气候评估报告显示,海洋吸收了80%全球变暖的热量,这部分热量会引起上层海水的受热膨胀。据统计,近20年来格陵兰冰盖融化量翻了两番,从1992—2001年的(51±65)Gt/年到2002—2011年的(221±37)Gt/年,这部分冰川的融化使海平面上升了(7.5±1.8)mm。这些现象的综合作用使得在过去的1个世纪里全球海平面平均上升速度为1.7~1.8 mm/年。对于中国而言,近百年来,海平面总上升量为14 cm,其中渤海海面上升5 cm,东海上升19 cm,南海上升20 cm。上升量超过20 cm的省市有江苏、上海和广东。如果海平面升高与全球气温上升之间的关系不变,未来100年海平面可能上升20~90 cm。
全球变暖还会导致上层海水水温上升,从而产生高强度的热带气旋。已有研究表明,从20世纪70年代以来,全球热带气旋的强度和频次都呈现出上升的趋势,其中在北太平洋、印度洋与西南太平洋增加最为显著。
另外,气温变暖将提升大气中平流层携水能力——气温每升高1℃大气中的水含量提高7%,大气中水含量的提高增加了暴雨天气发生的频次和强度。
IPCC 2014年发布的第5次气候变化评估报告中还指出:气候变化引起了一些地区降雨量和时空分布的变化,改变了当地的水文循环,影响水资源的数量和质量。许多地区均观测到降水量存在着明显的变化趋势:北美和南美东部、欧洲北部、亚洲北部和中部降水量显著增加,而萨赫勒、地中海、非洲南部、亚洲南部部分地区降水量减少。这种降雨量和时空分布的变化导致了降水多而集中的地区发生洪涝灾害的可能性提高,降水少而分散的地区发生旱灾的可能性上升。
综上所述,气候变化对水安全问题的影响是多方面和综合性的,二者间总体逻辑关系如图3所示。
2 气候变化对水安全的影响
2.1 气候变化对水资源安全的影响
目前面临的水资源安全问题主要包括水资源短缺和水污染。有研究表明,气候变化会加重这种全球性和地域性的水资源危机,并建立了多个模型预测气候变化对水资源的影响,结果表明:如果全球气温再升高2℃(即比工业革命前高2.7℃),全球处于极度缺水环境(<500 m3·人-1·年-1)的人口将会增加15%。
据中国水利部《2013年中国水资源公报》,中国总的水资源量为29528.8亿m3,其中包括地表水量27957.9亿m3,地下水量8081.1亿m3。中国总的水资源量看似充足,但人均水资源量却不足全球的1/4。水资源总量的分配中,松花江、辽河、海河、黄河、淮河、西北诸河6个北方的水资源一级区(简称北方6区)占5639亿m3,而长江(含太湖)、东南诸河、珠江、西南诸河4个南方的水资源一级区(简称南方4区)占23889.8亿m3。可见,在中国南方和北方水资源分配极不平衡:北方地区拥有全国65%的耕地面积却仅仅占有全国19%的水资源量。
全球性的气候变化进一步加剧了中国的水资源安全问题,一方面气候变化改变了降雨量和时空的分布,导致雨水的分布更加不平衡:一些原本“水多”的地区雨水更多,而一些原本就“水少”的地区雨水更少。统计数据显示,中国较为缺水的东北、华北地区夏季和秋季的降水量越来越少。相反,多雨的华南地区夏天和冬天的降雨量则越来越多。降雨量和时空分布不平衡加剧了中国水资源安全问题。
另一方面,气温变暖导致地表蒸发作用更为显著,河流径流量及土壤含水量下降,使可用的水资源减少;引起的高纬度和高海拔冰川融化,将使冰川衰退,导致下游以冰川融水为主要水资源的地区水资源量锐减。
2.2 气候变化对水环境安全的影响
水是污染物最主要的运输载体和溶剂,气候变化通过影响水文循环的各个要素和循环方式,改变了水环境中污染物的来源和迁移转化行为,最终破坏水环境安全。例如,气候变化导致的降水量和时空分布的改变会引起干旱、洪涝等极端水文事件发生的频率增加。发生干旱灾害时,水体中部分离子浓度显著升高,影响水体水质安全;同时,水体表面温度也会升高,导致水中溶解氧浓度下降,复氧能力降低,最终使水体的稀释和自净能力同时降低,水环境质量下降。
洪涝灾害发生时,一方面大量地表污染物进入水体,影响水质;另一方面,也会使大量的泥沙进入水体或造成沉积物的再悬浮作用,改变水体泥沙含量,进一步影响污染物的迁移转化作用,并最终影响水体的水质。另外,全球气候变化引起的气温升高和降水变化将对地表水环境中的主要离子浓度产生影响,可能导致湖泊的盐化和矿化作用。
2.3 气候变化对水生态安全的影响
全球气候变化最直接的反映是气温升高,随着气温的上升,河流湖泊等水体的水温也会升高。通常水体温度升高可以影响水体的密度、表面张力、黏性和存在形态,也会改变水温层分布和加速水体中化学反应和生物降解速率等。有研究表明,温度是水体富营养化的决定性影响因素之一,在强降雨冲刷地表给水体带入大量的氮、磷等营养物质和水体温度升高的综合作用下,会促进水体富营养化污染的发生。一旦水体发生富营养化污染,水体中的藻类及其他浮游生物大量繁殖,水体中溶解氧浓度迅速下降,水质恶化,水体中的鱼类和其他生物大量死亡,严重威胁水生态安全。
另外,气温升高引发的海平面上升将导致海水入侵沿海地区地下含水层,使沿海区域地表土壤盐渍化、地表水含盐量上升,水体中的动植物因无法耐受高盐渗透压而大量死亡,从而破坏沿海地区的水生态安全。
2.4 气候变化对水工程安全的影响
气候变化对水工程安全的影响主要有:1)气候变化导致的强降雨天气会在短时间内带来大量雨水,这部分雨水使得下游的防洪设施水位长时间居高不下,对下游的水工程安全产生严重的威胁,而全球变暖导致的高海拔地区的冰川融化,也会引起下游河流短期内径流量迅速升高,对下游冰湖的堤坝产生巨大威胁;2)气候变化会导致寒流和热浪天气发生频率升高,而这种极端的高温和低温天气对水利工程也十分不利。例如,当寒流天气发生时,水利工程表面的混凝土会迅速降温,而内部的混凝土由于降温较慢仍保持较高的温度,内外的温度差会产生剪切力,而当剪切力过大时,会使水利工程的混凝土结构产生裂缝,同时降低混凝土的脆度。同样,长时间的高温干旱天气会使得混凝土内部的水分快速消失,产生收缩和裂缝,威胁水工程的安全;3)海平面上升引起海水侵蚀海岸线、入侵沿海地下淡水层、沿海土地盐渍化。沿海土地的盐渍化会对沿海相关的水利工程特别是钢筋混凝土结构产生严重的腐蚀。
2.5 气候变化对供水安全的影响
气候变化会加剧供水安全问题:1)洪涝灾害发生时,洪水会携带大量的污染物进入水源地,破坏水源地的水质安全,引发城乡供水水质安全;2)干旱灾害会加剧区域水源短缺现象,使可用的水资源减少,造成城乡的供水困难;3)对于中国西北干旱地区,冰川和积雪融水对河川径流的补给占该地区内陆河流的径流补给的30%左右,因此,气候变化引起的冰川衰退虽然在短时间内可以提高下流河道的径流量,但长此以往,一旦冰川完全衰退,会导致下游地区的供水困难。
3 气候变化下的中国水安全对策
据IPCC 2007年气候变化评估报告可知,人类活动对近50年的气候变化负主要责任,而且根据预测,人类活动对气候变化的影响还在不断增强。因此,为应对气候变化背景下的水安全问题,主要可从以下两方面入手:一是阻止或延缓气候变化;二是提高人类自身应对水安全问题的能力。主要措施为:
1)提高能源利用效率,发展新能源,减少温室气体排放。根据IPCC对于气候变化的归因分析,温室气体的大量排放是气候变化的直接原因。因此,必须坚持节约能源和开发替代能源并重,减少温室气体的排放,这是缓解气候变化的根本途径。一方面,提高可再生能源在水处理方面的应用,如发展太阳能驱动海水淡化过程、风能驱动海水淡化过程;另一方面,通过改变传统工艺减少温室气体的排放。
2)开源节流,提高水资源利用效率,加速节水型社会的建设。根据中国水资源不足和空间分布不均的实际状况,必须“开源”与“节流”并重,同时提高水资源的利用率。在“开源”方面,可以通过推广新型的膜法水处理技术,如海水淡化、雨水回用及非常规水源的开发;在“节流”方面,必须做到节约用水,除加强相关宣传外,可以通过制定相关政策、法规加以保证和推动,在全社会形成节约用水的良好社会风气,建立节水型社会。
3)加强水资源的管理与监控。水资源管理是一个涉及社会、经济与环境的综合管理。针对中国目前水质情况复杂的现状,应当对江河湖泊的水文、水质等情况进行实时监控。并在此基础上,应用系统分析的理论和方法,通过对水生生态系统环境、功能、结构特征及各组分间相互作用的研究实施中国水安全实时预警预报,以确保中国水资源的开发利用沿着健康轨道发展。
4)建立城市应急供水系统。在阻止或延缓气候变化的同时还应当提高人类自身应对水安全问题的能力。城市应急供水系统在应对大规模城市严重缺水、重大水污染等突发事件时起着不可替代的作用。因此,应把应急供水系统纳入城市基础设施建设和水资源开发规划中,以当地水资源与水安全现状为背景,全面落实城市水安全应急供水系统建设,做到未雨绸缪。
4 结论
