航头镇2010—2012年户籍人口死亡监测分析
2014-03-10陈兰兰
陈兰兰
摘 要 目的:分析航头镇3年户籍人口死亡率、死因顺位及潜在减寿年数。方法:对航头镇3年户籍人口死亡结果进行ICD-10编码,分析不同年龄组死亡人数、死因顺位及潜在减寿年数。结果:该社区标化死亡率为6.79‰,男性高于女性;死因前5位为循环系统、肿瘤、呼吸系统、损伤和中毒及消化系统,占总死亡人数的91.49%;期望寿命为82.56岁,其中男性为79.59岁,女性为85.19岁;寿命损失最为严重的前3位依次为肿瘤、损伤中毒和循环系统疾病。结论:该社区主要死因为循环系统、肿瘤、呼吸系统、损伤和中毒及消化系统,应加快家庭医生队伍建设,加强对慢性病病人的健康促进工作。
关键词 死因统计 死因顺位 期望寿命 潜在减寿年数 死亡监测
中图分类号:R195 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2014)04-0045-04
Analysis of the statistics of the death causes of
household population in Hangtou Town from 2010 to 2012
CHEN Lanlan
(Hangtou Community Health Service Centre of Pudong New District, Shanghai 201316, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To analyze the mortality rate, order of the death causes and potential years of life lost of household population in Hangtou Town within three years. Methods: The causes of death in household population in Hangtou Town from 2010 to 2012 were coded with ICD-10 and the number of deaths, order of the death causes and potential years of life lost