Syndecan-1和乙酰肝素酶1在结直肠癌中的表达及对其转移和预后的影响
2014-01-23陈宇宁蒋富兵
陈宇宁 张 毅 蒋富兵
1.广东省惠州市第三人民医院消化内科,广东惠州 516002,2.广东省惠州市第三人民医院胃肠外科,广东惠州 516002
Syndecan-1和乙酰肝素酶1在结直肠癌中的表达及对其转移和预后的影响
陈宇宁1张 毅1蒋富兵2
1.广东省惠州市第三人民医院消化内科,广东惠州 516002,2.广东省惠州市第三人民医院胃肠外科,广东惠州 516002
目的 探讨Syndecan-1和乙酰肝素酶1(heparanase 1,HPA1)在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平和对其转移和预后的影响。 方法 采用原位杂交技术检测177例结直肠癌组织中Syndecan-1和HPA1的表达水平,比较Syndecan-1、HPA1 mRNA表达与结直肠癌临床病理指标、疾病预后的关系。 结果 在177例标本中,Syndecan-1 mRNA和HPA1 mRNA的阳性例数分别为75例和99例;Syndecan-1 mRNA及HPA1 mRNA阳性表达率与肿瘤浸润深度、TNM分期、淋巴结转移、远处转移和脉管癌栓密切相关(P<0.01);Syndecan-1 mRNA水平与HPA1 mRNA表达呈负相关(P<0.01);Syndecan-1 mRNA低表达平均生存时间和5年生存率低于高表达组,HPA1 mRNA阳性表达平均生存时间和5年生存率低于阴性表达组。 结论Syndecan-1低表达和HPA1高表达对结直肠癌的侵袭和转移具有协同作用;两者结合有助于术后评估疗效和判断预后。
Syndecan-1;乙酰肝素酶1;结直肠癌;预后
近三十年来,随着环境和生活方式等因素的改变,我国结直肠癌的发病率迅速增加,已成为增长最快的肿瘤之一[1-2]。Syndecan-1作为一种跨膜硫酸乙酰肝素蛋白多糖(HSPGs),是胞外基质的重要组成成分。新近研究发现,Syndecan-1与整合素、钙黏素等共同构成细胞间黏附分子复合体,参与胞间和胞外基质之间的黏附,具有促进细胞增殖,抑制肿瘤生长、转移,维持细胞分化等作用[3]。而乙酰肝素酶1(heparanase 1,HPA1)可以降解HSPGs的糖类侧链,促进肿瘤细胞浸润和转移[4]。目前关于两者对结直肠癌的转归情况报道较少,为此本研究检测了Syndecan-1和HPA1在结直肠癌组织中的表达水平,探讨它们对结直肠癌转移和预后的影响。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
收集2002年6月~2007年12月在本院消化内科和胃肠外科手术切除的原发性结直肠癌标本177例,所有患者术前均未接受放化疗,其中男129例,女48例;年龄39~76岁,平均54.8岁。除随访中死亡的病例,其余病例均随访5年以上,随访截止日期为2013年12月。生存期为从手术日期至随访截止日期或死亡日期。所有患者均签属知情同意书,本研究经过医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 实验方法
标本常规固定、脱水,石蜡包埋,切片后行Syndecan-1和HPA1 mRNA原位杂交检测。Syndecan-1和乙酰肝素酶寡核苷酸探针以及原位杂交试剂盒均购自武汉博士德公司,操作程序严格按照说明书进行。采用Masola等[5]推荐的方法,由2位病理医师采用双盲法作出判断,细胞质染成棕黄色颗粒为Syndecan-1和HPA1 mRNA阳性表现。根据阳性细胞占全部肿瘤细胞的百分比进行分级:<10%为(-);10%~50%为(+);51%~75%为(++);>75%为(+++)。 Syndecan-1 表达(-)~(+)为低表达组,(++)~(+++)为高表达组。将 HPA1 mRNA(-)者归为阴性表达组,(+)~(+++)者为阳性表达组。
1.3 统计学处理
所得数据采用SPSS 13.0软件进行统计学分析,采用χ2检验分析Syndecan-1、HPA1 mRNA表达与各项病理指标的关系,采用秩和检验进行Syndecan-1和乙酰肝素酶相关性分析,生存分析使用Kaplan-Meier法,用寿命表法计算生存率,用Log-rank检验进行比较,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 Syndecan-1 mRNA、HPA1 mRNA的表达与结直肠癌病理指标的关系
