Effects of Mechanical Sowing and Transplanting on Characteristics of Dry Matter Production in Middle-season Hybrid R ice
2015-02-05LiLIUXiaolongLEIQinglanTIANQiangZHANGGuangzhongHUANGWanjunEN
Li LIU,Xiaolong LEI,Qinglan TIAN,Qiang ZHANG,Guangzhong HUANG,Wanjun R EN*
1.College of Agronomy,Sichuan Agricultural University/Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology,Ecology and Cultivation in Southwest China,Wenjiang 611130,China;
2.Seed Administrative Station of Nanchong,Nanchong 637000,China;
3.Pixian Rural Development Bureau,Pixian 611700,China
Effects of Mechanical Sowing and Transplanting on Characteristics of Dry Matter Production in Middle-season Hybrid R ice
Li LIU1,2,Xiaolong LEI1,Qinglan TIAN1,Qiang ZHANG1,Guangzhong HUANG3,Wanjun R EN1*
1.College of Agronomy,Sichuan Agricultural University/Key Laboratory of Crop Physiology,Ecology and Cultivation in Southwest China,Wenjiang 611130,China;
2.Seed Administrative Station of Nanchong,Nanchong 637000,China;
3.Pixian Rural Development Bureau,Pixian 611700,China
To clarify the effects of mechanical sowing and transplanting on dry matter production of middle-season hybrid rice,a two-factor split plot design was used to study the effects of different sowing and transplanting methods and their interaction with the seedling number per hill or seeding time on dry matter accumulation, distribution and transformation of F You 498,a middle-season hybrid rice variety, under field conditions in 2012 and 2013.The results showed that there was a marked effect of the sowing and transplanting methods and their interaction with the seedling number per hill or seeding time on dry matter accumulation,distribution and transformation.The total population dry matter accumulation of the treatments with mechanical direct seeding(MDS)and machine-based transplanting(MT)was lower than that of the treatment with traditional manual transplanting(TMT).However,MDS had higher dry matter accumulation and accumulating rate in the jointing-earing stage,and maintained higher stem-sheath exportation,export rate and transformation than MT and TMT;MT had higher dry matter accumulation and accumulating rate in the heading-maturity period than MDS and TMT.Moreover,the treatments with low seedling number per hill or early seeding enhanced the assimilation of dry matter after heading,the ratio of dry matter accumulation after earing to biomass yield and the contribution rate of dry matter accumulation after earing,and a reasonable early sowing was favorable to increase the harvest index of middleseason hybrid rice under mechanical sowing and transplanting conditions.
Middle-season hybrid rice;Mechanical precision hill-direct-seeding;Mechanical transplanting;Characteristic of dry matter production
Materials and Methods
Test site and rice variety
The test was carried out in Huapai Vilalge,Gucheng Town,Chengdu City,Sichuan Province during 2012-2013 at 30°52′N,103°55′E.The test rice was F You 498,three-line indica hybrid rice,bred by Rice Institute of Sichuan Agricultural University and Chuanjiang Rice Institute,with growth term of 150 d.The preceding crop was vegetables and the soils were paddy soils developed based on brown alluviums and soil physical and chemical properties of soils of 0-20 cm were shown(Table 1).
Test design and field management
The test set sowing and planting method as a major factor,totaling 3 levels as per split block design,including the treatment as per direct seeding,machine-based transplanting and manual transplanting.In 2012,the sub-factor was the number of seedling per hole,with two levels,namely low and high seedling numbers per hole, and in 2013,the sub-factor changed to sowing term,totaling two levels, namely early and late sowing.As shown in Table 2,direct seeding of rice was conducted with a precision hill-direct-seeding machine developed by College of Engineering,SCAU,and the number of seedlings was determined in the stage when three leaves grew and a rice flower bloomed. Seedling transplanting was conducted with a VP6 high-speed transplanter. The test plot totaled 36.0 m2(12.0 m× 3.0 m),with three repetitions.Furthermore,every test plot was separated with plastic mulch to guarantee fertilizer and water management proceeded individually.Besides,pure N was applied at 180 kg/hm2,as per base tillering fertilizer-to-ear fertilizer rate of 6:4, involving the base fertilizer-to-ear fertilizer rate of 2:1 and spikelet-promoting fertilizer-to-spikelet-developing fertilizer rate of 5:5.Additionally,the quantities of P and K fertilizers were determined as per N∶P2O5∶K2O=2∶1∶2. Specifically,P fertilizers were applied totally once and K fertilizer was applied as per base fertilizer-to-ear fertilizer of 5∶5.Water management and disease or insect preventions were implemented as per high-yielding cultivation. Table 3 showed meteorological information of rice growing in 2012 and 2013.
Measurement items and methods
Rice in 20 holes were fixed and measured in every test plot.Specifically,the measurement proceeded in the peak of tillering stage,jointing stage, earing stage and ripening stage.The rice samples were collected from 5holes as per stem and tillering method (average)and divided into leaf,stemsheath and ear,followed by kill-out at 105℃for 60 min,and drying at 80℃to get a constant weight.Finally,the weights of dry matter were measured of different parts.