水资源是社会经济发展重要的物质基础之一。中国目前的水安全状况不容乐观,水安全问题已成为中国可持续发展急需解决的关键问题之一。分析表明,在全球气候变化的背景下,中国水资源总量将有所减少,时空分布更趋不均。同时,气候变化也将对水生态环境产生不利影响。在人口增长、经济发展和城市化水平不断提高的压力下,中国水安全状况将面临着前所未有的严峻考验。因此,需要采取一系列的行动来应对全球气候变化背景下的水安全问题。
还需指出的是,目前对于气候变化与水安全问题之间的关联以及对将来气候变化的预测仍然有一些不确定性。不同气候模式对云反馈、海洋热吸收、碳循环反馈等机制的描述差别很大,这也增加了对未来气候预估的不确定性,气溶胶等因素对气候系统和水循环的影响也仍然不确定。与气候平均值的变化研究相比,对极端气候事件变化的认识还有待深入,特别是一些小尺度的极端气候事件。未来气候变化的预估结果很大程度上依赖于模式和情景,提高未来气候变化对水安全问题影响预估的可靠性和信度,需要进一步完善气候系统模式、加强气候系统观测、提高对地球气候系统的科学认识。
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:233
水与废水处理中的膜生物反应器技术
樊耀波,王菊思
介绍了膜生物反应器的概念及其用于给水和废水处理的研究发展过程。膜生物反应器包括一体式系统、分离式系统和隔离式系统,并给出8例用于给水和废水处理的膜生物反应器的技术参数及水处理效果数据等。生物反应器其膜单元有超滤膜、微滤膜和萃取膜,用于脱氮、去除有机物及重点有毒物质的降解等。膜生物反应器的去除效率较高,有些COD去除效率达80%~90%,NH3-N去除效率达98%,膜生物反应器的出水浊度低,处理出水宜于回用。
生物反应器;膜技术;水处理
来源出版物:环境科学, 1995, 16(5): 79-82
被引频次:200
我国水资源污染与饮用水安全性研究
肖羽堂,张晶晶,吴鸣,等
摘要:对我国水资源状况和饮用水安全性进行了分析研究,结果表明:我国水资源贫乏,水资源环境污染日益严重。许多水厂不得不面临着使用更多的水质不符合要求的受污染水源原水作为生活饮用水水源。水污染主要是有机物和氨氮污染,常规净水工艺系统难以将这些污染物有效除去,降低了饮用水水质,对人体健康构成潜在威胁。随着人们生活水平的提高和健康安全意识的不断增强,对饮用水水质标准提出了更高要求。为从受污染的水源原水中除去对人体健康有害的污染物,提高饮用水的安全可靠性,强化传统工艺、替换传统的消毒剂、吸附、膜过滤和生物预处理等净水技术得到了国内外广泛重视和关注,尤其是经济、高效的生物除污染技术。
关键词:水资源;水污染;饮用水;安全;水处理
来源出版物:长江流域资源与环境, 2001, 10(1): 51-59
被引频次:178
膜技术应用于净水处理的研究和现状
董秉直,曹达文,范瑾初
摘要:膜技术被称为“二十一世纪的水处理技术”,现已受到越来越多的水处理工作者的关注。在综合大量国内外文献资料的基础上,主要介绍了国外膜分离技术在净水处理中的研究和应用现状。
关键词:膜分离;净水处理;截留分子量;膜污染
来源出版物:给水排水, 1999, 21(1): 28-32
被引频次:105
膜生物反应器在水处理中的研究及应用
郑祥,朱小龙,张绍园,等
摘要:膜生物反应器(MBR)是通过膜强化生化反应的水处理新技术。本文对MBR的特点、应用类型、水处理机理进行了阐述;综述了该技术在国内外的研究进展以及应用现状;并对MBR存在的问题与应用前景作了讨论,MBR有望在新世纪成为传统水处理方法的一种替代工艺。
关键词:膜生物反应器;废水处理;生化技术;膜技术
来源出版物:环境污染治理技术与设备, 2000, 1(5): 12-20
被引频次:87
膜生物反应器内泥水混合液可过滤性的研究
罗虹,顾平,杨造燕
摘要:膜生物反应器(MBR)是一种新兴的水处理技术,但目前膜造价较高,导致运行费用较高,因此研究提高膜通量的各种技术措施具有重要的意义。文中引入静态泥水混合液过滤试验,通过对取自运转中MBR的活性污泥混合液的过滤实验结果分析,着重阐述了影响活性污泥可过滤性的影响因素,并指出在维持MBR的运行中,改善活性污泥性状是一个不可忽略的方面。
关键词:膜生物反应器;活性污泥;可过滤性;膜阻力;膜通量
来源出版物:城市环境与城市生态, 2000, 13(1): 51-54
被引频次:75
减压膜蒸馏技术处理丙烯腈废水研究
沈志松,钱国芬,迟玉霞,等
摘要:用减压膜蒸馏(VMD)技术进行的处理废水中丙烯腈的实验室研究和中间试验,均取得了良好的结果。丙烯腈的去除率在98%以上,出水浓度低于5 mg/L,达到了排放控制的要求。理论分析和实验数据都说明,液相温度和流量对VMD的传质和丙烯腈的脱除效果有很大的影响。而中间试验的结果又表明,真空度、气液比、流程走向和纤维装填密度等工艺和设备参数在一定条件下对丙烯腈的脱除效果也有较大的影响。所有试验结果显示,作为一种新颖的水处理技术,VMD将在挥发性有机污染物的处理方面发挥重要的作用。
关键词:膜蒸馏;废水处理;丙烯腈
来源出版物:膜科学与技术, 2000, 20(2): 55-60
被引频次:71
膜技术在工业废水处理中的应用研究进展
曹阳,李遵龙
摘要:膜过滤技术是一种高效、低能耗和易操作的液体分离技术,同传统的水处理方法相比具有处理效果好,可实现废水的循环利用和对有用物质回收等优点。简要介绍了微滤、电渗析、反渗透、超滤、纳滤等膜分离技术的基本原理及特点,重点介绍了膜技术在含油废水、染料废水、造纸废水、含重金属废水和高浓度有机废水处理中的应用研究进展状况。并讨论了膜过滤技术的研究方向和发展前景。
关键词:膜技术;废水处理;膜研究进展
来源出版物:工业水处理, 2006, 26(4): 1-4
被引频次:69
我国膜分离技术研究生产现状及在水处理中的应用
续曙光,李锁定,刘忠洲
摘要:本文介绍了我国液体分离膜技术,主要是超滤、反渗透、微滤和电渗析的研究和开发现状及在水处理中的应用。
关键词:膜分离技术;水处理;应用
来源出版物:环境科学进展, 1997, 5(6): 72-76
被引频次:64
膜技术处理饮用水的研究
张捍民,张威,王宝贞
摘要:21世纪的今天,饮用水水质标准愈加严格,而水源污染日趋恶化,常规饮用水处理工艺出水安全性难以保证,已无法与现有的水质标准相适应,必须开发新的水处理技术。膜技术作为饮用水处理的一个独立工艺,是水处理领域最重要的技术突破,现已得到愈来愈多水处理工作者的关注。在综合研究国外文献资料的基础上,主要介绍了膜技术在国外饮用水处理中的应用。
来源出版物:给水排水, 2002, 28(3): 21-24
被引频次:58
膜技术在水处理中的应用与发展
张慧,朱淑飞,鲁学仁
摘要:膜技术方法很多,应用面也很广。本文对反渗透电渗杯超过滤、纳滤和微孔过滤等膜技术在国内水处理方面的应用概况作一综合介绍。
关键词:膜技术;膜技术应用;膜法水处理
来源出版物:水处理技术, 2002, 28(5): 256-259
被引频次:993
Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents-A critical review
Mohan, Dinesh; Pittman, Charles U
Abstract:Arsenic’s history in science, medicine and technology has been overshadowed by its notoriety as a poison in homicides. Arsenic is viewed as being synonymous with toxicity. Dangerous arsenic concentrations in natural waters is now a worldwide problem and often referred to as a 20th-21st century calamity. High arsenic concentrations have been reported recently from the USA, China, Chile, Bangladesh, Taiwan, Mexico, Argentina, Poland, Canada, Hungary, Japan and India. Among 21 countries in different parts of the world affected by groundwater arsenic contamination, the largest population at risk is in Bangladesh followed by West Bengal in India. Existing overviews of arsenic removal include