were analyzed in different age groups. Results: The standardized mortality rate was 6.79‰ in this community and the rate of the male was higher than that of the female. The top five leading death causes were circulatory system, tumors, respiratory system, injury and poisoning and digestive system, which totally accounted for 91.49% in all deaths. Their life expectancy at the birth was 82.56 years old, among whom the male was 79.59 years old and the female 85.19 years old. The top three leading diseases which resulted in the most serious loss of life were tumors, injury and poisoning and circulatory system diseases. Conclusion: The main causes of deaths in this community were circulatory system, tumors, respiratory system, injury and poisoning, and digestive system. The development of family doctors teams should be accelerated and health promotion should be strengthened for patients with chronic diseases.
KEY WORDS statistics of the death causes; order of the death causes; life expectancy; potential years of life lost; death detection
引起人类疾病和死亡的危险因素种类很多,由于不良行为生活方式导致的慢性非传染性疾病和意外伤害要占总死亡数的70.0%[1]。为了解航头镇居民的死因现状及其规律,评价居民的健康状况及行为方式的改变,和主要死因对健康的影响,我们进行了2010-2012年航头镇居民死亡监测分析。
1 材料与方法
1.1 资料来源
通过上海市公安局航头派出所获得航头镇2010-2012年户籍人口数及年龄构成。通过上海市死因监测系统获得航头镇2010-2012年户籍人口的个案监测信息,死因分类依据国际死因分类标准ICD—10分类编码。对不明原因死亡病例或填写不规范病例,均由航头社区卫生服务中心死亡统计条线人员进行核查。
1.2 分析指标
人口构成、粗死亡率、标准化死亡率(采用2011年全国人口结构标化)、死因构成比、期望寿命、潜在减寿年数(PYLL)、平均减寿年(AYLL)、减寿率(potential years of life lost rate, PYLLR)。减寿率= 减寿年÷统计组总人口数×1000‰
1.3 统计方法
将上海市死因监测系统中航头镇2010-2012年户籍人口的个案监测信息导出,汇总整理,使用Excel及SPSS 16.0软件进行统计分析。
使用简略寿命表法计算2010-2012年户籍人口的期望寿命。以70岁以下死亡为早死年龄,使用精确法计算2010-2012年户籍人口的潜在减寿年数、平均减寿年数及减寿率。
2 结果
2.1 全人口死亡情况及年龄别死亡率
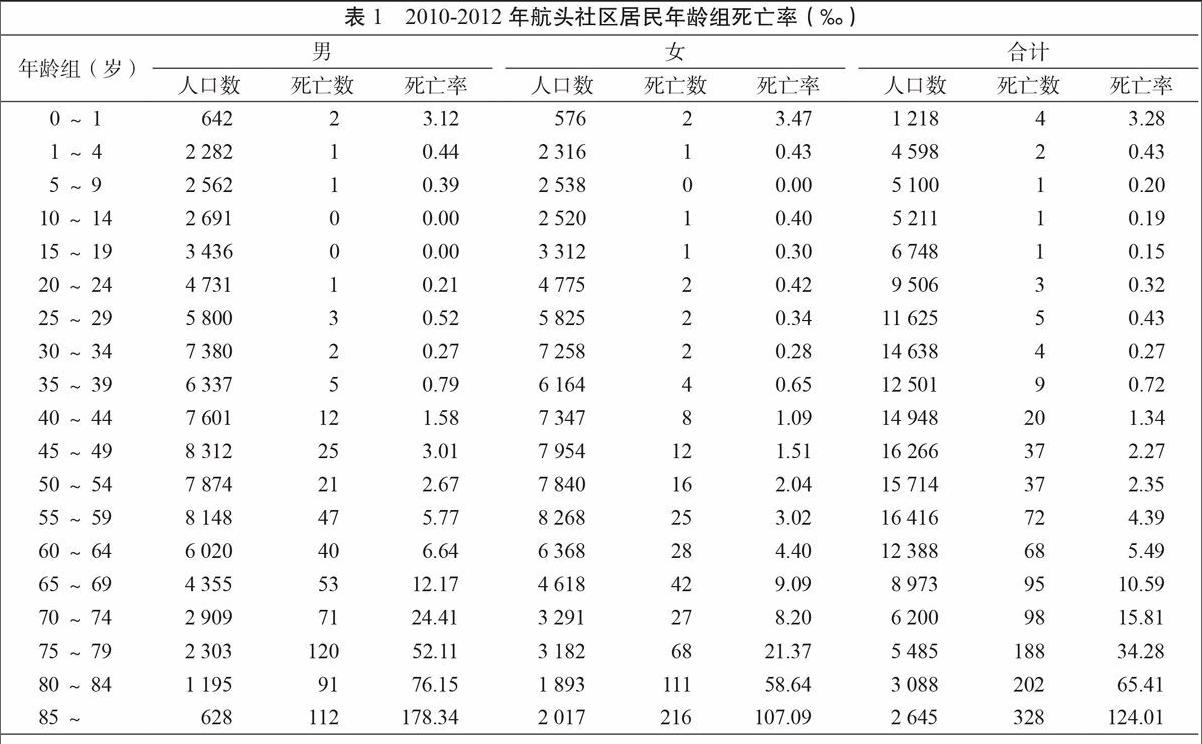
2010-2012年航头镇平均人口数为57 756人,其中男性28 402人,女性29 354人。3年死亡总人数为1 175人,其中男性607人,女性568人。总死亡率为6.78‰,其中男性7.12‰,女性6.45‰。标化死亡率为6.79‰,其中男性7.74‰,女性5.93‰。0~39岁年龄组男女死亡率较接近,40岁以上年龄组人口死亡率进入快速上升通道,死亡率逐年增加,且男性死亡率明显高于女性(表1)。
2.2 死因顺位
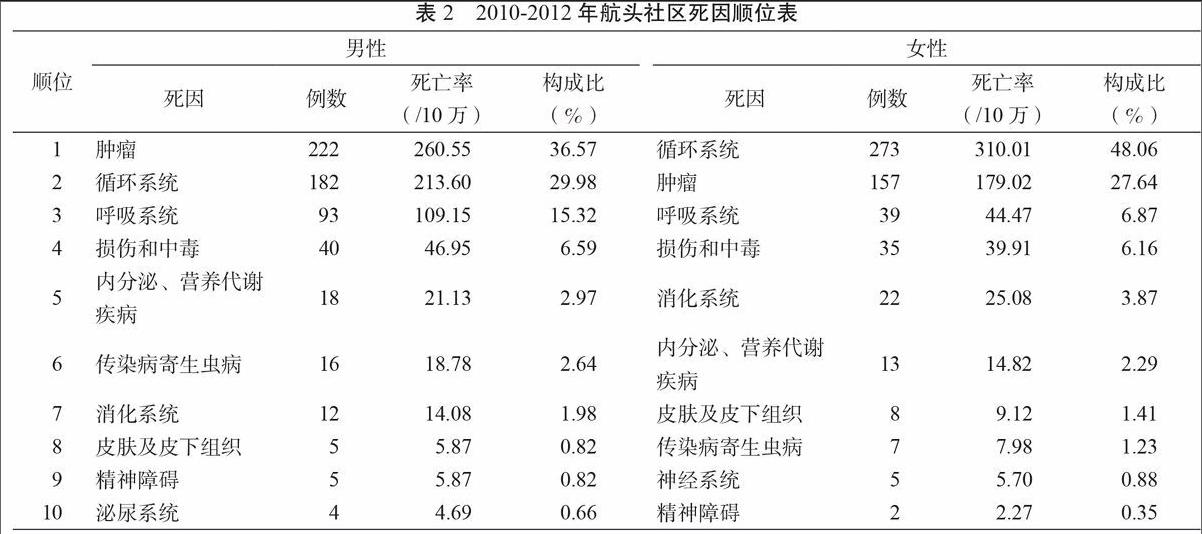
前10位为:循环系统、肿瘤、呼吸系统、损伤和中毒、消化系统、内营代、传染病和寄生虫病、皮肤及皮下组织疾病、神经系统疾病、精神障碍。前3位的循环系统、肿瘤和呼吸系统,占总死亡构成的82.21%。男性死因首位为肿瘤,其次为循环系统疾病与女性相反(表2)。
