Effect of Daidzein on Ileum Microflora Biodiversity in Hy-Line Variety Brown Layers
2014-03-01JiGuozhenandWangLi
Ji Guo-zhen,and Wang Li
College of Life Science and Technology,Southwest University for Nationalities,Chengdu 610041,China
Introduction
Intestinal bacteria play an important role in poultry based on their effects on the production,digestion,nutrient absorption,growth rate,the quality and safety of products (Gong et al.,2002;Singh et al.,2014).The natural process,establishing the climax community and inhibiting the pathogens by intensive competition,may be disturbed in intensive production conditions (Józefiak and Sip,2013).Bacterial communities of chicken can be affected by various factors,such as diet composition and feed physical traits,animal immunological and physiological responses to stress and pathogens,and feed additives (Hume et al.,2006).So far,there are many studies about the influence of feed additives on chicken microflora biodiversity,focusing on antibiotics (Knarreborg et al.,2002;Hume et al.,2006;Pedroso et al.,2006),tetracycline (Fairchild et al.,2005),and prebiotic supplementation (Kim et al.,2011).
Daidzein is present in a number of plants and herbs (Fedoreyeva et al.,2000).It can be found in food,such as soybean and its derivates (Tang et al.,2013;Cheong et al.,2014).Daidzein is widely used because of varied functions including anticancer (Choi and Kim 2013),improvement of glucose homeostasis (Cheong et al.,2014),antiestrogenic and neuroprotective effects (Choi et al.,2013).And it is also used in poultry production.Dietary supplementation of daidzein to poultry can improve preovulatory follicle development (Liu et al.,2007;Liu and Zhang et al.,2008),eggshell thickness,eggshell percentage,eggshell strength,eggshell Ca concentration (Etxeberria et al.,2013) and decrease the mortality (Shi et al.,2013).However,these studies are mostly concerning the metabolite,chemical nature of daidzein and the effect on performance.In this study,two molecular typing methods were used to preliminarily examine the effects on Hy-Line variety brown layers ileum microflora biodiversity with different levels of daidzein.
Materials and Methods
Animals,treatments,and samplings
A total of 660 40-week-old Hy-Line variety brown layers were randomly assigned in five dietary treatments.Each treatment had six replicates of 22 layers.The first three-week was preliminary trial period,and then normal experimental stage was 12 weeks from 43-week-old to 55-week-old.Each dietary treatment contained the same corn-soybean-mixed basal diet suggested by USA Hy-Line Company.The ration of the five dietary treatments was blended with different levels of the daidzein as 0,10,50,100,and 500 mg · kg-1.The hens were bred twice a day,with three ladder type-cage cultivation,free-foraging and timing-feeding.Then content samples from ileum were collected at 55-week-old.
DNA extraction
Two layers were randomly selected from each group.Terminal ileum content of each layer was sampled for 1 g.Samples of 12 layers of each treatment were well mixed.Then,total bacterial DNA was extracted using QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit,following the manufacturers'instructions.
Conditions used for RAPD-PCR
Ten kinds of primers were used in the experiment (S1,GTTTCGCTCC;S2,TGATCCCTGG;S3,CATCCC CCTG;S4,GGACTGGAGT;S5,TGCGCCCTTC;S6,TGCTCTGCCC;S7,GGTGACGCAG;S8,GTCC ACACGG;S9,TGGGGGACTC;S10,CTGCTGGG AC).The total volume of the reaction mixture was 20 μL consisting of 1.6 μL of genomic DNA as template,3 μL of PCR buffer (without Mg2+),1.8 μL of Mg2+,0.2 μL of Taq DNA polymerase,2.4 μL of dNTP Mix (2 500 μmol · L-1),4 μL of primer (10 μmol · L-1),and 7 μL of autoclaved deionized water.The amplification parameters included four cycles of 94℃,5 min;36℃,30 s;72℃,5 min,and then 40 cycles of 94℃,1 min;32℃,1 min;72℃,2 min.10 μL of PCR products was analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Conditions used for ERIC-PCR
Two primers of ERIC were used (E1,5'-ATGTAAGC TCCTGGGGATTCAC-3';E2,5'-AAGTAAGTGAC TGGGGTGAGCG-3').PCR reaction was performed in 20 μL with 2.3 μL of genomic DNA as template,2 μL of PCR buffer,1.4 μL of Mg2+,0.2 μL of Taq DNA polymerase,1.6 μL of dNTP Mix (2 500 μmol · L-1),1.2 μL of the concentrations each forward and reverse primers (10 μmol · L-1) and 10.1 μL of autoclaved deionized water.The reaction condition included an initial denaturation of 7 min at 94℃,followed by 40 cycles of 1 min at 95℃,1 min at 48℃,and 8 min at 65℃,with a final extension of 16 min at 65℃.10 μL PCR products were analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Data processing
Fingerprints of RAPD-PCR and ERIC-PCR were counted and analyzed by NTsys 2.10e.