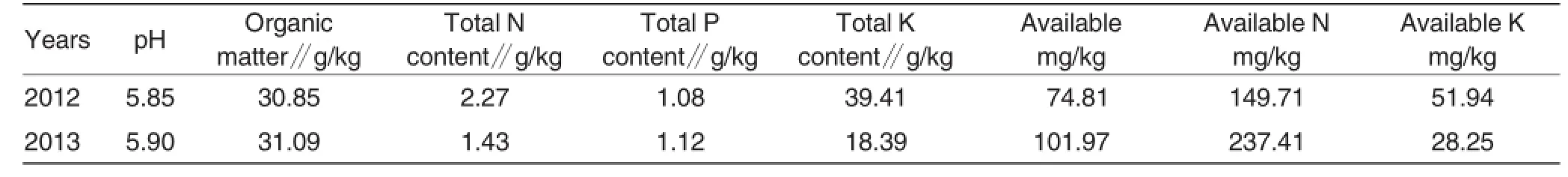
Table 1Soil conditions of experimental locations
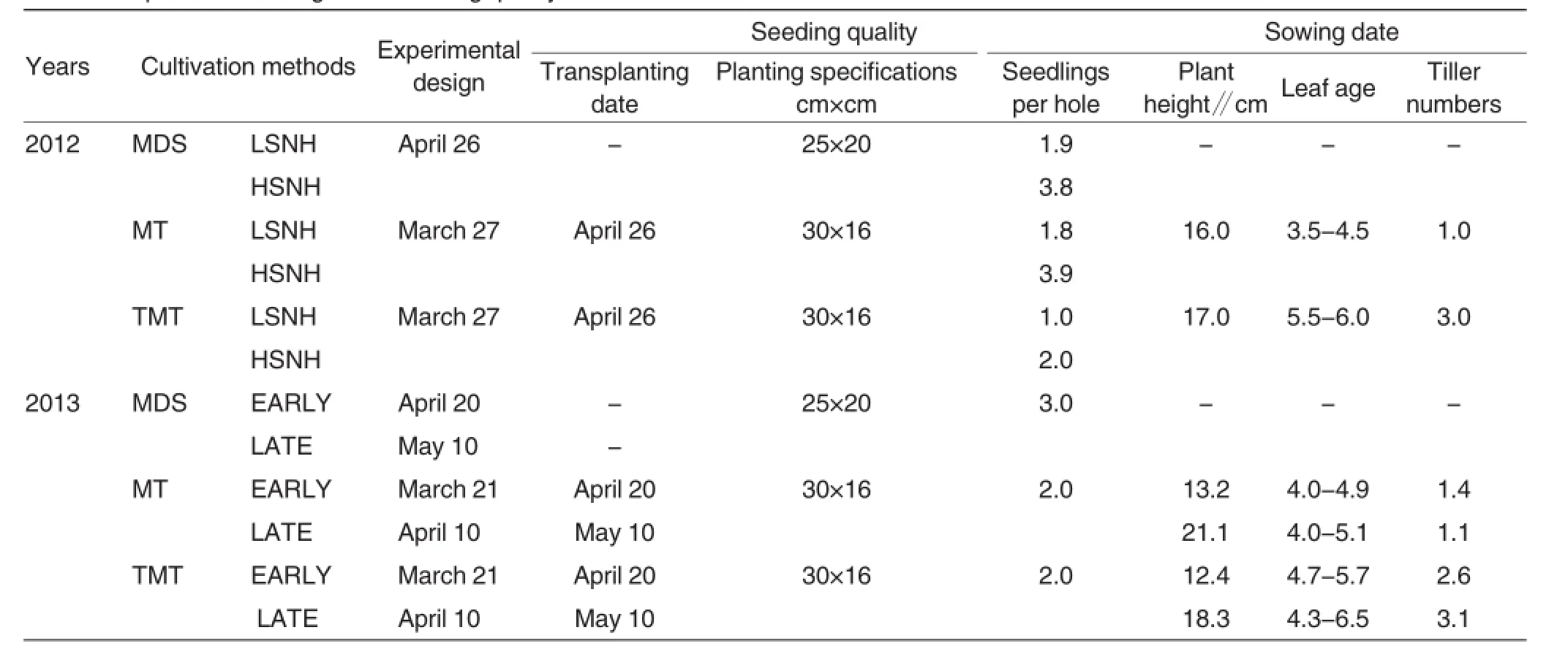
Table 2Experimental design and seedling quality
Data calculation and statistical analysis
Apparent export(t/hm2)=T he weight of dry matter(leaf and stem)in earing stage-T he weight of dry matter (leaf and stem)in ripening stage;
Apparent export rate(%)=A pparent export(leaf and stem)/T he weight of dry matter(leaf and stem)in earing stage×100;
Apparent conversion rate(%)=A pparent export(leaf and stem)/T he weight of dry matter of seeds in earing stage×100;
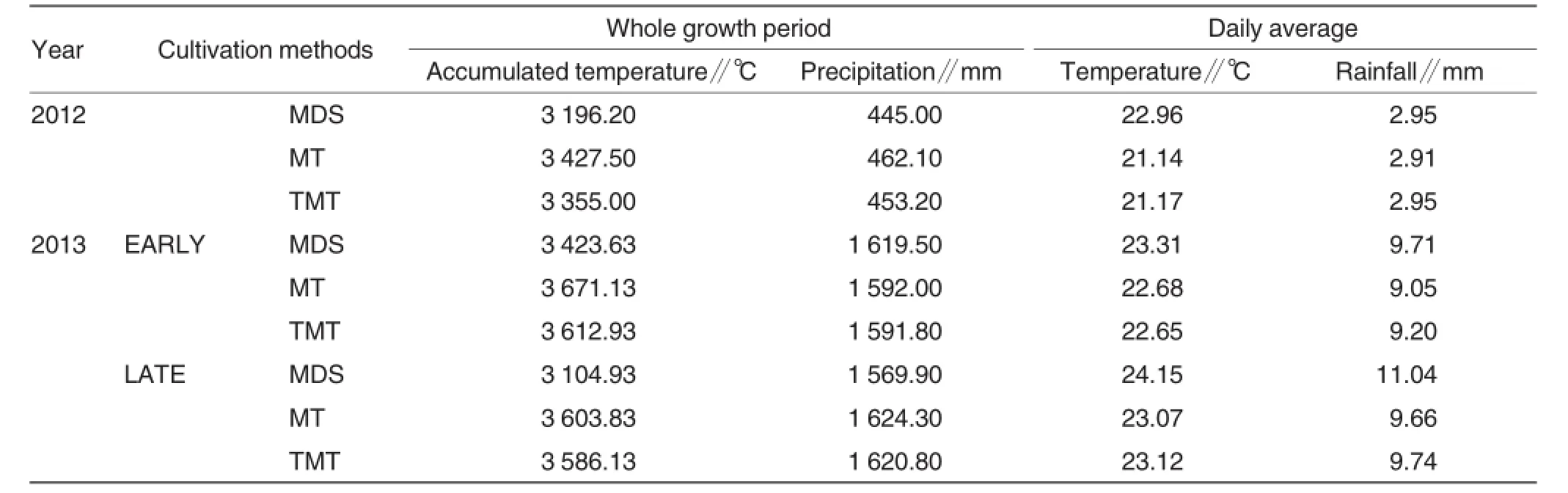
Table 3Meteorological condition of different sowing and transplanting methods
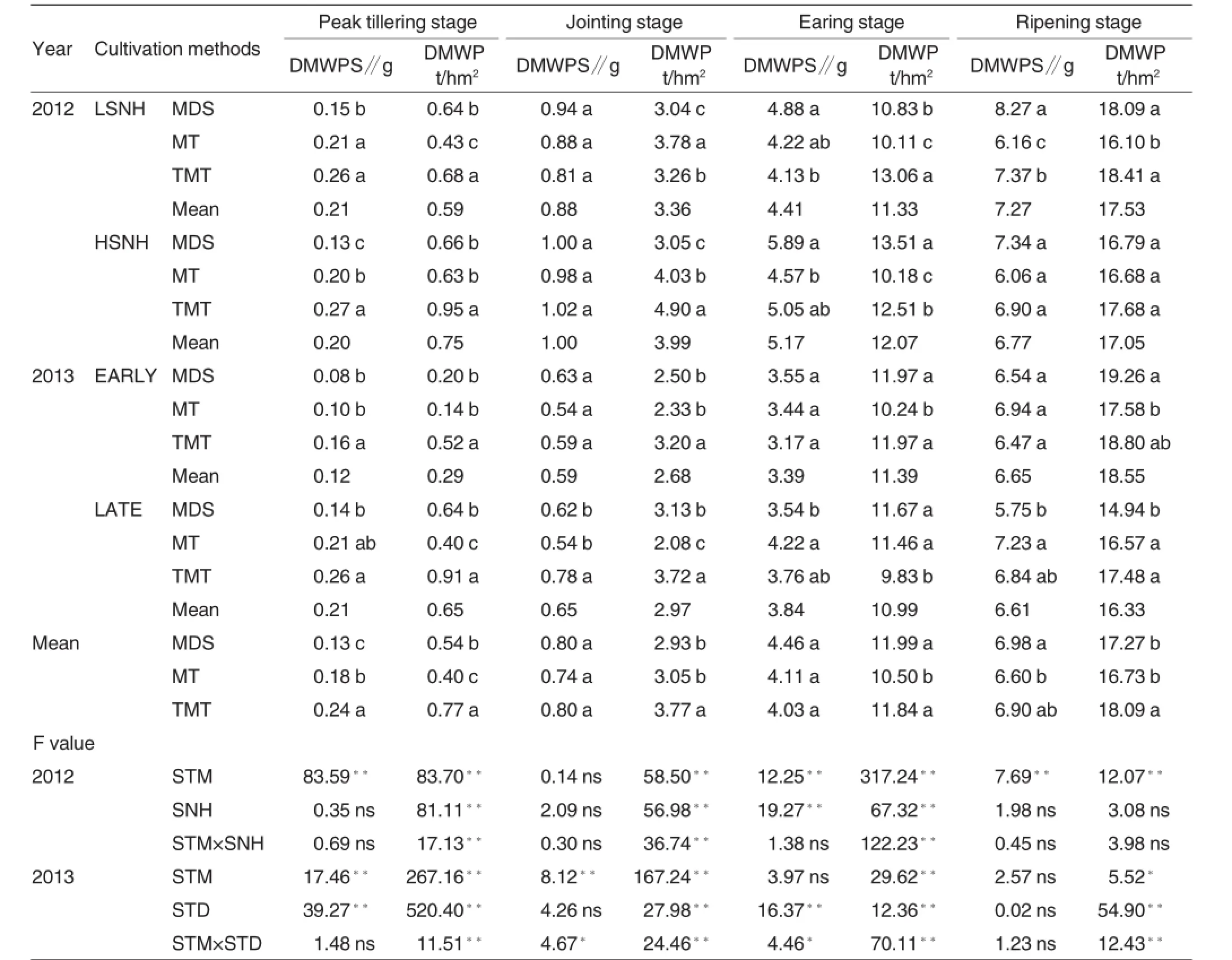
Table 4Dry matter weight of single stem and population at main growth stage of hybrid rice cultivar with different sowing and transplanting methods
Assimilation of materials after earing(t/hm2)=T otal weight of dry matter of ground parts in ripening stage-Total weight of dry matter of ground parts in earing stage;
The proportion of dry matter after earing(%)=A ssimilation of materials after earing/Total weight of dry matter of ground parts in ripening stage;
Assimilation rate of materials after earing(%)=The assimilation of materials after earing/The weight of dry matter of seeds in ripening stage×100;
The harvesting index(%)=The weight of dry matter of seeds in ripening stage/Total weight of dry matter of ground parts in ripening stage×100.
Data processing
The test data were processed with Microsoft Excel;analysis of variance was conducted with DPS7.05; the comparisons of significance differences were conducted on sample average as per LSD method.
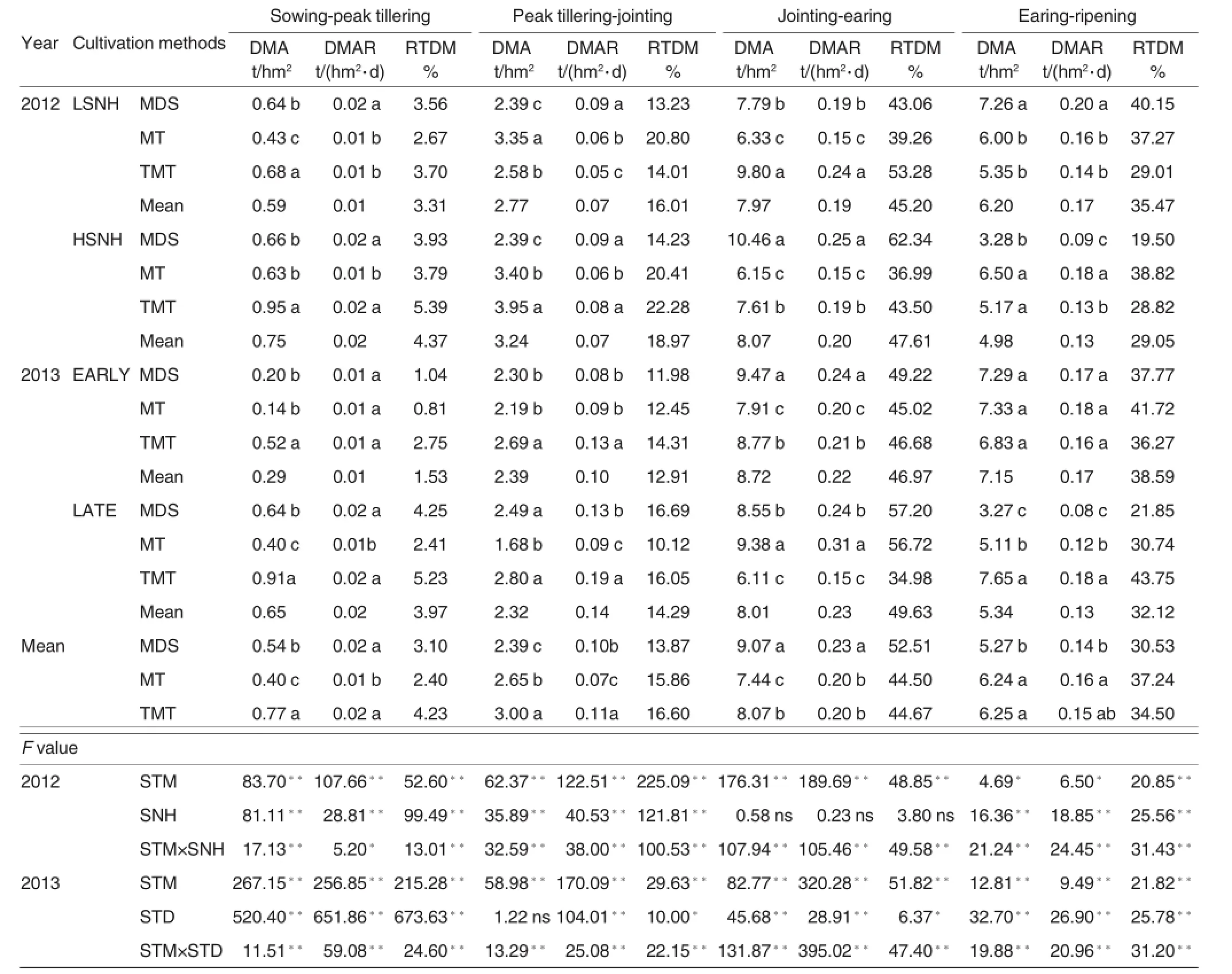
Table 5Dry matter accumulation of population,rate and its ratio to total dry matter in main growth period of hybrid rice cultivar with different sowing and transplanting methods
Results and Analysis
The weights of dry matters of single stem and rice population in growth stage
