On the Transm ission Mechanism of the Chinese Land Policy in Macroeconom ic-control:A Theoretical Study Based on Modified IS-LMModel
2014-04-10LinlinDIAOJinmingYAN
Linlin DIAO ,Jinm ing YAN
1.Economics Department,Beijing Administrative College,Beijing 100044,China;2.The Research Center for Land Planning,Renmin University of China,Beijing 100872,China
The modern land policy is not merely used to guide the rational use of land resources,and it plays an important role in the entire development planning and framework of development policies in a country or region[1].The traditional macroeconomic-control is to mainly use fiscal policies,monetary policies and other macro-policy instruments,to indirectly affect the choices ofmicroscopic subject,abate the fluctuations in the economy and ensure stable economic growth.With the change in government's regulation policies from demand management to supply adjustment,the central government explicitly brought forward the idea of adjusting the allocation of land resources to regulate the macroeconomic conditions in 2004.The land's participation in macroeconomic-control is mainly for the land supply arising from non-agricultural construction and the land demand of non-agricultural products.
1 Research progress and literature review
In the mainstream western macroeconomic-control theory,land policy has never been regarded as the fundamental policy tool as the monetary policies and fiscal policies,but it lacks no evaluation and analysis of economic utility and policy functions of land policy abroad,and a lot of controversies are concentrated in judging whether the role of land as basic factor of production for the economic growth of a country or region is positive[2]or negative[3-5].The intensity and direction of role of land policy is different in different countries with different context of economy and institution.The role of land resource consumption in promoting the level of economic activity also enters a bottleneck.But some scholars have pointed out that despite the great contribution of land element in less-developed countries and regions to economic growth,when it is faced with special policy and institutional environment,land extern ality during the process of urbanization,stability and efficiency loss of land market and other issues,the government's land intervention policies are difficult to avoid the social,ecological and environmental problems while regulating the economy[6-8].Therefore,more researches focus on the role of land policy in controlling urban sprawl,protecting agricultural land and promoting social wealth fairness.Since 1993,the domestic studies on the involvement of land policy in macroeconomic-control have produced a lot of literature.During 1993-1996,the studies on the involvement of land policy in macroeconomic-control paidmore attention to the exploration of concept,institutional base,measures,means and policy recommendations[9-10],and the effect of land policy regulation on macroeconomic development was hotly debated[11-13].During 1996-2003,Cai Yunpeng and Liu Jian(2001)studied the role of land reserve system in macroeconomic-control[14].Since 2003,the focus of studies has been placed on the supporting policies, practice effects, operating specifications, system design[15-16],and the mechanism of land policy's participation in macroeconomic-control.During this period,some scholars use the econometric means to assess the effect of land's participation in macroeconomic-control,and there are three main methods.(i)Feng Lei(2008, 2009)[17-18], Mao Zhenjiang (2007,2009)[19-20]measure the contribution of land element to economic growth using the spread Cobb-Dauglas production function.(ii)Yang Zhirong et al.(2008)[21]use time series model to measure the dynamic relationship between land supply and the main macroeconomic variables.(iii)Wu Kangping(2009)[22]and Song Hongmei(2009)[23]introduce land element in the IS-LMmodel to analyze the impact of land policy on economic aggregate,and use policy multiplier to evaluate the policy effect.There have been mature studies on the first two models,but it is difficult to reveal the mechanism of interaction between land policy and other regulation policies;the study method son the third model are simple,and the basic theoretical research and system construction remain to be further deepened.
2 Contentious issues
Notice of the State Council on Strengthening Land Regulation issued in 2004 clearly elevates the polices of strictly controlling new construction land and adjusting tax concerning construction land to the level of land regulation policy.It gives birth to some contentious issues posing challenges to the traditional economics at the theoretical level.(i)Variable mechanism issue.The macroeconomic-control is a short-term goal for the economy,and the short term equilibrium characteristics of the land market provide a premise for the effectiveness of land's involvement in macroeconomiccontrol,but there is"level deviation"between controlmeans and control objectives,that is,the policy implications are not consistent in the influence of adjusting land quantity,price,transfer quota[24]and other microscopic variables on total output,interest rate,monetary demand and other macroeconomic variables[25],as well as the direction and degree of influence.(ii)Model building issue.The traditional production function and the theory of economic growth do not contain land element,while the mainstream economics analysts believe that the land itself can be replaced by capital,labor and other factors of production or technological advances,and land supply is not essential for economic growth.In the regulated market mechanisms,it is an important issue about how to introduce land variable in traditional macroeconomic model to build a macroeconomic variable model affected by land and other factors,to achieve the combination of land policy,fiscal policy,and monetary supply policy[26].This article will study for these two issues,and include land element in the overall framework of national production to modify traditional IS-LMmodel.
