RHEL7中远程块存储的应用与配置
2014-03-13王金恒
王金恒
RHEL7中远程块存储的应用与配置
王金恒
(广东技术师范学院天河学院,广东 广州 510540)
最新版RHEL7中许多技术相对于RHEL6变化较大,本文重点介绍在RHEL7下iSCSI管理中提供存储的Target端与访问存储Initiator端的原理、应用与配置。
存储;Target;Initiator
1.引言
存储系统的架构主要有DAS、NAS、SAN。DAS是直连式存储,处理数据完全依赖于主机操作系统,因此对数据进行处理的时候,就会影响到主机的性能,比如数据的备份与还原,这样对业务系统影响很大;NAS是网络附加存储,它主要通过交换机连接服务器并提供NFS或CIFS文件系统存储,性价比高,扩展能力也强,但是开销高,延迟大,不利于高性能的集群应用;SAN是存储区域网络,它主要是通过光缆或者以太网电缆连接服务器并提供Block存储,价格昂贵,但高带宽,低延迟,能满足电信、银行的大数据量的关键业务应用。
iSCSI属于SAN的一种,它主要是在TCP/IP网络上传输SCSI指令,来访问远程的Block存储。随着以太网的快速发展,iSCSI的市场销量也在快速发展,虽然带宽和性能与FC SAN还存在一定的差距,但是可以节约企业很多成本,而且其基于以太网,管理维护都变得简单。
2.远程块存储的应用与配置
iSCSI提供存储的一端称为Target,而访问存储的一端是Initiator。RHEL7中可以实现Target端,在配置时与RHEL6有所差别,在RHEL7主要是通过targetcli来进行配置,访问存储在RHEL6与RHEL7中差不多。下面就重点介绍一下在RHEL7中,两端具体配置。
如图1所示,Target上准备提供两个存储,分别是300М的逻辑卷/dev/rhel/lv01,200М的文件/diskfile,服务器的IQN是iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1,而只有客户端的IQN为iqn.2014-09.com.example:desktop1才可以访问Target端的存储,服务器工作在IP为192.168.1.1的端口3260上,具体的步骤如下:

图1 Target端的架构拓扑设计图
2.1 提供存储的Target端的应用与配置
步骤1:准备存储
(1)300М的逻辑卷
[root@localhost~]#lvcreate-n lv01-L 300М rhel
(2)200М的文件,文件可以不必提前创建
步骤2:安装target端的管理工具targetcli
[root@localhost~]#yum install targetcli-y
步骤3:进入targetcli模式,对target进行配置
[root@localhost~]#targetcli
(1)创建一个block存储
/>/backstores/block create block1/dev/rhel/lv01
(2)创建一个文件存储
/>/backstores/fileio create file1/diskfile 200М
(3)为target创建一个IQN(iSCSI Qualified Name),此步骤会创建一个TPG(Target Portal Group)。
/>/iscsi create iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1 Created target iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1.Created TPG 1.
(4)为客户端配置ACL,只有iqn.2014-09.com.example:desktop1这个客户端才可以访问此Target
/>/iscsi/iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1/tpg1/ acls create iqn.2014-09.com.example:desktop1
(5)在此TPG中创建LUN,把之前创建的存储激活,分别为LUN0与LUN1
/>/iscsi/iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1/tpg1/ luns create/backstores/block/block1
Created LUN 0.
/>/iscsi/iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1/tpg1/ luns create/backstores/fileio/file1
Created LUN 1.
