Analysis of Social Capital's Effect on Income of Poor Households:A Case Study in Sichuan Province
2014-04-10LuSUNJunwenLIUBaofengCHEN
Lu SUN,Junwen LIU,Baofeng CHEN*
1.College of Economics&Management,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100083,China;2.Information Centre of the State Council Leading Group Office of Poverty Alleviation and Development,Beijing 100083,China
1 Introduction
In recent years,more and more evidence prove that the third kind of resource allocation way-social capital has a major influence on the economic growth,social justice and poverty reduction,except for material capital and human capital(Xin Meng 1995,Qiren Zhou 19977)[1-2].At the same time,scholars agree that whether personal income or household income is under the influence of social capital(Meichuang Wu 2006)[3].Grootaert(2001)found that social capital is more important and for the poor and its effect is more significant in terms of increasing family welfare than human capital based on the research of Bolivia and Burkina Faso[4].In number of previous studies,two ways mainly through the social capital influences income that are the direct effect of social capital and the indirect effect on income through human capital and material capital.Firstly,different social capital brings various development opportunities for individual or family,and different status will cause the differences of the opportunities for using the public resources(Zhouliang Xie,2009)[5].Higher status is closely connected with high value social resources,such as rights,the use and disposition of public goods,the power of appointment,decision rights and so on.Meanwhile,individuals having this social capital are more likely to participate in the use,transform and disposition of the resources;therefore,they will have more chances to increase their self-interests.In addition,different types of resources often exchange with each other.Individuals having high level of the position of one kind of resource also tend to be in relatively high position in other resources.The owners of power resources exchange the power for wealth with the owner of wealth resources,through negotiation and trading.Thus,the result is that the person with higher social status also has higher income.Secondly,social network can infiltrate into all aspect of life,using human relationship can also get more chances for study,promotion employment investment as well as direct material help.Social network is closely linked with labor mobility,it has a resource and information integration function in the labor migration process and further affects their income.Social capital and human capital investment have close connection,constantly realizing their own reproduction in the form of dynamic transformation.Through the study,Chaoming Wang(2009)suggests that under other basic conditions same,the lower amount of social capital correspond to lower the amount of human capital,they are interrelated[6].Bourdieu(1997)thought that social capital has important influence on education investment:opportunity to receive education and its level,as well as the economic and social benefits of education investment in the future,are all closely related with social capital[7].Social capital not only can promote the increase of education investment quantity,but also can improve the quality of education investment.
2 Selection of the model of social capital impact on the income of farming household in impoverished areas
As a kind of capital that having special properties and production capacity,social capital can be seen as a factor of production different from material capital and human capital.Therefore,with the deepening of the study,scholars gradually began to put social capital into the analytical framework of various kinds of classical theories.Since the 1980s,the new economic sociology expanded the production function of the neoclassical economics to be composed by material capital,human capital and social capital.
Based on Cobb-Douglas production function(Y=A(t)KαLβ,0<α,β<1.Astands for technical progress,KandLfor capital and input of labor,αandβfor the output elasticity of capital and labor),there have been scholars added human capital and social capital into the function to study.Romer,etc.(1992)put human capital into production function and got the formulaY(t)=K(t)αH(t)β(A(t)L(t))1-α-β[8].Fafchamps and Minten(2002)put social capital into production function,thinking that social capital improves the production efficiency of capital and labor[9].Their production function expressed as:Y(t)=[F(s)K]α[G(s)L]β,in which,F(s)andG(s)stand for the influence of social capital to the production efficiency of capital and labor.Then,Hirokazu Ishise and Yasuyuki Sawada(2009)put social capital into C-D production function as the independent factor affecting economic growth,that isY(t)=K(t)αH(t)βS(t)γ(A(t)L(t))1-α-β-γ[10].On the basis of previous studies,the article put the social capital(S)into the production function as an independent factor and labor(L)is replaced by human capital(H)in order to examine the influence degree of the social capital to the farmers’income in the poverty areas.In addition,it is necessary to add ground(G)into the production function as an independent factor,considering the ground as the important means of production in the farmers’production progress in poverty areas has a great influence on their income.Therefore,Yi(t)=AKi(t)αGi(t)βHi(t)γSi(t)ε.In the formula,Yi(t)is the family annual income of farming householdiin impoverished area at timet,Ais for the technological progress in the farmer’s production process because of the means of production renewing,Ki(t)is the family material input of farming householdiin impoverished area at the moment oft,Gi(t)is the ground stock of farming householdiin impoverished area,Hi(t)is the human capital stock of farming householdiin impoverished area at the moment oft,Si(t)is the family social capital stock of farming householdiin impoverished area at time oft.m,β,γ,εrespectively stand for family material capital,ground,human capital and output elasticity of social capital of farming household.Then this article uses the basic form to conduct regression analysis on the model.