3 Modification of IS-LMmodel
The IS-LMmodel(Investment Saving-Liquidity Preference Money Supply)is a macroeconomic tool that demonstrates the relationship between interest rates and real output,in the goods and services market and the money market.This tool is sometimesused not only to analyze the fluctuations of the economy but also to find appropriate stabilization policies.
3.1 Analysis of rationality of introducing land element in IS-LMmodel Regulation of land is divided into total supply regulation,structural regulation and control of land access conditions[27].The land policy in this article mainly refers to land supply policy namely total control.The analysis of the influence of land variable changes on allocation of capital between total supply and total demand to establish links bet ween land element and macroeconomic variables,is the starting point for the theoretical analysis of land policy's involvement in macroeconomic-control.There are four reasons.(i)The improved model emphasizes the association among land market,monetary market and product market,with the total variable as research subject.(ii)In traditional ISLMmodel,both total supply and total demand are expressed in monetary form,and the monetary capital is the medium for the linkage between land variable and supply and demand variable.(iii)In traditional IS-LMmodel,the supply adjust menthas a lag,and the institutional arrangement of middle-term or long-term planning of land supply is in line with the characteristics.(iv)China's economic growth is the input-based growthmode driven by capital and land.The micro-economic body is highly dependent on the double factor inputs,and less sensitive to changes in interest rates.The impact of land on investment should beman if est.
3.2 Analysis of total supply and total demand framework including land elementTo describe the role of the land element in the overall framework of national production,land is introduced in the total supply and total demand function of three-sector economy[28],we comply with the following hypotheses:(i)All investments and consumer spending concerning land can not be reused in the short term;(ii)Under certain technical level,there is incomplete replacement between assets,and there is a difference among land assets,financial assets and physical capital,characterized by different response of various capital needs to interest rate and the influence of capital factor substitution on the elasticity of original investment structure to interest rate;(iii)The land element has effects on marginal propensity to consume and elasticity of investment to interest rate.
3.2.1 Total demand including land element.The land demand is a part of consumption,investment and government purchase.The consumption(C)is divided into land consumption(CL)and non-land consumption(CNL);the investment(I)is divided into land investment(IL)and non-land investment(INL);the government purchase(G)is divided into government land purchase)and non-government land purchaseThe total demand equation including land element is as follows:
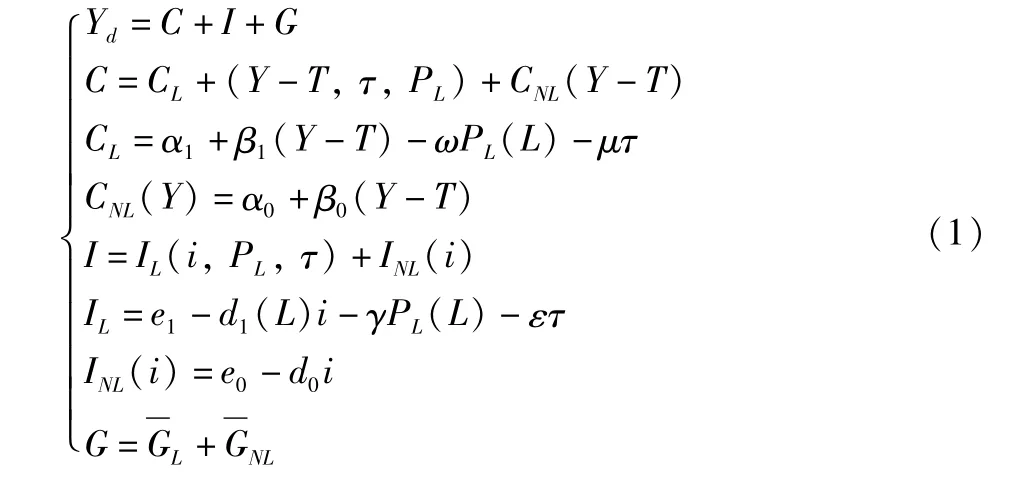
In Equation(1),Y,i,Trepresent the equilibrium yield level,interest rate level and total tax revenue,respectively;nonland consumption(CNL)is the function of total yield(Y),and non-land investment(INL)is determined by interest rates level(i);αi(i=0,1)is the spontaneous consumption part,βi(i=0,1)is the marginal propensity to consume,ei(i=0,1)is spontaneous investment spending,anddi(i=0,1)is the elasticity of investment to interest rate,0<βi,di≤1;land consumer demand(CL)and investment demand(IL)are not only determined by total yield and interest rates,respectively,but also determined by land price and tax rate;the control variablesPLandτare land price and land tax rate,respectively,and land price is the function of supply volume(L);ω,μ(γ,ε)are the elasticity of land consumption(investment)to land price and land tax rate,respectively;government purchase(G)hinges on the government budget and fiscal spending policies,assumed as exogenous variable.The demand equation(Equation 1)has a practice basis in the actual economic life.