Study on the Current Situation and Source Apportionment of PM 2.5 Pollution in China
2015-02-02NianliangCHENGShangyinGAOYuntingLIBingfenCHENGKuikuiYUAN
Nianliang CHENG,Shangyin GAO,Yunting LI,Bingfen CHENG,Kuikui YUAN
1.Beijing Municipal Environmental Monitoring Center,Beijing 100048,China;2.Tsinghua Holdings Human Settlements Environment Institute,Beijing 100083,China;3.Shanxi Academy for Environmental Planning,Taiyuan 030002,China
1 Introduction
With China's rapid economic development,accelerated process of urbanization and expansion of industrial scale,the regional air pollution is worsening[1].The recent haze with fine particulate matter as characteristic pollutants occurring in many areas of China,has posed a huge threat to visibility,public health and urban landscape[2-3].The fine particulate matter is a dominant factor causing the haze phenomenon,which consists of primary particles and secondary particles directly discharged into the air.The primary particles are mainly composed of dust particles and carbon black particles arising from the combustion of plant and fossil fuel;the secondary particles are mainly composed of sulfate,nitrate and ammonium,often causing greater pollution than conventional air pollutants[4].The newly revisedAmbient Air Quality Standards(GB3095-2012)in 2012[5]included PM2.5in the conventional air quality assessment,and it was the first time for China to develop PM2.5standards.Monitoring shows that the average annual concentration of PM2.5in many cities of China exceeds the national standard,and the study of pollution levels and characteristics of PM2.5in atmosphere can provide a theoretical basis for further researching its source and prevention measures.Using the scientific source apportionment method to determine the source of PM2.5is the key to control and governance,and the source apportionment of atmospheric particulate matter is mainly to carry out qualitative or quantitative identification of sources of atmospheric particles.China's source apportionment studies started late,and it did not perform the source apportionment studies until the late 1980s[6].At present,the source apportionment methods mainly include source checklist method,source model method,receptor model method and the method of combining source model with receptor model.China now mainly uses the receptor model as the analytical instrument.InTechnical Guide for Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Particulate Matter(Trial)developed in 2013[7],it proposed requirements on the source apportionment work of cities,urban agglomeration and regions by stages.Based on a lot of technical literature,this paper uses the fine particulate matter concentration data of key environmental protection cities in 2013 to summarize the pollution situation of fine particulate matter in China and source apportionment of fine particulate matter in the key cities,in order to provide a reference for other staff,and thus provide comprehensive effective information for management departments to minimize the adverse effects of PM2.5pollution.
2 Data sources
The PM2.5concentration data of 74 cities in 2013 are from Greenpeace[8]which collects full-year daily hourly PM2.5data about all stations in 2013 from public information platform of the Ministry of Environmental Protection and local environmental protection departments.On this basis,using the arithmetic average method,we calculate the annual average value of PM2.5in different cities,respectively.The 74 cities are the first batch of cities implementingAmbient Air Quality Standards(GB3095-2012),and they have more complete and continuous PM2.5monitoring data than other cities.The fine particulate matter concentration and source apportionment results of some other cities are from literature and related research reports.
3 PM 2.5 concentration distribution in China
3.1 Spatial distribution of PM 2.5 in ChinaAccording to new Ambient Air Quality Standards,the average annual concentration of PM2.5at35μg/m3reaches the standard.In accordance with the air quality ranking of74 cities released in 2013,the averageannu-al concentration is highest in Xingtai City,up to 155μg/m3;the average annual concentration is lowest in Haikou City,up to 25.6 μg/m3.The average annual concentration of PM2.5in nearly 92%of cities does not meet the national standards.The average annual concentration in the northern city of China is calculated at 89.9 μg/m3;the average annual concentration in the southern city of China is calculated at59.4μg/m3;the average annual concentration in the eastern city of China is calculated at70.6μg/m3;the average annual concentration in the central city of China is calculated at 76.6μg/m3;the average annual concentration in the western city of China is calculated at 59.9μg/m3.The average annual concentration is highest in the northern cities while the average annual concentration of fine particulate matter is lowest in the southern cities.There are also air pollution problems in the central provinces,and the average annual concentration of PM2.5in Xi'an,Zhengzhou,Wuhan,Chengdu,Hefei,Taiyuan and other cities reaches more than twice the national standard.