technologies that have traditionally been used (oxidation, precipitation/coagulation/membrane separation) with far less attention paid to adsorption. No previous review is available where readers can get an overview of the sorption capacities of both available and developed sorbents used for arsenic remediation together with the traditional remediation methods. We have incorporated most of the valuable available literature on arsenic rernediation by adsorption (similar to 600 references). Existing purification methods for drinking water; wastewater; industrial effluents, and technological solutions for arsenic have been listed. Arsenic sorption by commercially available carbons and other low-cost adsorbents are surveyed and critically reviewed and their sorption efficiencies are compared. Arsenic adsorption behavior in presence of other impurities has been discussed. Some commercially available adsorbents are also surveyed. An extensive table summarizes the sorption capacities of various adsorbents. Some low-cost adsorbents are superior including treated slags, carbons developed from agricultural waste (char carbons and coconut husk carbons), biosorbents (immobilized biomass, orange juice residue), goethite and some commercial adsorbents, which include resins, gels, silica, treated silica tested for arsenic removal come out to be superior. Immobilized biomass adsorbents offered outstanding performances. Desorption of arsenic followed by regeneration of sorbents has been discussed. Strong acids and bases seem to be the best desorbing agents to produce arsenic concentrates. Arsenic concentrate treatment and disposal obtained is briefly addressed. This issue is very important but much less discussed.
Keywords:adsorption; arsenic; adsorbents; solid waste utilization; activated carbons; low-cost adsorbents; arsenic remediation; arsenic removal; arsenic adsorption
来源出版物:Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 142(1-2): 1-53
被引频次:813
Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review
Chong, Mengnan; Jin, Bo; Chow, Christopher WK
Abstract:In recent years, semiconductor photocatalytic process has shown a great potential as a low-cost, environmental friendly and sustainable treatment technology to align with the “zero” waste scheme in the water/wastewater industry. The ability of this advanced oxidation technology has been widely demonstrated to remove persistent organic compounds and microorganisms in water. At present, the main technical barriers that impede its commercialisation remained on the post-recovery of the catalyst particles after water treatment. This paper reviews the recent R&D progresses of engineered-photocatalysts, photoreactor systems, and the process optimizations and modellings of the photooxidation processes for water treatment. A number of potential and commercial photocatalytic reactor configurations are discussed, in particular the photocatalytic membrane reactors. The effects of key photoreactor operation parameters and water quality on the photo-process performances in terms of the mineralization and disinfection are assessed. For the first time, we describe how to utilize a multi-variables optimization approach to determine the optimum operation parameters so as to enhance process performance and photooxidation efficiency. Both photomineralization and photo-disinfection kinetics and their modellings associated with the photocatalytic water treatment process are detailed. A brief discussion on the life cycle assessment for retrofitting the photocatalytic technology as an alternative waste treatment process is presented. This paper will deliver a scientific and technical overview and useful information to scientists and engineers who work in this field.
