Polarization Independent Dual-band Metamaterial Based Radar Absorbing Structure(RAS)for Millimeter Wave Applications
2014-04-17ShivNarayanLathaandJha
Shiv Narayan,Latha S. and R M Jha
1 Introduction
The radar absorbing materials(RAM)and structures(RAS)are widely used in aerospace sectors to reduce the RCS of the aircraft,electromagnetic shielding of high reflection surfaces and metal surfaces etc.The stealth technique is the most typical application of electromagnetic(EM)wave absorption technology.Using this technique,the aircraft and warships can evade detection by reducing their radar cross-section(RCS).The conventional EM radar absorbers were designed based on either lossy materials such as Dallenbach layer[Hatakeyama and Inui(1984)]or resistive sheet separated by dielectric spacers such as Salisbury screen and Jaumann absorber[Fante and McCormack(1988);Knott and Lunden(1995)].These absorbers are thicker and absorb EM wave satisfactorily over narrow range of frequency or at single frequency.Moreover,the absorbers based on lossy materials such as magnetically loaded dielectric,is difficult to analyze at microwave frequencies.
Recently,multi-band radar communication systems are used to detect and track the aircraft and warships.This leads to the high demand of multi-band EM radar absorbers with reasonable bandwidth in aerospace sectors.This can only be accomplished by metamaterial(MTM)based radar absorbing structures.Since the permittivity and permeability of metamaterial structures are controlled independently by varying the unit cell dimensions of its electric resonant and magnetic resonant components[Narayan et al.(2012;Choudhury et al.(2012)].The metamaterial based structures can be impedance-matched to free-space to achieve perfect EM absorption[Lee and Lee(2012)].The metamaterial based multi-band radar absorbers are designed in two ways;one is metamaterial layer with multi-resonant unit cells backed by metal sheet and another type of MTM-RAS is designed by cascading of lossy DPS layers and metamaterial layers such as ENG,MNG,and DNG etc.Although first method facilitates the design of very thin multi-band radar absorbers,such absorbers exhibit very narrow bandwidth at the resonances.For instance,some metamaterial based multi-band thin radar absorbers were realized by Shen et al.(2011),Zhu et al.(2010),and Singh et al.(2011)with metal backing plate in microwave and millimetre wave frequency regimes,exhibit narrow bandwidth at the resonances.Moreover,the metal backed absorbers may not be useful for stealth applications because it enhances the RCS of the structure outside the band due to the metal backing plate.
Later method is a better option to design multi-band radar absorber with reasonable bandwidth for stealth applications since it does not use metal backing plate.In view of this,Oraizi and Abdolali(2008)presented the design and analysis of wideband metamaterial RAS in microwave frequency region.Further,Narayan et al.(2013)presented the EM analysis of metamaterial based single-band RAS designed by cascaded lossy DPS and metamaterial layers without metal backing plate,for millimetre wave stealth applications.
In the present paper,a metamaterial based radar absorbing structure has been proposed for dual-band characteristics in millimeter wave frequency regime.The proposed structure consists of cascaded MNG(mu-negative)and DPS(double positive)layers.The EM performance analysis of this structure is carried out based on transmission line transfer matrix(TLTM)method for both TE and TM polarizations.The proposed metamaterial-RAS shows excellent absorption(>90%)over the frequency range of 111-131 GHz at first resonance and from 164.5-185 GHz at second resonance without metal backing plate.In addition,it shows very low power reflection(<6%)corresponding to both resonant frequencies.
2 Theoretical Considerations
The side view of a six-layered metamaterial based RAS is shown in Figure 1,where the EM wave is intended to incident on DPS layer at incidence angleθinc.According to TLTM method,a multilayered metamaterial structure can be represented as multiple sections of transmission line.The characteristic impedance and propagation constant associated to each section depends on the incidence angle,frequency,and polarization of the incidence wave.
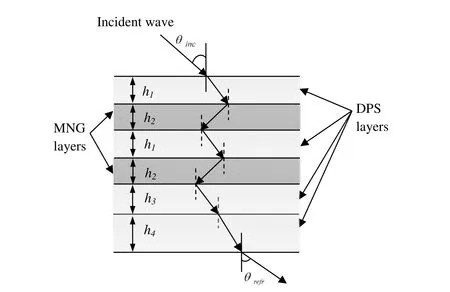
Figure 1:Side view of dual-band MTM-RAS structure
In TLTM method,the transfer matrix of each layer is determined by cascading the wave amplitude matrix of the layer and discontinuity matrix between the consecutive layers.The transfer matrix of entire structure is obtained by cascading the transfer matrix of individual layer.