Using Kriging interpolation method,we perform the spatial interpolation of the average annual concentration of PM2.5in China.Kriging or Gaussian process regression is a method of interpolation for which the interpolated values are modeled by a Gaussian process governed by prior covariances,as opposed to a piecewise polynomial spline chosen to optimize smoothness of the fitted values[9].Fig.2 shows that in terms of spatial distribution,the regions with relatively high PM2.5concentration often have large area coverage,showing obvious regional characteristics.The high-value areas are mainly distributed in the North China Plain,the Sichuan Basin,eastern Hubei,northern Hunan,and the Yangtze River Delta region.These regions are economically developed,where the population is more concentrated and pollutant emission is large.The Sichuan Basin is mainly affected by terrain and weather conditions,and the pollutants are not easy to diffuse.In North China,due to considerable coal burning in winter and frequent temperature inversion,the air pollution is severe,and the dust and sand weather is frequent in spring,so the fine particulate matter concentration is also high.The average concentration of PM2.5throughout the region reaches 80μg/m3or more,which is consistent with the depiction of global air quality map released by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration(NASA)(http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/healths apping.html).In the southern regions,affected by East Asian monsoon and frequent precipitation,the average concentration of particulate matter is low.In the western regions,the source emission is low,so the average concentration of fine particulate matter is not too high.
3.2 Seasonal distribution of PM 2.5 in ChinaTo further analyze seasonal variation of PM2.5in various cities,we consult the relevant literature,and produce a summary as shown in Table 1.
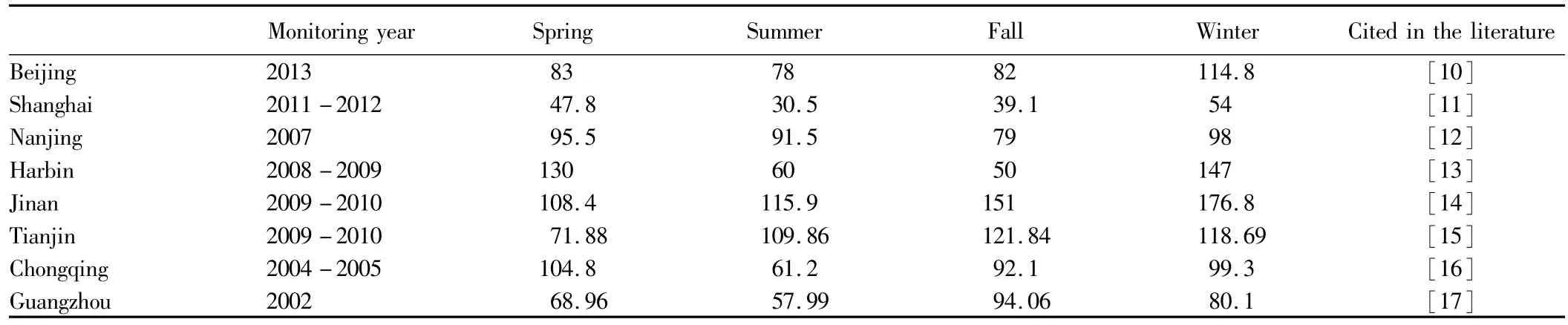
Table 1 Seasonal variation of PM 2.5 in different cities(μg/m3)
In terms of seasonal distribution,a full year is divided into spring(March to May),summer(June to August),fall(September to November)and winter(December,January and February).From the summarized literature results in Table1,it is found that in terms of seasonal changes in PM2.5concentration in the eight cities,it is sequenced as follows:winter>spring>autumn>summer.The PM2.5mass concentration in winter and spring is significantly higher than in summer and fall.The highest values occur in winter,and the average concentration in winter in the eight cities is 111.1μg/m3;the lowest values occur in summer,and the average concentration in winter in the eight cities is 75.6 μg/m3.There is little difference in the concentration between spring and fall.The average concentration of PM2.5in winter in the northern cities is significantly higher than in the southern cities.Winter is the heating season,so the pollution is heavy.In the southern cities,the precipitation is great,and the average concentration of particulate matter is not too high.Due to unstable weather system changes,the dispersion conditions in Spring and fall are better than in other seasons.
4 Source apportionment results of the key cities
Coal,cars,cooking fumes and burning firewood in rural areas are all direct sources of PM2.5,forming the primary particulate matter;sulfur dioxide,nitrogen oxides in the exhaust after the coal and oil combustion as well as the volatile organic matter generated in the process of motor vehicle use,oil processing and solvent use,produce physical and chemical reaction in the air,forming secondary particulate matter.The particulate matter source apportionment methods include receptor model method,source inventory method,diffusion model simulation method,and the combination of source model and receptor model.Source inventory method is to identify the major sources of emissions that contribute to the receptor according to the collection of pollutants emitted by various sources of emissions into the air in a certain time span and space.Source model method is to estimate the contribution of pollution sources to receptors according to various pollution sources intensity data,meteorological data and atmospheric chemical processes.Receptor model method is to estimate the contribution of various pollution sources to receptors based on the chemical,physical and biological information of atmospheric particulate matter,including CMB model on the basis of source and receptor component spectrum and statistical model only based on receptor component spectrum.The combination of source model and receptor model is to use the two models at the same time,making analytical results more reasonable.Currently receptor model is widely used in China,and CMB model is used in 47%of current domestic literature and reports on source apportionment[6].To better illustrate the PM2.5sources in various cities of China,we consult the literature and research reports published on PM2.5source apportionment in China,and summarize the PM2.5source apportionment results of each city.