Keywords:TiO2; photocatalysis; water treatment; photocatalytic reactors; kinetic modelling; water qualities; life cycle analysis; mineralization; disinfection
来源出版物:Water Research, 2010, 44(10): 2997-3027
被引频次:665
Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review
Fu, Fenglian; Wang, Qi
Abstract:Heavy metal pollution has become one of the most serious environmental problems today. The treatment of heavy metals is of special concern due to their recalcitrance and persistence in the environment. In recent years, various methods for heavy metal removal from wastewater have been extensively studied. This paper reviews the current methods that have been used to treat heavy metal wastewater and evaluates these techniques. These technologies include chemical precipitation, ion-exchange, adsorption, membrane filtration, coagulation-flocculation, flotation and electrochemical methods. About 185 published studies (1988-2010) are reviewed in this paper. It is evident from the literature survey articles that ion-exchange, adsorption and membrane filtration are the most frequently studied for the treatment of heavy metal wastewater.
Keywords:heavy metal wastewater; treatment technology; review
来源出版物:Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407-418
被引频次:501
Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): Membrane fouling and membrane materialMeng, Fangang; Chae, So-Ryong; Drews, Anja; et al.
Abstract:Membrane bioreactors (MBRs) have been actively employed for municipal and industrial wastewater treatments. So far, membrane fouling and the high cost of membranes are main obstacles for wider application of MBRs. Over the past few years, considerable investigations have been performed to understand MBR fouling in detail and to develop high-flux or low-cost membranes. This review attempted to address the recent and current developments in MBRs on the basis of reported literature in order to provide more detailed information about MBRs. In this paper, the fouling behaviour, fouling factors and fouling control strategies were discussed. Recent developments in membrane materials including low-cost filters, membrane modification and dynamic membranes were also reviewed. Lastly, the future trends in membrane fouling research and membrane material development in the coming years were addressed.
Keywords:membrane bioreactor (MBR); membrane fouling; extracellular polymeric substances (EPS); soluble microbial products (SMP); membrane modification
来源出版物:Water Research, 2009, 43(6): 1489-1512
被引频次:479
Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges
Greenlee, Lauren F; Lawler, Desmond F; Freeman, Benny D; et al.
Abstract:Reverse osmosis membrane technology has developed over the past 40 years to a 44% share in world desalting production capacity, and an 80% share in the total number of desalination plants installed worldwide. The use of membrane desalination has increased as materials have improved and costs have decreased. Today, reverse osmosis membranes are the leading technology for new desalination installations, and they are applied to a variety of salt water resources using tailored pretreatment and membrane system design. Two distinct branches of reverse osmosis desalination have emerged: seawater reverse osmosis and brackish water reverse osmosis. Differences between the two water sources, including foulants, salinity, waste brine (concentrate) disposal options, and plant location, have created significant differences in process development, implementation, and key technical problems. Pretreatment options are similar for both types of reverse osmosis and depend on the specific components of the water source. Both brackish water and seawater reverse osmosis (RO) will continue to be used worldwide; new technology in energy recovery and renewable energy, as well as innovative plant design, will allow greater use of desalination for inland and rural communities, while providing more affordable water for large coastal cities. A wide variety of research and general information on RO desalination is available; however, a direct comparison of seawater and brackish water RO systems is necessary to highlight similarities and differences in process development. This article brings to light key parameters of an RO process and process modifications due to feed water characteristics.
Keywords:desalination; reverse osmosis; brackish water; seawater; drinking water; membranes
来源出版物:Water Research, 2009, 43(9): 2317-2348
被引频次:409
Physico-chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals
Kurniawan, TA; Chan, GYS; Lo, WH
Abstract:This article reviews the technical applicability of various physico-chemical treatments for the removal of heavy metals such asCd(II). Cr(III), Cr(VI), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) from contaminated wastewater. A particular focus is given to chemical precipitation, coagulation-flocculation, flotation, ion exchange and membrane filtration. Their advantages and limitations in application are evaluated. Their operating conditions such as pH, dose required, initial metal concentration and treatment performance are presented. About 124 published studies (1980-2006) are reviewed. It is evident from the survey that ion exchange and membrane filtration are the most frequently studied and widely applied for the treatment of metal-containinated wastewater. Ion exchange has achieved a complete removal of Cd(II), Cr(III), Cu(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II) with an initial concentration of 100 mg/L, respectively. The results are comparable to that of reverse osmosis (99% of Cd(II) rejection with an initial concentration of 200 mg/L). Lime precipitation has been found as one of the most effective means to treat inorganic effluent with a metal concentration of higher than 1000 mg/L. It is important to note that the overall treatment cost of metal-contaminated water varies, depending on the process employed and the local conditions. In general, the technical applicability, plant simplicity and cost-effectiveness are the key factors in selecting the most suitable treatment for inorganic effluent.
Keywords:electroplating industry; heavy metal uptake; inorganic effluent; metal-contaminated water; water pollution control
来源出版物:Chemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 118(1-2): 83-98
被引频次:391
Removal of selected pharmaceuticals, fragrances and endocrine disrupting compounds in a membrane bioreactor and conventional wastewater treatment plants
Clara, M; Strenn, B; Gans, O; et al.
Abstract:Eight pharmaceuticals, two polycyclic musk fragrances and nine endocrine disrupting chemicals were analysed in several waste water treatment plants (WWTPs). A membrane bioreactor in pilot scale was operated at different solid retention times (SRTs) and the results obtained are compared to conventional activated sludge plants (CASP) operated at different SRTs. The SRT is an important design parameter and its impact on achievable treatment efficiencies was evaluated. Different behaviours were observed for the different investigated compounds. Some compounds as the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine were not removed in any of the sampled treatment facilities and effluent concentrations in the range of influent concentrations were measured. Other compounds as bisphenol-A. the analgesic ibuprofen or the lipid regulator bezafibrate were nearly completely removed (removal rates>90%). The operation of WWTPs with SRTs suitable for nitrogen removal (SRT > 10 days at 10 degrees C) also increases the removal potential regarding selected micropollutants. No differences in treatment efficiencies were detected between the two treatment techniques. As in conventional WWTP also the removal potential of MBRs depends on the SRT. Ultrafiltration membranes do not allow any additional detention of the investigated substances due to size exclusion. However, MBRs achieve a high SRT within a compact reactor. Nonylphenolpolyehtoxylates were removed in higher extend in very low-loaded conventional WWTPs, due to variations of redox conditions, necessary for the degradation of those compounds.