3 Regression analysis of social capital influence on income in im poverished areas
3.1 Data collectionBy cluster sampling,1 000 poor households from 31 villages in four counties around Sichuan Liangshan area are chosen and 958 questionnaires are available in the research.Survey content includes three parts:(i)basic information of the farmer individuals and families:age,sex,nationality,education degree,marital status,health condition and so on;(ii)production and living conditions:household income and expenditure,household assets,economic conditions in the village in any order,the causes of poverty,and so on;(iii)situation of social capital:farmer’s relatives and friends,communications,transportation,career situation,the situations of cooperation and trust,etc.
3.2 Selection and measure of main variables
3.2.1 Family material capital.By material capital we measure the production goods and materials existing for a long time,such as machines,equipment,factor building,communications and transport facilities and so on.To the farming household in impoverished area,their material capital in production process mainly refers to the various material costs of buying farming machines and transport equipment as well as the cultivation costs during the process of production activities in order to get income.Therefore,this study regards productive assets stock of farming household as variable measuring family material capital.
3.2.2 Family human capital.The family human capital is measured by integrated computation on the basis of degree index and educated years.Namely,Hi=There,Histands for the human capital stock of familyI,Xijfor the number of labor population on the leveljeducation in that family,andEjfor the degree index corresponding to leveljeducation.In this study,the education degree surveyed is divided into four classes:illiterate,primary school,junior school and senior the above.Combined with the actual situation of compulsory education in our country,the education years of the four types of people are defined as zero year,six years,nine years and twelve years.Using the nine-year compulsory education as the stander,the degree indexes are respectively taken as e0/9,e6/9,e9/9,e12/9.Based on the above,the human capital stock of familyiis:Hi=Xi0×e0/9+Xi6×e6/9+Xi9×e9/9+Xi12×e×12/9.And labor(L)is replaced by human capital(H)in the production function of farming household in impoverished area in order to avoid repeating the influence effect.
3.2.3 Family social capital.(i)Choice of measuring dimensions.Domestic and overseas scholars’findings indicate that the measurement of social capital in rural areas is a complex process,and many scholars have not formed a unified social capital measurement system in rural areas,so this article combined the above findings with comprehensive analysis of the regional characteristics to obtain the region dimensions of social capital measurement.Integrated all kinds of domestic and foreign literature,the measurement of social capital can be drawn mainly from the following dimensions of:social networks,community participation,reciprocity,trust,sharing,cooperation,volunteerism,and community cohesion,community feeling of belonging,collective action,and social support.(Putnam 1993,Knack and Keefer1997,Guisoetal.2004,Beugelsdijk and Van Schaik 2005,Rupasinghaetal.2006,De Silvaetal.2007)[11-16].However,for these dimensions,academic circles also raised doubts:First,some dimensions are the result of social capital,but not social capital itself,for example,collective action,community cohesion and sense of belonging,have causal relationships respectively;Second,some dimensions are not suitable for direct measurement of social capital in rural areas,such as volunteerism.Putnam advocates the role of volunteerism in social capital,believing that the decline in U.S.citizen volunteerism is an important reason for the decline of social capital.However,there is almost no social intermediary organizations in rural areas in China,especially in the west and thus to directly measure whether the villagers have the"volunteerism"in the eyes of Putnam is relatively difficult.Thus,we will use the community involvement with the spirit of volunteerism to make up for this shortfall.Third,reciprocity and social support also have some overlaps,social support between neighbors itself is the expectation of getting mutual support in the future.Then according to the preliminary results of the local investigation of social capital,because of the local economic and social development,social capital formed through economic activities is relatively small.There is little rural cooperative organization in the sample areas.At the same time,there is no large-scale leading industry about agriculture;single household is still the main production mode of cultivation.The so-called combination of centralization and decentralization,a mode of production and operation,here only see the"decentralization",and"centralization"is seldom seen.The pattern of manifestation is that there is no collective economy and unified technical services and etc.also are not very developed.So cooperation and community participation dimensions are removed,the remaining reserves the social network,trust,mutual aid dimensions to measure.