Finally,the reflection and transmission coefficients of the entire structure are determined with the help of transfer matrix of the structure for different incident angles and different polarizations.
The propagation constant(γlz)oflthsection of the transmission line for both TE and TM polarization can be expressed by Oraizi and Afsahi(2009)

whereµlandεlrepresent the permeability and the permittivity of thelthlayer respectively.ωis the angular frequency.θlrepresents the incidence angle at thelthlayer.
By using the Snell’s law forlthand(l+1)thlayer,the incidence angle at each layer are related by

The intrinsic impedance of thelthlayer is determined by

The transfer matrix of a multilayered metamaterial-RAS structure can be expressed as
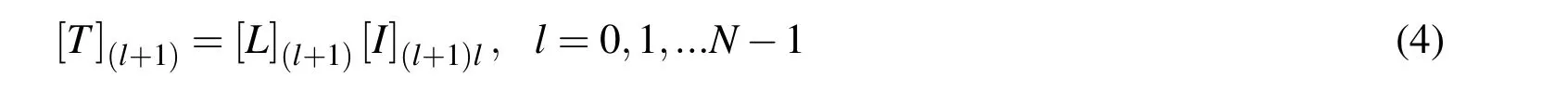
whereNis the number of layers.The wave amplitude transmission matrix[L](l+1)and discontinuity transfer matrix[I](l+1)lbetween two consecutive layers can be computed using the expressions given in[Oraizi and Afsahi(2009)].
The transmission coefficient(t)and reflection coefficient(r)of the proposed structure are related by
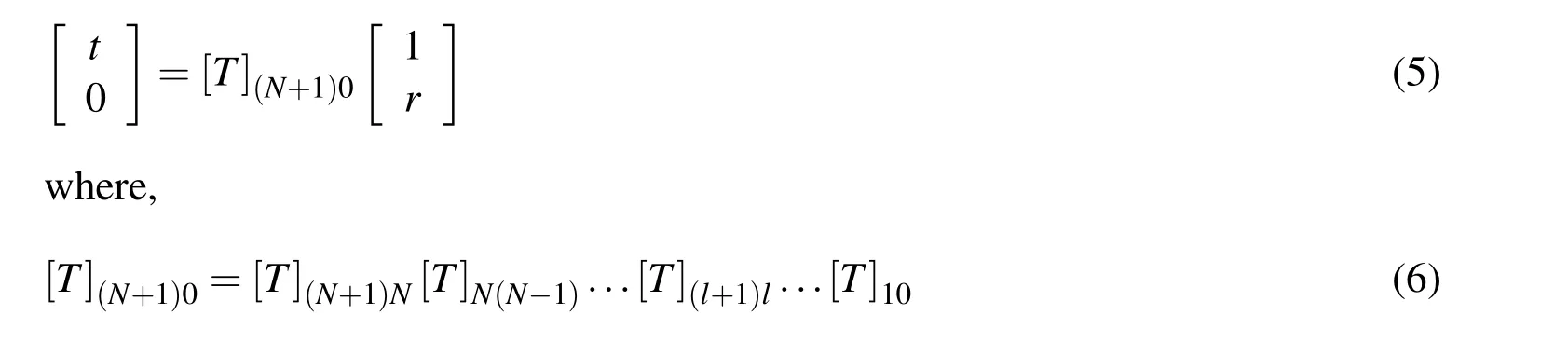
The power reflectionR,and power transmissionT,of the proposed structure can be calculated by

The proposed metamaterial-RAS consists of cascaded lossy DPS layers and MNG layers.The complex permittivity of the lossy dielectric layers(DPS)is computed by using the dispersion relation,given by Chenet al.(2004)

whereε′is the real part of the complex permittivity.σand tanδrepresent the conductivity and loss tangent of the dielectric material,respectively.Whereas the MNG(mu-negative)layer consists ofsquare split ring resonators(SSRRs)and its relative permeability is determined by Lorentz and Resonance model[Pendryet al.(1999)]as

wherefmoandfmpare the magnetic resonant frequency and magnetic plasma frequency of the square SRR,respectively.
