Effects of Glycidamide on Activity and Progesterone Biosynthesis of Rat R2C Leydig Cells
2015-02-05WeiXUJianxiaSUNShunBAIMingweiLILuonaWENJieshengLIUHongyeLIYadongHUANGWeibinBAI
Wei XU,Jianxia SUN,Shun BAI,Mingwei LI,Luona WEN,Jiesheng LIU,Hongye LI, Yadong HUANG,Weibin BAI*
1.Department of Food Science and Engineering,College of Life Science,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China;
2.Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Light Industry,Guangdong University of Technology,Guangzhou 510006,China
Effects of Glycidamide on Activity and Progesterone Biosynthesis of Rat R2C Leydig Cells
Wei XU1,Jianxia SUN2,Shun BAI1,Mingwei LI1,Luona WEN1,Jiesheng LIU1,Hongye LI1, Yadong HUANG1,Weibin BAI1*
1.Department of Food Science and Engineering,College of Life Science,Jinan University,Guangzhou 510632,China;
2.Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Light Industry,Guangdong University of Technology,Guangzhou 510006,China
[Objective]This study aimed to investigate the effects of glycidamide(GA) on growth and progesterone biosynthesis of rat R2C Leydig cells cultured in vitro. [Method]The R2C Leydig cells were treated with GA with concentrations of 0.25, 0.5,0.75,1,2,4 and 6 mmol/L respectively for 48 h.TheIC25,IC50andIC75values of GA were all detected by MTT assay.The Leydig cells were treated with GA at concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75respectively for 48 h,and then the morphology of Leydig cells was observed.After the Leydig cells were treated with GA for 4 h, the cellular DNA damage was measured by the comet assay technique;and after the Leydig cells were with treated with GA for 24 h,the progesterone biosynthesis amount was detected by radioimmunoassay(RIA).[Result]GA could inhibit the viability of R2C Leydig cells,and itsIC25,IC50andIC75were 0.635,0.872 and 1.198 mmol/L,respectively.The GA at concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75affected the growth and morphology of rat R2C Leydig cells in varying degrees.The 4-h treatment of GA could significantly damage the DNA of R2C Leydig cells,and the 24-h treatment of GA at concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75all reduced the progesterone biosynthesis amount.[Conclusion]GA could inhibit the growth and progesterone biosynthesis of rat R2C Leydig cells.
Glycidamide;R2C Leydig cells;Cell activity;DNA damage;Progesterone
A crylamide(AA)is a chemical widely distributed in common foods and industries[1-2].It is considered a possible carcinogen for humans[3].In April,2002,the Swedish National Food Administration announced that large amounts of acrylamide will be generated during the heat treatment process of chips,coffee,toast,etc[4-5].This discovery has aroused widespread concern.It has been reported that acrylamide has genotoxicity,neurotoxicity and reproductive toxicity,and it is a possible carcinogen for humans[6-7].Glycidamide (GA)is a more active metabolite of acrylamide[8].Siriet al.[9]investigated the effects of AA and GA on sperm cells in testises of male rats.They found that compared with AA,GA could more significantly damage the sperm cells and affect the reproductive function in rats.However,the mechanism of reproductive toxicity of GA to male rats is still unknown.In this study, the toxicity of GA to rate R2C Leydig cells cultured in vitro was investigated, and the reproductive toxicity mechanism of GA was also discussed, thereby providing a basis for the safety assessment of GA.
Materials and Methods
Materials,reagents and instruments
The R2C Leydig cells were pro-
The reagents used in this study included GA(CAS:79-07-01;purity: 98%)(Shanghai Jingchun Reagents Co.,Ltd.),F12 medium,horse serum (Sigma Corporation),fetal calf serum, trypsin(GIBCO Corporation),dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO),MTT(AMRESCO Company),low melting point agarose, normal melting point agarose(FMC Corporation),Tris,EDTANa2,Triton X-100(Genview Corporation)and progesterone RIA kit(Beijing North Biotechnology Institute).
The equipment and instruments used in this study included incubator (37℃),microplate reader(Thermo Fisher Scientific Corporation),refrigerated centrifuge(Jintan Fuhua Instrument Co.,Ltd.)and GC-1200 γ RIA counter(Zhongjia Branch of HKUST Innovation Co.,Ltd.).
