Research on Factors Influencing Fertilizer Application of Farmer Households in Anhui Province
2014-04-10ZhiweiWANG
Zhiwei WANG
Food and Drug College,Anhui Science and Technology University,Fengyang 233100,China
Agricultural products constitute the material foundation and basic guarantee for human beings.With rapid economic growth and the gradual improvement in our living standard,our government and residents are increasingly aware of the safety of agricultural products.The Survey Report on Food Safety in the Circulation Field issued by the Ministry of Commerce indicates that95.8%of the urban consumers and 94.5%of the rural consumers attach importance to the quality and safety of agricultural products.These proportions have been increased by 13.2%and 36.4%respectively as compared with that of the year 2006.However during the transitional development of China,the satisfaction degree of urban and rural consumers with agricultural products has dropped significantly due to the frequent food safely incidents inclusive of agricultural products[1].Although the occurrence of adverse situation with regard to the safety of agricultural products has been caused by multiple factors in various links from farmland to dining-table,there is no denying that the excessive application of fertilizers and unreasonable fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households constitute one of the important factors that affect the quality and safety of agricultural products.
As one of the necessary inputs for agricultural production,chemical fertilizer has long been an important material for the production of agricultural products and has played an important role in maintaining and increasing agricultural production.However,excessive and unreasonable fertilizer application behaviors have caused serious pollutions that allow of no ignorance to the ecological environment.Our country has become one of the countries with maximum level of fertilizer usage and intensity around the world.Statistics show that the total amount of fertilizer usage in China has increased from over 1 200 t in 1980 to over 5 700 t in 2011,indicating a growth rate of nearly 5 times.The agricultural acreage of China accounts for less than 10%of the world's total acreage.However,the annual usage of fertilizer has accounted for 1/3 of the total fertilizer usage of the world.The fertilizer usage per hectare(converted into scalar quantity)has increased rapidly from 94.83 kg to 430.43 kg,which is much greater than the safe upper limit of fertilizer use intensity(225 kg/hm2)that has been set by the developed countries[2].Besides,due to the massive use of fertilizers,the faeces and straws that could have been recycled are discarded and become the important"carbon source"and' pollution source"[3].The unreasonable and non-regulated fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households can lead to soil hardening,land capability decline,worsening conditions for the growth and development of agricultural crops and the eutrophication of water environment,which will further affect the yield and quality of agricultural products directly.Therefore,in the context of environment&climate changes,farmland shrinking,increase in rigid demands of population,and that fertilizer will continue to play an integral role for a long term as an important element for agricultural production,it will be the most important and realistic approach to further observe farmer behaviors,analyze the principal factors influencing the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households,implement institutional supply and moderate market mechanism actively to regulate the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households,and minimize human impact so as to reduce the impact of fertilizer application on the safety of agricultural products at present and in the future.
1 Description of program implementation and sample statistics
1.1 Investigation method and data source
1.1.1 Questionnaire design.The questionnaire is designed closely around the topic of decision-making research on the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households on the basis of comprehensive analysis and reference of relevant research literature.The questionnaire falls into 3 parts:basic characteristics of fertilizer users,behaviors of fertilizer users during fertilizer application and the cognition of fertilizer users on fertilizer application behaviors.There are totally 19 questions that are connected with each other.
1.1.2 Sampling method and model selection.This survey is conducted in 5 counties(districts)(Dangshan County,Datong District,Shou County,Taihu County and Lixin County)that are randomly selected from 5 prefecture-level cities(Suzhou City,Huainan City,Lu'an City,Anqing City and Bozhou City)in Anhui Province.In each county(district),5 townships are selected randomly.And in each township,1 village will be selected as the survey sampling area randomly.In order to ensure the authenticity,validity and rationality of the survey,random sampling has been applied.All the farmer households under investigation are scattered households with the experience of fertilizer application.They are family-based production and business units and haven't participated in any forms of cooperatives.Due to the limitations of location,language,resources,time and other factors,this questionnaire survey has been conducted by the team of home-returning students on the basis of one-on-one interview and in the form of answering questions at the scene.A total of 140 questionnaires have been issued,and 126 valid ones have been retrieved,resulting in an effective rate of 90%.In model selection,the Binary Logistic model has been applied for data analysis in this paper.
