弹力纤维瘤的CT及MR诊断
2014-04-16姚立辉戴文静孙玲玲
姚立辉,戴文静,曾 乔,孙玲玲
(1.中国医科大学附属第四医院放射科,辽宁 沈阳 110032;2.中国医科大学附属盛京医院放射科,辽宁 沈阳 110004)
弹力纤维瘤又名背部弹力纤维瘤,是一种罕见的良性软组织肿瘤样增生性疾病,好发于肩胛下角区深部软组织,中老年女性多见[1]。现回顾性分析8例患者的弹力纤维瘤的CT及MR表现,探讨CT及MR对弹力纤维瘤的诊断价值。
1 材料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2010年6月—2013年9月在我院接受CT及MR检查并经手术病理证实的8例弹力纤维瘤患者,均为女性,年龄41~88岁,平均年龄(59.2± 6.7)岁;病史10天~5年,其中7例患者以“发现肩胛下角下方肿物”为主诉就诊,1例患者为胸部平扫时意外发现,5例患者双侧同时受累,2例位于右侧,1例位于左侧;5例患者局部疼痛不适伴上肢活动时背部异物感,3例患者无临床症状。
1.2 设备与方法
采用GE LightSpeed VCT 64排128层螺旋CT机和GE SIGNA HDe 1.5T MR。所有患者均接受胸部CT平扫,扫描范围自肺尖至肺底,其中2例于平扫后接受胸部双期增强扫描,增强扫描采用高压注射器经肘前静脉注射非离子型对比剂碘佛醇(320 mgI/mL),总量80 mL,流率3.5 mL/s,分别于注药后30 s(动脉期)和60 s(静脉期)进行扫描。扫描参数:管电压120 kV,管电流250 mA,层厚、层间距均为2.5 mm。采用软组织函数重组。1例患者接受MR扫描;扫描范围上方达胸廓上口,下缘至肋弓水平;行轴位、冠状位及矢状位成像。扫描参数:轴位T1:TR 520.00,TE 8.88,TI 0.00;轴位T2:TR 2840.00,TE 86.26,TI 0.00;轴位 STIR:TR 4 820.00,TE 69.44,TI 150.00;冠状位T1:TR 660.00,TE 8.89,TI 0.00;冠状位 STIR:TR 4 600.00,TE 71.87,TI 150.00。
1.3 图像分析
所有图像均由2位(或2位以上)高年资医师采用盲法分析,记录病变部位、形态、内部特征及强化方式,如果存在异议,最终经协商达成一致。
1.4 手术及病理
所有患者均进行肿瘤切除术。将标本固定,石蜡包埋,4 μm层厚切片,HE染色,光镜观察切片。
2 结果
2.1 CT及MR检查结果
CT平扫8例患者共13个肿块均位于背部肩胛下区内侧前锯肌及背阔肌深层,呈扁丘状,基底位于胸膜侧,于肋骨骨膜及肋间韧带分界不清;双侧5例,右侧2例,左侧1例(图1a);其中2例患者共4个病灶进行双期增强扫描,4个病灶均未见确切强化(图2、3);1例患者1个病灶行MR平扫,显示病灶位于左背部前锯肌内侧梭形肿块,以等T1等T2信号为主,其内夹杂条纹状短T1长T2信号(图1b、1c、1d),STIR序列病灶内脂肪组织高信号消失。
2.2 手术及病理结果
术中见肿块位于前锯肌、背阔肌及菱形肌深面,无包膜,其表面覆有脂肪组织,基底部与肋骨骨膜及肋间韧带粘连。肿块切面呈灰白色,间有黄色灶状颗粒;镜下可见束状排列的胶原纤维、粗大的弹力纤维、灶状的脂肪组织,可伴有少量成熟的纤维母细胞或肌纤维母细胞,间质可见到黏液样组织。

图1 为同一患者。图1a:CT平扫:左背部肩胛骨下前锯肌内侧见半圆形软组织肿物,范围约6.2 cm×2.4 cm× 6.5 cm,密度不均,主要呈肌肉密度,内见条纹状脂肪密度与肌肉密度交替排列,内缘与肋骨及肋间肌分界不清,外缘与前锯肌脂肪间隙消失,前锯肌受压向外移位。图1b~ 1d:MR轴位T1、T2及STIR序列:左背部前锯肌内侧见梭形肿块影,以等T1等T2信号为主,其内夹杂条纹状短T1长T2信号。Figure 1. Same patient.Figure 1a:plain CT:The semicircular soft tissue mass under the left scapular angle area,the extent of the mass about 6.2 cm×2.4 cm× 6.5 cm,mass were flat mound-like or semi-circular in shape,mainly were muscular-like density.The inner edge had no clear boundary between adjacent ribs and intercostal muscle,fat gap disappears between the mass and serratus anterior muscle,serratus anterior was displaced outward.Figure 1b~1d:MRI axial T1,T2and STIR sequences:The fusiform mass inside serratus anterior in left back,with isointense T1and isointense T2signal mixed with stripes of fat which had hyperintense T1and hyperintense T2signal.


