Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Accumulation and Distribution of Dry Matter in Broomcorn Millet
2015-02-05LingCHENZhijunQIAOJunjieWANGHaigangWANGXiaoningCAOJunliDONG
Ling CHEN,Zhijun QIAO,Junjie WANG,Haigang WANG,Xiaoning CAO,Junli DONG
Institute of Crop Germplasm Resources,Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key Laboratory of Crop Gene Resources and Germplasm Enhancemengt on Loess Plateau,Ministry of Agriculture,Taiyuan 030031,China
Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Accumulation and Distribution of Dry Matter in Broomcorn Millet
Ling CHEN,Zhijun QIAO*,Junjie WANG,Haigang WANG,Xiaoning CAO,Junli DONG
Institute of Crop Germplasm Resources,Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key Laboratory of Crop Gene Resources and Germplasm Enhancemengt on Loess Plateau,Ministry of Agriculture,Taiyuan 030031,China
[Objective] To understand the effect of nitrogen application on dry matter accumulation and allocation dynamics in broomcorn millet.[Method]The accumulation and distribution of dry matter were studied using cultivars Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi at different levels of nitrogen fertilizer at the jointing stage.[Result]The results showed that increasing N application led to the increase of green leaf area and the delay of leaf senescence,which was beneficial to the accumulation of dry matter. Appropriate nitrogen application(90 kg/hm2)could coordinate the translocation rate of dry matter among different plant parts,thereby enhancing the yield of broomcorn millet;among different organs,the contribution rate of stem to kernel was greater than that of leaf to kernel;there was obvious correlation between dry matter and yield.For Jin Shu 7,leaf area and dry weight of spike showed significant negative correlation with yield.[Conclusion]The formation of grain yield of broomcorn millet involved the accumulation and allocation of dry matter,the appropriate amount of nitrogen application(90 kg/hm2)could improve the rates of translocation and contribution of dry matter,thereby promoting the yield of broomcorn millet.
Nitrogen application;Broomcorn millet;Dry matter accumulation;Allocation rate
N itrogen fertilizer application is an important technical measure for improving crop yield, excessive nitrogen fertilizer not only reduces its utilization efficiency,but also leads to crop lodging,thereby decreasing the yield[1-3].Research on other crops showed that increasing nitrogen fertilizer application improves leaf area index of crops,increases dry matter accumulation of crops in the whole growth period;the appropriate amount of nitrogen can also increase the contribution rate of dry matter,ben efitting the high yield of crops[4].The grain yield of crops relies on the biological yield or the dry matter accumulation of crops,and the accumulation and distribution of dry matter among stem,leaf and sheath are important factors for grain yield formation[5-8].The more dry matter is assigned to the reproductive organs within a certain time,the more the grain yield will be[9]. There are few studies about dry matter accumulation in the broomcorn millet during plant growth and development under different levels of nitrogen application.In this study,the effects of nitrogen application at jointing stage on dry matter of stems,leaves and ears, total dry matter accumulation and distribution of Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi were studied,so as to provide a theoretical basis for promoting the highyield cultivation and production of broomcorn millet.
Materials and Methods
Experimental materials
The experiment was conducted in Dongyang Base of Shanxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences in 2011.The tested varieties were Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi.The contents of soil nutrient were:16.80 g/kg organic matter, 0.89 g/kg total nitrogen,57.42 mg/kg available nitrogen,7.3 mg/kg rapid available phosphorus and 107 mg/kg rapidly available potassium.
Experimental design
There were five nitrogen treatments,0 kg/hm2(N0),45 kg/hm2(N1), 90 kg/hm2(N2),135 kg/hm2(N3),180 kg/hm2(N4),respectively,and each repeated three times.The area of each plot was 15 m2,the line spacing was 33 cm.Basal fertilizers before sowing were N 120 kg/hm2and P 90 kg/hm2. All other management was the same as that of normal field production.