3 EM Design of Dual-band Metamaterial RAS
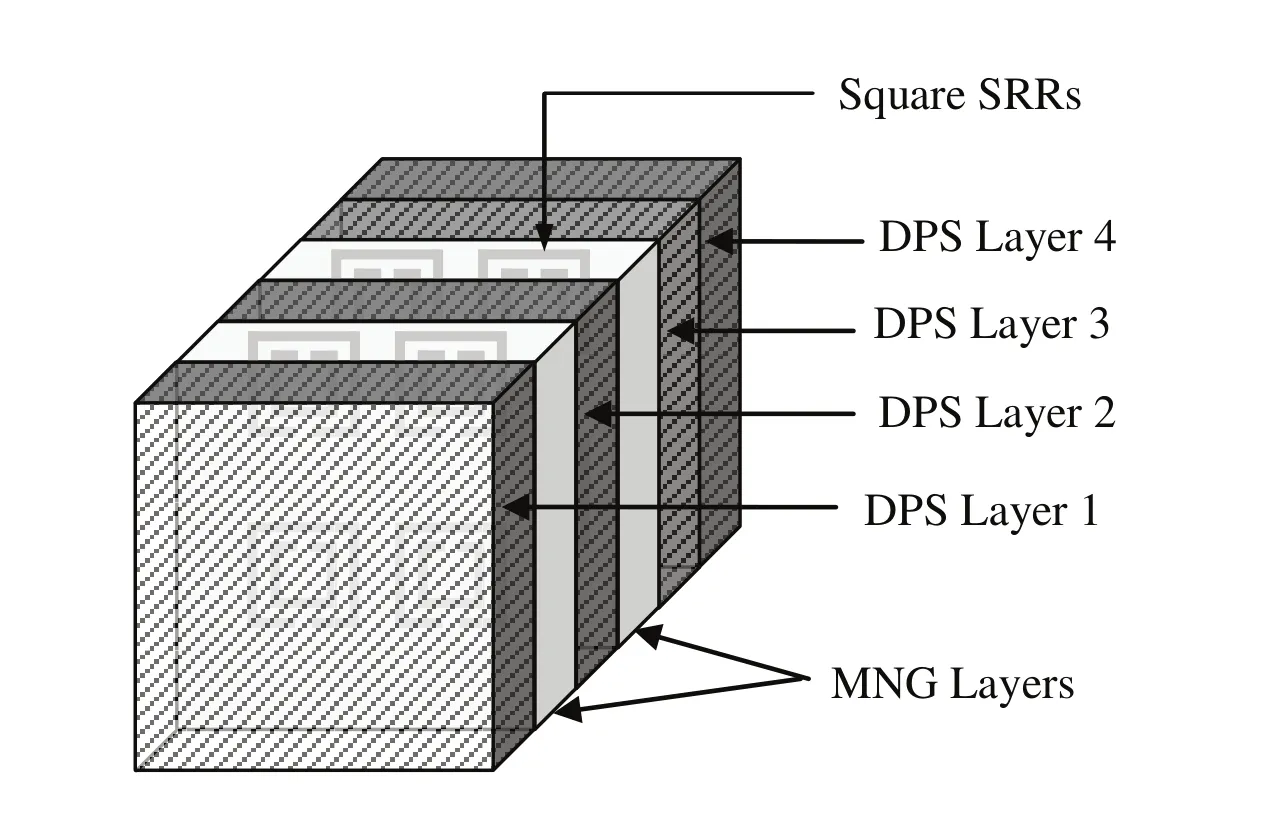
Figure 2:Schematic of dual-resonant MTM-RAS structure
In the present work,a six-layered metamaterial-RAS structure is considered(Fig.2),which consists of cascaded DPS and MNG layers.Both MNG layers of the proposed MTM-RAS are identical in terms of thickness and dielectric properties,and each MNG layer consists of square shaped split ring resonator withεr=1.15.The design parameters of square SRR are optimized to be periodicity,p=2.0 mm,side length of the square,a=1.4 mm,separation between the rings,d=0.034899µm,and thickness of the ring,w=0.09 mm.The proposed MTM-RAS has four lossy DPS layers,where DPS layers 1 and 2 are identical in terms of thickness and dielectric properties.
The thickness of DPS layer 3 and 4 is considered to beλ/4 andλ/2,respectively that act as the resistive sheet for the proposed MTM-RAS structure.The details of the layers of proposed metamaterial-RAS with optimized thicknesses are given in Table 1.