在结直肠癌177例标本中,Syndecan-1 mRNA高表达者为 75例(42.4%),低表达者 102例(57.6%);HPA1 mRNA阴性表达78例(44.1%),阳性表达99例(55.9%)。在结直肠癌标本中,Syndecan-1 mRNA和HPA1 mRNA阳性颗粒在细胞质着色(图1、图2)。Syndecan-1 mRNA和HPA1 mRNA的表达在肿瘤浸润深度、TNM分期、淋巴结转移、远处转移和脉管癌栓中差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(表 1)。Syndecan-1 mRNA 与 HPA1 mRNA的表达呈显著负相关(r=-0.832,P<0.01)。

图1 结直肠癌Syndecan-1 mRNA表达
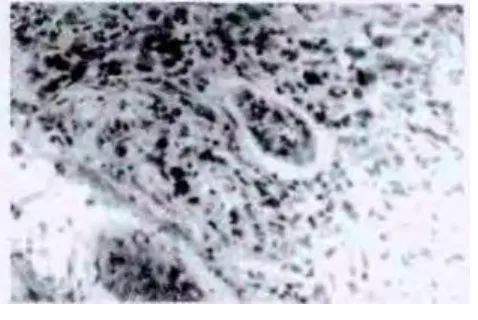
图2 结直肠癌HPA1 mRNA表达
2.2 Syndecan-1 mRNA、HPA1 mRNA表达与结直肠癌预后的关系
Syndecan-1 mRNA高表达患者的平均生存时间为65.2个月,是低表达组的2.1倍(31.3个月),5年生存率(51.6%)显著高于低表达组(26.4%)(χ2=25.97,P<0.05)(图3)。HPA1 mRNA阴性表达患者的平均生存时间为67.6个月,是阳性表达组的2.2倍(30.7个月),5年生存率(53.2%)显著高于阳性组(24.6%)(χ2=23.19,P<0.05)(图 4)。

表1 177例结直肠癌患者Syndecan-1 mRNA、HPA1 mRNA表达和病理指标的关系[n(%)]

图3 Syndecan-1表达与结直肠癌患者生存的关系

图 表达与结直肠癌患者生存的关系
3 讨论
Syndecan-1是Syndecan家族的一种表达于成熟上皮细胞、浆细胞、前B细胞表面的跨膜蛋白聚糖,其硫酸乙酰肝素侧链上可特异性地结合多种生物活性分子,与脂蛋白、病原体等胞吞吐作用有关[6-7]。有研究发现,Syndecan-1在细胞膜上的表达对维持正常肠道黏膜细胞的形态至关重要;其在大肠腺瘤向大肠癌的转化中表达缺失[8]。本研究结果显示,结直肠癌组织Syndecan-1表达降低与浸润深度、脉管侵犯、淋巴结转移、远处转移,TNM分期密切相关,说明Syndecan-1参与了结直肠癌侵袭转移的过程。目前研究发现,在机体许多恶性肿瘤形成、转移过程中,肿瘤细胞表面的Syndecan-1蛋白表达明显减少,导致细胞丧失生长抑制功能[9],使肿瘤细胞能大量增殖,并具有极强的侵袭活性[10],这与本研究结论基本符合。Syndecan-1表达降低的患者,5年生存率显著低于高表达者,提示该基因表达程度可能成为评估结直肠癌预后的指标。
HPA1多在免疫器官、平滑肌细胞等处表达,其机制包括促进肿瘤血管生成[11]、免疫监视逃逸,改变细胞间、细胞与基质间的黏附等[12]。许多研究发现,HPA1在实体肿瘤组织中的表达与临床病理资料有显著相关性,揭示了HPA1与肿瘤发展的相互关系[13-14]。本研究结果显示,HPA1的表达与结直肠癌浸润深度、淋巴结转移、脉管侵犯及远处转移等均呈正相关,且阴性表达组5年生存率明显高于阳性组。这进一步证实了HPA1与结直肠癌的侵袭和预后明显相关,与相关文献类似[15]。
亚洲人(特别是东亚人)结直肠癌的发生迅速,往往没有腺瘤这一阶段,这使得结直肠癌早期发现难度较大[16]。Syndecan-1和HPA1是很有前景的切入点,可以对结直肠癌生长全程监控,并为评估病情和预后提供有力的参考。
综上所述,Syndecan-1和HPA1对肿瘤的生长、侵袭和转移具有协同作用;联合检测Syndecan-1和HPA1有助于结直肠癌患者术后评估疗效和判断预后。
[1]Chen W,Zheng R,Zhang S,et al.Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer registries,2009[J].Chin J Cancer Res,2013,32(3):106-112.
[2]李细苟.1999~2008年中山市古镇镇居民恶性肿瘤死亡情况分析[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(18):155-158.
