Evaluation in vitro of an Experimental Antibacterial Silk Suture
2013-12-20CHENXiaojie陈晓洁Aifeng吕爱凤WANGLuPETHILESibandaHOUDandan侯丹丹LUMingkang陆明康WANGWenzu王文祖WUYonggao吴永高
CHEN Xiao-jie(陈晓洁),LÜ Ai-feng(吕爱凤),WANG Lu(王 璐) ,PETHILE Sibanda,HOU Dan-dan(侯丹丹),LU Ming-kang(陆明康),WANG Wen-zu(王文祖),WU Yong-gao(吴永高)
1 Key Laboratory of Textile Science and Technology,Ministry of Education,Donghua University,Shanghai 201620,China
2 College of Textiles,Donghua University,Shanghai 201620,China
3 HORCON Medical Product Co.,Ltd.,Nantong 226103,China
Introduction
In wound closure,using sutures is a very important process.Sutures are always in the structure of monofilament or multifilament,made by natural or synthetic biomedical textile materials such as collagen,silk,nylon,and PET.Though during the past three decades,a series of degradable synthetic sutures have been used in surgery successfully,silk braided suture is still widely used in ocular,neural,and cardiovascular as well as a variety of other tissues[1]due to its natural nature,good tying quality,and moisture absorption ability.A braid is a textile structure which intersects yarns by a braiding machine which gives sutures good tenacity and knot strength[2].
But as a kind of natural protein fiber,silk easily trends to microbial infection and prolong the persistence of bacteria on wounds.Beyond that,braided structure may easily harbor bacteria into gaps and between filaments[3].Both of these will increase the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs)which are common infections after surgery.SSIs not only impact operation quality,increase treatment cost,but also prolong pain and hospital stays of patients.According to a report of 2009,a single SSI increases the average hospital stay of 9.7 d and the cost by $ 27 288[4].In the Guidelines for the prevention of SSIs published by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC),the important role of suture in SSIs has been emphasized[5-6].As an implant,suture is the medium for the transport of bacterial to the surgical incision.If sutures own antibacterial nature,they may prevent the adhesion and growth of bacteria on the sutures.Some researches and patents have reported that coating sutures with antibacterial agents provide an effective strategy for reducing SSIs[7].
In this work,antibacterial silk sutures are developed.4-quinolones,which was one of the widely used synthetic antimicrobial agents in hospital,was used as the antimicrobial agent.Polycaprolactone (PCL)was used as controlled-release material.Antibacterial properties,sustained efficacy conditions and release of antibacterial agent were investigated.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and methods
1.1.1 Suture material
Silk braided sutures all in size 2-0 were supplied by HORCON (Jiangsu, China).Coated VICRYL*Plus antibacterial sutures (coated polyglactin 910 suture with triclosan)(ETHICON,Somerville,NJ,USA)in size 2-0 were served as the reference.
1.1.2 Antibacterial solution
PCL particles were added into acetic acid to make a 5%concentration solution,wherein the molecular weight of PCL was 180 000.The 4-quinolones was one of the widely used synthetic antimicrobial agents in hospital.Then 10 mL PCL solution was extracted and 0.025 g 4-quinolones powder was added into,so that the concentration of 4-quinolones in solution was 2 500 mg/L[8].The powder was distributed uniform in PCL solution after magnetic stirring apparatus mixing 3 h.
1.1.3 Antibacterial treatment
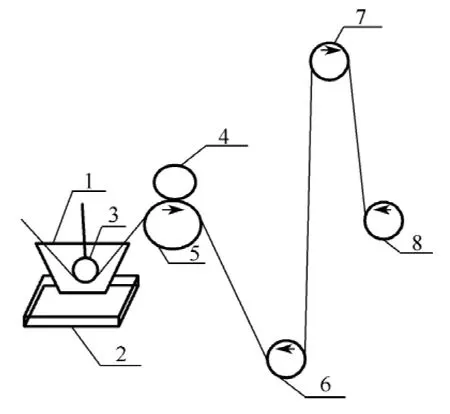
Fig.1 Structural scheme of coating equipment
The coating of silk braided sutures was similar with the starching of yarns,the detailed procedure included:(1)the prepared antibacterial solution was poured into dipping tank 1 to immerse dipping roller 3,heating machine 2 could be used at 30 -40℃to keep the activity of antibacterial solution;(2)the suture passed across the dipping roller 3,then went through the space between the rubber roller 4 and the stainless steel roller 5 below;(3)after pressed by the rubber roller 4 and the stainless steel roller 5,the suture came to guide rollers 6 and 7 as a long distance for drying by room temperature;(4)the suture finally rounded on the rattler 8,and the rattler 8 kept rotated 40 r/min.