Keywords:wastewater treatment; endocrine disrupting chemicals; pharmaceuticals; musk fragrances; membrane bioreactor; removal efficiency
来源出版物:Water Research, 2005, 39(19): 4797-4807
被引频次:390
Removal of pharmaceuticals and fragrances in biological wastewater treatment
Joss, A; Keller, E; Alder, AC; et al.
Abstract:The removal of seven pharmaceuticals and two fragrances in the biological units of various full-scale municipal wastewater treatment plants was studied. The observed removal of pharmaceuticals was mainly due to biological transformation and varied from insignificant (< 10%, carbamazepine) to > 90% (ibuprofen). However, no quantitative relationship between structure and activity can be set up for the biological transformation. Overall, it can be concluded that for compounds showing a sorption coefficient (K-d) of below 300 L kg-1, sorption onto secondary sludge is not relevant and their transformation can consequently be assessed simply by comparing influent and effluent concentrations. The two fragrances (HHCB, AHTN) studied were mainly removed by sorption onto sludge. For the compounds studied, comparable transformation and sorption was seen for different reactor types (conventional activated sludge, membrane bioreactor and fixed bed reactor) as well as for sludge ages between 10 and 60-80 days and temperatures between 12 degrees C and 21 degrees C. However, some significant variations in the observed removal currently lack an explanation. The observed incoming daily load of iopromide and roxithromycin in medium-sized municipal wastewater treatment plants (up to 80000 population equivalents) is generated by only a small number of patients: the consequences for representative 24 h composite sampling are discussed. Generally, the paper presents a method for setting up mass balances for micropollutants over entire wastewater treatment plants, including an estimation of the accuracy of the quantified fate (i.e. removal by sorption and biological transformation).
Keywords:degradation; sorption; municipal wastewater; membrane bioreactor; pharmaceuticals; musk fragrances
来源出版物:Water Research, 2005, 39(14): 3139-3152
被引频次:369
Membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment
Chang, IS; Le Clech, P; Jefferson, B; et al.
Abstract:Membrane bioreactors (MBRs), in which membranes are applied to biological wastewater treatment for biomass separation, provide many advantages over conventional treatment. However, membrane fouling in MBRs restricts their widespread application because it reduces productivity and increases maintenance and operating costs. Recently much research and development has taken place to investigate, model, and control membrane fouling processes. However, unified and well-structured theories on membrane fouling are not currently available because of the complexity of the biomass matrix, which is highly heterogeneous and includes living microorganisms. Membrane fouling in MBR systems can be reversible (i.e., removable by physical washing) or irreversible (removable by chemical cleaning only), and can take place on the membrane surface or into the membrane pores. Although establishing a general model to describe membrane fouling in such a process is made extremely difficult by the inherent heterogeneity of the system, the nature and extent of fouling in MBRs is strongly influenced by three factors: biomass characteristics, operating conditions, and membrane characteristics. Fouling control techniques which have been investigated include low-flux operation, high-shear slug flow aeration in submerged configuration, periodical air or permeate back flushing, intermittent suction operation or addition of powdered activated carbon (PAC). Of these, only PAC addition is currently not used in existing large-scale installations.
Keywords:membrane; wastewater treatment; sewage; biomass; biological treatment
来源出版物:Journal of Environmental Engineering ASCE, 2002, 128(11): 1018-1029
被引频次:254
Membrane separation bioreactors for wastewater treatment
Visvanathan, C; Ben Aim, R; Parameshwaran, K
Abstract:With continuing depletion of fresh water resources, focus has shifted more toward water recovery, reuse, and recycling, which require an extension of conventional wastewater treatment technologies. Downstream external factors like stricter compliance requirements for wastewater discharge, rising treatment costs, and spatial constraints necessitate renewed investigation of alternative technologies. Coupled with biological treatment processes, membrane technology has gained considerable attention due to its wide range of applicability and the performance characteristics of membrane systems that have been established by various investigations and innovations during the last decade. This article summarizes research efforts and presents a review of the how and why of their development and applications. The focus is on appraising and comparing technologies on the basis of their relative merits and demerits. Additional facts and figures, especially regarding process parameters and effluent quality, an used to evaluate primary findings on these technologies. Key factors such as loadings rates, retention time, cross-flow velocities, membrane types, membrane fouling, and backwashing, etc. are some of the aspects covered. Membrane applications in various aerobic and anaerobic schemes are discussed at length. However, the emphasis is on the use of membranes as a solid/liquid separator, a key in achieving desired effluent quality. Further, technology development directions and possibilities are also explored. The review concludes with an economic assessment of the technologies because one of the key technology selection criteria is financial viability.