As shown in Table 4,the sowing and planting method has effects on the weights of dry matters of single stem and rice population in growth stage. The number of seedling per hole,sowing term,and interactions with sowing and planting method all have extremely significant effects on weight of dry matter of rice population in peak tillering stage,jointing stage and earing stage.In ripening stage,however,the weight of dry matter is mainly under influence of sowing and planting method,sowing term and interactions. For example,the weights of average rice population kept 27.12%,18.75% and 6.53%higher in peak tillering stage,jointing stage and earing stage in treatments of highseedlings number per hole compared with the treatments with low seedlings number per hole.In contrast,the weight of dry matter of individual stem and rice population were higher in the treatment with low seedlings number per hole,which were 7.39%and 2.82%higher.On the other hand,for early-sowing treatment, the weights of dry matters of individual stem and rice population were lower compared with late-sowing treatments in peak tillering stage and jointing stage.As rice grew,however,the weights of dry matters of rice population in earing stage by early sowingwere higher compared with late-sowing treatment,as well as dry matter of stem and rice population in ripening stage.These incorporated that early sowing is conductive to accumulation of dry matter for middle-season hybrid rice in ripening stage.Furthermore,the sowing and planting method plays a key role for dry matter weight of individual stem of middle-season hybrid rice in peak tillering stage.Specifically, average weight of dry matter of individual stem is significantly lower as per mechanized cultivation than that as per traditional manual transplanting in peak tillering phase.Additionally,sowing and planting method has significant or extremely significant effects on the weight of dry matter of rice population in major growth phase.For instance,dry matter weights of rice population by mechanical direct seeding and mechanical transplanting both were significantly lower compared with the treatment as per traditional manual transplanting in peak tillering stage, jointing stage and ripening stage and from high to low were the treatment as per direct seeding,the treatment of rice cultivation as per traditional manual transplanting and mechanical transplanting.
The accumulation of dry matter and the proportions in different growth phases