1.2 Evaluation of antibacterial suture
1.2.1 Zone of inhibition assay
Sutures before and after treatment both were evaluated by zone of inhibition assay[9-10].In this paper,gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S.aureus)ATCC 25923 and gramnegative Escherichia coli (E.coli)ATCC 25922 were selected as tested bacteria.Organisms were cultured using tryptic soy broth (TSB)at 37℃and were shaken in shake bed for 14 h to form challenge inocula which was then measured by ultraviolet spectrophotometer (TU-1901)to guarantee each 1 mL inocula contains approximately 108colony-forming units(CFU)of S.aureus or E.coli.Melted tryptic soy agar (TSA)at 60℃was poured into sterile dishes and allowed to solidify.Then sterile soft cotton buds dipped with challenge inocula coated TSA dishes well-proportionately.The cut suture pieces (5 cm)were placed on the middle of the surface of each dish.Then the dishes were cultivated for 18 h in a 37℃ incubator.After incubation,the zones of inhibition of each dish were measured with an electro-vernier caliper.According to ISO 20645:2004 Textile fabrics-determination of antibacterial activity-agar diffusion plate test[11],inhibition zones were calculated by the following formula,data were the mean of double samples,and each sample was measured in three different places.
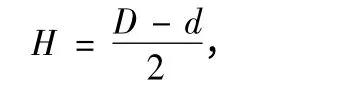
where,H was the inhibition zone (mm),D was the total diameter of specimen and inhibition zone in mm,and d was the total diameter of specimen (mm).
1.2.2 Sustained efficacy assay
If suture samples proved to be antimicrobial after zone of inhibition assay,they were transferred daily onto new petri dishes growing a similar number of bacteria.The assay was terminated when the zone of inhibition disappeared[12].
1.2.3 Release of antibacterial agent
A standard curve of absorbance-concentration can be achieved by using a series of solution with known concentrations and measured absorbance at each known concentration point.Then depending on this standard curve,the concentration of the sample can be detected by measuring the absorbance of the sample[13].The detailed procedure included:(1)the maximum absorption wave length was 289 nm by using TU-1901 to test the spectrum of the antimicrobial solution;(2)a standard curve of absorbance-concentration was achieved by using a series of phosphate buffered saline (PBS) buffer with different concentration and measured absorbance at each know concentration point,and the relationship between absorbance and concentration was:A =0.051 2C (A was absorbance,C was concentration);(3)the suture with antibacterial treatment was placed in 20 mL PBS buffer with pH 7.2,then placed in a 37℃incubator,and replaced with a new buffer every 24 h,at last the absorbance of buffer after removing suture was tested.
1.2.4 SEM
Untreated and treated sutures were placed in petri dishes equipped with 20 mL TSB medium respectively,inoculated 0.1 mL S.aureus whose concentration was 108CFU/L,and then the dishes were cultivated at 37℃ for 18 h in the incubator.After washed by sterilized PBS buffer with pH 7.2,10%formaldehyde was added dropwise and bacteria were fixed at 4℃for 30 min in the fridge.The 70% and 99% alcohol were added dropwise on the suture in order,and then sutures were dried in super clean bench at room temperature for 1 h.The dried sutures were observed under a field emission scanning electron microscope (SEM,HITACHI/SU8010).