Keywords:membrane bioreactor; membrane technology; solid/liquid separation; membrane air diffusers; membrane fouling; backwashing; micro-porous membranes
来源出版物:Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2000, 30(1): 1-48
·推荐论文摘要·
氧化石墨烯基水处理膜研究进展
芦瑛,张林,李明,等
摘要:氧化石墨烯(GO)具有片层薄、亲水性好、水分子在其片层间运动速度快等特点,通过调节GO膜片层间隙尺寸可实现对溶质的截留,因而在水处理方面表现出优异的分离性能。本文综述了氧化石墨烯基膜的制备方法,包括真空抽滤法、喷涂法、旋涂法和浸涂法和层层自主装法等。介绍了氧化石墨烯基膜在反渗透、纳滤、渗透汽化等方面的研究进展,并对未来在水处理领域的应用进行了展望。
关键词:氧化石墨烯;膜制备;膜分离;水处理
来源出版物:科技导报, 2015, 33(14): 32-35联系邮箱:李明,lmroeket@163.com
反渗透膜生物污染的影响因素及控制方法的研究进展
李晨,杨禹,高鑫,等
摘要:由于人口的增长和淡水资源的短缺,各种水处理技术应运而生,其中RO技术作为一项新兴膜分离技术,在海水淡化、污水处理、再生水回用等方面都有着广泛的应用。但是膜污染问题的存在,成为膜技术在饮用水和污水处理中广泛应用的瓶颈。其中生物污染对膜的破坏性最为严重,其污染也最难控制。回顾了生物污染的形成过程,主要列举了影响生物膜初始形成的几种因素:菌体特性、膜表面特性、进水组分等。同时讨论了生物污染的控制和预防方法,包括预处理、RO膜表面改性和微生物群体感应抑制。最后根据目前国内外的研究现状,展望了生物污染未来的研究前景。
关键词:反渗透膜;生物污染;初始阶段;影响因素;控制与预防
来源出版物:水处理技术,2015, 41(2): 1-5联系邮箱:李晨,shengkelichen1992@126.com
混凝技术去除水中新兴污染物的研究进展
王东升,姜巍,肖峰,等
摘要:常规水处理工艺通常不能完全将水中新兴污染物(ECs)去除,残留的污染物仍然具有相当大的环境风险,如何有效地去除水中痕量新兴污染物是一个函待解决的难题。本文概述了新兴污染物的来源、种类和危害,并分析了混凝工艺去除新兴污染物的可行性,重点介绍了新兴污染物性质、混凝剂种类和投加量、pH和水中溶解性物质对混凝效果的影响机制,并介绍了混凝与氧化、膜过滤及吸附等工艺的组合集成技术。在此基础上,对未来混凝技术去除新兴污染物的研究方向和发展趋势进行了展望。
关键词:新兴污染物;混凝;影响因素;组合工艺
来源出版物:环境工程学报,2015, 9(7): 3069-3076联系邮箱:王东升,wgds@rcees.ac.cn
膜分离技术在垃圾渗滤液处理中的应用
罗丹,晏云鹏,全学军
摘要:垃圾渗滤液是一种重污染的有毒有机废水,对生态环境造成了严重的威胁。本文综述了垃圾渗滤液现有的膜处理技术,与传统处理工艺相比,膜技术具有低能高效等优点,是未来渗滤液处理技术的重要发展方向。由于垃圾渗滤液组成的复杂性,根据不同处理目的,微滤膜(ME)、超滤膜(UE)、纳滤膜(NF)和反渗透膜(RO)4种膜在垃圾渗滤液处理中都得到了一定的应用。总结发现,其中MF和OF对渗滤液的处理效果较差,一般作为渗滤液的预处理技术;NF和RO对渗滤液的处理效果较好,主要作为其深度处理技术。然而,膜污染阻碍了膜技术在渗滤液处理方面的发展与应用,为此可通过研究开发新型膜材料、有效的预处理技术和膜分离工艺优化等方面来防止膜污染的发生,以便膜技术在渗滤液及其他水处理方面得到更加广泛的应用。
关键词:废水;膜;纳滤;膜污染;污染防止
来源出版物:化工进展, 2015, 34(8): 3133-3141联系邮箱:全学军,hengjunq@cqut.edu.cn
多巴胺在污水处理中的应用与展望
王新鹏,郭周义
摘要:主要探讨了多巴胺在污水处理中的优势、自聚—附着机理及其在膜技术和吸附方面的应用以及前景展望,并对目前的研究热点—多巴胺与石墨烯复合材料在水处理中的优缺点与应用现状进行了比较,指出多巴胺在污水处理方面具有良好的应用前景。
关键词:水处理;多巴胺;自聚—附着;膜技术;吸附
来源出版物:工业水处理, 2015, 35(2): 19-22
光催化—膜分离棍合技术的水处理应用研究进展
费锡智,杨晶晶,白仁碧
摘要:介绍光催化一膜分离藕合工艺,它是在传统光催化技术中粉末催化剂难分离回收和废水处理后水质不够理想的基础上进行研发的。总结了不同构型的光催化膜反应器的特点及其存在的局限性,并简述了新型光催化膜反应器工艺运行时需考虑的因素。分析表明悬浮型光催化膜反应器的光催化效率明显高于负载型光催化膜反应器;针对悬浮式光催化膜反应器面临的由压力驱动引起的高能量输入和膜污染问题,指出光催化与渗透气化或膜蒸馏联用工艺所具有的独特优势。认为光催化/膜分离藕合工艺在水处理领域具有重要前景,今后研究应集中在高活性光催化剂的开发、高抗氧化性和耐污染的膜制备及光催化膜反应器结构的优化上。
关键词:光催化氧化技术;膜分离技术;光催化—膜反应器
来源出版物:水处理技术,2014, 40(12): 11-18联系邮箱:费锡智,feixizhi123@126.com
高藻和高有机物湖泊型原水处理技术集成与示范
高乃云,马艳,楚文海,等
摘要:“十一五”期间,针对太湖水源高藻、高有机物、高氨氮、高臭味和藻毒素等污染特征,开展高效生物预处理、高效化学预处理及强化常规处理和深度处理以及超滤膜把关处理工艺等关键技术研究,并辅以安全消毒技术研究。通过技术研发、技术集成和综合示范,形成预处理藕合技术→强化常规处理→臭氧—生物活性炭深度处理→超滤膜联用的多级屏障处理工艺流程,依托于无锡自来水公司完成的中桥水厂高藻和高有机物原水膜深度处理集成技术工程示范,形成针对高藻型湖泊原水用水安全的技术保障体系,示范工程饮用水水质达到《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB5749—2006),工艺流程受到长三角地区普遍的认可,正在大规模地推广应用。
关键词:高藻;高有机物;臭氧—生物活性炭;超滤膜;多级屏障;水专项
来源出版物:给水排水, 2013, 39(3): 13-16
微波辅助水处理研究应用进展
纪仲光,王军,栾兆坤
摘要:从水处理功能材料制备与改性、催化氧化处理废水、废水消毒及膜分离处理废水等方面综述了微波在水处理中应用及研究现状,重点介绍了微波在膜蒸馏水处理中的研究进展,以期拓展微波在水处理中应用的广度与深度。
关键词:微波;水处理;膜分离;膜蒸馏
来源出版物:给水排水, 2013, 39(S1): 400-404
超滤技术在给水处理中的应用及发展状况
郑晨,马晓力
摘要:超滤技术是一种膜分离技术,在给水处理领域的应用己趋于成熟。随着环境污染问题日益严重化以及CB 5749—2006《生活饮用水卫生标准》对饮用水水质各项指标要求的严格化,传统水处理技术己经无法满足人们的需求,发展与推广以超滤技术为代表的新型水处理技术非常必要。通过对超滤技术概况及其工程应用实例的介绍,分析了超滤技术的发展瓶颈以及市场技术前景。
关键词:超滤技术;膜技术;给水处理
来源出版物:环境工程, 2013, 31(增刊): 163-195
Polymer-matrix nanocomposite membranes for water treatment
Yin, Jun; Deng, Baolin
Abstract:One of the grand challenges to sustain the modern society is to secure adequate water resources of desirable quality for various designated uses. To address this challenge, membrane water treatment is expected to play an increasingly important role in areas such as drinking water treatment, brackish and seawater desalination, and wastewater treatment and reuse. Existing membranes for water treatment, typically polymeric in nature, are still restricted by several challenges including the trade-off relationship between permeability and selectivity (also called Robeson upper boundary in membrane gas separation), and low resistance to fouling. Nanocomposite membranes, anew class of membranes fabricated by combining polymeric materials with nanomaterials, are emerging as a promising solution to these challenges. The advanced nanocomposite membranes could be designed to meet specific water treatment applications by tuning theft structure and physicochemical properties (e.g. hydrophilicity, porosity, charge density, and thermal and mechanical stability) and introducing unique functionalities (e.g. antibacterial, photocatalytic or adsorptive capabilities). This review is to summarize the recent scientific and technological advances in the development of nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. The nanocomposite membranes were classified into (1) conventional nanocomposite, (2) thin-film nanocomposite (TEN), (3) thin-film composite (TFC) with nanocomposite substrate, and (4) surface located nanocomposite, based on the membrane structure and location of nanomaterial. Challenges and future research directions in developing high performance nanocomposite membranes were also discussed.