Measurement items and methods
At each growth stage,5 plants with the same growth condition were selected.Measurements were also made every 7 days after flowering. Grain yield of each plot was determined after harvesting.
Green leaf area=Length×Width× 0.75.
For the determination of dry matter weight of overground part,first fresh weight was determined,then different plant parts were treated in oven at 105°C for 15 min,then at 80℃until their mass was constant.
During grain filling period,move ratio(MR)and transportation ratio (TR)of organic dry matter are calculated by the following formulae[9-10].
MR=(The maximum organ dry mass after flowering-Organ dry mass of the mature period)/The maximum organ dry mass after flowering×100%;
TR=(The maximum organ dry mass after flowering-Organ dry mass of the mature period)/The maximum organ dry mass after flowering×100%.
Data processing
Data were processed using Microsoft Excel 2003 and DPS7.05 statistical softwares.
Results and Analyses
The effect of nitrogen application at jointing stage on green leaf area of broomcorn millet
It can be seen from Fig.1,the leaf area of Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi showed the trend of increasing firstly and reached its maximum on August 2,and subsequently decreasing.The leaf area of Jin Shu 7 was significantly higher than that of Huang Mizi.Generally,the leaf area under different nitrogen levels was different,leaf area increased with the increase of nitrogen fertilizer application,N4 and N3 with high nitrogen treatments showed the maximum effect among all treatments.
The accumulation and distribution characteristics of dry matter of broomcorn millet under different nitrogen levels
It can be seen from Fig.2A and Fig.2E,dry matter accumulation showed a gradually increasing trend with the growth stages and reached its maximum around August 30,then declined toward September 6.Dry matter accumulation in Jin Shu 7 by the N3 treatment was significantly higher than all other treatments.There were significant differences in dry matter accumulation in response to different nitrogen treatments,total amount of dry matter was in the order of N3>N2>N0>N1>N4 from August 23 to September 6.For Huang Mizi,N3 treatment in the early growth stage showed the maximum dry matter accumulation,and it showed that the accumulation pattern of total dry matter was similar to that of Jin Shu 7 at the later stage of maturing.In general,total dry matter accumulation of Jin Shu 7 was higher than that of Huang Mizi.
It can be seen in Fig.2B and Fig.2C,for Jin Shu 7,dry matter accumulation in leaf and stem at the N3 level was higher than that of all other treatments,and showed peak around August 30.Leaf dry matter was about 12.9%of the total dry matter,whereas stem dry matter was 64%of the total dry matter.As shown in Fig.2F and Fig.2E,for Huang Mizi,dry matter accumulation in leaf and stem showed similar pattern to Jin Shu 7,the different point was:dry matter accumulation in leaf and stem under N4 treatment showed the maximum value before August 30,the dry matter accumulation in stem was about 42%of the total dry matter,and that in the leaf was about 15.1%of the total dry matter.At the later stage of maturing,N3 treatment showed the maximum dry matter accumulation in the leaf and stem.
It can be seen from Fig.2D and Fig.2H,spike dry weight of Jin Shu 7 under N3 treatment showed the maximum level,whereas that of Huang Mizi under N4 was the maximum,and the two both appeared around August 30. Spike dry weight was 37.6%and 40.5%of the total dry weight for Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi,respectively.
Dry matter transport and distribution
As seen in Table 1,the mobility and transportation rates of the leaf dry matter were greater than these of the stem,and there were differences on MR and TR among all treatments,the MR and TR of the leaf dry matter of Jin Shu 7 were the maximum under N2, followed by N3,N4,N1 and N0,and the MR and TR of the stem dry matter were in the order of N2>N3>N1>N0>N4.For Huang Mizi,the rates in leaf and stem showed maximum under N4 treatmenr and minimum under N3 treatment.
The relationship between dry matter accumulation and yield
From Table 2,it can be seen that the leaf area and yield of Jin Shu 7 showed significant negative correlation,and the correlation coefficient was 0.99,total dry weight and yield showed significant negative correlation with the correlation coefficient of 0.86. For Huang Mizi,the dry weight of spike showed significant negative correlation with that of leaf and stem,while the dryweight of all the other parts showed extremely significant correlation.