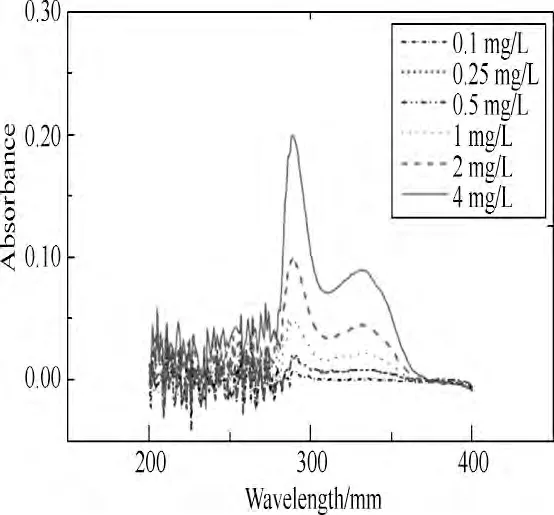
Fig.2 Spectra of the antibacterial agent
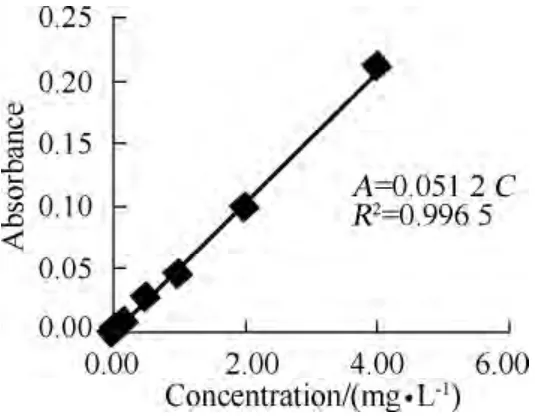
Fig.3 The standard curve of absorbance-concentration
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Zone of inhibition assay
The results of zone of inhibition assays of untreated and treated sutures against S.aureus and E.coli are listed in Table 1.Both the treated sutures exhibited distinct zones of inhibition against S.aureus and E.coli,and the inhibition zones were greater than 1 mm.In contrast,the untreated sutures had no zone.Figure 4 shows the representative pictures.According to BS EN ISO 20645:2004[11],this indicates treated sutures show good effects against S.aureus and E.coli.

Table 1 Zone of inhibition assay
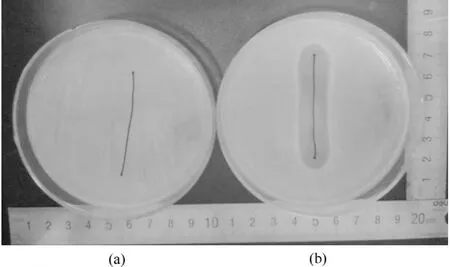

Fig.4 Zone of inhibition assay:(a)untreated and (b)treated
2.2 Sustained efficacy assay
Figure 5 shows the results of sustained efficacy assays of coated VICRYL*Plus suture and coated 4-quinolones suture against S.aureus.The zones of inhibition of the antibacterial silk braided suture lasted for 7 d,which consisted with the skin wound healing (7-10 d).Inhibition zones fitted well as a logarithmic curve which decreased gradually by time,controlled the release of 4-quinolones ideally.Compared with successful commercial production,both the days of sustained efficacy and the variation trend of release are equaled well.