Results
Total bacterial DNA was extracted from the sample of each concentration group.Then,10 μL aliquot of each extracted DNA was analyzed by 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis.The result showed that the length of DNA fragment was 23 000 bp (Fig.1).Its quality was suitable for further experiments.
RAPD-PCR random primer S10 with multi-stripe was selected.As shown in Fig.2,bands of RAPD fingerprints were ranging in size from about 400 bp to 1 200 bp and the number of bands varied between 2 and 5.Fingerprints of ERIC-PCR were distributed from about 100 bp to 1 900 bp,and the number of bands was from 5 to 10 in Fig.3.Combining Fig.2 with Fig.3,the number of bands was the most in 10 mg · kg-1and 50 mg · kg-1daidzein groups.And there was a drastic reduction of the f ingerprint bands in 500 mg · kg-1daidzein group.
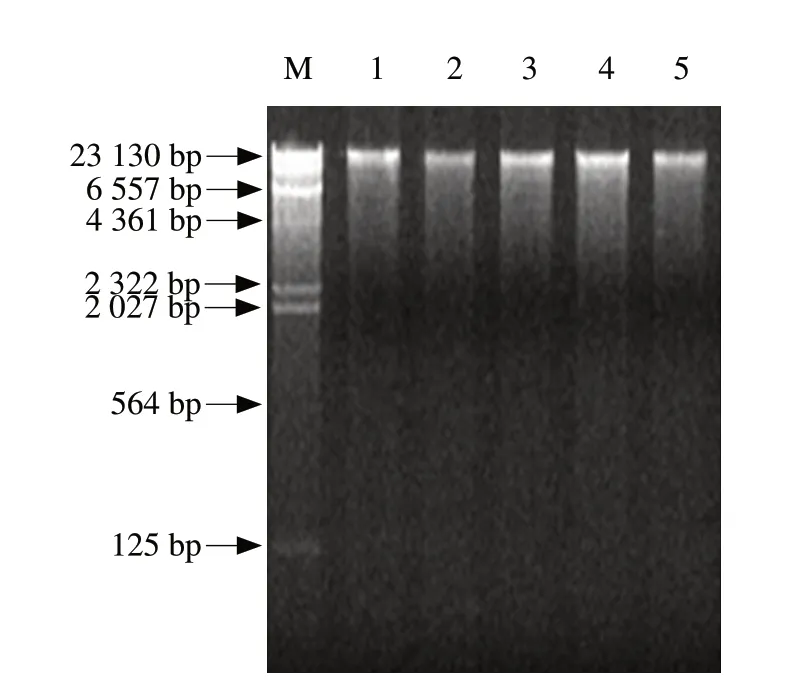
Fig.1 Total bacteria DNA
Cluster analyses based on RAPD-PCR showed that similarity of ileum microflora ranged from 33.3% to 83.3% (Fig.4).Similarity among 500 mg · kg-1group and other groups was 33.3%.Similarity between the groups of 10 mg · kg-1and 50 mg · kg-1was 83.3%.The result of ERIC-PCR indicated that similarity ranged from 50.0% to 90.0% (Fig.5).Similarity among 500 mg · kg-1group and other groups was 50.0%,and similarity between group of 10 mg · kg-1and 50 mg · kg-1was 90.0%.Four samples were clustered,except the group of 500 mg · kg-1.According to two methods,the conclusions were basically the same.