1.2 Basic characteristics of respondentsMale farmers have held a larger majority in this survey.The total number of them is 82,accounting for 65.1%of the total number of samples.89 of the respondents are aged 40 or above,accounting for 70.6%of the total number.Respondents with relatively lower degree of education(educational level of junior high school or below)account for 77.8%of the total number of samples.53.2%of the respondents have been engaged in agricultural production for over 20 years.99 of the respondents have family members of4 and above,accounting for78%of the total number of samples.The annual household income of the respondents is on the low side.Only 21.4%of them have an annual income of higher than 50 000 yuan.Among the respondents,67 of them do part-time jobs in the slack farming season,accounting for 53.2%of the total number of samples.In the meantime,79.4%of the respondents have never employed labor force for agricultural production in busy farming season.
1.3 Fertilizer application behaviors of respondents The analysis on fertilizer application of farmer households is very complex,and the behaviors observed from different angles present significant differences.For the sake of typicality,this research has divided the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households involved into concrete behaviors of 3 stages(before fertilizer application,during fertilizer application and after fertilizer application)according to the continuity of the fertilizer application behaviors for statistical analysis.
1.3.1 Behaviors of farmer households before fertilizer application.The behaviors of farmer households before fertilizer application mainly involve 4 aspects,including knowledge training on chemical fertilizer,sense of identification with guidance of agricultural technicians,considerations in fertilizer purchasing and the need for deep and extensive soil cultivation.
The survey results show that the number of farmer households who have attended fertilizer knowledge trainings accounts for only 7%of the total number of samples.That is to say,93%of the households haven't attended any training.With regard to the guidance effect of agricultural technicians,69%of the households deem the guidance as effective,and 31%of them say that they are not very clear about it.No one thinks that the guidance of agricultural technicians is of no effect.This indicates that most farmer households have anticipations to agricultural technology expansion.Only a few of them are not familiar with the promotion and training of agriculture science and technology,but they do not reject it.Through further investigation on the considerations of farmer households in fertilizer purchasing,it has been found that price and the growth conditions of crops remain to be the their primary considerations.And the above factors account for 77%and 76.2%of the total number of samples respectively.Only 5.6%of the farmer households will consider whether the fertilizer is environment friendly.
Besides,deep and extensive soil cultivation will promote the root development of crops and increase production.Statistics show that 60%of the respondents conduct deep and extensive soil cultivation before fertilizer application,and the remaining 40%of them do not conduct deep ploughing before fertilizer application,which will lead to the underutilization of fertilizers.Some of the fertilizer retained on soil surface will flow into rivers and lakes along with rainfalls and cause pollution to surface water.
1.3.2 Behaviors of farmer households during fertilizer application.The behaviors of farmer households during fertilizer application mainly include the following 3 aspects:fertilizer usage for every 667 m2of wheat in a season,application method for base fertilizer during fertilization,and the kinds of additional fertilizers applied each year.
For the amount of each kind of fertilizer applied by the users,statistics show that the average fertilizer inputs for every 667m2of wheat in a season are as follows:18.8 kg bio-organic fertilizer,135.3 kg farmyard manure,45 kg nitrogen phosphorus and potassium,and 16 kg micronutrient fertilizer.
Base fertilizer may help to create suitable soil conditions for the growth and development of crops.With regard to the application method of base fertilizer,57%of the farmer households choose to spread base fertilizer before ploughing,and 43%of them choose to spread base fertilizer after ploughing.According to the moisture content of farmland,the base fertilizer can be applied in deep soil by means of deep furrow application or ploughing after fertilizer spreading.In drought years,deep furrow application is generally adopted.That is,apply fertilizer in the furrow along with the soil upturning process of plow,and then turn up soil to cover the fertilizer.For the farmland with heavy and wet soil,the method of ploughing after fertilizer spreading is applied to bury fertilizer into the soil.However in our practical investigation,we have found that most farmer households will not choose the method of application after ploughing or application before ploughing according to the actual conditions of the soil.They just continue with their consistent way.
Additional fertilizer is applied to supplement the insufficient nutrients of base fertilizer.The application of additional fertilizer is quite flexible and should be conducted according to the element deficiency diseases of crops presented in different growth periods.In the application of additional fertilizers,77%of the farmer households choose to apply striking root fertilizer and nitrogen fertilizer before transplanting.The application amounts of leaf fertilizer and jointing fertilizer are of similar level,accounting for 50.8%and 47.6%of the total number of samples respectively.Fewest farmer households choose to apply booting nitrogen fertilizer,accounting for only 26.2%.In the survey,it has been found that the application of additional fertilizers is primarily based on the self experience of farmer households.There is no scientific basis for it.In this way,excessive application and waste of fertilizers are very likely to occur.
