Jacobi Elliptic Numerical Solutions for the Time Fractional Variant Boussinesq Equations
2014-05-13GEPREELKhaled
GEPREEL Khaled A
M ath.Departement,Faculty ofScience,TaifUniversity,Kingdom ofSaudiArabia; M athematicsDepartment,Faculty ofScience,Zagazig University,Egypt.
Jacobi Elliptic Numerical Solutions for the Time Fractional Variant Boussinesq Equations
GEPREEL Khaled A∗
M ath.Departement,Faculty ofScience,TaifUniversity,Kingdom ofSaudiArabia; M athematicsDepartment,Faculty ofScience,Zagazig University,Egypt.
Received 27 November 2013;Accepted 8 April 2014
.Thef ractionalderivativesinthesenseofCaputo,andthehomotopyper turbation m ethod are used to construct the app roxim ate solu tions for non linear variant Boussinesq equations w ith respect to tim e fractional derivative.Thism ethod is efficient and pow erful in solving w ide classes of nonlinear evolution fractional order equations.
Homotopyper turbationmethod;f ractionalcalculus;nonl inear timef ractionalvariant Boussinesq equations.
1 In troduction
Fractional d ifferential equations have caughtm uch attention recently due to the exact descrip tion of non linear phenom ena.First there w ere alm ost no p ractical app lications of fractional calcu lus,and itw as considered by m any au thors as an abstract area containing on ly m athem aticalm anipu lations of little or no use.Nearly 30 years ago,the parad igm began to shift from pu rem athem atical form u lations to app lications in various fields.Du ring the last decade Fractional Calcu lus has been app lied to alm ost every field of science,engineering,and m athem atics.Several fields of app lication of fractional d ifferentiation and fractional integration are already w ell established,som e others have just started.M any app lications of fractional calcu lus can be found in tu rbu lence and fluid dynam ics,stochastic dynam ic system,p lasm a physics and controlled therm onuclear fusion,non linear con trol theory,im age p rocessing,non linear biological system s, astrophysics[1–11].H istoricalsumm aries of the developm entsof fractional calcu lus canbe found in[1–3].There has been som e attem p t to solve linear p roblem sw ith m u ltip le fractional derivatives(the so-called m u lti-term equations)[2,12].Notm uch w ork has been done for nonlinear p roblem s and on ly a few num erical schem es have been p roposed to solve non linear fractional d ifferential equations.M ore recently,app lications have included classes of non linear equation w ith m u lti-order fractional derivative and thism otivates us to develop a num erical schem e for their solu tions[13].M ost of fractional d ifferential equations do not have exact analytical solu tions,hence considerable heed has been focused on the app roxim ate and num erical solu tions such as Adom ian decom position m ethod[14–17],variational iteration m ethod[18,19],hom otopy pertu rbationm ethod[20–22],hom otopy Analysism ethod[23,24]and so on.
Consider thenonlinear variant Boussinesq equations[25]

Lu[25]used the Jacobi ellip tic functions to obtain the exact solutions for tw o variant Boussinesq equations(1.1).Zayed etal.[26]haveused thehom otopy pertu rbationm ethod and Adom ian decom positionm ethod to introduce the app roxim ate solutions for non linear variant Boussinesq equations(1.1).
In this article,w e give a new m odelof the tim e fraction variant Boussinesq equations of the form

This system has been d iscussed bym any au thorsw henα→1.We usehom otopy pertu rbation m ethod to calcu late an app roxim ate solu tion of tim e fraction varian t Boussinesq equations(1.2)w hich is a generalization of the given solu tion in[25,26].
2 Prelim inariesand notations
In this section,w e give som e basic definitions and p roperties of the fractional calcu lus theory w hich w ill be used fu rther in this paper.Form ore details see[2].For the finite in terval[a,b],w e define the follow ing fractional in tegraland derivatives.

Definition2.2.The Riemann-Liouville fractional integral operator oforderα≥0,ofa function f∈Cµ,µ≥-1,is defined as

Properties of the operator Jαcan be found in[2],w em ention on ly the follow ing:For f∈Cµ,µ≥-1,α,β≥0 andγ>-1:

The Riem ann-Liouville derivative has certain d isadvantages w hen trying to m odel real-w orld phenom ena w ith fractional d ifferen tial equations.Therefore,w e shall introduce am od ified fractional d ifferential operator Dαp roposed by M.Capu to in hisw ork on the theory of viscoelasticity[2].
Definition2.3.Form tobe thesmallest integer thatexceedsα,theCaputo time-fractionalderivative operator oforderα>0 isdefined as