(ii)Selection of measuring method.According to the related literatures about social capital,the measurement of social capital has the following categories:measurement according to the level,measurement based on the elements,network measurement method and cognitive structure measure method.Network measurement method ignores the cognitive level of social capital,lacking of the comprehensiveness;while the stratification is only based on the difference between research perspectives,making no difference to measure method essentially.Although measurement based on the elements considers comprehensive,the possible correlation between the two can cause error to the simple total amount of measure.Based on the research content and the nature of data,in this study cognitive structure comprehensive measurement are used(Putnam 1995)[17].The total amount of family social capital is acquired through factor analysis method.Based on the data from 958 valid questionnaires and its quantification,the study uses the factor analysis in the SPSS18.0 software and initial extract the main ingredient of these 11 questions.According to the principle of eigenvalue greater than 1,the study got the results of KMO and Bartlett’s test of sphericity in Kaiser standardized orthogonal rotation:the KMO of this analysis is 0.709 greater than 0.5,so it passed the KMO sphericity test;and chi-square value of Bartlett’s sphericity test is 1839.759,reaching significant levels(P=0.000<0.001).The cumulative variance contribution rate reached 59.6%,nearly 60%.Therefore the results of this analysis can be considered concentrated.In addition,the contribution rate of each factor of the four main components is more than 0.5,so the study thinks that each factor can explain much of the principal components.Furthermore,in the reliability analysis,The Cranbach’s a measured by these data is 0.690 and Cranbach’s a coefficient based on standardized items is 0.685,both are greater than 0.6(Nunnally 1978)[18].So we can determine the problem setting in the factor analysis is reasonable,and the analysis has higher reliability degree.According to the test results above and the three determination principles of factor analysis,we ultimately determine each component of social capital and its various constituent factors for the contribution of the main ingredients(Table1).Then we get the formula of family social capital(SC)as:
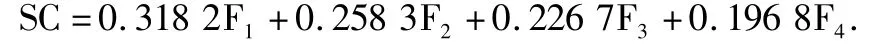
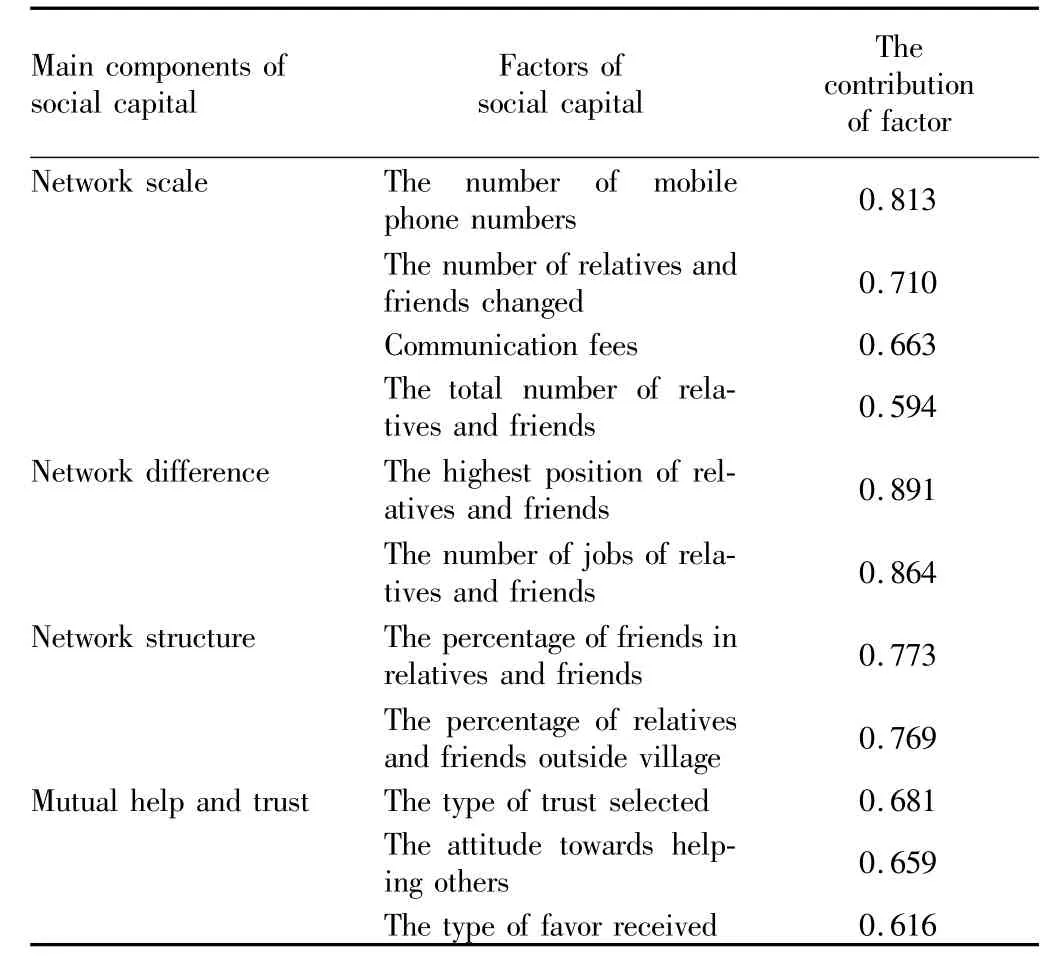
Table 1 Main components and contribution of factors of social capital
3.3 Determination of the modelTransform the two sides of the front selected production function with logarithmic firstly.And some certain policy measures(including direct financial allowances,relief supplies,medical care and indirect agricultural infrastructure construction,village renovation and so on)been taken for the particular farming households are identified of"poverty"as their per capita income is lower than 2300 Yuan.Therefore,in order to analyze the changes of the incomes of farmers in poor areas better,we put"whether the poor"as a kind of institutional factors,being added to the regression model in the form of control variables.According to the designated poverty line,the poverty households are assigned to"1",the non-poverty households assigned to"0".The model with system variable is as follows:
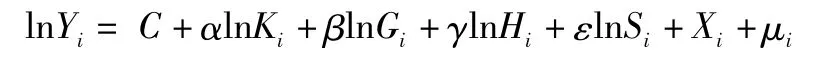
In the form,Yistands for the family income of the farming householdiin impoverished areas of that year,Kifor the family material capital and productive assets of the farming householdiof that year,Gifor the family ground area,Hifor the family human capital,Sifor the social capital stock of the year,Xifor whether the household in poverty or not,μifor a random variable.
3.4 Model estimationThis article uses the least squares method(OLS)in the model regression and in the application of SPSS18.0 software.In the model,family income of farming household income is the dependent variable.The material capital,ground area,human capital and social capital of family are treated as the independent variables.And the study adds the institutional factors as the control variable only in Model.
3.4.1 All the samples.We can see from the regression results(Table 2)that:the main variables estimated coefficients passed the significant test.R2value adjusted by prediction equations is 0.584,small model fit.F-test value is269.212,passing the 1%significance test.The regression results show that the output elasticity of social capital is0.118,that is to say social capital investment increased by 10 percent each,will bring an increase of 1.18%of household income.Also,the symbol of the output elasticity of social capital is positive;indicating that with the increase of social capital,the trend of income is growing.Family output elasticity of material capital and human capital are 0.178 and 0.244,positive,consistent with previous research findings and in line with the actual situation.Material capital and human capital have a positive effect for the farming household’s family income.
Three types of capital,social capital output elasticity is smaller than the other two.The reasons could in this study is the objects surveyed are mainly poor ethnic minority households in remote mountainous areas,with less the amount of investment in family social capital and the quality not high,so its contribution to income is not high.However,the investment of social capital has a positive effect to raise family income.Although the output elasticity of human capital investment is large,the period to get the output is longer,with a certain time lag.While in terms of the farming household in impoverished areas,the material capital investment only plays a temporary role,not changing their own out of poverty capabilities fundamentally.Therefore,in terms of farming household in impoverished areas out of poverty,based on human capital and material capital investment,increasing the investment in social capital is likely to get results in the short term.In addition,from the regression results,the system variables"whether poor households"can also be seen as a family characteristic variables.This variable also passed the t test significantly,indicating that it is influential to the income of farming household.Coefficient for this variable is negative,indicating a low family income of the poor households,which illustrates from the side that the new"poverty line"for targeting the poor delineation is correct.
