异丹叶大黄素下调膀胱癌细胞的细胞周期蛋白D1表达并诱导G0/G1细胞周期阻滞*
2013-09-14方勇,侯琦,卢瑜
方 勇, 侯 琦, 卢 瑜
(1浙江大学医学院,附属邵逸夫医院肿瘤内科,浙江杭州310016;2中国医学科学院,协和医科大学药物研究所,北京100050;3南京军区杭州疗养院疗养二科,浙江 杭州310007)
膀胱癌是泌尿系统最常见的肿瘤[1],无论是发病率还是死亡率均占首位,近年来发病率呈增长趋势[2]。而浸润性膀胱癌常出现威胁生命的远处器官转移,患者几乎100%死亡。因此如果能寻找到一种天然化合物,可抑制膀胱癌细胞的侵袭和转移,进而降低死亡率,这将具有极其重要的临床意义[3]。
近年来的研究已经证实了膀胱癌的发展、预后均与细胞周期蛋白D1(cyclin D1)有关[4]。多项临床研究表明,膀胱肿瘤早期即存在着异常细胞周期蛋白D1的表达[4-5]。细胞周期蛋白D1的过度表达与预后不良相关,可显著降低患者术后的远期生存率[6]。细胞周期蛋白D1是一个重要的细胞周期调控蛋白,通过结合细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4(cyclin-dependent kinase 4,CDK4)、磷酸化以及失活视网膜母细胞瘤蛋白(retinoblastoma protein,pRb),在G1到S过渡的细胞周期进程中发挥着重要作用[7]。因此,下调细胞周期蛋白D1的表达和功能成为抗肿瘤研究领域中靶向药物研究的重要热点之一。
从多种中药成份中提取出的寡聚二苯乙烯类化合物(oligostilbenes)具有多种生物学活性,尤其是抗肿瘤的活性正引起众多研究者的关注[8-9]。我们研究从植物买麻藤中提取分离的中药单体成分异丹叶大黄素(isorhapontigenin,ISO)对膀胱癌细胞的增殖、细胞周期蛋白D1表达水平、G0/G1细胞周期阻滞及迁移的影响。
材料和方法
1 材料
ISO由中国医学科学院北京协和医学院药物研究所提供,被溶解在DMSO,浓度为10 mmol/L,并进一步用DMSO稀释,最后DMSO终浓度为0.1%(V/V)进行细胞培养实验。相同浓度的DMSO(0.1%,V/V)被用来作为阴性对照。
抗CDK4、CDK6、细胞周期蛋白A、细胞周期蛋白B1、细胞周期蛋白D1、细胞周期蛋白E、P21、P53以及GAPDH抗体均购自Santa Cruz。抗P27抗体购自Abcam。新生牛血清和DMEM购自Gibco。DMSO购自Sigma,ATP生物荧光检测试剂盒购自Promega。人源性膀胱癌UMUC3细胞由美国纽约大学医学院HUANG Chuanshu教授实验室惠赠。由于UMUC3膀胱癌细胞株遗传背景和较强的转移倾向,并且高表达细胞周期蛋白D1,所以选定该细胞株进行后续的实验。
2 方法
2.1 ATP生物荧光检测法检测细胞活性 将UMUC3细胞在含有10%新生牛血清、1×105U/L青霉素及100 mg/L链霉素的DMEM培养基中,37℃、5%CO2条件下培养,每3 d传代1次。以5×103cells/well的密度接种于96孔培养板,以不同浓度ISO(0、5、10、20、40 和 60 μmol/L)作用于细胞共 48 h。提取ATP,荧光扫描仪测定荧光强度,软件分析药物各浓度抑制率,计算IC50,绘制抑制曲线,评估药物作用。
2.2 UMUC3细胞周期蛋白D1表达的检测 采用Western blotging法检测UMUC3细胞株细胞周期蛋白D1蛋白表达情况。进行蛋白质的提取、定量和分离。转膜后先后与10 g/L脱脂奶粉、鼠抗人抗体(细胞周期蛋白D1、细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4、细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶6、细胞周期蛋白A、细胞周期蛋白B1、细胞周期蛋白D1、细胞周期蛋白E、P21、P27、P53和GAPDH)I抗4℃孵育过夜,过氧化物酶偶联的II抗孵育,运用ECL Western blotting kit显色并扫描实验结果。
2.3 UMUC3细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA表达的检测收集UMUC3细胞约1×106,按TRIzolTM试剂盒说明书提取总RNA,逆转录反应体系:模板RNA 2 μg,10 mmol/L dNTP 1 μL,RNA 酶抑制剂(RNasin)335 nKat,Oligo dT181 μL,AMV 逆转录酶1 μL,5 × 逆转录酶缓冲液5 μL,终体积为25 μL,42℃水浴30 min,采用PubMed的Primer BLAST软件设计细胞周期蛋白D1基因PCR引物(扩增产物大小408 bp),序列如下:上游引物 5’-GAGGTCTGCGAGGAACAGAAGTG-3’,下 游 引 物 5’-GAGGGCGGATTGGAAATGAACTTC-3’。同时以 GAPDH作为内参照(扩增产物大小285 bp),上游引物5’-AGAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTTG-3’,下游引物 5’-AGGGGCCATCCACAGTCTTC-3’。PCR产物经2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,MGIAS-1000凝胶成像系统扫描定量并拍照。