3 Basic idea of hom otopy pertu rbationm ethod
We illustrate som ebasic concep tsof thehom otopy pertu rbationm ethod for the follow ing non linear fractionald ifferentialequation[23–25]

subject to the initialand boundary cond itions
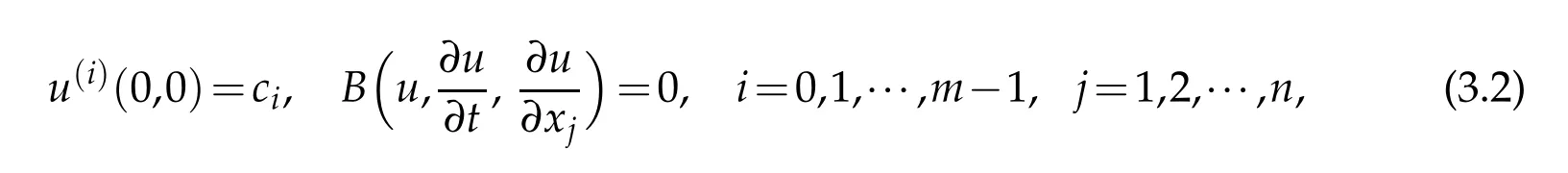

In view ofHe’shom otopy pertu rbation technique[27],w e can construct the follow ing sim p le hom otopy

The hom otopy param eter p alw ays changes from zero to unity.In case p=0,Eq.(3.3)or (3.4)becom es

w hen p=1,Eq.(3.3)or Eq.(3.4)turnsout to be theoriginal fractionald ifferentialequation.
In view of hom otopy pertu rbation m ethod,w e use the hom otopy param eter p to expand the solu tion in the follow ing form

For non linear p roblem s,let us set Nu(x,t)=S(x,t).Substitu ting Eq.(3.6)into Eq.(3.3) or Eq.(3.4)and equating the term sw ith identical pow er of p,w e can obtain a series of fractional d ifferen tialequations of the form

w here the functions S0,S1,S2,···satisfy the follow ing equations
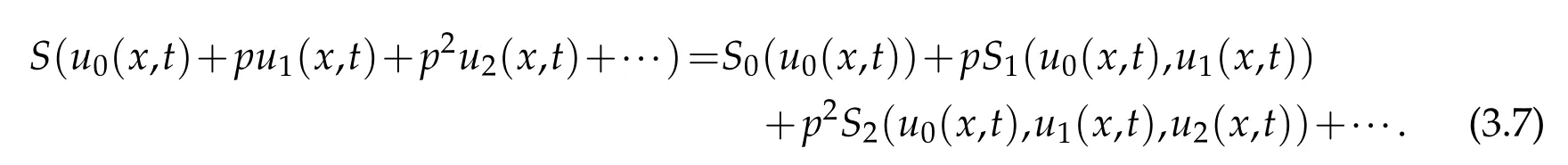

On setting p=1,w e getan accu rate app roxim ation solu tion in the follow ing form

4 HPM for them u ltip le-term fractional Boussinesq equation
In this section,to dem onstrate the effectiveness of our app roach,w e w ill app ly HPM to construct app roxim ate solu tions for the non linear tim e fraction varian t Boussinesq
equations

w ith the initial cond ition

w here sn(kx,m)is a Jacobiellip tic sine function w ith them odu lus 0<m<1 andλ,k are arbitrary constan ts.By the hom otopy pertu rbation technique,w e construct a hom otopy V(r,p):Ω×[0,1]→R w hich satisfies

Accord ing to thehom otopy pertu rbationm ethod,w e can firstuse theem bedd ing parameter“p”as a sm allparam eter,and assum e that the solutionsof Eqs.(4.4)and(4.5)can be w ritten asa pow er series in“p”as follow s

Substitu ting the Eqs.(4.6),(4.7)in to Eqs.(4.4)and(4.5)and arranging the coefficien ts of”p”pow ers.A fter som e calcu lation,w e have
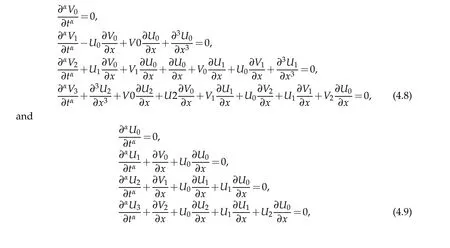
and so on.
Substitu ting the Eqs.(4.2),(4.3)into Eqs.(4.8)and(4.9),w e deduce after som e calculation that

and so on.
On setting p=1,w e get an accu rate app roxim ation solu tions for Eq.(4.1)in the fol-
low ing form

In the specialcasew henα→1,w eget the app roxim ate solu tionsof the non linear variant Boussinesq equations(1.1)take the follow ing form