1.3.3 Behavior and cognition after fertilizer application.The behavior and cognition of farmer households after fertilizer application involve the following 3 problems:the disposal of fertilizer packages after application,cognition on the negative effects of excessive fertilizer application,and the cognition on new technologies for formula fertilization by soil testing.
For the disposal of bottles and bags of chemical fertilizers and pesticides after application,69.8%of the farmer households choose to discard them near the farmland or canal directly;19.8%of them choose to pile them up together with the other industrial and domestic wastes;and only 7.2%of them will place them at special recycling stations.Only a small number of farmer households have a sense of environmental protection.
In addition,the fertilizer application behaviors of chemical fertilizers depend largely on their cognition of such behaviors.When asked"whether the excessive fertilizer application will cause harm to soil conditions and water quality",5%and 9%of the farmer households hold the views that excessive fertilizer application causes no hazards or very minor hazards.The number of farmer households deeming the hazards as"general"and"significant"account for 40%and 39%of the total number of samples respectively.And only 7%of them consider the hazards as"very serious".Thus it can be seen that most farmer households recognize that excessive fertilizer application will contribute to environmental pollution,but only a small number of them are aware of the gravity of the problem.
Formula fertilization by soil testing is an effective way to improve land utilization efficiency and achieve scientific farming.But farmer households have low awareness of the technologies on formula fertilization by soil testing.Survey results show that only6 farmer households have tried formula fertilization by soil testing.A major proportion of them have never heard of formula fertilization by soil testing,and the number accounts for58%of the total number of samples.Up to42%of the farmer households have heard of but never tried this technology.Only 20%of the farmer households who have heard of the technology want to have a try,but there is a lack of technical guidance.

Table 1 Definition of variables and sample statistics
2 Empirical analysis
On the basis of the descriptive analysis on the individual characteristics,family characteristics and related behaviors of respondents before,during and after fertilizer application,a binary Logistic model has been built from the perspective of household characteristics to further explore the characteristic factors that affect the fertilizer application of farmer households.Variable explanations involved in the model are shown in Table2,and the corresponding binary Logistic model is expressed as:
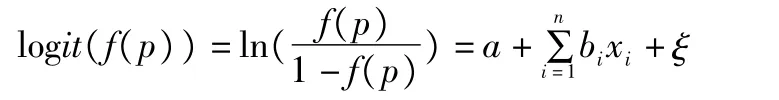
where f(p)is the probability of dependent variable y=1;a is constant term,is regression coefficient;xiis the factor that affects the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households,including the variables of individual characteristics and production&operation characteristics;n equals to 126;andξis the random error subject to normal distribution.
In this research,3 typical behavior characteristics including whether to perform deep and extensive soil cultivation,how to apply base fertilizer during the application and how to dispose the bags after fertilizer application have been considered as the representative behaviors before,during and after fertilizer application respectively.Through empirical research,the household characteristics that affect fertilizer application behaviors have been studied.
Statistical software SPSS16.0 is applied to conduct Binary Logitic regression analysis on the cross-section data of the 126 samples under investigation.The results are shown in the following Table 2,Table 3 and Table 4:
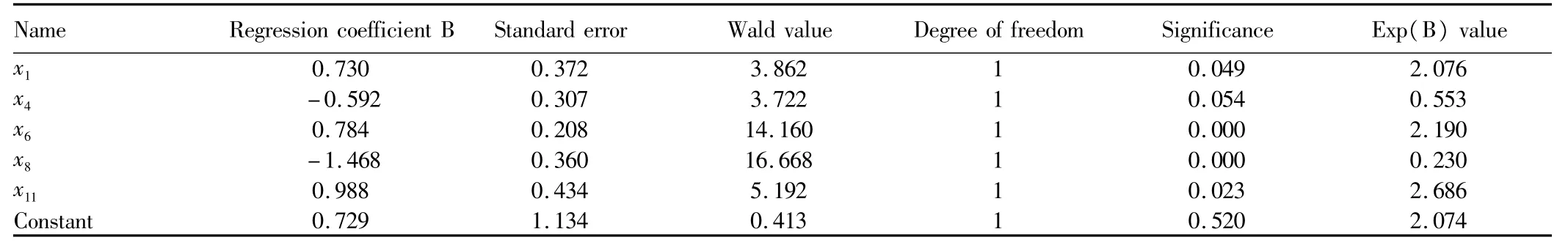
Table 2 Logistic regression results for deep and extensive cultivation

Table 3 Logistic regression results for base fertilizer application

Table 4 Logistic regression results for bag disposal after fertilizer application
Through further analysis,the models that affect the fertilizer application behaviors of farmer households are shown below:

From Formula(I),it can be seen that the choice regarding whether to perform deep and extensive soil cultivation before fertilizer application depends largely on the factors including gender,years of experience in agricultural production,number of family members,non-agricultural income and the area of rented land.It shows a negative relationship with the years of experience in agricultural production and the non-agricultural income,and has a positive relationship with the other factors.