2.4 PI染色法和流式细胞术检测 胰酶消化并收集细胞,70%乙醇固定,4℃保存。600×g离心5 min,并用 PBS 液(含有0.5%BSA 和0.1%Triton X-100)洗2次。加入PI染色液避光保存30 min后,用流式细胞仪(Beckman Coulter)检测细胞周期DNA含量和凋亡细胞百分数。
2.5 细胞划痕实验 在6孔板中,以含10%FBS的DMEM培养UMUC3细胞直到生长到80%,以丝裂霉素处理1 h,抑制细胞的分裂。以无菌的移液器吸头划痕,用无血清的PBS洗涤3次后,去除划下的细胞,加入含1%FBS血清在37℃、5%CO2条件下培养,根据指定的时间进行拍照,直到细胞长满划痕区域。以细胞迁移分析软件(Cell Migration Analysis Software,Muscale LLC)定量分析细胞的迁移能力。
3 统计学处理
计量数据以均数±标准差(mean±SD)表示。对各组之间采用t检验或方差分析,用SPSS 13.0统计学软件进行数据分析,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果
1 ISO抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖
ISO 的化学结构是 4'-甲氧基-3,3',5-三羟基二苯乙烯(4-methoxyresveratrol),见图 1A,分子量为258 D。我们首先通过实验证实ISO对UMUC3细胞增殖的影响。UMUC3与不同剂量ISO(0~60 μmol/L范围)共同培养48 h后,倒置相差显微镜下观察,如图1B所示,20 μmol/L以上浓度显著抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。通过ATP生物荧光检测法检测细胞增殖活性,证实ISO抑制膀胱癌细胞呈明显剂量依赖性,UMUC3细胞株的 IC50为(22.5 ±2.8)μmol/L(n=3),见图1C。进一步通过流式细胞术检测,5 μmol/L ISO作用48 h后可诱导细胞出现G0/G1细胞周期阻滞,但不会诱导细胞凋亡;而20 μmol/L ISO可诱导UMUC3细胞出现典型的凋亡峰(Sub-G1峰),见图1D。

Figure 1.ISO inhibited proliferation of human bladder cancer UMUC3 cells.A:the structure of ISO.B:under phase-contrast microscope,representative images of UMUC3 cells pretreated with more than 20 μmol/L of ISO showed the inhibition of proliferation(×400).C:the UMUC3 cells were treated with different concentrations of ISO for 48 h,and followed by the detection of ATPase assay.Mean ± SD.n=3.**P <0.01 vs 0 μmol/L.D:flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle of UMUC3 cells treated with different concentrations of ISO for 48 h.20 μmol/L ISO could induce typical sub-G1(apoptosis)peak.图1 ISO可显著抑制膀胱癌UMUC3细胞的增殖
2 ISO可下调膀胱癌细胞细胞周期蛋白D1蛋白和mRNA表达
UMUC3与不同剂量(0~20 μmol/L)的 ISO培养24 h收集UMUC3细胞的蛋白质后,经Western blotting检测均可见分子量为37 kD的细胞周期蛋白D1的表达受到显著抑制(图2A)。检测其它细胞周期调控蛋白,ISO并未对CDK4、CDK6、细胞周期蛋白A 、细胞周期蛋白B1、细胞周期蛋白D1、细胞周期蛋白E、P53、P21和P27等产生影响。图像分析系统表明(图2B),5、10 和 20 μmol/L ISO 呈剂量依赖性抑制细胞周期蛋白D1蛋白表达(P<0.01)。同时,RT-PCR检测结果显示,ISO可显著下调UMUC3细胞细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA表达,见图2C。
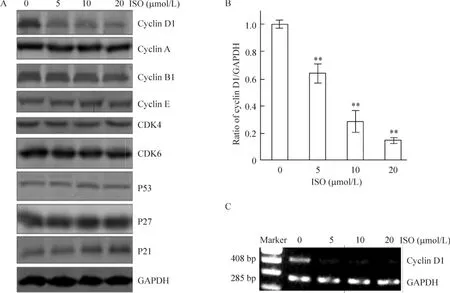
Figure 2.The protein and mRNA levels of cyclin D1 could be significantly down-regulated by ISO.A:the protein expression of cyclin D1,cyclin A,cyclin B1,cyclin E,CDK4,CDK6,P53,P27 and P21 detected by Western blotting.B:the ratio of cyclin D1/GAPDH in the UMUC3 cells pretreated with ISO.Mean ± SD.n=3.**P <0.01 vs 0 μmol/L.C:the mRNA expression of cyclin D1 detected by RT-PCR.图2 ISO可下调UMUC3膀胱癌细胞周期蛋白D1蛋白和mRNA表达