图3 为同一患者,双侧肩胛骨下角区前锯肌及背阔肌内侧见软组织密度影,内夹杂条纹状低密度区,右侧呈半圆形,左侧呈丘状,右侧范围约为6.3 cm×3.4 cm×6.5 cm,左侧范围约为6.3 cm×1.7 cm×4.5 cm,内缘不清,外缘与前锯肌及背阔肌脂肪间隙存在,增强扫描肿块未见强化。Figure 3. Same patient with bilateral soft tissue lesion under the latissimus dorsi muscle and serratus anterior muscle and the inferior angle of scapula,there were striated low-density areas within the inclusions.The size of right semicircular mass was about 6.3 cm×3.4 cm×6.5 cm.The size of the left maundy mass was about 6.3 cm×1.7 cm×4.5 cm.Their inner edge were unclear.The fat gap between the mass and the latissimus dorsi and serratus anterior muscle existed.Lesions showed no enhancement on enhanced scan.
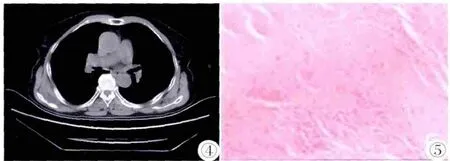
图4 双侧肩胛骨下方前锯肌内侧见丘状软组织影,其内夹杂条纹状低密度区,右侧范围约为5.4 cm×2.3 cm× 4.5 cm,左侧范围约为2.8 cm×2.0 cm×3.0 cm,与周围软组织分界欠清。 图5 病理:光镜下大量粉染胶原纤维,其内有梭形细胞弥漫分布,未见病理核分裂,其内有红染小球状结构,串珠或波浪状分布。病理诊断:弹力纤维瘤。Figure 4. The bilateral moundy soft tissue lesions under the serratus anterior muscle and the inferior angle of scapula,the striated low-density areas within the inclusions.The right mass size was of about 5.4 cm ×2.3 cm×4.5 cm,the extent of left side was about 2.8 cm×2.0 cm×3.0 cm.They had no clear boundary with surrounding soft tissues. Figure 5. Pathology:A lot of pink dyed collagen fibers under light microscope,with diffuse distribution of spindle cells,no aryokinesis.There were small red stained spherical structures,beaded or wave-like in distribution.Pathological diagnosis:EFD.