It can be concluded from Table 5 that the accumulation of dry matter achieved the highest from jointing to earing and earing to ripening phases, with higher accumulation rates.It is obvious that sowing and planting method,and the interactions with the number of seedling per hole and sowing term had significant effects on accumulation of dry matter,accumulation rate and the proportion to total dry matter.Specifically,from peak tillering to jointing stages,the accumulation of dry matter of rice by mechanized cultivation kept lower compared with the treatment of cultivation as per traditional manual transplanting.From jointing to earing stages,however,the accumulation quantity and rate both were higher in the treatment as per direct seeding compared with the treatments as per mechanical transplanting and traditional manual transplanting.Besides,the accumulation quantity of the treatment by mechanized direct seedling was 18.00%and 17.55% higher compared with the treatments by mechanical transplanting and manual transplanting in terms of the proportion of accumulated dry matter to total dry matter.On the other hand,the accumulation quantity and rate of the treatments by mechanical transplanting and manual transplanting kepthigher compared with the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding from earing to ripening stages.What’s more,the proportion of accumulation quantity of dry matter to total dry matter accumulation maintained 21.98% and 7.94%higher compared with the treatments as per mechanical direct seeding and manual transplanting, respectively.Meanwhile,average accumulation quantity and rate of dry matter and the proportion to total accumulation quantity were 24.50%, 30.77%and 22.10%in the treatments with low seedling number per hole were higher compared with the treatments with high seedling number per hole.Nevertheless,the accumulated dry matter and the proportion were always higher in the treatment with high seedling number per hole compared with the treatment with low seedling number per hole in previous growth stages.Although late sowing effectively improves quantity and rate of dry matter accumulation during sowingpeak tillering stages,as well as the proportions,the indices started declining thereafter.For example,the quantity and rate of accumulated dry matter and the proportion were 25.31%, 23.53%and 16.77%lower in the treatments as per late sowing compared with the treatments by early sowing.