3 ISO可诱导膀胱癌细胞出现G0/G1细胞周期阻滞
结合图1D和图2的结果,5 μmol/L ISO可显著性下调细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA水平,但不会诱导细胞凋亡。因此后面的实验均采用5 μmol/L ISO进行研究。经流式细胞术检测,5 μmol/L ISO作用于膀胱癌细胞12 h和24 h后,可出现不同程度G0/G1细胞周期阻滞。与对照组(47.33%)进行比较,在没有显著诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡的情况下,可分别在12 h(58.82%)和24 h(63.942%)显著诱导细胞 G0/G1期生长停滞 (P <0.01),见图3。

Figure 3.ISO induced G0/G1arrest of human bladder cancer UMUC3 cells.Exposure of UMUC3 cells to 5 μmol/L ISO led to significant induction of G0/G1growth arrest at both 12 h(47.33%vs 58.82%)and 24 h(47.33%vs 63.94%).AP:apoptosis.图3 ISO可诱导膀胱癌细胞出现G0/G1细胞周期阻滞
4 ISO可显著抑制膀胱癌细胞的迁移活性
经细胞划痕实验证明,与未加ISO预处理进行比较,5 μmol/L ISO均可在12 h和24 h显著抑制膀胱癌细胞的迁移活性(P<0.01),见图4。

Figure 4.ISO inhibited the migration of human bladder cancer UMUC3 cells detected by wound-healing assay.Cells were wounded and then treated with DMSO or ISO(5 μmol/L).At 0,12 and 24 h,phase-contrast pictures of the wounds at the same locations were taken and then migrated cells in the wound were counted.Mean ± SD.n=3.**P <0.01 vs control.图4 ISO可显著抑制膀胱癌细胞迁移活性
讨 论
泌尿系统来源的膀胱上皮肿瘤是我国最常见的泌尿系统恶性肿瘤。近年来发病率呈明显上升趋势,晚期患者接受进一步化放疗的治疗效果仍不理想[10]。本研究证实,ISO可抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖,可下调细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA和蛋白水平,诱导膀胱癌细胞出现细胞G0/G1周期阻滞,并可抑制膀胱癌细胞迁移。
在我国,约25%的膀胱癌患者最终可发展为肌层浸润性膀胱癌或转移性膀胱癌。我们实验室近期的研究证实,从植物买麻藤中提取分离的中药单体成分ISO,剂量在20~60 μmol/L浓度条件下,能显著下调包括人膀胱癌细胞在内的多种肿瘤细胞X连锁凋亡抑制蛋白(X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein,XIAP)水平,诱导细胞凋亡,发挥其抗肿瘤作用[3]。在本项研究中,我们证实低浓度 ISO(5 μmol/L)不仅能抑制膀胱癌UMUC3细胞株的细胞增殖,并可有效地下调细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA和蛋白质水平的表达,诱导细胞周期G0/G1期阻滞。
1991年发现细胞周期蛋白 D1,又称 PRAD1、CCND1、BCL-1,其基因位于 11q13,长约 15 kb,含 5个外显子,4个内含子,编码的蛋白含295个氨基酸残基,分子量37 kD[11],为细胞内主要的癌基因之一。许多研究证据表明,在各种促进细胞炎性增殖的反应,包括致癌物质诱导细胞产生突变的过程中,首先可引起细胞周期的改变[12]。在肿瘤形成过程中,细胞周期蛋白D1比细胞周期蛋白D2和D3更加重要[13]。细胞周期蛋白D1对细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶进行正调控,而周期素激酶抑制剂(cyclin kinase inhibitor,CKI)对细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶进行负调控,一旦这种正负调控的平衡被破坏,细胞就可能异常增殖进而恶变。本研究证实ISO可下调细胞周期蛋白D1 mRNA的表达,但没有影响CDK4和CDK6表达,也没有对另一类包括P21、P27和P53等CKI蛋白产生显著影响。