(6)使Target工作在IP地址为192.168.1.1与端口为3260上
/>/iscsi/iqn.2014-09.com.example:serverdisk1/tpg1/ portals create 192.168.1.1
(7)查看最后的结果
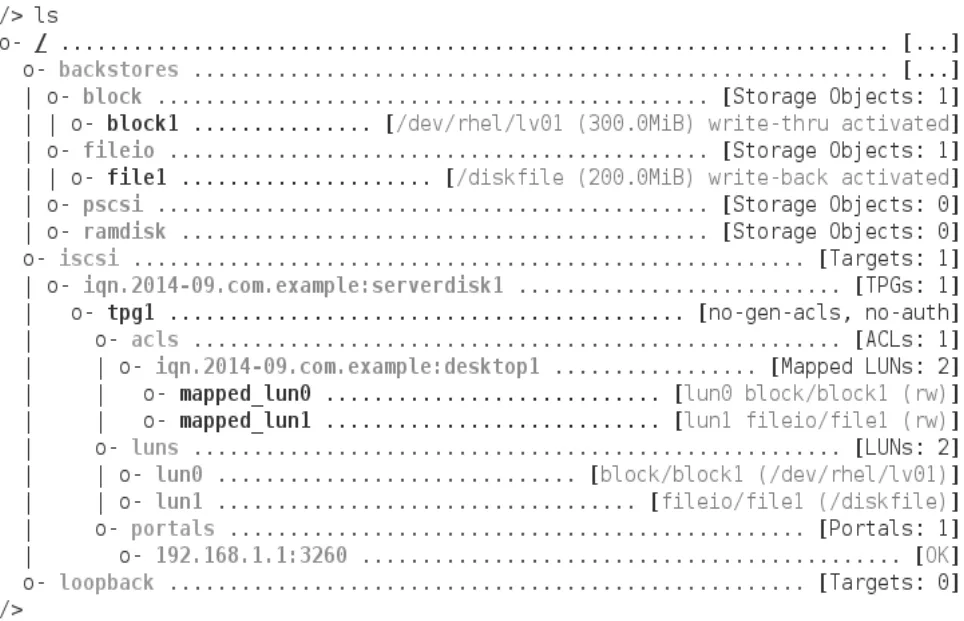
图2 Target端的配置
(8)退出并保存配置
/>exit
(9)关闭防火墙
[root@localhost network-scripts]#systemctl stop firewalld
2.2 访问存储Initiator端的应用与配置
步骤1:设置主机名并关闭防火墙
[root@localhost network-scripts]#hostnamectl set-hostname desktop1.example.com
[root@localhost network-scripts]#systemctl stop firewalld
步骤2:安装initiator端RPМ包
[root@localhost~]#yum install iscsi-initiator-utils
步骤3:在initiator端修改IQN
[root@localhost~]#vim/etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi
InitiatorName=iqn.2014-09.com.example:desktop1
步骤4:启动并启用iscsi服务
[root@localhost~]#systemctl enable iscsi
[root@localhost~]#systemctl start iscsi
步骤5:发现Target端存储
[root@localhost~]# iscsiadm-m discovery-t st-p 192.168.1.1
192.168.1.1: 3260, 1 iqn.2014- 09.com.example:serverdisk1
步骤6:登录Target端存储
[root@localhost~]#iscsiadm-m node-T iqn.2014-09. com.example:serverdisk1-p 192.168.1.1-l
步骤7:查看新添加的iSCSI设备,发现已经多了sdb与sdc。
[root@localhost~]#lsblk
<输出省略>
步骤8:格式化/dev/sdb
[root@localhost~]#mkfs-t xfs/dev/sdb
步骤9:查看/dev/sdb的UUID号码
[root@localhost~]#blkid/dev/sdb
/dev/sdb: UUID="907fa63c-1466-4a93-9996-cefcfd3a781d"TYPE="xfs"
步骤10:写入/etc/fstab
[root@localhost~]#vim/etc/fstab
UUID=907fa63c-1466-4a93-9996-cefcfd3a781d/database
xfs_netdev 0 0
步骤11:创建挂载点
[root@localhost~]#mkdir/database
步骤12:测试挂载
[root@localhost~]#mount/database
[root@localhost~]#df-h/database
Filesystem Size UsedAvail Use%Мounted on
/dev/sdb 297М 16М 282М 6%/database
3.总结
RHEL7中的Target端的配置变化比较大,相比RHEL6中的修改文件的配置,变得更加复杂,但是配置思路还是非常清晰的。在实际应用中,大部分的企业会购买相关的iSCSI存储,本文提供的远程块存储的应用与配置技术能够给企业的管理员和部分自学RHEL7的爱好者提供很好的参考。
[1]赵立权,翟勇,凤羽辉.高校Linux教学势在必行[J].云南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2010,(05).
[2]念青.Red Hat Linux 7.3安装(二)[J].电脑爱好者,2012,(17).
TheApplication and Configuration of RHEL7 Remote Block Storage
Wang Jinheng
(Tianhe College of Guangdong Polytechnic Normal University,Guangzhou 510540,Guangdong)
tract】 Мany technologies of the latest version of RHEL7 changes greatly comparing to RHEL6.This paper emphatically introduces the principle,application and configuration of Target terminal and Initiator terminal in iSCSI under the RHEL7.
words】 storage;target;initiator
王金恒,女,湖南衡阳人,硕士,讲师,研究方向:网络与Web技术。