Keywords:nanocomposite; polymeric membrane; mixed-matrix; water treatment; antifouling
来源出版物:Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 479: 256-275
Modification of membrane surfaces via microswelling for fouling control in drinking water treatment
Du, Jennifer Runhong; Peldszus, Sigrid; Huck, Peter M; et al.
Abstract:To increase membrane fouling resistance a new membrane post-treatment process, i.e solvent induced microswelling, was used to increase membrane surface hydrophilicity and smoothness. Driven by interfacial free energy minimization, the surface of microporous membranes will reassemble when exposed to a dilute aqueous solution of a suitable solvent. To prove this concept, three commercial membranes for water treatment were used: a polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane and poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration and microfiltration membranes. The membrane physiochemical properties were characterized by pure water permeation, contact angle, X-ray-photoelectron spectroscopy and roughness measurements. After the membranes were post-treated with dilute aqueous solutions of a suitable solvent, membrane surface hydrophilicity and smoothness were effectively increased while the permeance of pure water was maintained. After 18 h of permeation using surface water, the modified poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membrane exhibited a 50% higher flux and the same permeate water quality compared to the unmodified membrane. The microswelling conditions (including processing time and temperature, type and amount of solvents) affected the extent of the surface reassembly and thus the surface properties and anti-fouling behavior. These results show that microswelling treatment induced by dilute solvent solutions is a promising method for altering membrane surface properties for fouling control in drinking water treatment.
Keywords:surface modification; fouling control; microswelling; hydrophilicity; roughness
来源出版物:Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 475: 488-495
Formation of micro-channels in ceramic membranes-spatial structure, simulation, and potential use in water treatment
Lee, Melanie; Wang, Bo; Wu, Zhentao; et al.
Abstract:In this study, alumina membranes with distinct types of micro-channels have been developed via a fingering induced phase inversion and sintering technique. The designed membrane morphologies were achieved by using five different solvents DMSO, NMP, DMAc, EWE and TEP, which led to unique changes in the macroand microstructures of the membranes. The micro-channel shapes vary from long, straight, cylindrical and densely packed (DMSO) to pear-shaped conical structures (NMP and DMAc). When DMF and TEP were used, symmetric membranes with sponge-like structure were formed. These micro-channels display a regular and periodic distribution and also have a hierarchical spatial structure with a distribution in number, length and width along the depth of the membranes. Dead end water permeation tests reveal that the micro-channels can greatly reduce the resistance to water permeation. Furthermore, the microstructures also vary with a change in solvent, and different membrane pore sizes were observed. The initialisation of the micro-channels was interpreted using the Rayleigh-Taylor instability, driven by acceleration on the interface and facilitated by a difference in density between the suspension and the coagulant. The spacing between the microchannels and their hierarchical structure was quantitatively mimicked using R-T Instability theory and the simulation results matched the experimental results reasonably well.
Keywords:asymmetric structure; alumina membranes; micro-channels; Rayleigh-Taylor instability; water treatment
来源出版物:Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 483: 1-14
Fouling-tolerant nanofibrous polymer membranes for water treatment
Lee, Jang-Woo; Jung, Jiyoung; Cho, Young Hoon; et al.
Abstract:Nafion/polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofibrous membranes with electrostatically negative charges on the fiber surface were fabricated via electrospinning with superior water permeability and antifouling behaviors in comparison with the conventional microfiltration membranes. The fiber diameter and the resultant pore size in the nanofibrous membranes were easily controlled through tailoring the properties of the electrospinning solutions. The electrospun Nafion/PVDF nanofibrous membranes revealed high porosities (>80%) and high densities of sulfonate groups on the membrane surface, leading to praiseworthy water permeability. Unexpectedly, thewater permeability was observed as proportional to the fiber diameter and pore size in the membrane. The presence of sulfonate groups on the membrane improved the antifouling performance against negatively charged oily foulants.
Keywords:electrospinning; nanofibrous membrane; charged membrane; antifouling Nafion; polyvinylidene fluoride; water treatment
来源出版物:ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(16): 14600-14607
Fabrication of porous matrix membrane (PMM) using metal-organic framework as green template for water treatment
Lee, Jianyuan; Tang, Chuyang Y; Huo, Fengwei; et al.
Abstract:Pressure-driven membranes with high porosity can potentially be fabricated by removing template, such as low water stability metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) or other nanoparticles, in polymeric matrix. We report on the use of benign MOFs as green template to enhance porosity and interconnectivity of the water treatment membranes. Significantly enhanced separation performance was observed which might be attributed to the mass transfer coefficient of the substrate layer increased in ultrafiltration (UF) application.
来源出版物:Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 3740
Recent progresses on fabrication of photocatalytic membranes for water treatment
Zhang, Xiwang; Wang, David K; da Costa, Joao C. Diniz
Abstract:Compared to conventional separation membranes, photocatalytic membranes possess a number of unique properties, such as anti-fouling, anti-microbial, superhydrophilicity, concurrent photocatalytic oxidation and separation, all of which make them an attractive technology in water treatment. Moreover, the problem of photocatalyst separation which is the main obstacle of photocatalysis processes can be resolved by the photocatalytic membranes thereby advancing their practical application. This article presents an overview of this new type of membrane, with a focus on recent progresses achieved on their fabrication methods. Based on membrane materials, they are broadly categorized into pure inorganic and inorganic-polymer hybrid membranes. The fabrication methods are separately reviewed and discussed for these two membrane categories. In addition, future perspectives on membrane development and feasibility are given. The paper would provide new insights into the development of photocatalytic membranes and their potential in water treatment.
Keywords:photocatalysis; membrane; photocatalytic degradation; TiO2
来源出版物:Catalysis Today, 2014, 230:47-54
Preparation and characterization of electro-spun nanofiber membranes and their possible applications in water treatment
Feng, C; Khulbe, K. C; Matsuura, T; et al.
Abstract:Nano-scale materials can be designed to exhibit novel and significantly improved physical and chemical properties. Polymer nanofibers, an important class of nano-materials, have attracted increasing attention in the last 10 years because of their high surface-to-mass (or volume) ratio and special characteristics attractive for advanced applications. In particular, electro-spun nanofiber membranes (ENMs) have high porosity, interconnected open pore structure and tailorable membrane thickness. Moreover, their high surface hydrophobicity makes them suitable for membrane distillation (MD). In this paper, recent progresses are reviewed on the preparation of different types of nanofibers with different secondary nanostructures, including hollow nanofibers. Applications of hollow nanofibers for membrane separation processes are then discussed based on an imaginary design of hollow nanofiber module. Application of ENMs in MD is, on the other hand, not a product of imagination but experiments have already been conducted in various laboratories, as reviewed in this paper. In particular, the experimental results obtained in our laboratory for desalination of saline water and gases stripping of VOCs are highlighted. By using an electrospun PVDF nanofiber membrane, saline water with NaCl content of 6% was successfully desalinated for more than 20 days with no indication of membrane wetting. The PVDF ENM could also be successfully used in gas-stripping of chloroform, representing VOCs, with mass transfer coefficients higher than hollow fiber membranes. It is expected that MD by ENMs can be applied for many other purposes such as waste water treatment, food processing, and treatment of pharmaceutical products.