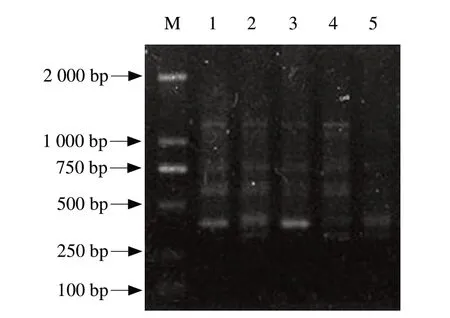
Fig.2 RADP-PCR fingerprints of five samples
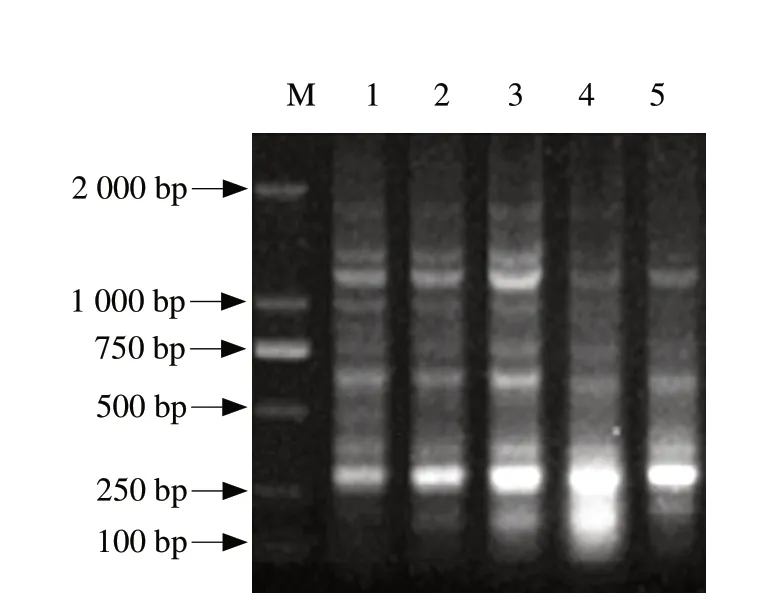
Fig.3 ERIC-PCR fingerprints of five samples
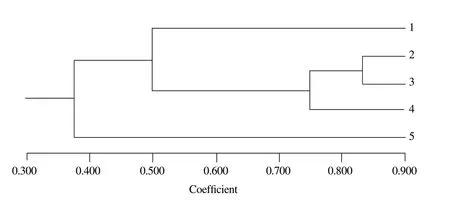
Fig.4 Dendrogram generated using NTsys2.10e based on RADP-PCR fingerprints (Fig.1)
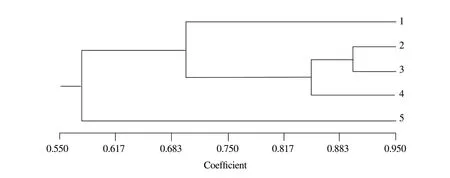
Fig.5 Dendrogram generated using NTsys2.10e based on ERIC-PCR fingerprints (Fig.2)
Discussion
Random amplified polymorphic deoxyribonucleic acid analysis by PCR (RAPD-PCR) is a widely-used PCRfingerprinting technique which gives an advantage in which molecular preliminary information of the species studied is not necessary and polymorphism pattern obtained usually varies among the species.This technique involves the amplification of random segments of genomic DNA,using short arbitrary primers without the requirement of previous knowledge of genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)(Welsh and McClelland,1990).The number and positions of primer binding sites are unique to a particular bacterial strain (Sabat et al.,2013).RAPD-PCR,a molecular typing method,is used to identify the bacterial (Rezinciuc et al.,2013),detect genetic variability (Saxena et al.,2014) and study genotoxicity (Rocco et al.,2014;Salem et al.,2014).Enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC) sequences,known as intergenic repeat unit,are presented in many copies in the genomes of Escherichia coli,Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria (Hulton et al.,1991).In ERIC-PCR,a band pattern is obtained by amplification of genomic DNA located between ERIC elements or between ERIC elements and other repetitive DNA sequences (Zulkifli et al.,2009).This method is utilized to study the genetic diversity (Fendri et al.,2013;Ramazanzadeh et al.,2013) and genotypic characterization of bacteria (Paixao et al.,2013).In this study,two molecular typing methods were used to analyze assessment of Hy-Line variety brown layers ileum microflora biodiversity with different levels of daidzein to make the result be convinced.