(i)Land demand is the derived demand,mainly affected by total yield,land price,tax rate and lending rates.(ii)As shown in Fig.1,land supply has particularity,and since government plays a direct role in determining the supply in the land market,before reaching the supply and demand equilibrium point(LE),the land supply is less than demand(L′S<L′D).In the area whereL<L0(L0as the lowestpoint),due to the existence of economies of scale in the land market,the supply curve is a curve sloping downward to the right(∂PL/∂L<0).Once the large-scale land development is carried out,the costs will be rapidly reduced.When supply exceeds demand(L0<L<),it follows the general law of supply[29],∂PL/∂L>0;China now is in the economic growth transitional period,land supply"bottleneck"and inefficient land development issues coexist,and the land market as a whole is in the area whereL0<LE,which will inevitably lead to the realization of high-priced land deals.(iii)When all other conditions remain unchanged,if the land price is higher,the cost of same amount of land obtained will be higher,and the consumption and investment of land will be accordingly decrease,so the land price is negatively correlated with land demand(YdL),and the land supply is thus positively correlated with land demand.The increase in land supply can stimulate land-related consumption and investment demand(Equation 2,3).(iv)The production function can be used to analyze the macroeconomic growth factors atmacro-level.On the one hand,the amount of land input affects the investment efficiency;on the other hand,with the increase in land supply,the elasticity of investment to interest rate will weaken[d1(L)≤d0],and the greater the land supply,the lower the sensitivity of investment to the interest rate[∂d1(L)/∂L<0],so the land supply weakens the regulation of fiscal policies.(v)The higher the land tax rate,the higher the cost of obtaining and retaining land,the smaller the land consumer demand and investment demand,so the land tax rate is negatively correlated with land demand.(vi)In addition,the loan interest rate directly affects the land financing costs,and also has a negative impact on land investment.
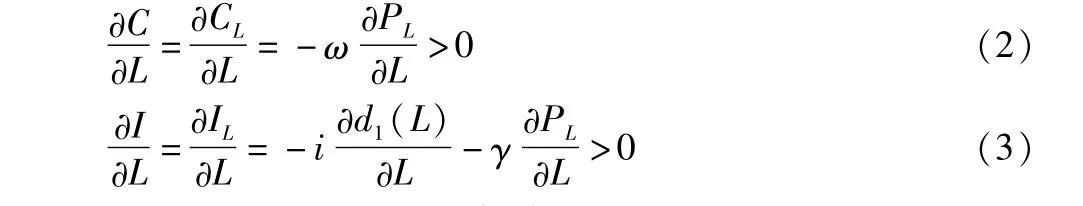
The total demand level(Yd)is eventually determined by interest rates,total tax,government purchase,land supply and land tax rate,expressed as:
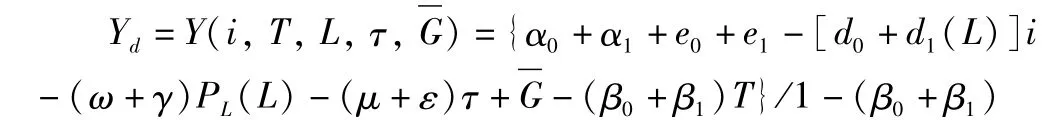
Through the foregoing analysis,it is found that the government affects the total demand by monetary policy,fiscal policy,land supply policy and land tax policy.
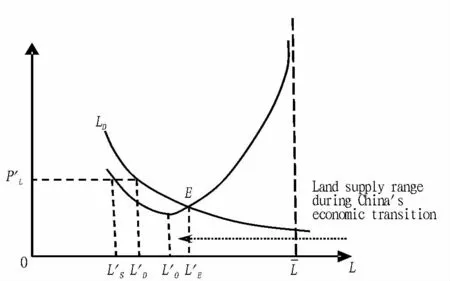
Fig.1 The equilibrium of supply and demand in land market of China
3.2.2 Total supply including land element.In the total supply equation of national income,the tax(T)is divided into land tax(TL)and non-land tax(TNL).tis the non-land tax ratio,and non-land tax is the function of equilibrium yield(Y).The land tax is related to total trading volume of land(product of land supply and priceL·P)and land tax rate(τ).It be deduced:
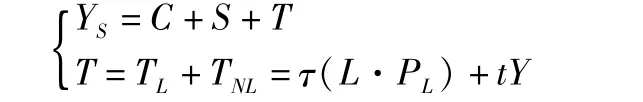
In the total supply equation,we simplify the tax expression,and use the form of proportional tax to simulate land tax and nonl and tax.