It can be seen from Formula(II)that the choice on the method of fertilizer application relies heavily on the factors including the years of education,the taking of part-time jobs,annual household income,total area of family cultivation and the area of leased land.It is positively correlated with the years of education and the total area of family cultivation,and is negatively correlated with the other factors.
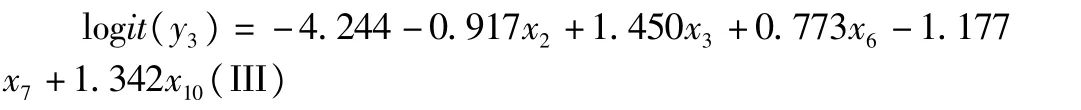
From Formula(III),it can be seen that the disposal of fertilizer bags after fertilizer application is significantly affected by the age,years of education,number of family numbers,annual household income and the area of leased land of the farmer households.Among these factors,it is negatively correlated with the age and annual household income.
3 Conclusions
Through the investigation on 126 farmer households in 5 counties(districts)in Anhui Province,statistical description and model analysis have been conducted for the fertilizer inputs of farmer households as well as the influencing factors.Research results indicate that most farmer households hold a positive attitude toward the guidance of agricultural technicians and want to obtain such guidance and training,but only a very few of them have actually received the trainings on the knowledge of pesticides and chemical fertilizers.Although the farmer households have certain understanding of the adverse impact posed by excessive fertilizer application on the environment,they don't really know what kind of behaviors will cause environmental pollution during their own operation procedures.Formula fertilization by soil testing is a scientific fertilizing method that has attracted extensive attention in recent years.But in rural areas,most farmer households have never heard of formula fertilization by soil testing.This indicates that they have very few channels to learn about new technologies.In addition,the behaviors of farmer households before,during and after fertilizer application are affected by the basic characteristics including age,years of education,number of family members,the taking of part-time jobs,annual household income,total area of family cultivation and the area of leased land etc.to varying degrees.The research results indicate that the basic measures for solving potential quality and safety problems of agricultural products from the source include improving the cultural education and environmental cognition of farmer households,offering farmer households with rational fertilization information through the training and promotion of agricultural technologies,speeding up land circulation among different households,achieving land operation of suitable scale,and strengthening the promotion and application of new agricultural technologies such as formula fertilization by soil testing.These measures are also important approaches for improving rural ecological environment.
(This article chinse version has been published in"Guangdong Agricultural Sciences"2014 first issue).
[1]Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China.Investigation report of circulation domain food safety,2008[EB/OL].[2009-05-04].http://www.agri.gov.cn/jjps/t20090428_1263450.htm.(in Chinese).
[2]ZHANG F,HU H.Study on farmer's chemical fertilizer input behavior and non-point source pollution[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2012,24(1):183-186,206.(in Chinese).
[3]Lou XF,Nair J.The impact of landfilling and composting on greenhouse gas emissions—A review[J].Bioresource Technology,2009(100):3792-3798.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Study on Causes of Slow Progress in Promoting the Application of Food Traceability System in China
- Numerical Simulation and Moist Potential Vorticity Analysis of Torrential Rain in Jiangxi Province during June 2010
- Evaluation on Optimal Scale of Rural Fixed-asset Investment-Based on Microcosmic Perspective of Farmers' Income Increase
- The Estimation Methods for Agricultural Surplus Labor Based on Stochastic Frontier Production Function
- On the Poverty in the Rocky Desertification Areas of Southwest China Based on AHP:A Case Study of Liupanshui City in Guizhou Province
- Countermeasures for Tobacco Branding and Industrial Development in Enshi Prefecture