Methods
Detection of effect of GA on activity of R2C cells by MTT assayThe R2C Leydig cells at the logarithmic phase were inoculated in 96-well plates with 200 μl of suspension and total 4×103cells per well.The serumfree GA at concentrations of 0.25,0.5, 0.75,1,2,4 and 6 mmol/L(diluted with F12)was added to the plates 24 h later.There were three replications for each group.The blank group,with three repeated wells,was also arranged.A certain amount(10 μl)of MTT with concentration of 5 mg/ml was added to each of the wells 48 h later.Subsequently,the plates were all placed in the incubator(37℃).After 4 h,the liquid in the wells was all removed,and a certain amount(200 μl) of DMSO was added to each of the wells.Then,the plates were placed on a shaker and shaken for 10 min.Finally,the absorbances of all the wells were determined at 570 nm with microplate reader.The cell activity inhibition rate was calculated in accordance with the following formula:
Cell activity inhibition rate(%)= [1-(Absorbance of treatment group-Absorbance of blank group)/(Absorbance of control group-Absorbance of blank group)]×100%.
TheIC25,IC50andIC75values of GA were analyzed using Graphpad.Observation of effect of GA on morphology of R2C cells with inverted microscopeThe suspension with concentration of 1×106cells/ml was inoculated in 6-well plates.Subsequently,the GA with concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75was added respectively.After 48-h treatment,the morphology of R2C Leydig cells was observed with inverted microscope.
Detection of damage of GA to R2C cells by comet assayWhen the R2C Leydig cells grew to the logarithmic phase,they were inoculated in 6-well plates with a concentration of 1× 105cells/ml.After 24-h culture,the GA at concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75were added to the plates respectively. After 4 h,the R2C cells in the control group and the three treatment groups were all dissociated,centrifuged and washed once with PBS.
The R2C cells were resuspended in 0.8%low melting point agarose (LMP).A certain amount(100 μl)of resuspension was added on each glass side that had been pre-coated with a layer of normal melting point agarose,and then a layer of LMP was added on the top.After the agarose was solidified,the slides were placed in the lysis buffer(0.1 M EDTA,2.5 mmol/L NaCl,10 mmol/L Tris,pH 10.0,1%Triton×100,10%DMSO)at 5℃for 1 h.The slides were placed in alkaline electrophoresis buffer(0.3 M NaOH,1 mM EDTA,pH 13.6)for 20 min,and then subjected to electrophoresis(25 V,1 h)under alkaline conditions(pH 13.6).Subsequently, the slides were washed three times with Tris-HCl solution(pH 7.5)with 5 min per time.After stained with EB(20 μl,20 μg/ml),the slides were covered with coverslips.
The photographing was carried out using a fluorescence microscope, and the electrophoresis results were analyzed using CASP.
Detection of effect of GA on progesterone biosynthesis in R2C cells by radioimmunoassay(RIA)The R2C cell culture was diluted to 1×106cells/ml at the logarithmic phase.The cells were inoculated to 6-well plates with 1 ml of culture per well.After 24 h, the cells were treated with GA with concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75, respectively.After another 24 h,the supernatants were collected and stored at-20℃.The progesterone biosynthesis amount was determined according to the instructions of progesterone RIA kit.
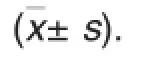
Results and Analysis
Inhibiting effect of GA on growth of R2C cells
The detection results by MTT assay showed that the inhibition rate of R2C cell ability was increased with the increased concentration of GA(Fig.1). TheIC25,IC50andIC75values of GA to R2C Leydig cells were 0.635,0.872 and 1.198 mmol/L,respectively.As shown in Fig.2,after the R2C cells were treated with GA at concentrations ofIC25,IC50andIC75for 48 h,the R2C cells became smaller,and they were changed from irregular polygonal to elliptical.The cell number was reduced,and the adhering ability of R2C Leydig cells was also reduced.The inhibiting effect of GA on cell growth was dose-dependent.
Damage effect of GA to DNA in R2C cells
Compared with that in the control group,the tailing phenomenon was more obvious in the three treatment groups in which the R2C Leydig cells were treated with GA at different concentrations for 4 h.The tail DNA content,tail length and Olive tail moment (OTM)were all increased with the in-crease of GA concentration.Particularly,the tail DNA content,tail length and Olive tail moment(OTM)in theIC50 andIC75 treatment groups were all significantly higher than those in the control group(Fig.3,Fig.4).It indicates that GA can induce DNA damage in R2C Leydig cells.
Effect of GA on progesterone biosynthesis in R2C cells
The determination results of progesterone biosynthesis amount in R2C cells showed that compared with that in the control group,the progesterone biosynthesis amounts in the three treatment groups were all significantly (P<0.05)reduced(Fig.5),and the decrement of progesterone biosynthesis amount was dependent on the concentration of GA.