3.2.3 Discussion on modification of IS curve and land policy effect.The determination of equilibrium income in three-sector economy is as follows:

Then there is:
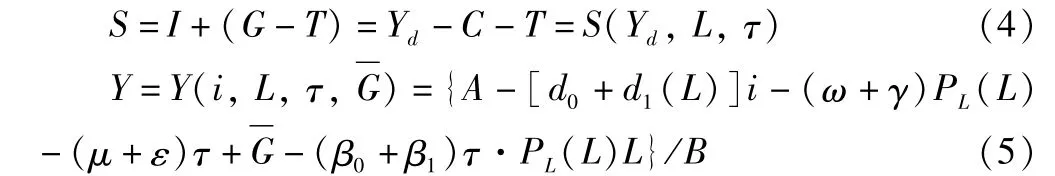
whereA=α0+α1+e0+e1,B=1+(1-t)(β0+β1).
Under equilibrium conditions,the national savings(S)is the expression of total demand,land supply and land tax rate(Equation 4).When the land element is not included,the national savings are only determined by total yield.The final determination of equilibrium yield is Equation 5,which is also the expression of IS curve modified by land element.This expression corresponds to the level of total yield under any given interest ratei,fiscal policy,land supplyLand land tax rateτ.Calculating the first-order partial derivatives of Equation 5 to land tax rate and land supply,respectively:

According to the above relationship,the land tax rate has a negative effecton economic output,and the tax abatement policies directly stimulate investment and consumption of private land,so the production and employmenteventually increase.Since0<t,τthe direction of regulation of land supply change on total yield depends on the price elasticity of land supplyη(η=In the land supply and demand market,the land supply has no price elasticity in the short term,but limited elasticity in the long term,so the value of supply elasticity coefficient(absolute value)is close to1 or less than 1,that is,within the range of0≤|η|≤1,it is discussed as follows:(i)If the land supply is completely inelastic,namelyη→0,there isindicating that the land regulation policies are extremely effective.(ii)When the land supply is inelastic in the supply and demand relationship,namely 0<|η|<1,it is divided into two cases.(a)If-1<η<0,in theLS<L0part of land supply curve(Fig.1),M<0,then∂Y/∂L>0.Themarginal output of land input is positive,that is,increasing the land supply can play a role in stimulating the total social demand;increasing the total yield and decreasing the land supply can inhibit the investment and consumption,thereby reducing the total demand.And∂2Y/∂L2>0,it indicates that the positive impact of land supply on total out put gradually increases,and the economymay be in expansion or recovery phase.(b)If 0<η<1,in theL0<Ls<part of land supply curve,M≥0,then∂Y/∂L<0,∂2Y/∂L2<0.The marginal output of land input is negative.Due to the law of diminishing marginal returns,the negative effects of land supply on total yield gradually increase,indicating that the economy is in transition or a recession(depression)period,and there may be excess supply of land.Continuing to increase land supply will result in a waste of resources,and exacerbate the economic downturn.Appropriately inhibiting the scale of land supply is conducive to steady growth.(iii)If the land supply has single elasticity,namely|η|=1,it is divided into two cases.(a)Ifη=-1,M=0,then∂Y/∂L=0.Regardless of changes in the supply of land,there is no effect on economic output,and it is the in efficient area of land policy.(b)Ifη=1,thenM=2PL(η=1),The degree of influence of land supply on economic output depends on the land price with supply elasticity of1.In summary,when using land policy to regulate macroeconomic operation,the government should adoptex pan sionary or austere land policy according to the price elasticity of land supply and economic stage.Fig.2 describes the effect of changes in land supply on total yield under different supply elasticity,and gives the visual analysis of effect of land regulation policies in the transitional period.Since the land supply in the transitional period is in the phase of decreasing returns to scale,the cost is greatly increased due to increase in the amount of land.Therefore,the elasticity of supply is small,and the negative effect of land supply on total yield is strong.The economic structure and industrial structure during this period are being adjusted,and the blind expansion of land development scale can easily lead to imbalance in factors of production.We should not overlook the effect of long-term control policies,because the elasticity of land supply in the long term has been proved to be greater than in the short term.