The proportions of dry matter distributions of rice organs in different growth stages
As shown in Table 6,the distribution of dry matter of leaf maintained higher from peak tillering to jointing stages;the proportion of stem-sheath dry matter kept higher in jointing and earing stages;the proportions of dry matter of leaf and stem-sheath dropped the lowest in ripening stage; the distribution proportion of dry matter in ears accomplished the peak in ripening stage.Furthermore,the number of seedling per hole,sowing term, and sowing and planting method would effectively adjust the distribution of dry matter of rice organs.In peak tillering stage,jointing stage,and earing stage,the proportion of dry mater of leaf was always lower in the treatment with low seedling number per hole that that with mature seedlings, but of stem-sheath was higher.The proportion of dry matter of leaf in the treatment with high seedling number per hole was 6.26%and 0.59%higher in ripening stage,but dry matter of ear was 2.26%higher in the treatment with low seedling number per hole in the same stage,which indicated that the treatment with low seedling numberper hole would improve distribution of dry matter of ears in ripening stage.As for sowing term,it affects significantly or extremely significantly rice in terms of dry matter distribution in peak tillering and ripening stages.Specifically, average distribution of dry matter of leaf in peak tillering stage and ripening stage was as follows:the treatment as per early sowing<the treatment as per late sowing,which was in contrary to dry matter of stem-sheath;the proportion of dry matter of ear was 2.01% higher in the treatment as per early sowing in ripening stage.In addition to that,sowing and planting method and the interactions with the number of seedling per hole and sowing term had significant effects on distribution proportion of dry matter.In general,the proportion of dry matter in leaf kept higher in the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding and mechanical transplanting compared with the treatment as per traditional manual transplanting in different growth terms; the proportion of stem-sheaths was higher in the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding compared with the treatments as per mechanical transplanting and manual transplanting in earing stage;the proportion in the treatments cultivated by hand kept higher compared with the rest methods in peaking tillering,jointing and ripening stages;the proportions of ear in earing stage from high to low were the treatment as per direct seeding, mechanical transplanting and manual transplanting;the proportion of ears in ripening stage was 2.34%and 1.63% higher compared with the treatments as per direct seeding and manual transplanting.
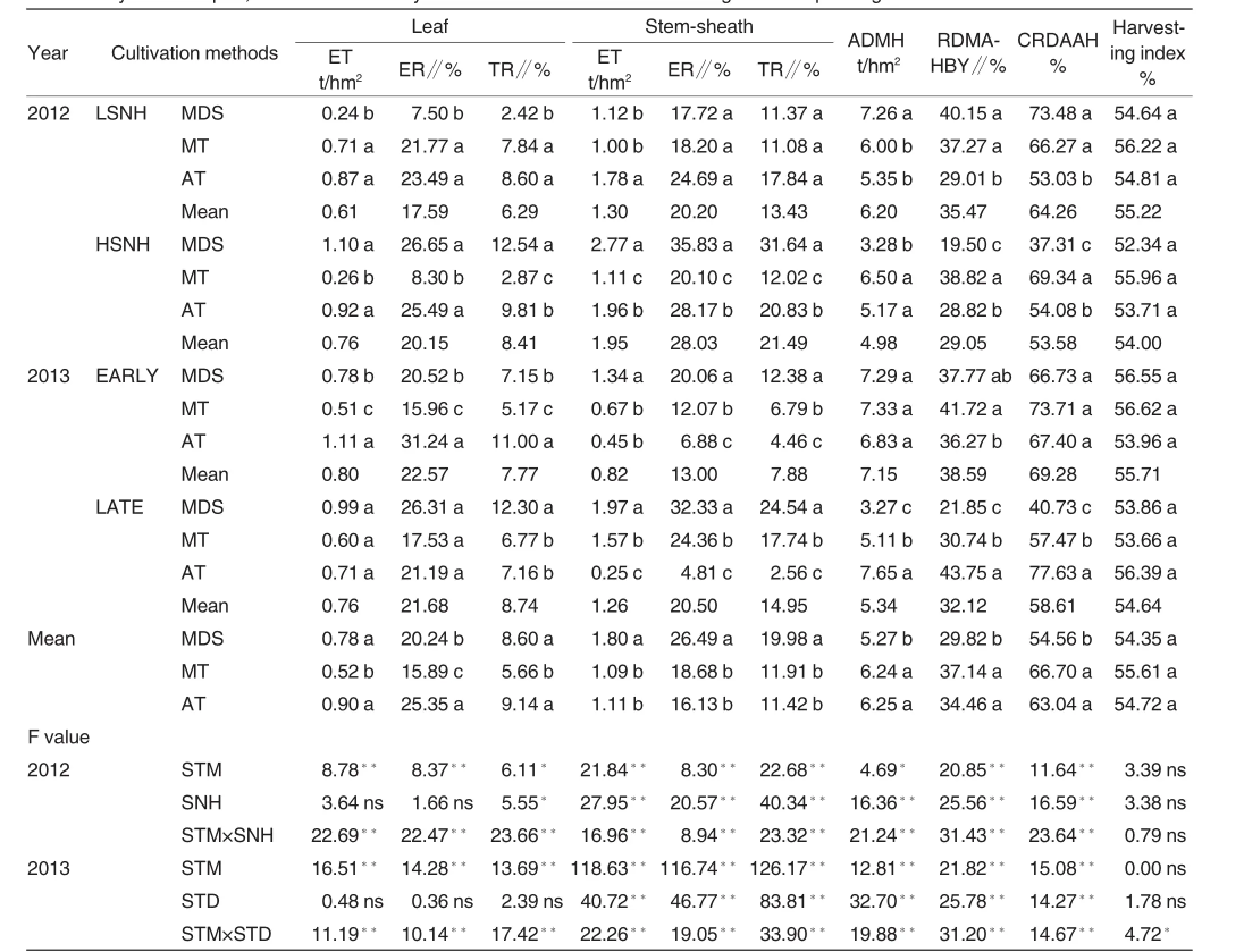
Table 7Dry matter export,transformation of hybrid rice cultivar with different sowing and transplanting methods
Transportation of dry matter before earing and accumulation characters after earing
As shown in Table 7,sowing and cultivation method,and the interactions with the number of seedling per hole and sowing term had significantly or extremely significant effects on export quantity,rate and transformation rate of dry matter of leaf and stemsheath.Specifically,the export quantity,rate and transformation rate of dry matter of leaf and stem-sheath showed similar as follows:the treatment with low seedling number per hole<the treatment with high seedling number per hole.Furthermore,the export quantity and rate of leaf in the treatment as per early sowing kept a little higher,but the export quantity, rate and transformation rate of dry matter of stem-sheath were 34.92%, 36.59%and 47.29%lower compared with the treatment as per late sowing. On the other hand,the export quantity and rate and transformation rate of leaf were as follows:the treatment as per mechanical transplanting<the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding<the treatment as per manual transplanting,and export quantity and rate and transformation rate of stemsheath kept higher in the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding.After earing,assimilation quantity,the proportion of dry matter,and the contribution of dry matter were all significantly or extremely significantly under influence of sowing and planting method, the number of seedling per hole,sowing term,and the interactions and the rules can be concluded the indices were higher in the treatment as per mechanical direct seeding;the treatment with young seedling and as per early sowing improved assimilation quantity,the proportion and contribution rate of dry matter after earing.Additionally,the harvesting index in the treatment with low seedling number per hole kept 2.26%higher,and in the treatment as per early sowing was 1.96%higher.In conclusion,the harvesting index is under influences of interactions between sowing term and sowing and planting method,and the cultivations with mechanical direct seeding as per early sowing,with mechanical transplanting as per early sowing and as per traditional manual transplanting would improve harvesting index.
Discussions
The production characters of dry matter of rice are a result of accumulation and distribution of photosynthates in organs of rice.Peng et al.[16]believed that rice yield can be increased by improving the quality of rice population and advancing dry matter accumulation.Previous researches demonstrated that the cultivation method has significant effects on accumulation and distribution of dry matter of rice[3-5,17-18].Before determination of yield,seedling and nitrogen,the accumulation of dry matter actually proceeds slowly,but the accumulated dry matter increases and the process works faster[18].Ma et al.[19]believed that the accumulation of dry matter from earing to grain-filling stages was the fastest in the treatment as per traditional manual transplanting, as well as the treatment by direct seeding.Li et al.[2]researched that rice grew better cultivated by hand compared with mechanical transplanting and direct seeding;accumulated dry matter reached the best from sowing to jointing stage;the production capacity was maximal from jointing to earing stages and from earing to ripening stages.The research suggested that sowing and planting method and the interactions with the number of seedling per hole and sowing term have significant effects on accumulation,distribution and transportation of dry matter of middle-season hybrid rice;the accumulation of dry matter by mechanical direct seed-ing and mechanical transplanting were lower compared with cultivation as per traditional manual transplanting in peak tillering stage,jointing stage and ripening stage,but the accumulation quantity and rate from jointing to earing stages kept higher in the treatment by mechanical direct seeding compared with the treatment of cultivation as per traditional manual transplanting, and from earing to ripening stages maintained higher in the treatment as per mechanical transplanting;the export quantity and rate and transformation rate of dry matter of stem-sheaths were all high;the proportion and contribution of accumulated dry matter after earing kept higher after earing,and the distribution capacity of dry matter to ear performed stronger in the treatment cultivated by hand.
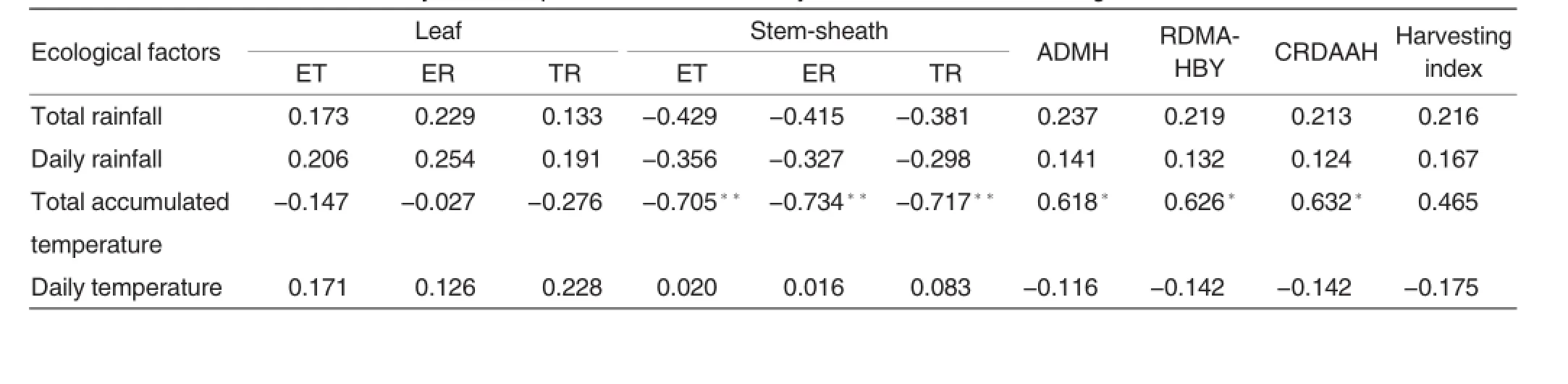
Table 8Correlation coefficients of dry matter export,transformation of hybrid rice cultivar with ecological factors
Rice cultivated by varied methods tend to be volatile in terms of use of nutrients and sunshine upon individual plant and environment,having effects on rice,individually or population[2]. Wang et al.[1]and Tong et al.[20]explored that eco-environment has significant effects on dry matter accumulation of rice.The research indicated that export quantity and rate,transformation rate of dry matter,assimilation quantity after earing,the proportions and contribution of dry matter after earing were all significantly or extremely significantly affected by total temperature accumulation in growth term(Table 8);the treatment with low seedling number per hole as per early sowing improved assimilation quantity after earing,the proportions and contribution of dry matter after earing;harvesting index is under influences of interactions between sowing term and sowing and planting method and the cultivation by mechanical direct seeding as per early sowing,mechanical transplanting as per early sowing and traditional manual transplanting as per late sowing all enhanced harvesting index.
Mechanized cultivation of rice is an important part of whole-course mechanization of rice production.Previous researches show that mechanized cultivation would improve work efficiency,yield and reduce rice growth term[12,21-22];rice population would be better by mechanical precision hill-direct-seeding[21];it is a way for increasing yield of mechanized-cultivated rice by taking advantage of dry matter accumulation[1].Chen et al.[23]believed that the advantage of dry matter production of super-high yielding rice is before earing stage.Huang[24]investigated that it is an effective way for accomplishing a high yield by reducing dry matter accumulation in early stage, and improving dry matter production in middle and later stages.Zou et al.[25]thought the accumulation of dry matter should be with a proper proportion of rice in every specific growth term.Zhu et al.[26]pointed out that the accumulation of dry matter should be maintained at a proper level before earing.Ying et al.[6]explored that the advantage of dry matter accumulation of super-high yielding rice should be in middle or later stages.Wu et al.[27]believed that biomass can be improved by increasing accumulation of dry matter in per unit area.The research incorporated that the appropriate number of seedlings per hole and sowing term is conductive to rational distribution and transformation of dry matter.Therefore,the proportions of dry matter can be well distributed in specific growth terms effectively by coordination of machines and cultivation techniques to increase biomass.