3 讨论
弹力纤维瘤是一种罕见的软组织肿瘤样病变。由Jarvi和Saxen于1961年首次报道并命名。据统计,约93%的弹力纤维瘤发生于肩胛骨下方,位于前锯肌、背阔肌及菱形肌的深面,多与肋骨骨膜及肋间韧带粘连。该病也可发生于其他部位,如股骨大粗隆、三角肌、坐骨结节、乳腺、胸壁侧方、足踝部、腋窝、心脏三尖瓣、胃、腹股沟区、椎管内、口腔黏膜、眼眶、肩关节内、乙状结肠等[2-3,7-14]。虽然在世界卫生组织软组织肿瘤分类标准(2002)中,将弹力纤维瘤归类为良性的成纤维细胞/肌成纤维细胞肿瘤,但弹力纤维瘤究竟是一种真性肿瘤还是反应性纤维组织增生性病变仍有争议。多数学者认为本病由肩胛骨下角和胸壁之间的慢性损伤和机械摩擦引起,是异常弹性组织发生的反应性肿瘤样增生,而并非真性肿瘤[4-5],而有学者用细胞遗传学分析发现2例患者的染色体克隆异常,表明弹力纤维瘤可能为肿瘤源性而不是反应性过程[6]。
弹力纤维瘤好发于中老年女性,双侧多见[5,21]。本组患者年龄41~88岁,均为中老年女性,多为双侧发病,与文献报道基本一致。本病大多数患者无不适,罕见症状包括肩胛骨周围疼痛和不适,肩部活动时撞击感或活动受限[15]。
弹力纤维瘤的大体病理多呈扁圆形,无真正的包膜,边界不清,可延伸至周围肋骨骨膜和胸筋膜内,剖面呈灰白淡黄相间,可有灶状囊性变;镜下可见束状排列的胶原纤维、粗大弹力纤维和灶状脂肪组织,可伴有少量成熟的纤维母细胞或肌纤维母细胞;VG染色后,深紫色束状排列的弹力纤维边缘呈锯齿状[4-5,16-17]。
CT及MR对弹力纤维瘤的术前诊断有较高的价值。CT空间分辨力高,可明确病灶的部位和范围。MRI具有较高的组织分辨力,能分辨病变内的纤维组织及脂肪成分。典型弹力纤维瘤病变位于肩胛下角区内侧前锯肌、背阔肌及菱形肌深层,肋骨及肋间肌外侧,常覆盖第6~8肋区域胸壁;肿块周围肌肉呈弧形受压外移,两者间有或无脂肪间隙,邻近组织无受侵征象。弹力纤维瘤的临床及影像学表现较具特征性,结合临床及影像学(CT及MR)表现多可确诊,从而使无症状患者免于活检或手术[18-20]。不典型的弹力纤维瘤需于血管瘤、硬纤维瘤、滑膜囊肿和恶性纤维组织细胞瘤等进行鉴别。血管瘤CT表现为不均质中等密度软组织肿块,内可见脂肪密度影,其形态不规则,范围较大,常侵及胸壁肌层和肋间组织,典型者内可见静脉石,增强扫描明显强化;MR表现为以长T1长T2信号为主的混杂信号,增强扫描呈明显强化。硬纤维瘤可发生于全身各处,多见于腹壁,亦可发生于肩胛区骨骼肌内,CT平扫表现为骨骼肌样软组织影,形态不规则,浸润生长或呈结节状,局部边界不清,可直接侵犯肌肉和邻近骨质,增强后病变明显强化;MR平扫T1WI呈等信号或稍高信号,T2WI呈高信号,增强扫描病变明显强化。含蛋白或粘液较多的滑膜囊肿CT平扫呈软组织密度,边界清晰,增强扫描无强化;MR平扫T1WI呈等信号,T2WI呈高信号,增强扫描无强化。恶性纤维组织细胞瘤CT平扫密度不均,多见坏死,边界不清,增强扫描呈明显不均匀强化;MR平扫T2WI多呈高信号,增强扫描呈不均匀明显强化。确诊主要依靠病理。
综上所述,弹力纤维瘤的临床及影像学(CT及MR)表现具有一定的特征。中老年女性患者单侧或双侧肩胛下角区无症状性软组织肿块,应考虑弹力纤维瘤的可能[21]。CT及MR检查多能做出明确诊断,二者联合更有助于弹力纤维瘤的确诊。
[1]Fibla J,Molins L,Marco V,et al.Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi[J]. Joint Bone Spine,2007,74(2):194-196.