The studies on daidzein mostly focus on two directions.One is the point of daidzein chemical nature,resemblance with estrogen (Bayer et al.,2001;Staar et al.,2005),and metabolite and decomposition of the daidzein (Kang et al.,2007;Rufer et al.,2008;Matthies et al.,2009).The other one is about daidzein as supplements in the feed,especially on poultry.There were some differences in results because of diversity in environment,subject,purpose,and so on.However,discovery of present study focused on the changes of ileum microflora biodivesity with different levels of daidzein,consisted with some of previous researches.Supplementation of 10 mg · kg-1daidzein significantly increased egg weight (P<0.01),and supplementation of 50 mg · kg-1daidzein significantly increased laying rate and decreased the riao of feed to egg (P<0.01).Supplementation of 50 mg · kg-1daidzein brought the conomic benefits (Gu et al.,2013).Spleen index (P<0.05),ND-HI titers and ERFC (P>0.05) of laying hens were improved by 20 mg · kg-1daidzein;ND-HI titers were enhanced significantly (P<0.05),and spleen index and ERFC (P>0.05) increased at the dose of 30 mg · kg-1.Dietary daidzein can improve humoral immune function and cell immune function (Gu et al.,2004).After feeding Hy-Line variety brown layers diets supplemented with 0,10,50 and 100 mg · kg-1of daidzein for 12 weeks,eggshell thickness,eggshell percentage,eggshell strength,and eggshell Ca concentration increased linearly with increasing dietary daidzein supplementation,and the mean egg production,egg mass and feed conversion of the whole experiment period were significantly quadratic response to increasing dietary daidzein supplement.No observed adverse effect level was considered to be 50 mg · kg-1(Gu et al.,2013;Shi et al.,2013).
Conclusions
Effects on Hy-Line variety brown layers ileum microflora biodiversity with different levels of dadzein were analyzed by RAPD-PCR and ERIC-PCR.Ileum microflora biodiversity with 10 mg · kg-1or 50 mg · kg-1of daidzein was indicated rich and might be beneficial to intestinal bacteria of Hy-Line variety brown layers.
Cheong S H,Furuhashi K,Ito K,et al.2014.Daidzein promotes glucose uptake through glucose transporter 4 translocation to plasma membrane in L6 myocytes and improves glucose homeostasis in Type 2 diabetic model mice.Journal of Nutrition Biochemistry,25(2): 136-143.
Choi E J,Kim G H.2013.Antiproliferative activity of daidzein and genistein may be related to ERα/c-erbB-2 expression in human breast cancer cells.Molecular Medicine Reports,7(3): 781-784.
Choi R C,Zhu J T,Yung A W,et al.2013.Synergistic action of flavonoids,baicalein,and daidzein in estrogenic and neuroprotective effects: a development of potential health products and therapeutic drugs against alzheimer's disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/635694.
Etxeberria U,Fernández-Quintela A,Milagro F I,et al.2013.Impact of polyphenols and polyphenol-rich dietary sources on gut microbiota composition.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,61(40): 9517-9533.
Fairchild A S,Smith J L,Idris U,et al.2005.Effects of orally administered tetracycline on the intestinal community structure of chickens and on tet determinant carriage by commensal bacteria and Campylobacter jejuni.Appl Environ Microbiol,71(10): 5865-5872.
Fedoreyeva S A,Pokushalovaa T V,Veselovaa M V,et al.2000.Isoflavonoid production by callus cultures of Maackia amurensis.Fitoterapia,71(4): 365-372.
Fendri I,Hassena A B,Grosset N,et al.2013.Genetic diversity of foodisolated Salmonella strains through Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) and Enterobacterial Repetitive Intergenic Consensus (ERICPCR).PLoS One,8(12): e81315.
Gong J H,Forster R J,Yu H,et al.2002.Molecular analysis of bacterial populations in the ileum of broiler chickens and comparison with bacteria in the cecum.FEMS Microbiology Ecology,41(3): 171-179.
Gu H,Shi S R,Tong H B,et al.2013.Effects of daidzein on performance,blood parameters and economic benefits in laying hens during the late laying period.Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,25(2): 390-396.
Gu Z L,Ma X H,Wu X J,et al.2004.Effect of dietary daidzein on immune function in laying hens.Chinese Journal of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine,40(10): 15-17.
Gu H,Shi S R,Chang L L,et al.2013.Safety evaluation of daidzein in laying hens: part II.Effects on calcium-related metabolism.Food and Chemical Toxicology.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.064.
Hulton C S,Higgins C F,Sharp P M.1991.ERIC sequences: a novel family of repetitive elements in the genomes of Escherichia coli,Salmonella typhimurium and other enterobacteria.Molecular Microbiology,5(4): 825-834.
Hume M E,Clemente-Hernandez S,Oviedo-Rondon E O.2006.Effects of feed additives and mixed Eimeria species infection on intestinal microbial ecology of broilers.Poultry Science,85(12): 2106-2111.
Józefiak D,Sip A.2013.Bacteriocins in poultry nutrition–a review.Annals of Animal Science,13(3): 449-462.
Kang N J,Lee K W,Rogozin E A,et al.2007.Equol,a metabolite of the soybean isoflavone daidzein,inhibits neoplastic cell transformation by targeting the MEK/ERK/p90RSK/activator protein-1 pathway.The Journal of Biological Chemistry,282(45): 32856-32866.