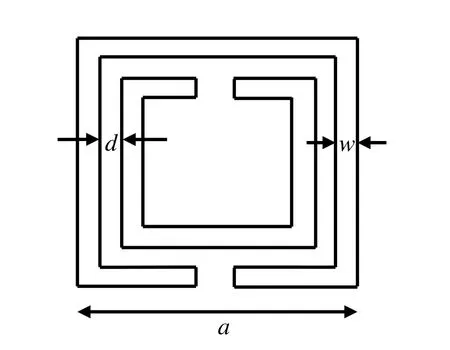
Figure 3:Schematic of a unit cell of square split ring resonator(SSRR)

Figure 4:Lumped equivalent circuit model of square SRR
The schematic of a unit cell of square split ring resonator is shown in Figure 3.It consists of two concentric square shaped rings with gap in between them on opposite side of each ring.Here,arepresents the side length of the outer square ring,wdenotes the width of the square loop,anddis the distance between the rings.When magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the ring,the ring begins to conduct and leads to current flow.The current flowing through the rings will enable it to acts as an inductor and the dielectric gap(d)between the rings will lead to mutual capacitance[Vidyalakshmi and Raghavan(2010)].Hence the equivalent circuit of the SSRR will be a parallelLCresonant circuit(Fig.4).The magnetic resonance of square SRR can be determined by equivalent lumpedLCresonant circuit(Fig.4).The resonant frequency ofLCresonant circuit is calculated by

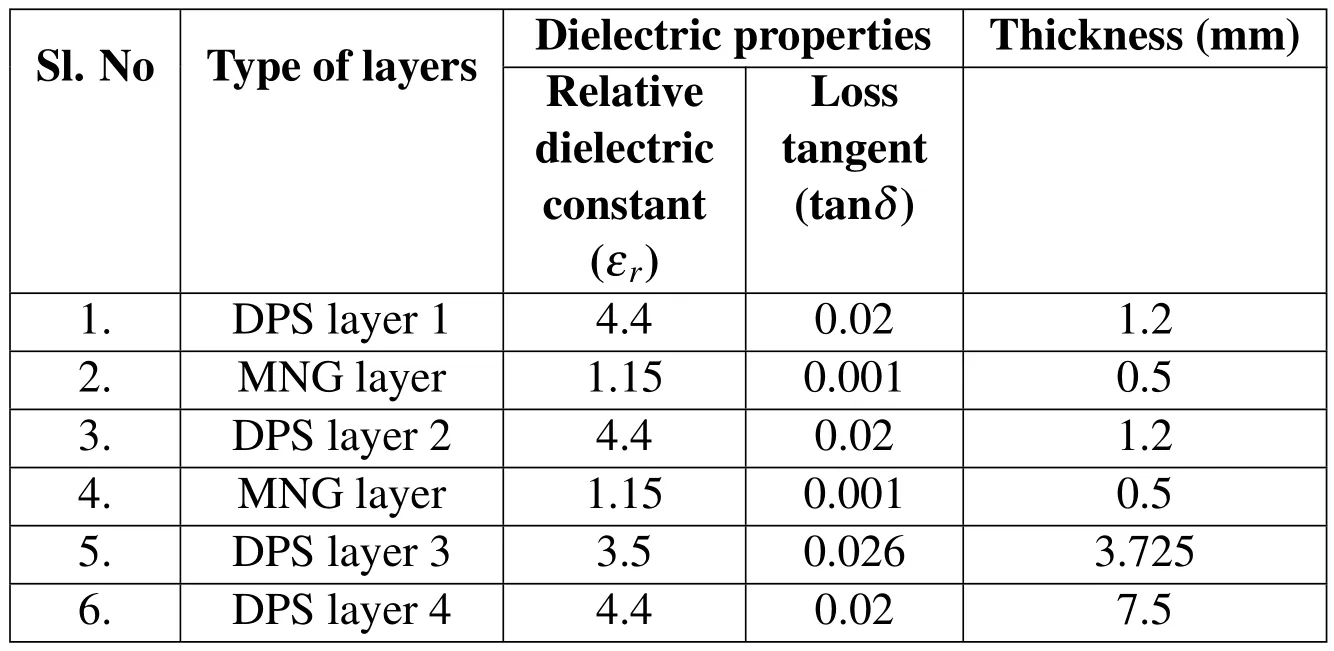
Table 1:Designed details of layers of dual-band metamaterial-RAS structure
where,Csrepresents the equivalent capacitance andLis the effective inductance due to both square rings.
The magnetic plasma frequency of the structure is given as

whereF=4(a/p)2is the fractional volume occupied by the unit cell.Hereprepresents the periodicity of SSRR unit cell.