2.3 期望寿命
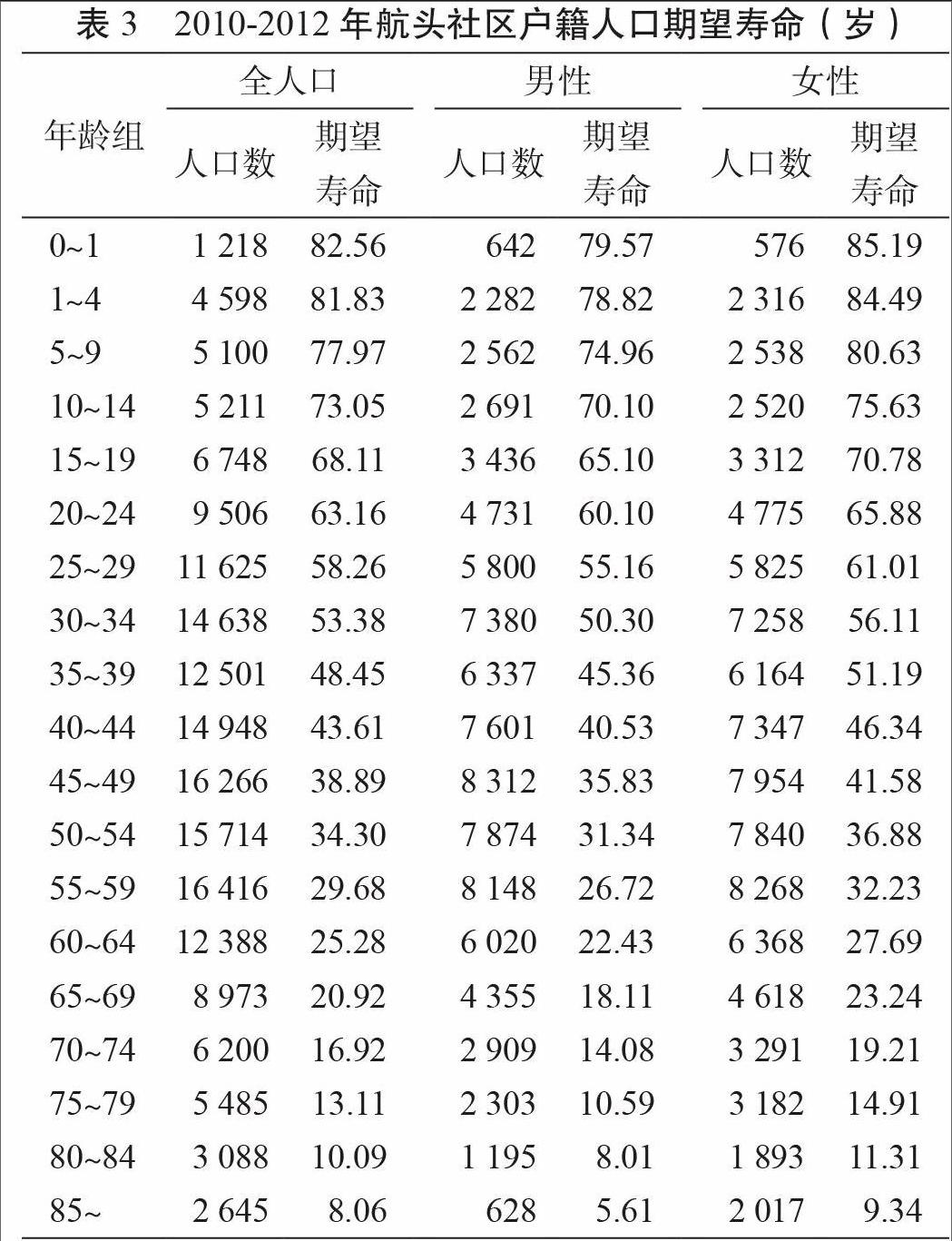
2010-2012年航头社区0~1岁新生儿期望寿命为82.56岁,其中男性为79.59岁,女性为85.19岁(表3)。
2.4 减寿年数(PYLL)
肿瘤是致使寿命损失最为严重的因素,总共致使寿命损失2 559人年,其中男性1 468人年,女性1 091人年。男性平均减寿年数最长因素为损伤和中毒,达到20.56岁,女性为先天性心脏病,达到55.50岁(表4)。
3 讨论
2010-2012年航头社区65岁以上户籍人口占15.23%,大大超过了老年化国家人口7%的标准。2010-2012年航头社区的年平均标化死亡率为6.79‰,明显低于2011年国家公布的7.14‰的人口死亡率。
2010-2012年航头社区死因顺位前3位分别为循环系统、肿瘤、呼吸系统疾病,占到总死亡构成比的82.21%,航头社区户籍人口主要致死因素为慢性非传染病。这与人们生活水平的提高,生活行为习惯的变化,吸烟、饮酒、多食少运动、精神压力过大等不良行为生活方式越来越多的出现有很大关系。
2010-2012年航头社区人均期望寿命为82.56岁,较之上海市2011年期望寿命82.51岁略高。航头社区男性期望寿命为79.57岁,女性为85.19岁,而上海市2011年男性期望寿命为80.23岁,女性为84.80岁。航头社区男性期望寿命略低于上海市平均水平,女性略高,但总体水平相差不大,表明航头社区人均期望寿命接近全市平均水平。
调查显示,航头社区居民寿命损失最主要的疾病是肿瘤,而损伤和中毒是低年龄组的首位原因,与文献报道基本一致[2]。因此,进一步加强社区肿瘤三级预防,提高围产期及新生儿保健水平,可有效降低婴儿死亡率[3]。
参考文献
[1] 孔灵芝. 慢性非传染性疾病流行现状、发展趋势及防治策略[J]. 中华慢性病预防与控制, 2002, 10(1): 1-2.
[2] 邹志霆, 潘忠伦, 黄艳萍. 贵州省监测人群潜在期望减寿年数分析[J]. 实用预防医学, 2005, 39(3): 220-221.
[3] 杨春凤, 陈仲庆, 刘文斌, 等. 上海市五角场镇2010年居民死因分析[J]. 上海预防医学, 2012, 24(3): 160-162.
(收稿日期:2013-08-22)