[3]Zhang S,Qing Q,Wang Q,et al.Syndecan-1 and heparanase:potential markers for activity evaluation and differential diagnosis of crohn′s disease[J].Inflamm Bowel Dis,2013,19(5):1025-1033.
[4]Ramani VC,Purushothaman A,Stewart MD,et al.The heparanase/syndecan-1 axis in cancer:mechanisms and therapies[J].FEBS J,2013,280(10):2294-2306.
[5]Masola V,Gambaro G,Tibaldi E,et al.Heparanase and syndecan-1 interplay orchestrates fibroblast growth factor-2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells[J].J Biol Chem,2012,287(2):1478-1488.
[6]Carulli S,Beck K,Dayan G,et al.Cell surface proteoglycans syndecan-1 and-4 bind overlapping but distinct sites in laminin α3 LG45 protein domain[J].J Biol Chem,2012,287(15):12204-12216.
[7]Manon-Jensen T,Multhaupt HA,Couchman JR.Mapping of matrix metalloproteinase cleavage sites on syndecan-1 and syndecan-4 ectodomains[J].FEBS J,2013,280(10):2320-2331.
[8]Yang B,Yoshida K,Yin Z,et al.Chemical synthesis of a hep aran sulfate glycopeptide:syndecan-1[J].Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,2012,51(40):10185-10189.
[9]Hassan H,Greve B,Pavao MS et al.Syndecan-1 modulates p-integrin-dependent and interleukin-6-dependent functions in breast cancer cell adhesion,migration,and resistance to irradiation[J].FEBS J,2013,280(10):2216-2227.
[10]Xu Y,Yuan J,Zhang Z,et al.Syndecan-1 expression in human glioma is correlated with advanced tumor pro gression and poor prognosis[J].Mol Biol Rep,2012,39(9):8979-8985.
[11]Shevelev OB,Rykova VI,Fedoseeva LA,et al.Expression of Ext1,Ext2,and heparanase genes in brain of senescence-accelerated OXYS rats in earlyontogenesis and during development of neurodegenerative changes[J].Biochemistry,2012,77(1):56-61.
[12]Rops AL,van den Hoven MJ,Veldman BA,et al.Urinary heparanase activity in patients with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant,2012,27(7):2853-2861.
[13]Peerless Y,Simon E,Sabo E,et al.Normal colon tissue and colon carcinoma show no difference in heparanase pro moter methylation[J].Exp Mol Pathol,2013,94(2):309-313.
[14]Kutsenko OS,Kovner AV,Mostovich LA,et al.Expression of heparanase-1 in prostate gland tumors[J].Bull Exp Biol Med,2012,152(3):344-347.
[15]Baker AB,Gibson WJ,Kolachalama VB,et al.Heparanase regulates thrombosis in vascular injury and stent-induced flow disturbance[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2012,59(17):1551-1560.
[16]Sung JJ,Lau JY,Goh KL,et al.Increasing incidence of colorectal cancer in Asia:implications for screening[J].Lancet Oncol,2005,6(11):87l-876.
The impact of mRNA expression of syndecan-1 and heparanase1 in relation to tumor progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer
CHEN Yu-ning1ZHANG Yi1JIANG Fu-bing2
1.Department of Gastroenterology,the Third People′s Hospital of Huizhou City in Guangdong Province,Huizhou 516002,China;2.Department ofGastrointestinal Surgery,the Third People′s Hospital of Huizhou City in Guangdong Province,Huizhou 516002,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the mRNA expression of syndecan-1 and heparanase 1 in colorectal cancer,and their relationship between the progression and prognosis of the diseases.Methods In situ hybridization was used to examine mRNA expression of syndecan-l and HPA1 in 177 specimens of colorectal cancer.The relationship between mRNA expression and pathology indicators as well as prognosis of disease was observed.ResultsThe positive numbers of syndecan-1 mRNA and HPA1 mRNA were 75 cases and 99 cases.The expression of syndecan-1 mRNA and HPA1 mRNA were related to tumor invasion depth,lymph node metastasis,TNM,distant metastasis and vessel invasion (P<0.01).There was a negative relationship between Syndecan-1 mRNA and HPA1 mRNA expression(P<0.01).The mean survival time of cases with low expression of syndecan-1 mRNA was significantly shorter than that of cases with high expression.The mean survival time of heparanase mRNA positive cases was significantly shorter than that of cases with negative expression.ConclusionThe low expression of syndecan-1 and positive expression of HPA1 can predict the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer.They can be used as markers of progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer.
Syndecan-1;Heparanase 1;Colorectal cancer;Prognosis
R735.3
A
1674-4721(2014)04(c)-0015-03
2014-03-18 本文编辑:林利利)