[1]WANG X(王勋),DAI TB(戴廷波),JIANG D(姜东),et al.Yield formation and source-sink characteristics of rice genotypes under two different eco-environments(不同生态环境下水稻基因型产量形成与源库特性的比较研究)[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报),2005,16(4):615-619.
[2]LI J(李杰),ZHANG HC(张洪程), CHANG Y(常勇),et al.Characteristics of photosynthesis and matter production of rice with different planting methods under high-yielding and cultivation condition(不同种植方式水稻高产栽培条件下的光合物质生产特征研究)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2011,37 (7):1235-1248
[3]SANOH Y,MANO Y,OOKAWA T,et al. Comparison of dry matter production and associated characteristics between direct-sown and transplanted rice plants in a submerged paddy field and relationships to planting patterns[J].Field Crops Research,2004,87:43-58
[4]DENG F(邓飞),WANG L(王丽),LIU L (刘利),et al.Effects of cultivaiton methods on dry matter production and yield of rice under different ecological conditions(不同生态条件下栽培方式对水稻干物质生产和产量的影响)[J].Acta A-gronomica Sinica(作物学报),2012,38 (10):1930-1942
[5]CHEN S,CAI S G,CHEN X,et al. Genotypic differences in growth and physiological responses to transplanting and direct seeding cultivation in rice[J]. Rice Science,2009,16:143-150
[6]YING J F,PENG S B,HE Q R,et al. Comparison of high-yield rice in tropical and subtropical environments:Ⅰ.Determinants of grain and dry matter yields[J].Field Crops Research,1998, 57(1):71-84
[7]YANG B(杨波),XU DY(徐大勇), ZHANG HC(张洪程).Research on growth,yield,quality of rice under direct seeding,mechanical transplanting and artificial transplanting(直播机插与手栽稻生长发育产量及稻米品质比较研究) [J].Journal of Yangzhou University(A-gricultural and Life Science Edition)(扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版)),2012, 33(2):39-44
[8]ZHU DF(朱德峰),CHENG SH(程式华), ZHANG YP(张玉屏),et al.Analysis of status and constraints of rice production in the world(全球水稻生产现状与制约因素分析)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica (中国农业科学),2010,43(3):474-479
[9]HU CS(胡潮水).Research for the relationship between mechanical rice transplantation and its growth period of rice(水稻机插与其生育期关系研究)[J].中国农机化,2012,2:66-68
[10]ZHENG TX(郑天翔),TANG XR(唐湘如),LUO XW(罗锡文),et al.Effects of different irrigation methods on production of precision hill-direct-seeding super rice(不同灌溉方式对精量穴直播超级稻生产的影响)[J].Transactions of the CSAE(农业工程学报),2010,26(8): 52-55
[11]YU LH(于林惠),LI GH(李刚华),XU JJ (徐晶晶),et al.Population characteristics of machine-transplanted japonica rice based on high-yield demonstration fields(基于高产示范方的机插水稻群体特征研究)[J].Chinese Journal of Rice Science(中国水稻科学),2012,26(4): 451-456
[12]LUO XW(罗锡文),XIE FP(谢方平),QU YG(区颖刚),et al.Experimental investigation of different transplanting methods in paddy production(水稻生产不同栽植方式的比较试验)[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(农业工程学报),2004,20 (1):136-139
[13]ZHU DF(朱德峰),CHEN HZ(陈惠哲). Development of transplanting of rice transplanters and crop safety(水稻机插秧发展与粮食安全)[J].China Rice (中国稻米),2009,6:4-7
[14]QIAN YF(钱银飞),ZHANG HC(张洪程),WU WG(吴文革),et al.Effects of seedlings number per hill on grain yield and quality in different panicle types of mechanical transplanted Japonica rice(机插穴苗数对不同穗型粳稻品种产量及品质的影响)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica(作物学报),2009, 35(9):1698-1707
[15]HU JM(胡钧铭),JIANG LG(江立庚), XU SH(徐世宏),et al.The relationship between post-anthesis carbon and nitrogen remobilization and grain growth of high quality indica rice under different date(不同播期下优质稻桂花占、八桂香花后碳氮物质流转与籽粒生长相关性)[J].Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops(热带作物学报),2012,33(6): 1001-1008
[16]ZHANG XL(彭显龙),LIU YY(刘元英), LUO SG(罗盛国),et al.Effects of the site-specific nitrogen management on yield and dry matter accumulation of rice in cold areas of northeastern China(实地氮肥管理对寒地水稻干物质积累和产量的影响)[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica(中国农业科学),2006,39 (11):2286-2293
[17]HAYASHI S,KAMOSHITA A,YAMAGISHI J,et al.Genotypic differences in grain yield of transplanted and direct-seeded rainfed lowed rice(Oryza sativa L.)in northeastern Thailand[J]. Field Crops Research,2007,102:9-21
[18]JIANG P(蒋鹏),ZHAN K(詹可),MO YL (莫亚丽),et al.Effects of different cultivation patterns on yield and dry matter accumulation in double-cropping super rice(栽培方式对双季超级稻产量及干物质积累的影响)[J].Crop Research (作物研究),2008,22(4):270-274
[19]MA DR(马殿荣),CHEN WF(陈温福), SZU YS(苏英山),et al.Comparisons of dry matter accumulation between rice nursing seedlings scattering and other planting patterns(水稻乳苗抛栽与其它栽培方式干物质生产特性的比较研究)[J].Liaoning Agricultural Sciences(辽宁农业科学),2004,5:6-9
[20]TONG P(童平),YANG SM(杨世民), MA J(马均),et al.Photosynthetic characteristics and dry matter accumulation of hybrid rice varieties under different light conditions(不同水稻品种在不同光照条件下的光合特性及干物质积累)[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology(应用生态学报),2008,19(3): 505-511
[21]SHEN CB(沈才标),WANG JQ(王驾清), SUN ZG(孙祖高),et al.Introduction and application of rice direct seeder for precise and hill sowing(水稻精量穴直播机的引进及应用初探)[J].Shanghai Agricultural Science and Technology (上海农业科技),2012,3:36-37
[22]SHU SF(舒时富),ZHENG TX(郑天翔), JIA XN(贾兴娜),et al.Yield formation characteristics of precision hill-directseedinglte rice(精量穴直播晚稻的产量形成特性研究)[J].Journal of South China Agricultural University(华南农业大学学报),2010,31(1):96-98
[23]CHEN WF(陈温福),XU ZJ(徐正进), ZHANG WZ(张文忠),et al.Creation of new plant type and breeding rice for super high yield(水稻新株型创造与超高产育种)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica (作物学报),2001,27(5):665-672
[24]HUANG XF(黄幸福).A comparative study on high yield cultivation with various modes(不同稻作方式的高产栽培比较研究)[D].Yangzhou:Agricultural College of Yangzhou University(扬州:扬州大学农学院),2009.