Form the app roxim ate solu tionsare show n in Figs.1-4 the velocity U and the totaldep th havem inim um values near zero increase and then decrease period ically w ith the coord inate x,it is clear also that there are a slight increasing w ith an increasing of the tim e. A lso the behavior o f the app roxim ate solu tions are sim ilar to the behavior of the exact solu tion so that theapp roxim ate solu tionsare rabid ly convergence to theexactsolutions.
Using Tay lor seriesexpansion near t=0,w e get:
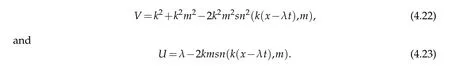
Theseare theexact solu tionsof the variant Boussinesq equationsequation(1.1)obtained w henα=1.These solu tions(4.22)and(4.23)are exactly the sam e solu tions obtained in[25].The com parison betw een the exact solu tions(4.22)-(4.23)and the app roxim ate solu tions(4.20)-(4.21)are show n in Table 1.
Table 1 leads to get the p roposed algorithm p roduced a rapid ly convergentseries.
The com parison betw een the exact solu tion(4.22)-(4.23)and the app roxim ate solutions(4.18)-(4.19)are show n in Table 2w henα=0.9999.
Table 2 leads to get the p roposed algorithm p roduced a rap id ly convergent series.

Table 1:The value of approximate solution(4.20)-(4.21)and the value of the exact solution(4.22)-(4.23)when α=1,t=0.1 and-50<x<50.

Figure 1:The approximate solution(4.21)shown in the figure(ii)in com parison w ith the exact solution(4.23) shown in(i)whenα=1,m=0.5,k=0.1,λ=0.5,-50<x<50 and 0<t<1.
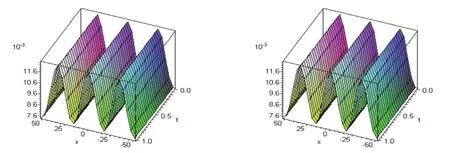
Figure 2:The approximate solution(4.20)shown in the figure(ii)in comparison with the exact solution(4.22) shown in(i)whenα=1,m=0.5,k=0.1,λ=0.5,-50<x<50 and 0<t<1.

Figure 3:The approximate solution(4.19)shown in the figure(ii)in com parison w ith the value of the exact solution(4.23)shown in(i)when m=0.5,k=0.1,λ=0.5,α=0.9999,-50<x<50 and 0<t<1.

Figure 4:The approximate solution(4.18)shown in the figure(ii)in com parison w ith the exact solution(4.22) shown in(i)m=0.5,k=0.1,λ=0.5,α=0.9999,-50<x<50 and 0<t<1.