细胞周期蛋白D1作为癌基因最早见于甲状旁腺癌,后被证实参与包括膀胱癌在内的多种实体瘤的分子病理机制。细胞周期蛋白D1表达并不限于某种病理类型,并且细胞周期蛋白D1在膀胱癌进展的各个阶段持续存在。曾文利等[15]证实膀胱癌组织的细胞周期蛋白D1阳性率明显高于正常膀胱黏膜和癌旁组织。细胞周期蛋白D1在癌变危险性大的良性病变、病理分级差以及浸润性膀胱癌组织内,均高表达并与预后密切相关。细胞周期蛋白D1在膀胱癌中的异常表达可能参与膀胱癌的发生、发展过程[14]。除膀胱癌外,细胞周期蛋白D1在其它多种人类肿瘤,包括乳腺癌[16]、子宫颈癌[17-18]、结肠癌[19]、前列腺癌[20]、肝癌[21]和皮肤癌[22]等均不同程度地高表达。因此,细胞周期蛋白D1是肿瘤细胞周期调控及药物治疗中潜在的治疗靶点。
例如,Li等[23]证实了在小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞(mouse embryonic fibroblast,MEF)中,细胞周期蛋白D1表达缺陷后细胞迁移活性明显减低。本实验结果证实ISO(5 μmol/L)可显著抑制细胞周期蛋白D1表达,并通过细胞划痕实验证实可下调膀胱癌细胞的迁移,与Li等的结果相一致。目前下调或抑制细胞周期蛋白D1表达的分子生物学方法包括:细胞周期蛋白D1亚型(全长细胞周期蛋白D1)与小分子细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4/6抑制剂PD0332991[24]、小分子干扰核糖核酸(RNA干扰)[25]、细胞周期蛋白D1基因敲除[26]和抑制糖原合成酶激酶(glycogen synthase kinase,GSK)3β 活性[27]。但这些基因治疗,目前仍具有稳定性差、需要多次重复给药、细胞膜通透性差、转染效率不稳定等不足。患者的安全性受到威胁,极大限制了临床使用。
因此,本研究将为治疗膀胱癌和其它肿瘤提供新的思路和治疗策略,为进一步研究细胞周期蛋白D1在参与实体肿瘤细胞迁移、肿瘤细胞G0/G1周期调控中的作用提供了新思路,也为临床采用中药单体综合治疗肿瘤提供了新的策略,尤其是对一些细胞周期蛋白D1基因高表达的肿瘤。
本研究还有不足之处,如:ISO可在mRNA和蛋白水平下调细胞周期蛋白D1表达水平,其具体机制尚不清楚;另外,ISO对细胞内细胞周期调控蛋白如CDK均未产生影响,但对其它信号转导途径如JNK/c-Jun、JAK/Stat等是否影响,这些都有待于进一步研究。
[1] Schned AR,Andrew AS,Marsit CJ,et al.Histological classification and stage of newly diagnosed bladder cancer in a population-based study from the Northeastern United States[J].Scand J Urol Nephrol,2008,42(3):237-242.
[2] Li C,Wu W,Liu J,et al.Functional polymorphisms in the promoter regions of the FAS and FAS ligand genes and risk of bladder cancer in south China:a case-control analysis[J].Pharmacogenet Genomics,2006,16(4):245-251.
[3] Fang Y,Yu Y,Hou Q,et al.The Chinese herb isolate isorhapontigenin induces apoptosis in human cancer cells by down-regulating overexpression of antiapoptotic protein XIAP[J].J Biol Chem,2012,287(42):35234-35243.
[4] Shariat SF,Ashfaq R,Sagalowsky AI,et al.Correlation of cyclin D1 and E1 expression with bladder cancer presence,invasion,progression,and metastasis[J].Hum Pathol,2006,37(12):1568-1576.
[5] Yuan L,Gu X,Shao J,et al.Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism is associated with risk and clinicopathologic characteristics of bladder cancer[J].DNA Cell Biol,2010,29(10):611-617.
[6] Lin DI,Lessie MD,Gladden AB,et al.Disruption of cyclin D1 nuclear export and proteolysis accelerates mammary carcinogenesis[J].Oncogene,2008,27(9):1231-1242.
