The Pyrolysis Experiments of Waste Rubber and Plastics in Rotary Kiln
2015-02-27LIHouyangLIGang
LI Hou-yang LI Gang
(College of Electromechanical Engineering,Qingdao University,Qingdao Shandong 266071,China)
0 Introduction
The production of municipal solid waste(MSW)every year reached 150 million tons,and increased at a rate of 8~10 percents[1].As one of the waste treatment technology,the pyrolysis has more advantages than the landfill or incineration,such as higher recovery rate,better reduction, less pollution.It is widely recognized and developed that the rotary kiln was used in pyrolysis of rubber and plastics with the advantages of low material limit and heated equably[2].In this paper,with combining the study on pyrolysis experiments in fixed bed[3],a continuous feeding rotary kiln pyrolyzer system was designed.The influence of residence time and temperature on the pyrolysis of waste rubber and plastics has been investigated.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Raw materials and catalyst
The rubber and PE plastic were crushed into powder with the average particle size of 3~5mm.The materials’proximate analysis, element analysis and heat value results were shown in Table 1.The rubber and plastics were blended in proportion of 4 to 1.The mass of the sample was 300g in each experiment.

Tab.1 Proximate Analysis,Element Analysis and Heat Value
1.2 Experimental
The pyrolysis experiments were carried out in a continuous feeding rotary kiln pyrolyzer system showed in Figure 1.

Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the rotary kiln pyrolyzer system1 spiral feeder;2 tumbler;3 electric heating furnace; 4 thermocouple;5char collection box; 6 condensing unit;7 filter;8 fan;9 gas collection box; 10 governor;11 control system
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Residence time
The residence time of sample in rotary kiln was one of the important factors to reflect the performance of the experimental and the productions.The residence time was calculated by using the following formulas[4]∶

In the formulas,L,D,N and α were the length,diameter,revolving speed and gradient of the tumbler respectively.When L was 1.2m,D was 0.1m and α was 1.5°,the conditions in table 2 were selected to contrast the effects of different residence times.

Tab.2 The experimental conditions to effects of residence time
The yields of products and proximate analysis of the solid product were showed in Figure 2 and 3.
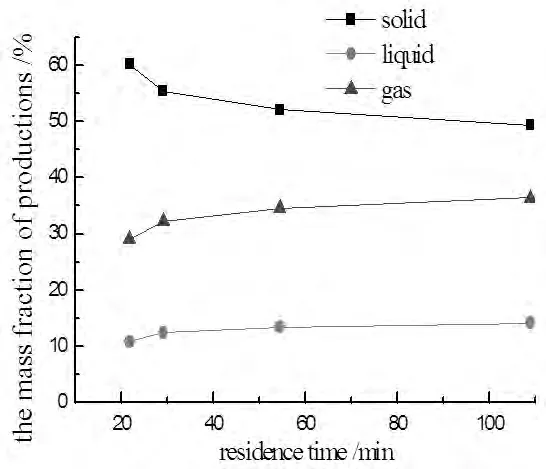
Fig.2 The yields of products to standing times
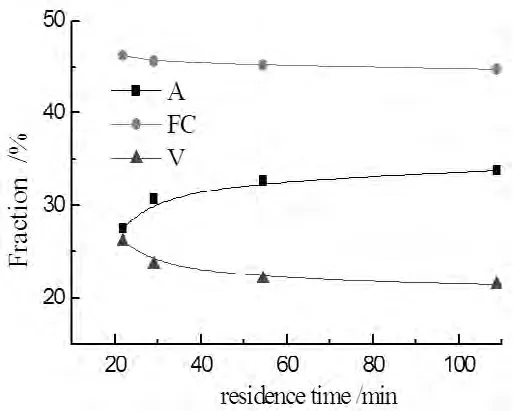
Fig.3 The proximate analysis of solid product
In figure 2,the solid production was most about 50~60%.The percent of gas production was about 30~40%.The liquid percent was least about 10%.With the residence time increasing,the percent of solid decreased and the rate also reduced and flattened out eventually because of the limit of pyroysis temperature.The extent of pyrolysis was lower when the residence time was too short,while the extent was not increased significantly when the time was too long.So it was reasonable that the revolving speed was 1~2r/min and the residence time was 60~100min.
With the pyrolysis extent rising,the volatilize products broke out more.The condensable products was condensed in the condensation system with ice water.The non-condensable gas consisted of micromolecule organics,such as H2,CO,CO2,CH4,C2H4,C2H6and so on.The percents of liquid and gas products increased and the rate also reduced.The rate of gas production was higher than the liquid,meaning thatthe macromolecalar carried out the second decomposition reaction into more micromolecule organics,and the gas products became more.
In figure 3,it was found that the sample was not pryrolyzed thoroughly.The variation of volatile matter was similar to that of the solid yields.The mass of ash was invariable,so the ash content increased in solid products with the mass of solid reducing.
2.2 Pyrolysis temperature
Thepyrolysistemperature wasanotherimportantfactor.The conditions in table 3 were selected to contrast the effects of different temperatures.
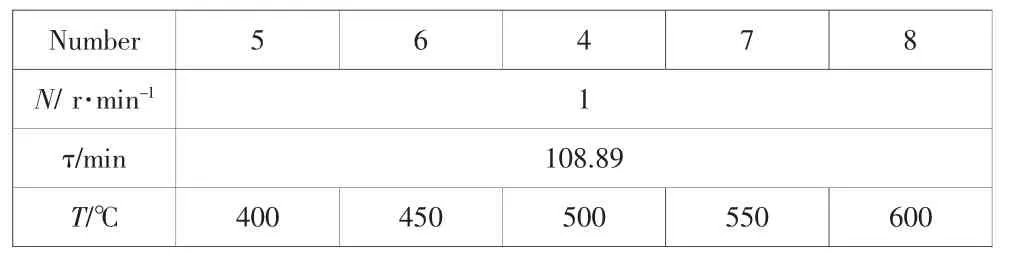
Tab.3 The experimental conditions to effects of temperature
The yields of products and proximate analysis of the solid product were showed in Figure 4 and 5.
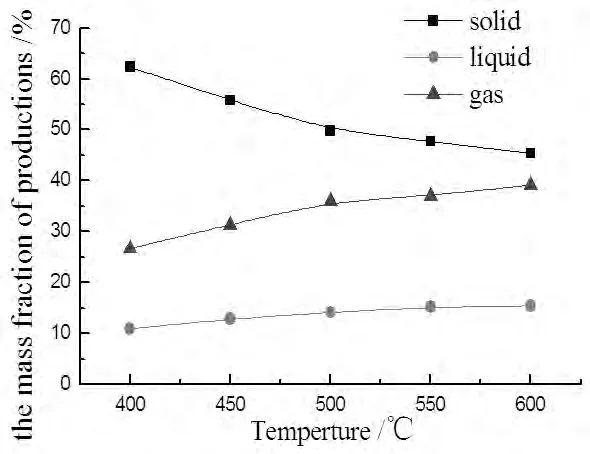
Fig.4 The yields of products to temperture
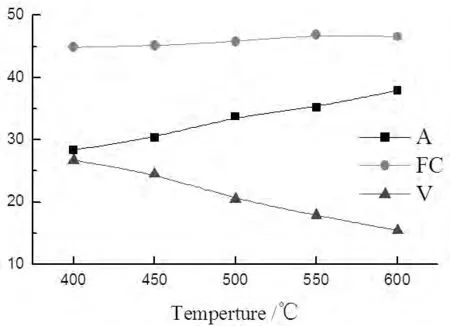
Fig.5 The proximate analysis of solid production
In figure 4,the extent of pyrolysis was lowest and the mass fraction of solid was high to 62.37%when the temperature was 400℃.The extent was improved by 17%and the solid reduced to 45.4% when the temperature was 600℃.The solid production decreased and the liquid and gas productions increased when the temperature varied from 400℃to 600℃.The rate of gas was higher than the liquid,especially in higher temperature.In all,the pyrolysis temperature was better maintained at 600℃。
In figure 5,the variation of volatile matter decreased,the ash content increased in solid products with the temperture in creasing.The fixed carbon varied non-distinctively,but the mass of ash was invariable, the fixed carbon was reduced in whole products relatively.
3 Conclusion
The yields of products were effected by the residence time and temperature in the pyrolysis of waste rubber and plastic in rotary kiln.
(1)When the temperature was constant,the longer was the standing time,the higher was the pyrolsis extent.The solid products decreased while the liquid and gas products increased.The revolving speed should be 1~2r/min.
(2)When the residence time was contant,it was better that the temperature was 600℃and the extent of pyrolysis was maximum.
[1]Ailian Wang,Shaodong Li.Research on the Status and Treatment Technologies of City Life Wastes in China[J]Jouranal of xi’an Shiyou University(Social Science Edition),2012,21(2)∶58-63.
[2]Hefa Cheng,Yuanan Hu.Municipal solid waste (MSW)as a renewable source of energy∶Current and future practices in China [J].Bioresource echnology, 2010,101(11)∶3816-3824.
[3]Hou yang Li,Cuiping Wang,Gang Li.Experimental study on the rubber/ plastics blending pyrolysis in TGA and fixed bed[J].Jouranal of Qingdao University (Engineering Technology Edition),2014,29(3)∶83-87.
[4]Aimin Li,Shuiqing Li,Jianhua Yan,et al.Experimental research on mean residence time of solid materials in rotary kiln[J].Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology,2002,18(2)∶152-157.