Table 2:The value of approximate solution(4.18)-(4.19)and the value of the exact solution(4.22)-(4.23)when m=0.5,k=0.1,λ=0.5,t=0.1,α=0.9999 and-50<x<50.
5 Conclusion
In this paper,the hom otopy pertu rbation m ethod has been successfu lly app lied to obtain thenum ericalsolutionsof the tim e fractionalderivative variant Boussinesq equation w ith the initialcond itions.From Figs.1-4,w e deduce thebehavior of theapp roxim ate solu tionsare the sam e behavior of the exact solu tionsat som e d ifferen t valuesα.Tables 1-2 lead to see the sm allerror betw een the app roxim ate solu tionsand the exactsolu tions for som e d ifferen t valuesα.Consequen tly,w e deduce the app roxim ate solu tions are rap id ly convergentseriesas theexactsolu tions.The hom otopy pertu rbationm ethod w as clearly very efficien tand pow erfu l technique in find ing the num ericalsolu tionsof the p roposed equations.
[1]Kilbas A.A.,Srivastava H.M.,and Tru jillo J.J.,Theory and App lications of Fractional Differential Equations,North-Holland M athem aticalStudies,204,Elsevier,Am sterdam,2006.
[2]Pod lubny I.,Fractional Differential Equation,Acad.Press,San Diego-New York-London, 1999.
[3]Sam ko S.G.,Kilbas A.A.,and M arichev O.I.,Fractional Integrals and Derivatives:Theory and App lications,Gordon and Breach,Langhorne,1993.
[4]El-Sayed A.M.A.,Fractional-order d iffusion-w ave equation.Int.J.Theor.Phys.,35(1996), 311-322.
[5]Herzallah M.A.E.,El-Sayed A.M.A.and Baleanu D.,On the fractional-order Diffusion-Wave p rocess.Rom.Journ.Phys.,55(2010),274-284.
[6]Herzallah M.A.E.,M uslih Sam i I.,Baleanu D.and Rabei Eqab M.,Ham ilton-Jacobi and fractional like action w ith tim e scaling,Nonl.Dyn.,NODY1873R1,(accep ted).
[7]M agin R.L.,Fractional Calcu lus in Bioengineering,Begell House Publisher,Inc.Connecticut,2006.
[8]West B.J.,Bologna M.,and Grigolini P.,Physics of Fractal operators,New York,Sp ringer, 2003.
[9]Jesus I.S.,M achado J.A.Tenreiro,Fractional control of heat d iffusion system s.Nonl.Dyn., 54(2008),263-282.
[10]Agraw alO.P.,Baleanu D.,Ham iltonian form u lation and a directnum ericalschem e for FractionalOp tim alControl Problem s.J.Vibr.Contr.,13(2007),1269-1281.
[11]Tarasov V.E.,Fractional vector calcu lus and fractional M axw ell’s equations.Annals of Physics,323(2008),2756-2778.
[12]He J.H.,Som e app lications of non linear fractional d ifferentialequations and their app lications.Bull.Sci.Technol.,15(1999),86-90.
[13]Erturk V.S.,M om ani Sh.,Odibat Z.,App lication of generalized d ifferential transform m ethod to m u lti-order fractional d ifferential equations.Comm.Nonl.Sci.Numer.Simulat., 13(2008),1642-1654.
[14]Daftardar-Gejji V.,Bhalekar S.,Solving m u lti-term linear and non-linear d iffusion w ave equations of fractional order by adom ian decom position m ethod.Appl.M ath.Comput.,202 (2008),113-120.
[15]Daftardar-GejjiV.,JafariH.,Solving am u lti-order fractionald ifferentialequation using adom ian decom position.Appl.M ath.Comput.,189(2007),541-548.
[16]Herzallah M.A.E.,Gep reel K.A.,App roxim ate solu tion to the tim e-space fractional cubic non linear Schrod inger equation.Appl.M ath.M ode.,36(2012),5678-5685.
[17]M om aniS.,Analyticalapp roxim atesolution for fractionalheat-likeand w ave-likeequations w ith variable coefficientsusing the decom positionm ethod.Appl.M ath.Comput.,165(2005), 459-472.
[18]Noor M.A.,M ohyud-Din S.T.,Variational iteration decom position m ethod for solving higher d im ensional initialboundary value p roblem s.Inter.J.Nonl.Sci.,7(2009),39-49.
[19]Sw eilam N.H.,Khader M.M.,A l-Bar R.F.,Num erical stud ies for am u lti-order fractional d ifferentialequation.Phys.Lett.,A 371(2007),26-33.
[20]GolbabaiA.,Sayevand K.,Fractionalcalcu lus-A new app roach to theanalysisofgeneralized fou rth-order d iffusion-w ave equations.Comput.M ath.Appl.,(2011)in p ress.
[21]Golbabai A.,Sayevand K.,The hom otopy pertu rbation m ethod form u lti-order tim e fractional d ifferentialequations.Nonl.Sci.Lett.,A 1(2010),147-154.
[22]Gep reelK.A.,The hom otopy perturbationm ethod to the nonlinear fractional Kolm ogorov-Petrovskii-Piskunov equations.Appl.M ath.Lett.,24(2011),1428-1434.
[23]Gep reel K.A.,M oham ed M.S.,Analytical app roxim ate solution for nonlinear space-tim e fractional K lein Gordon equation.Chinese PhysicsB,accep ted for publication(2012).
[24]Liao S.J.,The Proposed Hom otopy Analysis Technique for the Solu tion of Non linear Problem.Ph.D thesis,Shanghai Jiao Tong University;1992.
[25]Lu D.,Jacobiellip tic function solution for tw o variant Boussinesq equations.Chaos,Solitons &Fractals,24(2005),1373-1385.
[26]Zayed E.M.E.,Nofal T.A.and Gep reel K.A.,Hom otopy pertu rbation and Adom ian decom position m ethods for solving non linear Boussinesq equations.Comm.Appl.Nonl.Anal., 15(2008),57-70.
[27]He J.H.,New interp retation of hom otopy perturbationm ethod.Int.J.M odern Physic.,B,20 (2006),1-7.
10.4208/jpde.v27.n3.1 Sep tem ber 2014
∗Corresponding author. Email address: kagepreel@yahoo.com (K. A. Gepreel)
AMS Subject Classifications:02.30.Jr
ChineseLibraryClassifications:O175.2
杂志排行
Journal of Partial Differential Equations的其它文章
- Positive Solu tions of Non linear Ellip tic Prob lem in a Non-Sm ooth Planar Dom ain
- Quenching Tim e fora Sem ilinearHeatEquation w ith a Non linear Neum ann Boundary Cond ition
- WaveletCollocation M ethods for Viscosity Solu tions to Sw ing Op tions in Natu ral Gas Storage
- Liquid Crystal Flow sw ith Regu larity in One D irection
- Strong Solu tions for Nonhom ogeneousIncom p ressib le Viscous Heat-Conductive Fluidsw ith Non-New tonian Poten tial
- On Existence of Local Solu tions of a M ovingBoundary Prob lem M odelling Chem otaxis in 1-D