[2]Nagamine N,Nohara Y,Ito E,et al.Elastofibroma in Okinawa a clinicopathologic study of 170 cases[J].Cancer,1982,50(9): 1794-1805.
[3]Nishida A,Uetani M,Okimoto T,et al.Bilateral elastofibroma of the things with concomitant subscapular lesions[J].Skeletal Radiol,2003,32(2):116-118.
[4]Parratt MT,Donaldson JR,Flanagan AM,et al.Elastofibroma dorsi:Management,outcome and rewiew of the literature[J].J Bone Joint Surg Br,2010,92(2):262-266.
[5]Malghem J,Baudrez V,Lecouvet F,et al.Imaging study findings in elastofibroma dorsi[J].Joint Bone Spine,2004,71(6):536-541.
[6]Kuroda M,Hamaguchi M,Ohara M,et al.Elastofibroma:a histochemical,immunohistochemical,and ultrastructural study of two patients[J].Med Mol Morphol,2008,41(3):179-182.
[7]Hoffman JK,Klein MH,Mclnerney VK.Bilateral elastofibroma:a case report and review of the literature[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res, 1996,325:245-250.
[8]Marin ML,Perzin KH,Markowitz AM.Elastofibroma dorsi:prevalence in an elderly patient population as revealed by CT[J].AJR, 1998,171(4):977-980.
[9]Saint-Paul MC,Musso S,Cardot-Leccia N,et al.Elastofibroma of the stomach[J].Pathol Res Pract,2003,199(9):637-639.
[10]Potter TJ,Summerlin DJ,Rodgers SF.Elastofibroma:the initial report in the oral mucosa[J].Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod,2004,97(1):64-67.
[11]Bae SJ,Shin MJ,Kim SM,et al.Intra-articular elastofibroma of the shoulder joint[J].Skeletal Radiol,2002,31(3):171-174.
[12]McPherson FC,Norman LS,Truitt CA,et al.Elastofibroma of the foot:uncommon presentation:a case report and review of the literature[J].Foot Ankle Int,2000,21(9):775-777.
[13]Maldjian C,Adam RJ,Madjian JA,et al.Elastofibroma of the neck[J].Skeletal Radiol,2000,29(2):109-111.
[14]Sakatani T,Shomori K,Adachi H,et al.Elastofibroma of the sigmoid colon[J].Pathol Res Pract,2000,196(3):205-207.
[15]Ahmed MA,Subramanian SK,Al-Hashimi I,et al.Bilateral elastofibroma dorsi[J].Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J,2011,11(3): 415-416.
[16]Hayes AJ,Alexander N,Clark MA,et al.Elastofibroma:A rare soft tissue tumour with a pathognomonic anatomical location and clinical symptom[J].Eur J Surg Oncol,2004,30(4):450-453.
[17]Mccomb EN,Freely MG,Neff JR,et al.Cytogenetic in stability, predominantly involving chromosome 1,is characteristic of elastofibroma[J].Cancer Genet Cytogenet,2001,126(1):68-72.
[18]Alouini R,Allani M,Harzallah L,et al.Elastofibroma:Imaging features[J].J Radiol,2005,86(11):1712-1715.
[19]Mortman KD,Hochheiser GM,Giblin EM,et al.Elastofibroma dorsi:Clinicopathologic review of 6 cases[J].Ann Thorac Surg, 2007,83(5):1894-1897.
[20]Daigeler A,Vogt PM,Busch K,et al.Elastofibroma dorsi—differential diagnosis in chest wall tumours[J].World J Surg Oncol, 2007,5:15.
[21]丁长伟,刘鹏,张军,等.CT诊断背部弹力纤维瘤[J].中国医学影像技术,2012,28(6):1195-1198.
