Ophthalmic Evaluation of Children from the Tibet Plateau with Congenital Heart Disease
2014-09-17GuiqinWangQianShiLinSunJingWangLeiLiTianchangLiWeiWang
眼科学报 2014年3期
Guiqin Wang,Qian Shi,Lin Sun, Jing Wang, Lei Li, Tianchang Li,*, Wei Wang
1 Department of Ophthalmology, Navy General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
2 The Heart Center, Navy General Hospital, Beijing 100048, China
3 Changzhi Health School, Changzhi 046000, China


Materials and methods
General data
Distance acuity examination in bilateral eyes
Non-contact intraocular pressure measurement

Measurement of corneal thickness
Slit-lamp examination
Fundus examination


Statistical analysis

Results
Distant acuity

Anterior chamber depth

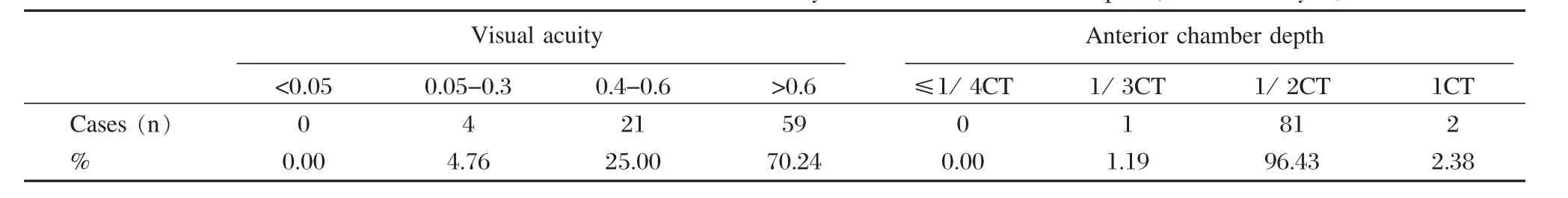
Table 1 Characteristics of distribution of visual acuity and anterior chamber depth (number of eyes)
Intraocular pressure


Table 2 Clinical data of intraocular pressure and corneal thickness (number of eyes)
Corneal thickness

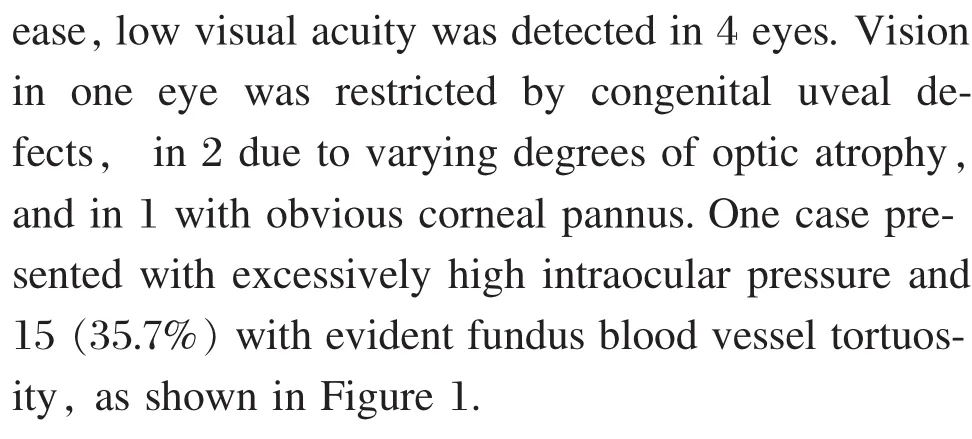
Ocular diseases
Discussion
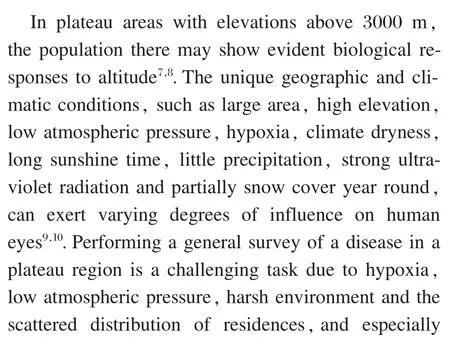
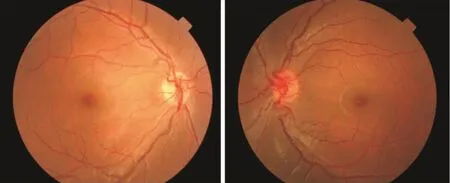
Figure 1 Fundus examination in children with congenital heart disease


杂志排行
眼科学报的其它文章
- Relationship between Refractive Error and Ocular Biometrics in Twin Children:the Guangzhou Twin Eye Study
- Ten-year Etiologic Review of Chinese Children Hospitalized for Pediatric Cataracts
- Clinical Features and Differential Diagnosis of Acute Idiopathic Blind Spot Enlargement Syndrome
- Relationship between Foxp3-3279 (rs376158) Polymorphism and Dust Mite Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Comparison of Postoperative Pain Following Laser-assisted Subepithelial Keratectomy and Transepithelial Photorefractive Keratectomy:a Prospective,Random Paired Bilateral Eye Study
- Clinical Observation of Transepithelial Corneal Collagen Cross-linking by Iontophoresis of Riboflavin in Treatment of Keratoconus