Table 1The mobility and transportation rates of different organs of broomcorn millet under different nitrogen levels
Conclusions and Discussions
Previous studies showed that the formation of crop yield depended on the accumulation of photosynthetic products and distribution,grain yield increased with the increase of dry matter,the more the dry matter accumulation,the higher the grain yield[11-12].In this study,it was showed that the application of nitrogen fertilizer at 135 kg/hm2(N3)increased dry matter accumulation significantly over other treatments for both Jin Shu 7 and Huang Mizi.After the jointing stage, dry matter accumulation of stem was higher than that of leaf,and the MR and TR showed maximum for both cultivars,which was consistent with the results of previous studies.Leaf area increased with the increase of the amount of nitrogen application,moreover,leaf area under N4 and N3 treatments was the maximum among all treatments,excessive nitrogen led to the unfavorable-delayed senescence,resulting in the reduction ofyield.The accumulation and distribution of dry matter of different organs varied obviously under different nitrogen levels.The MR and TR of stem and leaf under high nitrogen treatments(N3 and N4)in Jin Shu 7 showed a lower value,indicating that the nitrogen could promote the vegetative growth of plants,but did not benefit high yield.Therefore,further investigation is needed to improve fertilization techniques and fertilizer efficiency,and increase the assimilate accumulation and grain yield.
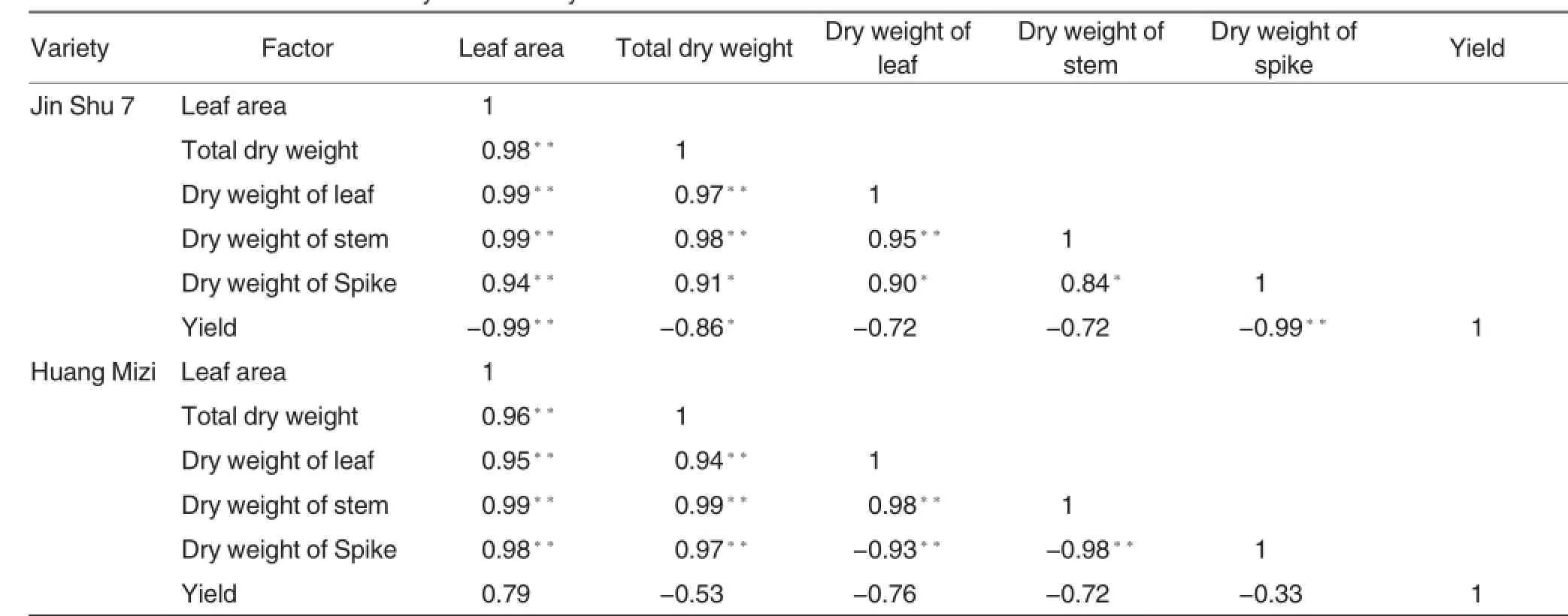
Table 2The correlation between dry matter and yield
[1]CUI ZL,ZHANG FS,CHEN XP,et al. In-season nitrogen management strategy for winter wheat:maximizing yields, minimizing environmental impact in an over-fertilization context[J].Field Crops Res,2010,116:140-146.