[25]ZOU YB(邹应斌),ZHOU SY(周上游), TANG QY(唐起源).Status and prospect of high yielding cultivation researches on China super hybrid rice (中国超级杂交水稻超高产栽培研究的现状与展望)[J].Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology(中国农业科技导报),2003,5(1):31-35
[26]ZHU CH(朱从桦),DAI Z(代邹),YAN FJ(严奉君),et al.Effects of different paddy field drainage degrees and panicle nitrogen fertilizer managements on photosynthetic productivity and nitrogen utilization of rice under triangle-planted system of rice intensification(晒田强度和穗肥运筹对三角形强化栽培水稻光合生产力和氮素利用的影响)[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica (作物学报),2013,39(4):735-743
[27]WU WG(吴文革),ZHANG HC(张洪程),QIAN YF(钱银飞),et al.Analysis on dry matter production characteristics of middle-season indica super hybrid rice(超级杂交中籼水稻物质生产特性分析)[J].Chinese Journal of Rice Science(中国水稻科学),2007,21(3): 287-293.
Responsible editor:Xiaoxue WANG
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
机械化播栽对杂交中稻干物质生产特性的影响
刘利1,2,雷小龙1,田青兰1,张强1,黄光忠3,任万军1*
(1.四川农业大学农学院/农业部西南作物生理生态与耕作重点实验室,四川温江611130;2.南充市种子管理站,四川南充637000;3.郫县农村发展局,四川郫县611700)
为探明机械化播栽方式对杂交中稻干物质生产的影响,2012~2013年采用两因素裂区试验设计,研究了播栽方式及其与穴苗数和播期互作对杂交中稻F优498干物质积累与分配、干物质输出与转化的影响。结果表明:播栽方式及其与穴苗数和播期的互作对杂交中稻干物质积累、分配和转运具有明显影响。机直播和机插处理的群体总干物质积累量低于手插处理,但机直播在拔节—抽穗阶段的干物质积累量和积累速率显著高于机插和常规手插,同时保持较高的茎鞘输出量、茎鞘输出率和茎鞘转化率,而机插在抽穗—成熟阶段具有较高的干物质积累量和积累速率。低苗和早播处理有利于提高抽穗后物质同化量、抽穗后干物质所占比例以及抽穗后干物质贡献率。适当早播能够有效提高杂交中稻机直播和机插的收获指标。
杂交中稻;机械精量穴直播;机插;干物质生产特性
农业部公益性行业科研专项(201303129);国家粮食丰产科技工程项目(2011BAD16B05);四川农业大学优秀硕士论文培育基金。
刘利(1987-),女,四川南充人,助理农艺师,硕士,主要从事作物高产高效优质生态理论技术研究,E-mail:liuli20080622@163. com。*通讯作者,E-mail:rwjun@126.com。
2015-05-04
修回日期 2015-06-11
Supported by Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201303129);National Science and Technology Project for Bump Crop (2011BAD16B05);Scientific Research Foundation of Sichuan Agricultural University.
*Corresponding author.E-mail:rwjun@126.com
Received:May 4,2015 Accepted:June 11,2015
R ice is one of staple food in China and plays a key role in crop safety.The production capacity and distribution characters of dry matter of rice have direct effects on economic yields[1]and it is researched that rice yield is of positive correlation with accumulations of total dry matter and in the period from heading to ripening stages[2].It is known that rice development,nitrogen use,accumulation and distribution of dry matter, yield and quality are under influence of the cultivation methods[3-7]and an appropriate cultivation method would effectively regulate production of rice dry matter and improve rice yield[4]. Recently,with rural to urban migration,it is urgent for China rice to develop modern rice technology oriented by mechanization[8],so that machinebased transplanting and direct seeding are born at the right moment[9].Zheng et al.[10]pointed out that moisture irrigation enhanced leaf area indices in tillering,booting,and full-heading stages of rice by mechanical direct seeding and increased biomass in ripening stage.Yu et al.[11]believed that nitrogen accumulation of rice by mechanized-transplanting took advantages before critical leaf age of productive tillering and after heading.Luo et al.[12]proposed that mechanized planting guaranteed a stable yield,reduced cost and increased work rate.It is widely known that mechanization of rice planting and the development of related technologies would improve rice production technology in China[13]. On the other hand,the appropriate number of seedlings per hole would improve rice population structure[14]and the date of seeding affects rice yield and quality by temperature and sunshine[15].At present,the researches are more on the effects of dry matter accumulation and cultivation methods of rice with different genotypes on production of rice dry matter.However, less attention is paid to the effects of the number of seedling per hole and seeding date on the production characters of dry matter of middle-season hybrid rice.The research took F You 498 as test materials and the treatment as per traditional manual transplanting as a control to explore accumulation and distribution of dry matters as per mechanical transplanting and seek the optimal cultivation method in order to provide references for application and extension of mechanized production technology for hybrid rice.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- The Effect of Crop Rotation on Soil Nematode Community Composition in a Greenhouse
- The Synergism of Chemical Herbicides and Aureobasidium pullulans for Control Cleavers (Galium aparine L.)in Wheat
- Changes of NF-κB,Bax and Caspase 3 in Apoptosis Induced by Ligustrazine Combined with Cis-dichlorodiamine Platinum in Human Gastric Carcinoma SGC-7901 Cell Lines
- Identification and Mutagenesis of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Chinese Sauerkraut
- Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Accumulation and Distribution of Dry Matter in Broomcorn Millet
- The Prediction of Population of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise