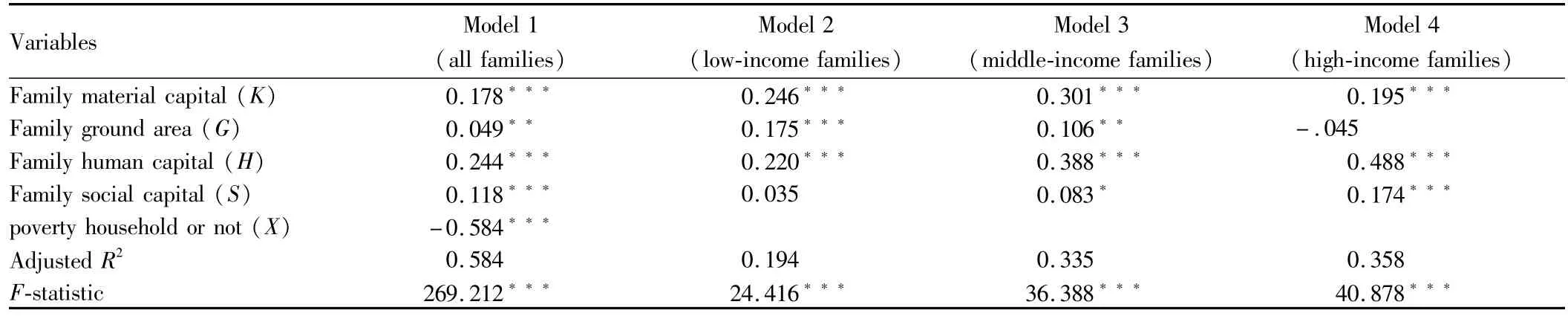
Table 2 Regression coefficients of different social capital dimensions' impact on income
3.4.2 Comparative analysis of social capital affects on different income levels.In order to investigate the extent of the effects of social capital on income in different income groups,the survey objects are divided into three categories by the poverty line of2 300 Yuan:less than 2 300 Yuan per capita income for low-income families,2300-4600 Yuan per capita income for middle-income families,and more than 4,600 Yuan per capita income for high in come families.Among the samples,the perceptions of three kinds of income level in the order from low to high are 33.92%,31.53%and 34.55%of the total.Since the sample size is large,here we use the mean of each group of social capital to study.The regression results of three kinds of income level are showed in the Table 2.Regression results show that:the three models of different income levels all pass the 1%significance test,indicating a good model fit.And the material capital and human capital of family in three models all pass the significance test.While family ground area does not pass the significance test in the model of high-income,indicating that ground area has little effect on income in high-in come households.The social capital passes the significance test in the model of middle and high-income levels but low-income,indicating such kind of capital has little effect on low in come households’family income.For more in-depth study of social capital why not have significant effect,we respectively put the four dimensions of social capital to replace the total amount of social capital into the regression model.Regression results show that:social scale,network difference and mutual trust among the four dimensions of social capital pass the 1%significance test,while the dimension of social network structure does not pass the significance test.That indicates the four dimensions of social capital,the network scale,network difference and mutual trust have effects on the income of low-income households.
4 Conclusions
The regression results above show that the extent of social capital impact on household incomes with different income levels has diversity in impoverished areas.
In the low-income households group,the regression results of the total social capital are not significant.However,when the four dimensions of social capital were placed in the regression model for analysis,we found that the scale of social networks,network differences and mutual trust impact on family income is significant for low-income households.The output elasticity is0.199,0.123 and-0.081.The social network scale every 10%increase caused 1.99%income improved;social network differences every 10%increase caused 1.23%income improved.That indicates the increase of the number of family and friends and their improvement of the social status can promote increasing income of the low-income households.While the output elasticity coefficient of mutual trust and a social network is negative.The index of the element after restoring to the form of production function is negative.That is,with increasing mutual trust in society,the income scale is reduced.This is mainly because the survey object of this study has certain ethnic particularity.Because of their traditional Yicultural characteristics,the mutual trust among the farming households in the region are established on family relationship with blood.It has little help for income increase.At the same time,the low-income households are limited on their own strength;the cost of helping others takes a certain weight in the proportion of income.The return of helping others is time-sensitive.After a long time can we receive the effectiveness.Short-term returns received are smaller compared to the cost.Therefore social mutual aid and income growth is reversed.In the high-income farming households,except the family ground area,the regression results of the other variables are significant.This is mainly because for high-income families,their main source of income is non-agriculture.Cultivated ground,as a major factor for agriculture production,has little impact on family in come mainly composed by non-agricultural income.It is not difficult to find that,comparing the three groups,output elasticity of social capital on low-income level is the smallest,but on the high-income level largest.The reason still is that the higher the income,the proportion of non-farm income is greater.As can be seen in the front conclusions,social capital can bring farmers more learning,employment and promotion opportunities,thereby help to improve their ability to self-generating income,to increase income,especially non-farm income.Visibly,increasing social capital investment brings a certain help to the farming households in impoverished areas,especially the high-income households.
[1]XIN M,Miller,Paul.Occupational segregation and its impact on gender wage discrimination in China’s rural industrial sector[J].Oxford Economic Papers,1995,47(1):136-55.
[2]ZHOU QR.Opportunity and ability:and flow and employment of rural labor in Chian[J].Management World,1997(5):81-100.(in Chinese)
[3]WUMC.Empirical analysis of the relationship between family social capital and household income[J].Shandong Economy,2006(2):19-22.(in Chinese)
[4]C.Grootaert.Does social capital help the poor--A synthesis of findings from the local level institutions studies in Bolivia,Burkina Faso,and Indonesia[J].Local Level Institutions Working Paper No.10 of the World Bank,2002.
[5]XIE ZL.Study of the influence factors of differences in personal income--based on the analysis of human capital and social capital in China[D].Nankai University,2009.(in Chinese)
[6]Chaoming Wang.Social capital and poverty:an interpretation of theoretical framework[J].Contemporary Economics,2009(17):11-13.(in Chinese)
[7]Bourdieu P.The forms of capital in education:culture,economy,and society[M].Oxford University Press,1997.
[8]Kehoe,Timothy J,Levine,et al.On characterizing equilibria of economies with externalities and taxes as solutions to optimization problems[J].Economic Theory,Springer,1992,2(1):43-68.
[9]Marcel Fafchamps,Bar Minten.Returns to social network capital among traders[N].Oxford Economic Papers,2002,54(2).
[10]Hirokazu Ishise,Yasuyuki Sawada.Aggregate returns to social capital:Estimates based on the augmented augmented-Solow model[J].Journal of Macroeconomics,2009,31(3):376-393.
[11]Putnam RD.Making democracywork:civic traditions in modern Italy Princeton[M].Princeton university press,1993.
[12]Knack S.,P.Keefer.Does social capital have an economic pay-off A cross-country investigation[J].Quarterly Journal of Economics107:1252-1288.
[13]Guiso L,Sapienza P,Zingales L.The role of social capital in financial development[J].The American Economy Review,2004,94(3):526-556.
[14]Beugelsdijk S,Schaik T.Social capital and growth in European regions:An empirical test[J].European Journal of Political Economy,2005b,21(2):301-324.
[15]Rupasingha A,S.J.Goetz,D.Freshwater.The production of social capital in US countries[J].Journal of Socio-Economics,2006(35):83-101.
[16]De Silva,Mary J.,Huttly,etal.Social capital and mental health:A comparative analysis of four low income countries[J].Social Science&Medicine,2007,64(1):5-20.
[17]Putnam R.Bowling alone:America’s declining social capital[J].Journal of Democracy 1995,6(1):65-78.
[18]Nunnally J.Psychometric theory[M].McGraw-Hill,New York,1978.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research on the Grain Producers around the Year of Chinese Population Peak
- Studies on the Development of Walnut Industry in Shangluo City Based on SWOT
- Evaluation of Grow th of Agricultural Listed Companies Based on AHP Weighting Method
- Competitiveness of China's Agricultural Product Export to the U-nited States of America
- The Curriculum System Development of Sightseeing Agriculture Major Based on Work Flow
- Land Use Conflict Changes and Driving Forces of Beibu Gulf Economic Zone