It can be found that although different cities use different source apportionment methods,the main source of fine particulate matter in the region is the local emissions,including coal-fired sources,industrial sources,vehicle exhaust,dust,secondary sources and regional transmission.Coal-fired sources,industrial sources and vehicle exhaust make the greatest contribution to PM2.5,and the contribution of various pollution sources to PM2.5is mainly related to local energy structure,economic development,and weather conditions.Fig.3 shows that vehicle exhaust contributes 10% -50%to PM2.5,while the contribution rate of other sources is10%-30%.Taking Beijing as an example,the literature results[10]indicate that vehicle contributed 22%to PM2.5in 2011,basically consistent with the study results of Tsinghua University[27]and Peking University[28-31].There is a slight difference between this study result and PM2.5source apportionment results released by Beijing Municipal Environmental Protection Bureau during 2012-2013[32].The differences between various research results are primarily due to variability of PM2.5,methods and researchers' subjective factors.At the same time,we should note the differences in the pollution status,source apportionment results and economic development between various cities,and avoid the pure emphasis on local PM2.5emission reduction.Due to lack of complete list of air pollution emission sources as yet,there are great uncertainties in the current studies on PM2.5source apportionment[33-34],and we need to further verify,assess and study the ways to effectively combine a variety of source apportionment methods to form reliable comprehensive source apportionment results and reduce errors in various links.
5 Conclusions
(i)PM2.5in China shows significant spatial and temporal distribution characteristics.PM2.5concentration is mainly distributed in the North China Plain,Sichuan Basin and Yangtze River Delta.The average annual concentration in North China is about 80μg/m3,and in terms of the seasonal variation in PM2.5concentration in various cities,it is sequenced as follows:winter>spring>autumn>summer.
(ii)Coal-fired sources,industrial sources and vehicle exhaust are the major sources of emissions making a significant contribution to PM2.5,and motor vehicle exhaust contributes about 10%-30%to PM2.5.
(iii)Only by conducting systematic large-scale monitoring can we have a clear understanding of PM2.5pollution in China.Due to the lack of detailed PM2.5source inventory and differences in the methods for source apportionment,there are great uncertainties in the current studies.
[1]REN ZH,WAN BT,SU FQ,et al.Several characteristics of atmospheric environmental quality in China at present[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2004,17(1):1-6.(in Chinese).
[2]WANGW,TANG DG,LIU HJ,et al.Research on current pollution status and pollution characteristics of PM2.5in China[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2000,13(1):1-5.(in Chinese).
[3]China National Environmental Monitoring Center.Monitoring report on haze pilot,2010[OL].(2011-07-04)[2011-10-19].http://www.cnemc.cn/publish/106/news/news_18191.html.(in Chinese).
[4]TANGXY,ZHANGYH,SHAOM,etal.Atmosphere environmental chemistry[M].Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006:425-428.(in Chinese).
[5]Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China.GB 3095-2012 environmental air quality standard[S].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press,2012.(in Chinese).
[6]ZHENGM,ZHANG YJ,YAN CQ,et al.Review on analysis method of source apportionmentof PM2.5[J].Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2014(68):1-7.(in Chinese).
[7]Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China.Air particulatematter source apportionment guide No.[2013]92(trial)[S].Beijing:China Environmental Science Press,2013.(in Chinese).
[8]Greenpeace.Rank of PM2.5annual concentration in 2013 from 74 cities[N/OL].Beijing:www.QQ.com,2013[2014-01-02].http://news.qq.com/a/20140109/013303.htm.(in Chinese).
[9]Davis,John C.Statistics and data analysis in geology(3rd Edition)[M].New York:John Wiley&Sons,Inc,2002:57-61.
[10]Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences.The compliance rate calculation of ambient air quality new standard in heavy pollution cities[R].Beijing:Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences,2012.(in Chinese).
[11]JIAO Y.Observational study of PM2.5mass concentration and aerosol optical characteristics in Shanghaiurban areas[D].Qingdao:Ocean University of China,2013.(in Chinese).