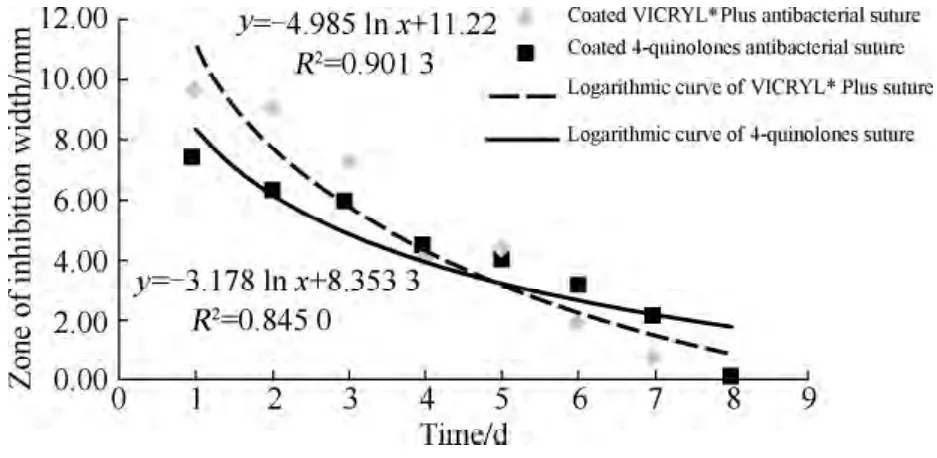
Fig.5 Sustained efficacy assays of coated VICRYL Plus suture and coated 4-quinolones suture
2.3 Release of antibacterial agent
For the antibacterial agent we used,the single maximum dosage is 200 mg,then the peak concentration (Cmax)is(2.92 ±0.54)mg/L 1-2 h after dose.The Cmaxmeans the highest concentration of plasma after the absorption of drug in the body.If Cmaxis higher than the safe range,it may cause toxic reaction.In other words,Cmaxis an important indicator to measure the absorption and safety of drug in the body[14].
As shown in Fig.6,the release concentration decreased from the 1st to the 5th day,and on the 6th day it became 0.This result was in keeping with the result of sustained efficacy assay of coated suture.The Cmaxwas 1.53 mg/L which was within the limits of safety range of the antibacterial agent.So,during the use of this antibacterial silk braided suture,it would not cause drug toxicity.
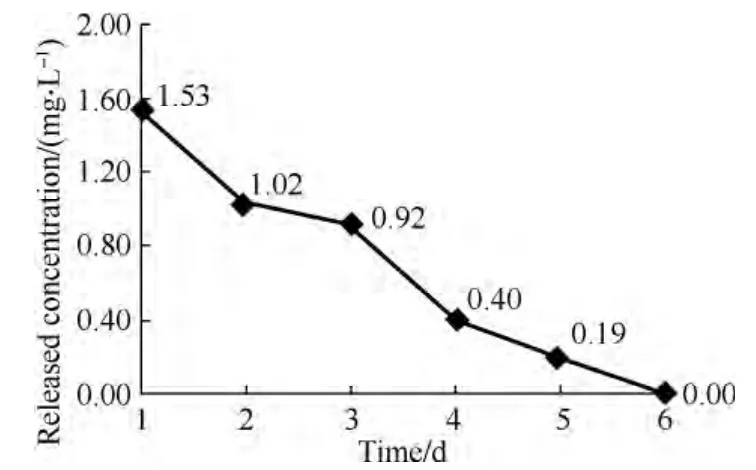
Fig.6 Sustained efficacy assay of antibacterial silk braided suture
2.4 SEM results
Figure 7 gave a typical SEM microstructure of surface changes and growth of bacteria of the antibacterial silk braided suture.It obviously showed that there was so much hairiness on the surface of untreated suture because of the uneven tension during the braided process of multi-strand silk raw.From Fig.7(b),the surface of the suture became uniform and smooth by the relatively high press of rollers and the coating of antibacterial solution.There was also less space between monofilaments,so that it decreased the risk of contaction and adhesion of bacteria.Clusters of cocci were seen on the surface of untreated suture clearly in Fig.7(c),while almost no bacteria could be seen on the surface of treated suture in Fig.7(d).Thus it proved that treated silk braided suture owned antibacterial property which could resist the adhesion and growth of bacteria effectively.