Keywords:nanofiber membrane; electro-spinning; membrane application
来源出版物:Separation and Purification Technology, 2013, 102: 118-135
Polymer nanocomposites with graphene-based hierarchical fillers as materials for multifunctional water treatment membranes
Crock, Christopher A; Rogensues, Adam R; Shan, Wenqian; et al.
Abstract:Phase inversion of polymer casting mixtures filled with hierarchical functional nanostructures is proposed as a synthetic route for the design of multifunctional membranes. The study tested the hypothesis that by regulating the relative content of components representingdifferent levels in the nanofiller hierarchy, the structure and additional functions of such membranes could be controlled separately. Exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets (xGnPs) decorated by Au nanoparticles (Au NPs), used as a model hierarchical nanofiller, were added to the casting mixture of polysulfone, N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone and polyethylene glycol prior to forming the membrane by phase inversion. The resulting porous asymmetric nanocomposites were shown to be permselective and catalytically active ultrafiltration membranes that were more resistant to compaction, more permeable than xGnP-free membranes and at least as selective. By designing membrane compositions with different relative amounts of Au-decorated xGnPs and Au-free xGnPs, the structure (controlled by the loading of xGnPs) and catalytic activity (controlled by the loading of Au NPs) could be controlled largely independently.
Keywords:graphene; polymer nanocomposites; mixed matrix membranes; multifunctional membranes; membrane catalysis; membrane reactors
来源出版物:Water Research, 2013, 47(12): 3984-3996
Granular iron oxide adsorbents to control natural organic matter and membrane fouling in ultrafiltration water treatment
Cui, Xiaojun; Choo, Kwang-Ho
Abstract:Fine iron oxide particles (IOPs) are effective in removing natural organic matter (NOM) that causes membrane fouling in water treatment, but the separation of used IOPs is problematic. This study focused on the fabrication and use of granular iron oxide adsorbents, in combination with ultrafiltration (UF) membranes while investigating the NOM removal efficiency and fouling control. Sulfonated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer beads were coated with two types of iron oxides (ferrihydrite and magnetite) and their performances were compared to that of fine IOPs. A significant amount of iron oxide coating (52-63 mg of Fe per g bead) was achieved by means of electrostatic binding and hydrolysis of iron ions. Iron oxide coated polymer (IOCP) beads were able to remove some amounts (similar to 20%) of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) comparable to that achieved by IOPs within a. short period of time (<15 min). Regenerated IOCPs exhibited the same sorption capacity as the fresh ones. The integrated IOCP/UF system operation with a 15-min empty bed contact time and 10-h cyclic regeneration maintained the 20% DOC removal with no sigh of significant membrane fouling. In contrast, a sharp transmembrane pressure buildup occurred in the UP system when no iron oxide pretreatment was applied, regardless of the types of membranes tested. Iron oxide adsorbed the NOM fraction with molecular weights of >1000 kDa which is believed to be responsible for severe UF fouling.
Keywords:natural organic matter; ultrafiltration; membrane fouling; iron oxide; polymer bead
来源出版物:Water Research, 2013, 47(13): 4227-4237
PAC membrane bioreactor as an alternative to biological activated carbon filters for drinking water treatment
Leveille, Simon; Carriere, Annie; Charest, Sebastien; et al.
Abstract:A high concentration powdered activated carbon (PAC) membrane bioreactor (MBR) was fed by clarified-ozonated surface water. As a control, a MBR without PAC was run in parallel. Water quality was also compared with a full-scale biological activated carbon (BAC) filter. Biological PAC inside the MBR caused a higher fouling rate as compared to the MBR without PAC, although it was still possible to maintain operation for about 3 months at 25 L m-2h-1before a chemical cleaning was needed. The fouling rate inside the MBR with PAC increased as the PAC age increased from 0 to 60 d. Full nitrification was achieved in the PAC-MBR down to 7 degrees C. Preozonation had no significant impact on dissolved organic carbon removal. Although the PAC-MBR globally provided superior removal of natural organic matter, haloacetic acid precursors and UV absorption at 254 nm (UVA254), its removal of trihalomethane (THM) precursors was inferior compared to the BAC filter. This effect was shown to be caused by the accumulation of suspended solids inside the bioreactor.
Keywords:activated carbon; biological treatment; drinking water; hybrid membrane process; THM; ultrafiltration
来源出版物:Journal of Water Supply Research and Technology-AQUA, 2013, 62(1): 23-34
编辑:卫夏雯
The role of chemical and physical interactions in natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes is systematically investigated, Results of fouling experiments with three humic acids demonstrate that membrane fouling increases with increasing electrolyte (NaCl) concentration, decreasing solution pH, and addition of divalent cations (Ca2+). At fixed solution ionic strength, the presence of calcium ions, at concentrations typical of those found in natural waters, has a marked effect on membrane fouling. Divalent cations interact specifically with humic carboxyl functional groups and, thus, substantially reduce humic charge and the electrostatic repulsion between humic macromolecules. Reduced NOM interchain repulsion results in increased NOM deposition on the membrane surface and formation of a densely packed fouling layer. In addition to the aforementioned chemical effects, results show that NOM fouling rate increases substantially with increasing initial permeation rate. It is demonstrated that the rate of fouling is controlled by an interplay between permeation drag and electrostatic double layer repulsion; that is, NOM fouling of NF membranes involves interrelationship (coupling) between physical and chemical interactions. The addition of a strong chelating agent (EDTA) to feed water reduces NOM fouling significantly by removing free and NOM-complexed calcium ions. EDTA treatment of NOM-fouled membranes also improves the cleaning efficiency dramatically by disrupting the fouling layer structure through a ligand exchange reaction between EDTA and NOM-calcium complexes.
natural organic matter; water treatment; nanofiltration membranes; humic substances; divalent cations; fouling control
典
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes Hong, SK Journal of Membrane Science 1997, 132 (2): 159-181 2 Fouling characterisation in membrane bioreactors Bouhabila, E Separation and Purification Technology, 2001, 22-23 (1-3): 123-132 3 Influence of the characteristics of natural organic matter on the fouling of microfiltration membranes Fan, LH Water Research, 2001, 35 (18): 4455-4463 4 Fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration Environmental Science & Technology, 2002, 36 membranes by natural waters Howe, KJ (16): 3571-3576 5 Membrane fouling in pilot-scale membrane Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39 Bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater Kimura, K (16): 6293-6299
Chemical and physical aspects of natural organic matter (NOM) fouling of nanofiltration membranes
Hong, SK; Elimelech, M
*摘编自《科技导报》2015年33卷14期:13~17页,图、表、参考文献已省略。