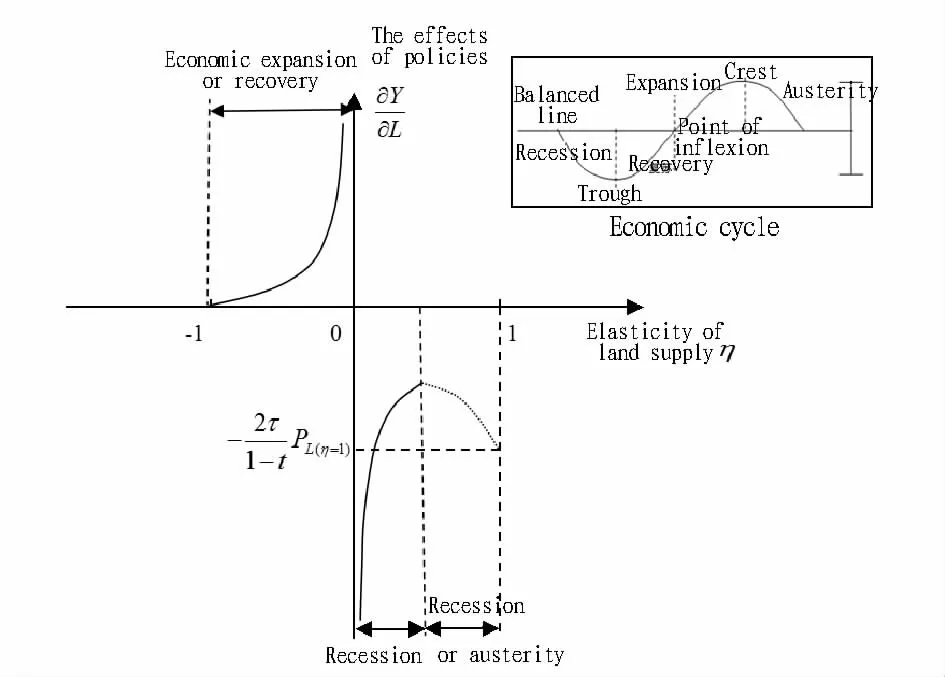
Fig.2 The corresponding relationship between effects of land policy and elasticity of land supply
3.3 Building of IS-LMmodel modified by land element and the effects of macroeconomic policies The essence of land's participation in macroeconomic-control is the influence of changes in land supply policies on land market,total demand and total supply,and tax adjustment and price adjustment are also involved.
3.3.1 Modification of traditional LMcurve.Traditional LMcurve indicates the process of monetary market equilibrium achieved by regulating demand in the case of given monetary supply.Different from the modification of product market IS curve,the land element can not directly affect various element variables of the monetary market.Assuming that monetary supply isMS.The monetary supply mainly includes trading demand and speculative demand,and when there is monetary marketequilibrium,the monetary amount of land demand isMS1,and the monetary amount of other demands isMS2,thenMS1+MS2=MS.Assuming that the changes in land element pricePLhave a small impact on the average social price levelP*,then there isP*=f(P0,PL)≈f(P0)(P0is the average price of all the other products except for land).Excluding the impact of price level,the equilibrium e-quation of monetary market containing land element is as follows:
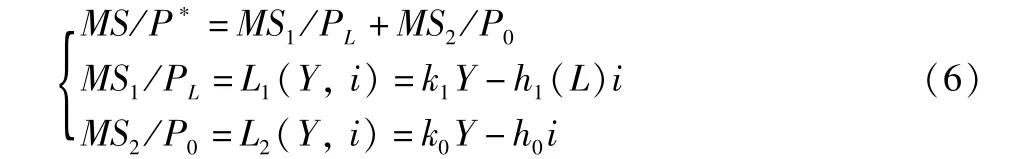
whereki(i=0,1)andhi(i=0,1)represent the income elasticity and interest rate elasticity of land monetary demand and nonland monetary demand,respectively,andh1(L)≤h0.Land becomes another form of wealth except money and securities,and the sensitivity of currency speculation demand to interest rates declines.The larger the amount of land supply,the lower the sensitivity[∂h1(L)/∂L<0].From Equation 6,we get:
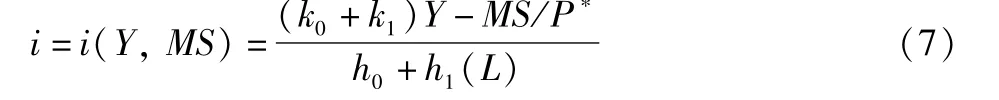
It is the expression of LMcurve containing land element.When there is monetary market equilibrium,the interest rate is determined by the monetary supply and the monetary demand caused by total income level.Land supply,price,tax rates and other variables do not directly constitute the variables affecting monetary supply and demand equations,but only influence the interest rate elasticity of currency speculation demand to have an indirect impact on monetary market equilibrium.