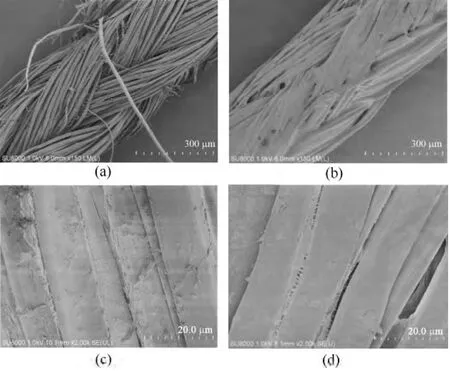
Fig.7 SEM photographs showing the surface changes:(a)untreated (×150),(b)treated (×150);and growth of bacteria on the surface of sutures:(c)untreated (×2000),(d)treated (×2000)
3 Conclusions
Silk braided sutures treated with antibacterial solution which was made from a combination of 4-quinolones and 5%PCL solution provide in vitro excellent antimicrobial efficacy against S.aureus and E.coli compared with untreated sutures.These antibacterial sutures demonstrate a similar sustained antibacterial efficacy against S.aureus with coated VICRYL*Plus antibacterial suture.The release of the antibacterial agent is also in the safe range.Our finding shows the potential of a new kind of antibacterial silk braided suture.
[1]Altman G H,Diaz F,Jakuba C,et al.Silk-Based Biomaterials[J].Biomaterials,2003,24(3):401-416.
[2]Viju S,Thilagavathi G.Fabrication and Characterization of Silk Braided Sutures[J].Fibers and Polymers,2012,13(6):782-789.
[3]Henry-Stanley M J,Hess D J,Barnes A M,et al.Bacterial Contamination of Surgical Suture Resembles a Biofilm [J].Surgical Infections,2010,11(5):433-439.
[4]de Lissovoy G,Fraeman K,Hutchins V,et al.Surgical Site Infection:Incidence and Impact on Hospital Utilization and Treatment Costs [J].American Journal of Infection Control,2009,37(5):387-397.
[5]Owens C D,Stoessel K.Surgical Site Infections:Epidemiology,Microbiology and Prevention[J].Journal of Hospital Infection,2008,70(S2):3-10.
[6]Fan C G.Interpretation of the Updated Guidelines for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection[J].Chinese Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery,2012,15(6):549-552.(in Chinese)
[7]Leaper D,McBain A J,Kramer A,et al.Healthcare Associated Infection:Novel Strategies and Antimicrobial Implants to Prevent Surgical Site Infection [J].Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England,2010,92(6):453-458.
[8]Wang L,Chen X J,Wu Y G,et al.Preparation Equipment and Method of Braided Silk Sutures with Sustained Antibacterial Efficacy,CN 103215779[P].2013-07-24.(in Chinese)
[9]Rothenburger S, Spangler D, Bhende S, et al.In vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of Coated VICRYL Plus Antimicrobial Suture (Coated Polyglactin 910 with Triclosan)Using Zone of Inhibition Assays[J].Surgical Infections,2002,3(11):79-87.
[10]Ming X T,Rothenburger S,Yang D C.In vitro Antibacterial Efficacy of MONOCRYL Plus Antibacterial Suture(Poliglecaprone 25 with Triclosan)[J].Surgical Infections,2007,8(2):201-208.
[11]China National Institute of Standardization.BS EN ISO 20645-2004,International Organization for Standardization,Textile Fabrics-Determination of Antibacterial Activity-Agar Diffusion Plate Test[S].
[12]Ming X T,Rothenburger S,Nichols M M.In vivo and in vitro Antibacterial Efficacy of PDS*Plus (Polidioxanone with Triclosan)Suture[J].Surgical Infections,2008,9(4):451-457.
[13]Gupta B,Jain R,Singh H.Preparation of Antimicrobial Sutures by Preirradiation Grafting onto Polypropylene Monofilament[J].Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2008,19 (12):1698-1703.
[14]Qian Z Y.Pharmacology [M].3rd ed.Beijing:Chinese Medical Science and Technology Press,2009:24-25.(in Chinese)
杂志排行
Journal of Donghua University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Effect of Molecular Weight of PCL on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of PCL/PET Composite Vascular Scaffold Prototype
- Development of Composite Textile Structures for Wound Dressing Applications
- Cranial Nerve Decompression Gasket
- Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Shape and Size
- Psychometric Properties of Geometrical Texture Features for Tactile Roughness Sensation of Fabric Surfaces
- Fabrication of Ethosome-Loaded Silk Fibroin/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofibrous Mats by Green Electrospinning