[7] Tashiro E,Maruki H,Minato Y,et al.Overexpression of cyclin D1 contributes to malignancy by up-regulation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 via the pRB/E2F pathway[J].Cancer Res,2003,63(2):424-431.
[8] Yamada M,Hayashi K,Ikeda S,et al.Inhibitory activity of plant stilbene oligomers against DNA topoisomerase II[J].Biol Pharm Bull,2006,29(7):1504-1507.
[9] Hagiwara K,Kosaka N,Yoshioka Y,et al.Stilbene derivatives promote Ago2-dependent tumour-suppressive microRNA activity[J].Sci Rep,2012,2(3):314-322.
[10] Yafi FA,Duclos M,Correa JA,et al.Contemporary outcome and management of patients who had an aborted cystectomy due to unresectable bladder cancer[J].Urol Oncol,2011,29(3):309-313.
[11] Heighway J.HaeIII polymorphism within 3'untranslated region of PRAD1 [J].Nucleic Acids Res,1991,19(19):5451.
[12] Lee CC,Yamamoto S,Wanibuchi H,et al.Cyclin D1 overexpression in rat two-stage bladder carcinogenesis and its relationship with oncogenes,tumor suppressor genes,and cell proliferation [J].Cancer Res,1997,57(21):4765-4776.
[13] Kim JK,Diehl JA.Nuclear cyclin D1:an oncogenic driver in human cancer[J].J Cell Physiol,2009,220(2):292-296.
[14] Wagner U,Suess K,Luginbuhl T,et al.Cyclin D1 overexpression lacks prognostic significance in superficial urinary bladder cancer[J].J Pathol,1999,188(1):44-50.
[15] 曾文利.Cyclin D1在膀胱癌中的表达及意义[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2011,20(4):354-357.
[16] Rajabi H,Ahmad R,Jin C,et al.MUC1-C oncoprotein induces TCF7L2 transcription factor activation and promotes cyclin D1 expression in human breast cancer cells[J].J Biol Chem,2012,287(13):10703-10713.
[17] Satinder K,Chander SR,Pushpinder K,et al.Cyclin D1(G870A)polymorphism and risk of cervix cancer:a case control study in north Indian population[J].Mol Cell Biochem,2008,315(1-2):151-157.
[18] 谭伟坚,张 林,仲 秋,等.宫颈上皮内瘤变及宫颈鳞癌中cyclinD1、Ki-67的表达及其意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(2):390-392.
[19] Ogino S,Nosho K,Irahara N,et al.A cohort study of cyclin D1 expression and prognosis in 602 colon cancer cases[J].Clin Cancer Res,2009,15(13):4431-4438.
[20] Fleischmann A,Rocha C,Saxer-Sekulic N,et al.Highlevel cytoplasmic cyclin D1 expression in lymph node metastases from prostate cancer independently predicts early biochemical failure and death in surgically treated patients[J].Histopathology,2011,58(5):781-789.
[21] 刘 娟,殷 飞,姚树坤.细胞周期素D1、视网膜母细胞瘤样蛋白2及微小染色体维持蛋白7在肝细胞癌中的表达及对预后的意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(2):304-309.
[22] Burnworth B,Popp S,Stark HJ,et al.Gain of 11q/cyclin D1 overexpression is an essential early step in skin cancer development and causes abnormal tissue organization and differentiation [J].Oncogene,2006,25(32):4399-4412.
[23] Li Z,Wang C,Jiao X,et al.Cyclin D1 regulates cellular migration through the inhibition of thrombospondin 1 and ROCK signaling [J].Mol Cell Biol,2006,26(11):4240-4256.
[24] Marzec M,Kasprzycka M,Lai R,et al.Mantle cell lymphoma cells express predominantly cyclin D1a isoform and are highly sensitive to selective inhibition of CDK4 kinase activity[J].Blood,2006,108(5):1744-1750.
[25] Huang H,Hu YD,Li N,et al.Inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis by non-small cell lung cancer cells transfected with cyclin D1-targeted siRNA[J].Oligonucleotides,2009,19(2):151-162.
[26] Meng H,Tian L,Zhou J,et al.PACSIN 2 represses cellular migration through direct association with cyclin D1 but not its alternate splice form cyclin D1b[J].Cell Cycle,2011,10(1):73-81.
[27] Yang K,Guo Y,Stacey WC,et al.Glycogen synthase kinase 3 has a limited role in cell cycle regulation of cyclin D1 levels[J].BMC Cell Biol,2006,7:33.