Conclusions
It has been reported that acrylamide has reproductive toxicity[10-11]. Moreover,many researches have shown that glycidamide,as a metabolite of acrylamide,plays a major role in the reproductive toxicity of acrylamide. GA can produce toxic effects on animal reproductive organs[12].In the research on rat,it has been proven that GA affects the reproductive function in animals through interfering with the synthesis of steroid hormones[13].However,this founding has not been validated by cell culturein vitro.In this study,the R2C Leydig cells are treated asin-vitromaterial,and the toxic effects of GA are discussed by detecting the biological activity and function in cells.
The results showed that GA could inhibit the activity and affect the normal growth state of R2C cells.The effects of GA above are all dose-dependent. Therefore,the GA interferes with the function of the reproductive system possibly by inhibiting the activity of germ cells.The results of comet assay show that GA can induce significant DNA damage in R2C Leydig cells. Studies have shown that DNA damage can trigger apoptosis and reduce cell viability or even death[14].So it can be inferred that the inhibiting effect of GA on R2C cells may be associated with the induced DNA damage by GA. Steroids play an important role in maintaining animal reproductive function[15].The main function of testicular Leydig cells is to secret testosterone[16-17].But it is difficult to isolate primary cells from rat,and the isolated cells cannot be passaged,limiting the application of rat as an evaluation model[18].Due to a lack of testosterone synthesis enzyme,R2C cells are a class of testicular interstitial cell stains that can only secret progesterone.The R2C cells have unlimited propagating ability.Therefore,the situation of testosterone synthesis can be fully reflected using progesterone,a precursor for testosterone synthesis,as an indicator.R2C Leydig cells are therefore a cell model for rapid evaluation of male reproductive toxicity[19-20].In this study,the R2C cells are treated respectively with GA at three different concentrations for 24 h.The results show that the GA at three different concentrations all can significantly reduce the progesterone synthesis in R2C Leydig cells,and the higher the GA concentration is,the larger the decrement in progesterone synthesis is.It can be concluded that GA can cause a decline in progesterone biosynthesis function in R2C cells.
Based on the results above,it can be speculated that GA blocks protein synthesis by damaging DNA in testicular interstitial cells,thereby reducing progesterone synthesis function and cell viability in R2C Leydig cells.The declined cell viability may affect cellular normal functions,eventually leading to a decreased function of the reproductive system.The specific mechanism of the toxicity of GA is needed to be studied further through researching certain key proteins and their mRNA levels in the progesterone biosynthesis pathway,providing a basis for clarifying the effects of GA on Leydig cells.
[1]GARGAS ML,KIRMAN CR,SWEENEY LM,et al.Acrylamide:Consideration of species differences and nonlinear processes in estimating risk and safety for human ingestion[J].Food and Chemical Toxicology,2009,47(4):760-768.
[2]FRIEDMAN M.Chemistry,biochemistry, and safety of acrylamide:A review[J].J Agric Food Chem,2003,51(16):4504-4526.
[3]KLAUNIG JE.Acrylamide carcinogenicity[J].Food Chem,2008,56(15):5984-5988.
[4]CLAUS A,CARLE R,SCHIEBER A. Acrylamide in cereal products:A review [J].Journal of Cereal Science,2008,47 (2):118-133.
[5]Z?DL B,SCHMID D,WASSLER G,et al.Intestinal transport and metabolism of acrylamide[J].Toxicology,2007,232 (1):99-108.
[6]PARK J,KAMENDULIS LM,FRIEDMAN MA,et al.Acrylamide-induced cellular transformation[J].Toxicol Sci, 2002,65(2):177-183.
[7]WANG H,HUANG P,LIE T,et al.Reproductive toxicity of acrylamide-treated male rats[J].Reprod Toxicol,2010,29 (2):225-230.
[8]BREVIK A,RUSNAKOVA V,DUALE N,et al.Preconceptional paternal glycidamide exposure affects embryonic gene expression:Single embryo gene expression study following in vitro fertilization[J].Reproductive Toxicology, 2011,32(4):463-471.
[9]HANSEN SH,OLSEN AK,SODERLUND EJ,et al.In vitroinvestigations of glycidamide-induced DNA lesions in mouse male germ cells and in mouse and human lymphocytes[J].Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis,2010,696(1): 55-61.
[10]WANG H,HUANG P,LIE T,et al.Reproductive toxicity of acrylamidetreated male rats[J].Reproductive Toxicology,2010,29(2):225-230.
[11]LEE JG,WANG YS,CHOU CC.Acrylamide-induced apoptosis in rat primary astrocytes and human astrocytoma cell lines[J].Toxicology in Vitro,2014, 28(4):562-570.