Kim G B,Seo Y M,Kim C H,et al.2011.Effect of dietary prebiotic supplementation on the performance,intestinal microflora,and immune response of broilers.Poultry Science,90(1): 75-82.
Knarreborg A,Simon M A,Engberg R M,et al.2002.Effects of dietary fat source and subtherapeutic levels of antibiotic on the bacterial community in the ileum of broiler chickens at various ages.Applied and Environmental Microbiology,68(12): 5918-5924.
Liu H Y,Zhang C Q.2008.Effects of daidzein on messenger ribonucleic acid expression of gonadotropin receptors in chicken ovarian follicles.Poultry Science,87(3): 541-545.
Liu H Y,Zhang C Q,Ge C,et al.2007.Effects of daidzein on mRNA expression of gonadotropin receptors and P450 aromatase in ovarian follicles of white silky fowls.Association Of Animal Production Societies,20(12): 1827-1831.
Matthies A,Blaut M,Braune A.2009.Isolation of a human intestinal bacterium capable of daidzein and genistein conversion.Applied and Environmental Microbiology,75(6): 1740-1744.
Paixao R,Moreno L Z,Sena de Gobbi D D,et al.2013.Genotypic characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica biotype 4/O:3 isolates from pigs and slaughterhouses using SE-AFLP,ERIC-PCR,and PFGE.Journal of Pathogens,50(4): 412-418.
Pedroso A A,Menten J F M,Lambais M R,et al.2006.Intestinal bacterial community and growth performance of chickens fed diets containing antibiotics.Poultry Science,85(4): 747-752.
Ramazanzadeh R,Zamani S,Zamani S.2013.Genetic diversity in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli by enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus (ERIC)-PCR technique in Sanandaj hospitals.Iranian Journal of Microbiology,5(2): 126-131.
Rezinciuc S,Galindo J,Montserrat J,et al.2013.AFLP-PCR and
RAPD-PCR evidences of the transmission of the pathogen Aphanomyces astaci (Oomycetes) to wild populations of European crayfish from the invasive crayfish species,Procambarus clarkii.Fungal Biology.http://dx.doi.ory/10.1016/j.funbio.2013.10.007.
Rocco L,Valentino I V,Scapigliati G,et al.2014.RAPD-PCR analysis for molecular characterization and genotoxic studies of a new marine fish cell line derived from Dicentrarchus labrax.Cytotechnology,66(3): 383-393.
Rufer C E,Bub A,Möseneder J,et al.2008.Pharmacokinetics of the soybean isoflavone daidzein in its aglycone and glucoside form: a randomized,double-blind,crossover study.American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,87(5): 1314-1323.
Sabat A J,Budimir A,Nashev D,et al.2013.Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance.Euro Surveill,18(4): 20380.http://www.enrosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?Ariticleld=20380.
Salem Z B,Capelli N,Grisey E,et al.2014.First evidence of fish genotoxicity induced by heavy metals from landfill leachates: the advantage of using the RAPD-PCR technique.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,101: 90-96.
Saxena S,Verma J,Shikha,et al.2014.RAPD-PCR and 16S rDNA phylogenetic analysis of alkaline protease producing bacteria isolated from soil of India: identification and detection of genetic variability.Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2014.03.001.
Shi S R,Gu H,Chang L L,et al.2013.Safety evaluation of daidzein in laying hens: part I.Effects on laying performance,clinical blood parameters,and organs development.Food and Chemical Toxicology,55: 684-688.
Singh K M,Shah T M,Reddy B,et al.2014.Taxonomic and genecentric metagenomics of the fecal microbiome of low and high feed conversion ratio (FCR) broilers.Journal of Applied Genetics,55(1): 145-154.
Staar S,Richter D U,Makovitzky J,et al.2005.Stimulation of endometrial glandular cells with genistein and daidzein and their effects on ERα-and ERβ-mRNA and protein expresion.Anticancer Research,25(3A): 1713-1718.
Tang S,Hu J,Meng Q,et al.2013.Daidzein induced apoptosis via down-regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and triggering of the mitochondrial pathway in BGC-823 cells.Cell Biochem Biophys,65(2): 197-202.
Welsh J,McClelland M.1990.Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers.Nucleic Acids Research,18(24): 7213-7218.
Zulkifli Y,Alitheen N B,Son R,et al.2009.Random amplified poly-
morphic DNA-PCR and ERIC PCR analysis on Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from cockles in Padang,Indonesia.International Food Research Journal,16: 141-150.