3.3.2 Modification of IS-LMmodel and effects of policies.By combining Equation 5 and Equation 7,we get the IS-LMequilibrium equation modified by land element:
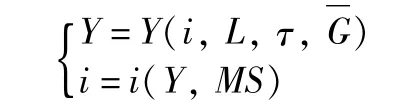
After arrangement,we get:
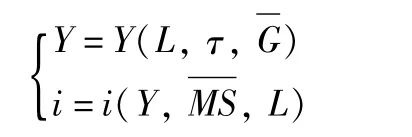
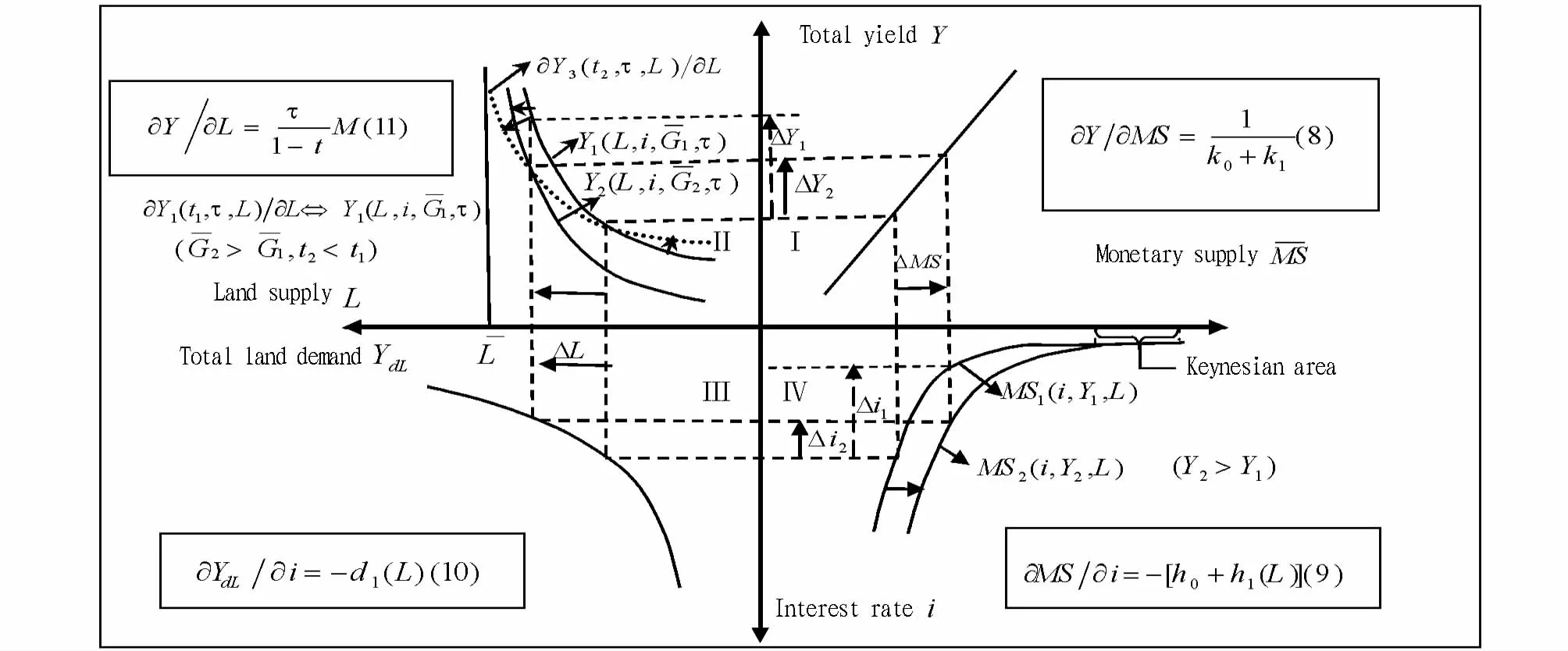
Fig.3 IS-LMequilibrium model modified by land element and policy response
We use the four-quadrant analysis chart of product market and monetary market to build the IS-LMequilibrium model modified by land element(Fig.3),and further analyze the effects of macroeconomic policies on equilibrium yield.Quadrant I,IV represent monetary market,and Quadrant II,III represent product market.Equation 8 to 11 are the expression of each quadrant,namely the derivation of policy variables to reflect the effects of policies.Quadrant I indicates the relationship between monetary supply and total yield,that is,in the case of constant interest rates,the increase in monetary supply leads to the incrementof total yield(ΔY2).According to the laws of supply and demand,the interest rate declines byΔi1,the increase in the monetary supply leads to an increase of total capital amount of social production,and the total output capacity increases byY1→Y2.The currency speculation demand increases,the monetary market equilibrium curvemoves to the right(MS1→MS2),and the interest rate will eventually fallbyΔi2(Quadrant IV).Land demand isa part of total demand,and the abatement in interest rate stimulates the land investment and consumption demand.Total land demand increases(Quadrant III),showing that land demand is the derived demand of capital.When there is supply and demand equilibrium in the land market,the total land supply is determined by the total land demandYdL=L.Under the conditions of constant proportioning of technical factors and factors of production,the land supply increase leads to the increment of total yieldΔY1(Quadrant II).The detailed analysis is as follows:(i)If there isΔY1=ΔY2,it indicates that the monetary market and product market achieve equilibrium at the same time,and there is a need to implement expansionary monetary policy and expansionary land policy at the same time.(ii)Under normal conditionsΔY1≠ΔY2,IS-LMequilibrium also requires the use of financial policy or other policies to achieve.IfΔY1>ΔY2,it uses expansionary fiscal policy,such as increasing government purchase spending,Y-L curve moves leftwardY1<Y2)or cutting tax(lowering the tax ratet1→t2,Y-L curve is rotated counterclockwiseY1→Y3).The increased government spending will have a crowding-out effect on private investment,and tax cutting increases the money invested in non-land element,while the decrease of land element has"growth drag"effecton total yield.In both cases,the total output declines,finally reachingΔY1=ΔY2,namely IS-LMequilibrium;conversely,ifΔY1<ΔY2,it uses austere fiscal policy to reach equilibrium,such as reducing government spending or