[12]WEIYX,YINY,YANGWF,etal.Analysis of the pollution characteristics&influence factors of PM2.5in Nanjing Area[J].Environmental Science and Management,2009,34(9):29-34.(in Chinese).
[13]WANGWS.Apportionment of air-borneparticulate during heating period in Harbin[D].Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology,2009.(in Chi-nese).
[14]YANG LX.Analysis on themain source of PM2.5pollution in Ji'nan City and its influence on visual range[D].Ji'nan:Shandong University,2008.(in Chinese).
[15]JIHL.Research on characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5and PM10in Tianjin City[D].Tianjin:Nankai University,2011.(in Chinese).
[16]WANG TG.Source apportionment and pollution characteristics of PM2.5in Chongqing[D].Chongqing:Chongqing University,2007.(in Chinese).
[17]LAISC.Characterizing the PM10and PM2.5urban aerosols in Guangzhou[D].Guangzhou:Sun Yat-sen University,2002.(in Chinese).
[18]YAN XH.The character and source apportionment of fine particles PM2.5in Baoshan District,Shanghai[D].Shanghai:East China University of Science and Technology,2011.(in Chinese).
[19]BAO Z,FENGYC,JIAO Z,et al.Characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5and PM10in Hangzhou[J].Environmental Monitoring in China,2010,26(2):44-48.(in Chinese).
[20]XIAO ZM,BI XH,FENG YC,et al.Source apportionment of ambient PM10and PM2.5in urban area of Ningbo City[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2012,25(5):549-555.(in Chinese).
[21]HUANG HJ,LIU HN,JIANGWM,et al.Physical and chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Nanjing[J].Climatic and Environmental Research,2006,11(6):713-722.(in Chinese).
[22]CHEN T.Analyse on resource apportionment of PM2.5in the center of Chengdu[D].Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2009.(in Chinese).
[23]YIF.Source apportionment for inhalable particles in the city atmosphere[D].Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2004.(in Chinese).
[24]YANG TZ.Chemical compositions and source apportionment of PM2.5in Changsha[D].Changsha:Central South University(CSU),2010.(in Chinese).
[25]ZHANGXM,ZHUANGMZ.Research on source apportionment of PM2.5in fine air particles of Xiamen[J].Xiamen Science&Technology,2007(3):41-43.(in Chinese).
[26]Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences.Study on on haze characteristics and control ways of typical areas[R].Beijing:Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences,2013.(in Chinese).
[27]HE KB,YANG FM,DUAN FK,et al.Atmospheric particulates and regional complex pollution[M].Beijing:Science Press,2011:165-185.(in Chinese).
[28]HUM.Study on physical and chemical characteristics,sources and formation mechanism of Beijing particulate air pollution and ultrafine particle[M].Beijing:Science Press,2009.(in Chinese).
[29]YUN,WEIYJ,HUM,etal.Characterization and source identification of ambient organic carbon in PM2.5in urban and suburban sites of Beijing[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2009,29(2):243-251.(in Chinese).
[30]ZHU XL,ZHANG YH,ZENG LM,etal.Source identification of ambient PM2.5in Beijing[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2005,18(5):1-5.(in Chinese).
[31]SONG Y,TANG XY,FANGC,etal.Source apportionmenton fine particles in Beijing[J].Chinese Journal of Environmental Science,2002,23(6):11-16.(in Chinese).
[32]Beijing Municipal Environmental Protection Bureau.Beijing released research achievement of PM2.5source apportionment[OL].(2014-04-16)[2014-04-19].http://www.bjepb.gov.cn/bjepb/323265/340674/396253/index.html.(in Chinese).
[33]ZHU T,WU L,BIXH,et al.Improving receptor models for ambient air particulate matter source apportionment[J].China Environmental Science,2010,30(7):865-870.(in Chinese).
[34]HAOMT,HOUWG,QU XH,etal.The method amending of improvedsource-analysis technique of atmospheric particulate matter[J].China Environmental Science,2005,25(2):138-141.(in Chinese).
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Integration of Medical Care and Endowment:A New Exploration of Endowment Mode in the Context of Population Aging
- The Distribution of Benefits for Players in Agricultural Industrial Chain
- Price Conduction Mechanism of China's W heat Industry Chain Based on VECM
- On the Development and Maintenance of Cigarettes Exported to North Korea
- Study of the Factors Influencing Entrepreneurial Farmers' Formal Financial Credit Demand and Credit Constraints in Sichuan and Chongqing
- The Research on the Construction of Monitoring and Evaluation System for the Operation of Marine Economy in Liaoning Province