[12]GHANAYEM BI,WITT KL,KISSLING GE,et al.Absence of acrylamide-induced genotoxicity in CYP2E1-null mice:evidence consistent with a glycidamide-mediated effect[J].Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis,2005, 578(1):284-297.
[13]CLEMENT FC,DIP R,NAEGELI H. Expression profile of human cells in culture exposed to glycidamide,a reactive metabolite of the heat-induced food carcinogen acrylamide[J].Toxicology,2007,240(1):111-124.
[14]ROOS WP,KAINA B.DNA damageinduced cell death by apoptosis[J]. Trends Mol Med,2006,12(9):440-450. [15]JANNINI EA,ULISSE S,D’ARMIENTO M.Thyroid hormone and male gonadal function[J].Endocrine Reviews, 1995,16(4):443-459.
[16]STOUT EP,LA CLAIR JJ,SNELL TW,et al.Conservation of progesterone hormone function in invertebrate reproduction[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci,2010, 107(26):11859-11864.
[17]WU JJ,WANG KL,WANG SW,et al.Differential effects of nonylphenol on testosterone secretion in rat Leydig cells[J].Toxicology,2010,268(1):1-7. [18]SUN JX,BAI S,BAI WB,et al.Toxic mechanisms of 3-monochloropropane-1,2-diol on progesterone production in R2C rat Leydig cells[J].J Agric Food Chem,2013,61(41):9955-9960.
[19]ZHANG QH,ZOU P,ZHAN HC,et al.Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase and cAMP are associated with cadmiummediated Leydig cell damage[J].Toxicology Letters,2011,205:183-189.
[20]KIM Y,RYU JC,CHOI HS,et al.Effect of 2,2’,4,4’-tetrahydroxybenzophenone(BP2)on steroidogenesis in testicular Leydig cells[J].Toxicology,2011, 288(1):18-26.
Responsible editor:Tingting XU
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
环氧丙烯酰胺对睾丸间质细胞R2C活性及孕酮合成功能的影响
许伟1,孙建霞2,白顺1,李名薇1,文罗娜1,刘洁生1,李宏业1,黄亚东1,白卫滨1*
(1.暨南大学生命科学学院食品科学与工程系,广东广州510632;2.广东工业大学轻工化工学院,广东广州510006)
[目的]研究环氧丙烯酰胺(GA)对体外培养的R2C细胞生长及孕酮合成的影响。[方法]用0.25、0.5、0.75、1、2、4、6 mmol/L浓度的GA作用于细胞48 h,MTT法获得GA作用浓度的IC25,IC50及IC75。用以上3种浓度的GA刺激细胞48 h,观察细胞形态。GA作用于细胞4 h后,通过彗星试验(Comet Assay)检测细胞DNA的损伤程度;放射免疫法(RⅠA)测定GA刺激细胞24 h后的孕酮合成量。[结果]GA能抑制R2C细胞活性,其IC25、IC50、IC75分别为0.635、0.872及1.198 mmol/L;3种浓度的GA能不同程度的影响细胞生长形态;作用4 h对R2C细胞DNA有损伤作用;各浓度组作用24 h后均能降低孕酮的合成量。[结论]GA能抑制R2C细胞增长及孕酮合成能力。
丙烯酰胺;睾丸间质细胞;细胞活性;DNA损伤;孕酮vided by the Biomedical Central Laboratory of Jinan University.
广东省高等学校优秀青年教师培养计划(Yq2013024);教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划;国家自然科学基金项目(31201402, 31201340)。
许伟(1989-),女,山东聊城人,硕士研究生,研究方向为生殖毒理评价,E-mail:xuwei0408@126.com。*
E-mail:baiweibin@163.com。。
2015-04-20
修回日期2015-05-25
Supported by Training Program for Outstanding Young Teachers in Higher Education Institutions,Guangdong Province(Yq2013024);Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University of Ministry of Education of China;National Natural Science Foundation of China(31201402,31201340).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:baiweibin@163.com
Received:April 20,2015 Accepted:May 25,2015
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Highly-efficient Stereo-cultivation Model in Kiwifruit Orchards Interplanting Konjak
- The Breeding of New Indica-japonica Intersubspecific Hybrid Rice Combination Chunyou 84
- Comparative Analysis between Triple Cross and Double Cross among Three Parents of Crop
- Optimization of Field Arrangement of Doublecropping Glutinous Sorghum and Soybean Intercropping Pattern
- Principal Component Analysis on Traits Related to Lodging Resistance of Plateau Japonica Rice
- Inheritance of Aroma of Good-quality Indica Type Rice PTGMS Line GHS and Its Application in Hybrid Rice Breeding