The expressions for effective inductance ofLCresonant circuit is given by Vidyalak shmi and Raghavan(2010)
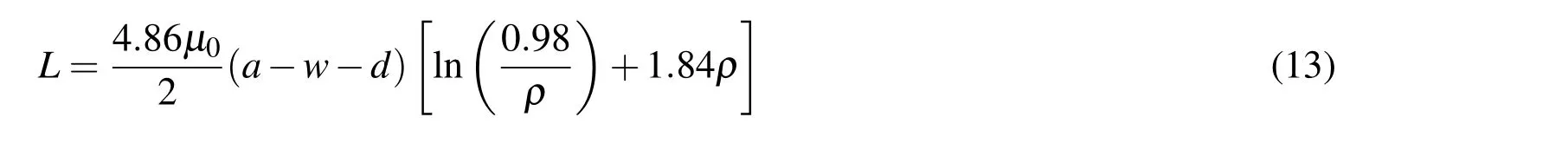
where,ρis the filling factor of inductance and is given as

The effective capacitance ofLCresonant circuit is expressed by

where,Cpulrepresents the capacitance per unit length between the rings and is given by


andK(k)denotes thecomplete elliptical integralof the first kind.
Using the above expressions,the magnetic resonance frequency and plasma resonance frequency of the square SRR can be determined.
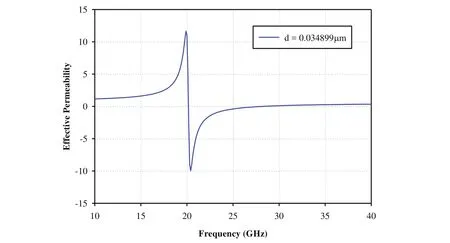
The effective permeability of square SRR is computed using equation(10).The frequency response of effective permeability of SRR is shown in Figure 5.It is observed that the proposed SRR resonates at 20 GHz and beyond this frequency,it exhibits negative permeability.The magnetic resonant frequency and magnetic plasma frequency of the square split ring resonator are computed by equations(11)and(12),respectively.Here,the square split ring resonator is designed for the magnetic resonant frequencyf0m=20 GHz,magnetic plasma frequencyfmp=28.22 GHz,and magnetic damping factor Γm=0.45473 GHz.
The optimized thickness of each layer of the proposed metamaterial-RAS is given in Table 1.The total thickness of the proposed MTM-RAS is found to be 14.625 mm at the operating wavelength(λ)of 14.9 mm.In order to achieve dual-resonant characteristics,the thickness of the DPS layer 3 and 4 are considered to be 7.5 mm(λ/4)and 3.725 mm(λ/2),respectively that acts as the resistive layer.The dualresonant characteristics are obtained by the optimization of thicknesses of MNG layers and DPS layers.
4 EM Performance Analysis
In the present paper,the EM performance analysis of metamaterial based RAS for dual-band characteristics has been carried out for both TE and TM polarizations based on TLTM method.The reflection characteristics of proposed metamaterial-RAS are investigated at normal as well higher incidence angles(30°and 45°)for both TE and TM polarizations as shown in Figure 6 and 7.It is observed that the proposed MTM-RAS exhibits dual-band characteristics at centre frequencies 120 GHz and 175 GHz.It shows less than 6%power reflection over the frequency range of 112.5-130 GHz at first resonance and less than 5%power reflection over the frequency range of 166-184 GHz at second resonance for both polarizations.Further,the absorption characteristics are studied at different incident angles(0°,30°,and 45°)for TE and TM polarizations(Figures 8 and 9).It is observed that the proposed metamaterial-RAS exhibits dual-resonant absorption at frequencies 120 GHz and 175 GHz with excellent power absorption for both polarizations.Moreover,it absorbs more than 90%power of incidence wave over the frequency range of 111-131 GHz at first resonance and from 164.5-185 GHz at second resonancew.r.t.incident angles 0°,30°,and 45°for TE and TM polarizations.
The transmission characteristics of the proposed structure are also studied at different incident angles(0°,30°,and 45°)for TE and TM polarizations as shown in Figures 10 and 11.It is observed that the power transmission through the MTMRAS is extremely low(<1.6%)over the frequency of interest corresponding to first and second resonant frequencies.Thus the proposed MTM-RAS exhibitsdual-band characteristics in millimeter wave frequency regime with wide bandwidth and excellent absorption at the resonances.