raising tax rate.On the basis of Equation 8 to 11,we get the following rela-tionship:Then we get the expression of land pricePLas follows:PL(supported only when-1<η<0).Specifically,whenΔL→0,namely when the land supply regulation is not implemented,=d0andwe get:This suggests that firstly,the land price is jointly determined by supply and elasticity of supply.When the elasticity of supply isat[-1,0],the greater the elasticity,the higher the land price,the weaker the intensity of adjustment.During the economic expansion or recovery period,the land price is high,and the regulation effect of expansionary land policy will be offset by high land price.Secondly,the land supply regulation plays a role in regulating the total economic yield,and also pushes up the price of land and boosts land price expectation.The rising land price is due to land demand increase arising from economic and population growth,and the government's control over land which intensifies the land speculation(land supply regulation).
We should realize that the starting point of theoretical analysis on land's involvement in macroeconomic-control lies in how it affects the composition of total supply and total demand,but there still may be some problems to be solved regarding this extended model at the application level.Firstly,any land policy tool is not the general medium in the entire economic system;secondly,it is uncertain aboutwhether there is substitutability between land variable and other economic variables.However,the supplementation of land policy indeed provides a new perspective for the studies on fiscal and monetary policies.The practice of the Chinese land macroeconomic-control during 2004-2011 proves that the land as a special factor playing a fundamental role in the economic operation and China's uniquemacroeconomic-control environment,have made land policy's macroeconomic regulation role feasible(Zhu Daolin,1996;Wang Yiming,2008;Liu Wenjia,2004).The analysis onmechanism of influence of land supply on interest rate and total yield based on improved IS-LMmodel demonstrates that the government can regulate the economic development by controlling the supply of land.Meanwhile,due to the special response mechanism of China's macroeconomic operation to land market,the effect of land supply change can be transmitted to the real estate market through land price and supply elasticity,and it is not totally dependent on the monetary means to directly regulate interest rates,so we can rely on the land policy(land supply regulation)and monetary policy to(monetary supply or interest rate regulation)inhibit investment and stabilize property prices.
[1]Deininger Klause W.Land policies for growth and poverty reduction[M].Washington DC,Oxford:World Bank and Oxford University Press,2003:26-41.
[2]Hausmann Ricardo,LantPritchett,DaniRodrik.Growth accelerations[R].NBERWorking Paper No.10566.Cambridge,Massachusetts:National Bureau of Economic Research,2004.