[2]ZHANG FS,WANG JQ,ZHANG WF,et al.Nutrient use efficiencies of major cereal crops in China and measures for improvement[J].Acta Pedol Sin,2008, 45(5):915-923.
[3]TRIPATHI SC,SAYRE KD,KAUL JN, et al.Growth and morphology of spring wheat(Triticum aestivum L.)culms and their association with lodging:effects of genotypes,N levels and ethephon[J]. Field Crops Res,2003,84:271-290.
[4]ZHANG HB,WU XY,YANG WY.Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on the accumulation and distribution of dry matter in replayplanting[J].Soybean Science,2006,25 (4):404-408.
[5]HU CH.Corn Cultivation Physiology[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press,1995: 1.
[6]TOLLENAAR M,DAYNARD TB.Effect of source-sink ratio on dry matter accumulation and leaf senescence of maize[J].Can J Plant Sci,1987,62: 855-860.
[7]KARLEM arlen DL,L’FLANNERY R, SADLER EJ.Dry matter nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium accumulation rate by corn on Norfolk loamy sand [J].Agron J,1987,79:649-656.
[8]HUANG ZH,SHEN L,SUN G,et al. Study on leaf area and dry matter accumulation and distribution in super highyield maize[J].Anhui Agric Sci,2007, 35(8):2227-2228.
[9]JIA GL,ZHANG SQ,DAI HP et al. Studies on dry matter accumulation and allocation of broomcorn broomcorn millet(Panicum miliaceum L.)at late jointing stage[J].Journal of Northwest A&F University(Nat.Sci.Ed.),2009,37(4): 86-90.
[10]GAO QR,SUN LZ,LIU BS.Accumulation,transportation and distribution of dry matter after anthesis in hybrid wheat[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2000,26(2):163-170.
[11]HUANG ZX,WANG YJ,WANG KJ,et al.Photosynthetic characteristics during grain filling stage of summer maize hybrids with high yield potential of 15 000 kg/ha[J].Sci Agric Sin,2007, 40(9):1898-1906.
[12]LI JS,DONG SQ.Study of organ up ground dry matter accumulation and partitioning[J].Beijing Agric Sci,1985 (2):19-21.
Responsible editor:Nanling WANG
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
Supported by the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System(CARS-07-12.5-A12).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:nkypzs@126.com
Received:March 18,2015 Accepted:June 5,2015
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- The Effect of Crop Rotation on Soil Nematode Community Composition in a Greenhouse
- The Synergism of Chemical Herbicides and Aureobasidium pullulans for Control Cleavers (Galium aparine L.)in Wheat
- Changes of NF-κB,Bax and Caspase 3 in Apoptosis Induced by Ligustrazine Combined with Cis-dichlorodiamine Platinum in Human Gastric Carcinoma SGC-7901 Cell Lines
- Identification and Mutagenesis of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Chinese Sauerkraut
- Effects of Mechanical Sowing and Transplanting on Characteristics of Dry Matter Production in Middle-season Hybrid R ice
- The Prediction of Population of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise