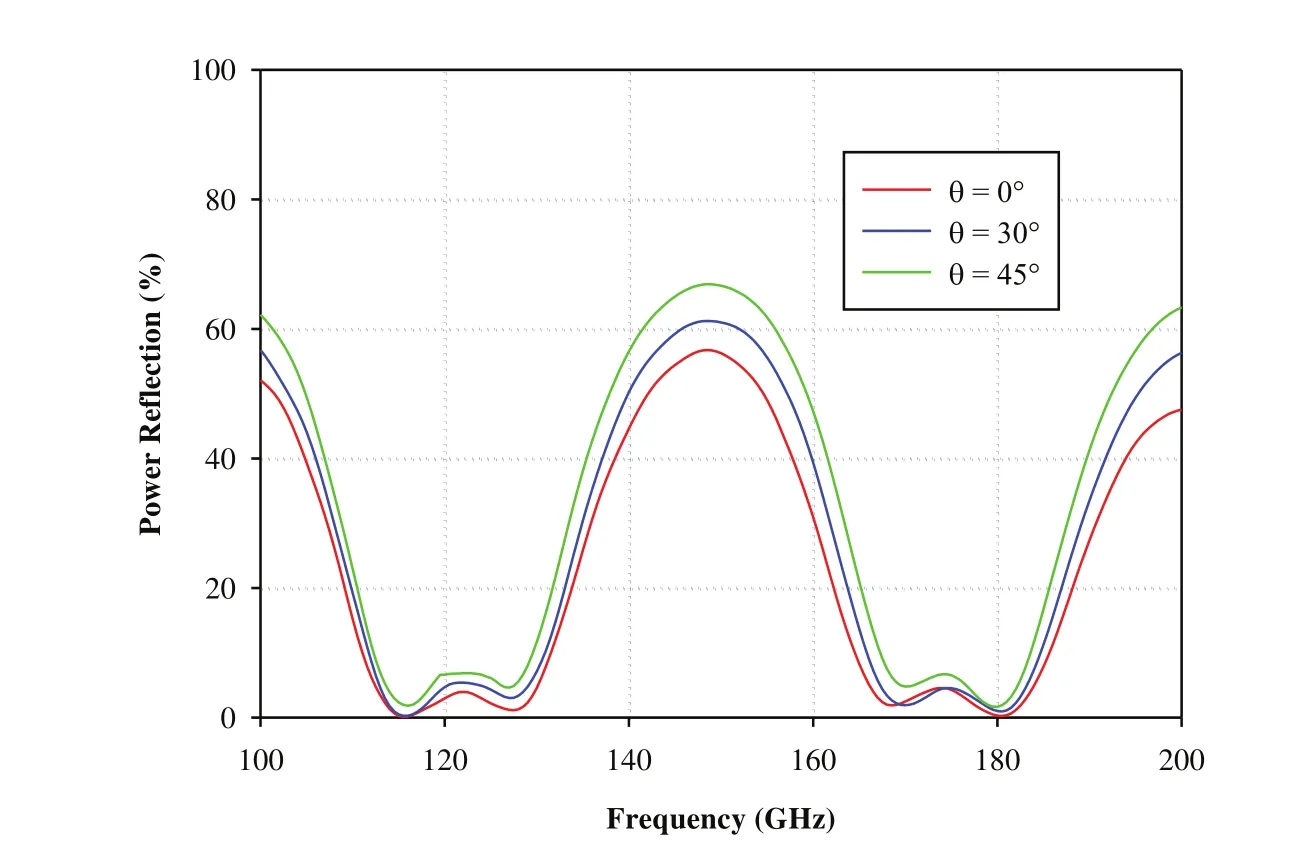
Figure 6:Power reflection characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TE polarization at different incident angles(0°,30°,and 45°)
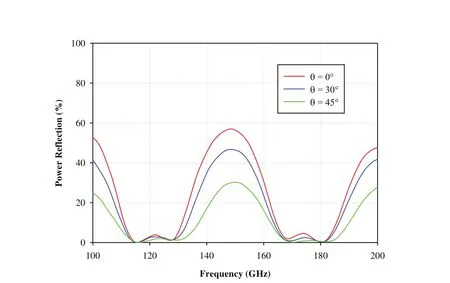
Figure 7:Power reflection characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TM polarization at different incident angles(0°,30°,and 45°)
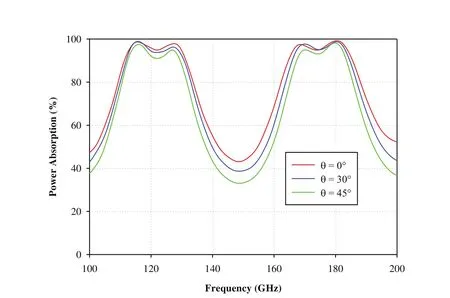
Figure 8:Power absorption characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TE polarization at different incident angles
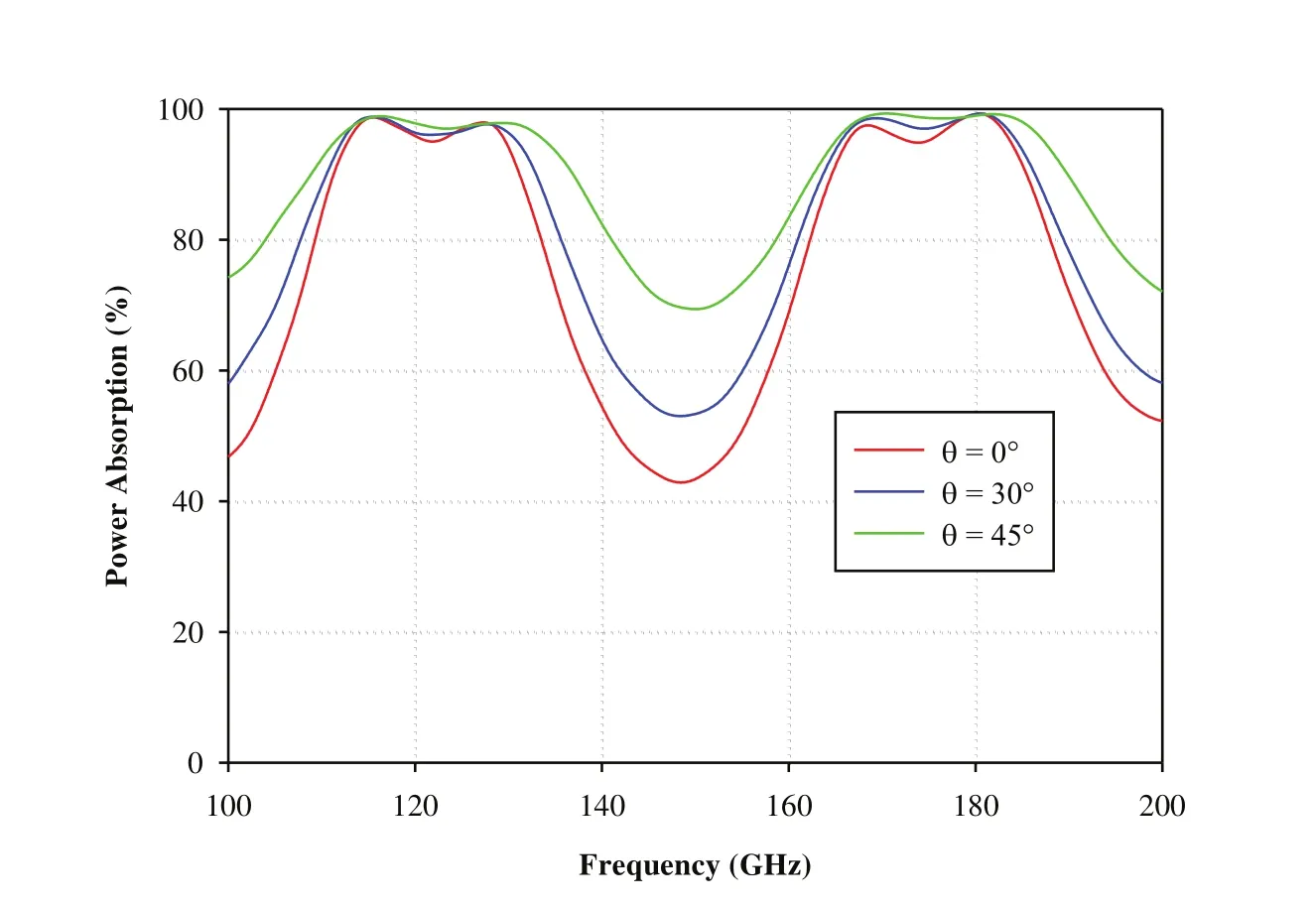
Figure 9:Power absorption characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TM polarization at different incident angles
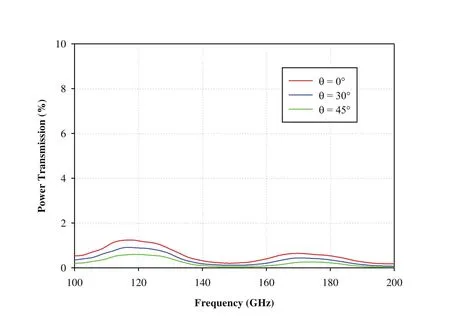
Figure 10:Power transmission characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TE polarization at different incident angles
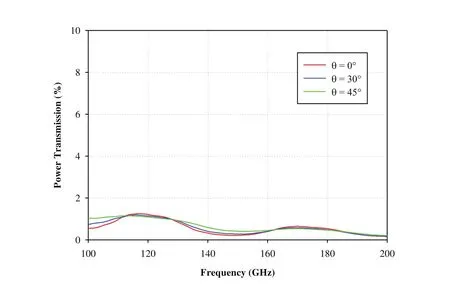
Figure 11:Power transmission characteristics of dual-band MTM-RAS for TM polarization at different incident angles
5 Conclusions
The EM analysis of a polarization independent dual-band metamaterial based radar absorbing structure(RAS)has been carried out in this paper using transmission line transfer matrix method.The proposed metamaterial-based RAS showed very low reflection at both resonant frequencies and excellent absorption(>90%)over the frequency range of 111-131 GHz at first resonance and from 164.5-185 GHz at second resonance for TE and TM polarizations without metal backing plate.It also showed very low(<1.6%)transmission over the frequency of interest for both TE and TM polarizations.Thus the proposed metamaterial-RAS find potential applications in millimeter wave frequency regime such as(i)RCS reduction of airborne platforms,(ii)Energy absorption for imaging,and chemical and biological sensing,(iii)EMI shielding in multi-band wireless communication systems to control multi-band EM radiation.
Chen,L.F.;Ong,C.K.;Neo,C.P.;Vardan,V.V.;Vardan,V.K.(2004):Microwave Electronics:Measurement and Material Characterization.John Wiley&Sons,UK,ISBN:0-470-84492-2.
Choudhury,B.;Bisoyi,S.;Jha,R.M.(2012):Emerging trends in soft computing techniques for metamaterial design and optimization.Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.31,pp.201-228.
Fante,R.L.;McCormack,M.T.(1988):Reflection properties of Salisbury screen.IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,vol.36,pp.1443-1454.
Hatakeyama,K.;Inui,T.(1984):Electromagnetic wave absorber using ferrite absorbing material dispersed with short metal fibers.IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,vol.MAG-20,pp.1261-1263.
Knott,E.F.;Lunden,C.D.(1995):The two-sheet capacitive Jaumann absorber.IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,vol.43,pp.1339-1343.
Lee,H.-M.;Lee,H.-S.(2012):A dual-band metamaterial absorber based with resonant-magnetic structures.Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters,vol.33,pp.1-12.
Narayan,S.;Latha,S.;Jha,R.M.(2013):EM analysis of metamaterial based radar absorbing structure(RAS)for millimetre wave applications.Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.34,no.2,pp.131-142.
Narayan,S.;Shamala,J.B.;Nair,R.U.;Jha,R.M.(2012):Electromagnetic performance analysis of novel multiband metamaterial FSS for millimeter wave radome applications.Computers,Materials&Continua,vol.31,pp.1-16.
Oraizi,H.;Abdolali,A.(2008):Design and optimization of planar multilayer antireflection metamaterial coatings at Ku band under circularly polarized oblique plane wave incidence.Progress In Electromagnetics Research C,vol.3,pp.1-18.
Oraizi,H.;Afsahi,M.(2009):Design of metamaterial multilayer structure as frequency selective surfaces,”Progress In Electromagnetics Research C,vol.6,pp.115-126.
Pendry,J.B.;Holden,A.J.;Robbins,D.J.;Stewart,W.J.(1999):Magnetism from conductors,and enhanced non-linear phenomena.IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques,vol.47,pp.2075-2084.
Shen,X.;Cui,T.J.;Zhao,J.;Feng,H.Ma;Jiang,W.X.;Li,H.(2011):Polarization-independentwide-angle triple-band metamaterialabsorber.OpticsExpress,vol.199,pp.9401-9407.
Singh,P.K.;Korolev,K.A.;Afsar,M.N.;Sonkusale,S.(2011):Single and dual-band 77/95/110 GHz metamaterial absorbers on flexible polyimide substrate.Applied Physics Letters,vol.99,pp.264101-1-264101-4.
Vidyalakshmi,M.R.;Raghavan,S.(2010):Comparison of optimization techniques for square split ring resonator.International Journal of Microwave and Optical Technology,vol.5,pp.280-286.
Zhu,B.;Huang,C.;Feng,Y.;Zhao,J.;Jiang,T.(2010):Dual-band switchable metamaterial electromagnetic absorber.Progress In Electromagnetics Research B,vol.24,pp.121-129.
杂志排行
Computers Materials&Continua的其它文章
- Emerging Trends in Terahertz Metamaterial Applications
- Effective Surface Susceptibility Models for Periodic Metafilms Within the Dipole Approximation Technique
- Some Applications of Metamaterial Resonators Based on Symmetry Properties
- Characteristics of a Single I-shaped Slitted Zeroth-Order Resonance Mushroom Antenna based on Metamaterials
- Active Metamaterials for Modulation and Detection