[3]Kuznets Simon.Economic growth and income inequality[J].The American Economic Review,1955,45(1):1-28.
[4]Ayres RU,Kneese AV.Production,consumption and externalities[J].American Economic Review,1969(59):282-297.
[5]Brock WA,Taylor MS.The green solow model[J].Journal of Economic Growth,2010,15(2):127-153.
[6]Brueckner JK.Growth controls and land values in an open city[J].Land Economics,1993,66(3):237-248.
[7]Nelson AC.Comparing states with and without growth management:Analysis based on indicators with policy implications[J].Land Use Policy 1999(16):121-127.
[8]Kironde L.Comments on management of Peri-Urban Land and Land Taxation[R].Kampala,Uganda:World Bank Regional Land Workshop,2002.
[9]QIMS.On the regulation role of land rent and land price to urban land use[J].China Land Science,1994,(7):16-20.(in Chinese).
[10]SHAO JC.Land rent and land price are the important and direct macrocontrol means[J].China Land Science,1996,10(A10):63-65.(in Chinese).
[11]ZHOU C.Discussion on the economic measures of land usemacro-control[J].China Land Science,1994(S1):6-10.(in Chinese).
[12]BO Q.Fully play the macro-control role of land[J].China Land,1995(5):31.(in Chinese).
[13]SHAO JC.Land rent and land price are the important and direct macro-control lever[J].China Land Science,1996,10(A10):63-65.(in Chinese).
[14]CAI YP,LIU J.The change of urban planning methods under market economy[J].Planners,2001,17(3):73-75.(in Chinese).
[15]WU CF,TAN YZ.Internal basis and outside condition——Analysis of macro-economic control facilities of land policy[J].China Land,2004(5):8-9.(in Chinese).
[16]HUANG XY,JIANG Y.Theoretical analysis and empirical study on interdependence between land market and macroeconomic[J].China Land Science,2006,20(4):2-8.(in Chinese).
[17]FEIL,WEIL,JIANG Y.Study on the contribution of land element to economic growth in China[J].China Land Science,2008(12):4-10.(in Chinese).
[18]FENG L,KONGWD.Practices of involving land policies into macroeconomic regulation in China since2003:Summary on characteristics,effects,and problems[J].China Land Science,2009(10):8-13.(in Chinese).
[19]MAO ZQ,ZUO YQ.Study on contribution rate of land to the secondary&service industry growth[J].China Land Science,2007(3):59-63.(in Chinese).
[20]MAO ZQ,ZUO YQ,GENG C.Re-discussion on land contribution to the secondary and tertiary industries in China[J].China Land Science,2009,23(1):19-24.(in Chinese).
[21]YANG ZR.A theoretical and empirical study on land supply policy participation intomacro-economy intervention[D].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2008.(in Chinese).
[22]WU KP,YANGWL.The effects of land supply scheme on macro control policies[J].South China Finance,2009(3):19-22.(in Chinese).
[23]SONGHM,LIJ,JIN XY.Construction and analysis of IS-LMmodel on land macro-regulation[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2009(11):285-286.(in Chinese).
[24]JIN XM.Land-regulated economy:A paradigm and its application to China’s landmacroeconomic intervention[M].Hangzhou:Zhejiang University Press,2007.(in Chinese).
[25]FENG L.Policy design for the land policies formacro-level control——Based on the analysis of Chinese practice[M].Inquiry Into Economic Issues,2010(9):99-104.(in Chinese).
[26]HUANG LX.Review on the studies of land policy to regulate macro-economy[J].Urban Problems,2010(3):76-80.(in Chinese).
[27]LIWZ.Playing the"gate"role of land,improving the effect of macroeconomic regulatory[J].Macroeconomic Management,2008(5):27-29.(in Chinese).
[28]GAO HY.Western economics[M].Beijing:China Renmin University Press,2003:506-517.(in Chinese).
[29]BIBD,CHAIQ,LIL.Land economics[M].Beijing:China Renmin University Press,2006:310-317.(in Chinese).
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Experience in New Socialist Countryside Planning and Construction and Recommendations:A Case Study of Haotang Village in Xinyang City of Henan Province
- Construction and Establishment of Sci-tech Platform for Agricultural Scientific Research Institutions:A Case Study of Tropical Crops Genetic Resources Institute of Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences
- The Type of Low-yielding Fields,Using Direction and Land Fertility Building Measures in Suiping County
- Detection and Analysis of Lead,Cadm ium and Arsenic Content in Common Vegetables
- The Development Model of Agricultural Insurance in Anhui Province
- Analysis on Technology road map of Agricultural Equipment Industry in Chongqing
