“种子处理和正确施药时间对菜豆炭疽病的防治效果”论文评述
2013-09-08韩启厚于海龙夏俊峰刘惠静
古 瑜 韩启厚 于海龙 夏俊峰 刘惠静 岳 欣 郎 朗
(天津科润蔬菜研究所,天津 300384)
“种子处理和正确施药时间对菜豆炭疽病的防治效果”论文评述
古 瑜 韩启厚 于海龙 夏俊峰 刘惠静 岳 欣 郎 朗
(天津科润蔬菜研究所,天津 300384)
本文对加拿大圭尔夫大学Gillard C L 教授等于2012年在Crop Protection上发表的一篇题为“种子处理和正确施药时间对菜豆炭疽病的防治效果”的研究论文(The control of dry bean anthracnose through seed treatment and the correct application timing of foliar fungicides)进行了评述。Gillard教授等以播种前杀菌剂处理种子的方法为对照,设计了几个施药时间点,探讨了菜豆生长过程中正确的施药时间点,即寻找作物与病菌相互作用、病情发展的关键时间点。旨在延续并提高化学杀菌剂对炭疽病菌的防治效果,提高菜豆产量和质量,节省种植者的投入,并有效地保护环境。文章内容新颖,可操作性强,对生产实践有指导意义。希望通过介绍该论文的试验内容和所取得的成果,为国内同行在菜豆炭疽病防治方面提供参考。
菜豆;炭疽病;精准施药法
Gillard等在Crop Protection〔2012,37:81-90〕上发表了一篇题为“种子处理和正确施药时间对菜豆炭疽病的防治效果”的研究论文(The control of dry bean anthracnose through seed treatment and the correct application timing of foliar fungicides)。文中Gillard教授等为找到菜豆(Phaseolus vulgarisL. )生长周期中病菌与寄主相互作用的关键时期,进行有针对性的化学防治,设计了几个施药时间点,通过试验总结出精准施药法,即全生育期只在3个关键时期进行药剂防治,便可达到高效防治炭疽病的效果,并可提高商品豆荚的产量和质量,节省农药使用量60%~70%,还可有效地保护环境,可谓一举数得。该方法是针对粒用菜豆炭疽病进行的试验,由于引起菜豆炭疽病的病原菌与荚用菜豆相同,因此对荚用菜豆也具有一定的借鉴作用。
据报道,菜豆炭疽病的传播途径主要是种子带菌(Tu,1981)。因此,普遍认为在生产中除了 使用抗病品种外,利用杀菌剂处理种子或严格控制环境条件可有效防治该病的发生(Tu,1988;Pastor-Corrales & Tu,1989)。有研究显示,在环境条件适宜炭疽病发生时,经过种子处理的菜豆比未经处理的菜豆炭疽病发病率明显降低(Tu,1983;Conner et al.,2009)。种子处理对轻度和中度炭疽病有效果,但对重度炭疽病效果不显著(Tu,1988)。在大豆生产中,使用甲霜灵+吡唑嘧菌酯或咯菌啨+精甲霜灵处理带菌土壤对大豆的产量有明显提高(Bradley,2008)。在加拿大,菜豆种子处理主要使用二嗪农+克菌丹+甲基托布津(Tu,1996)。但是,引起菜豆炭疽病的病原菌生理小种变异非常快,抗病品种对新生理小种失去抗性,病原菌对杀菌剂产生抗药性,类似现象在许多菜豆种植区不同程度出现。因此,为了在菜豆生产中减少损失,选用抗病品种同时进行种子处理非常必要。
该论文以播种前杀菌剂处理菜豆种子的方法为对照,设计了几个施药时间点,旨在寻找菜豆全生育期中正确的施药时间点,即作物与病菌相互作用、发展的关键时期。目的是延续并提高化学杀菌剂对炭疽病菌的防治效果,提高菜豆的产量和品质,节省种植者的投入,有效保护环境。
1 试验方法和结果简介
以粒用菜豆为试材,四叶一心期人工接种病原菌。人工喷药时期设4个:四叶一心期、始花期、全花期和全花期后10 d。试验采用完全随机区组设计,共设17个处理(表1),4次重复。其中种子处理设为2个,分别为6%二嗪农+18%克菌丹+14%甲基托布津197.6 g·hm-2和3.8 g精甲霜灵+2.5 g咯菌啨(用药量对应每公顷用种量的拌药量);生长期喷药时间点处理设7个,分别为四叶一心期、始花期、全花期、全花期后10 d、四叶一心期+全花期、始花期+全花期、始花期+全花期后10 d。以种子处理为对照。
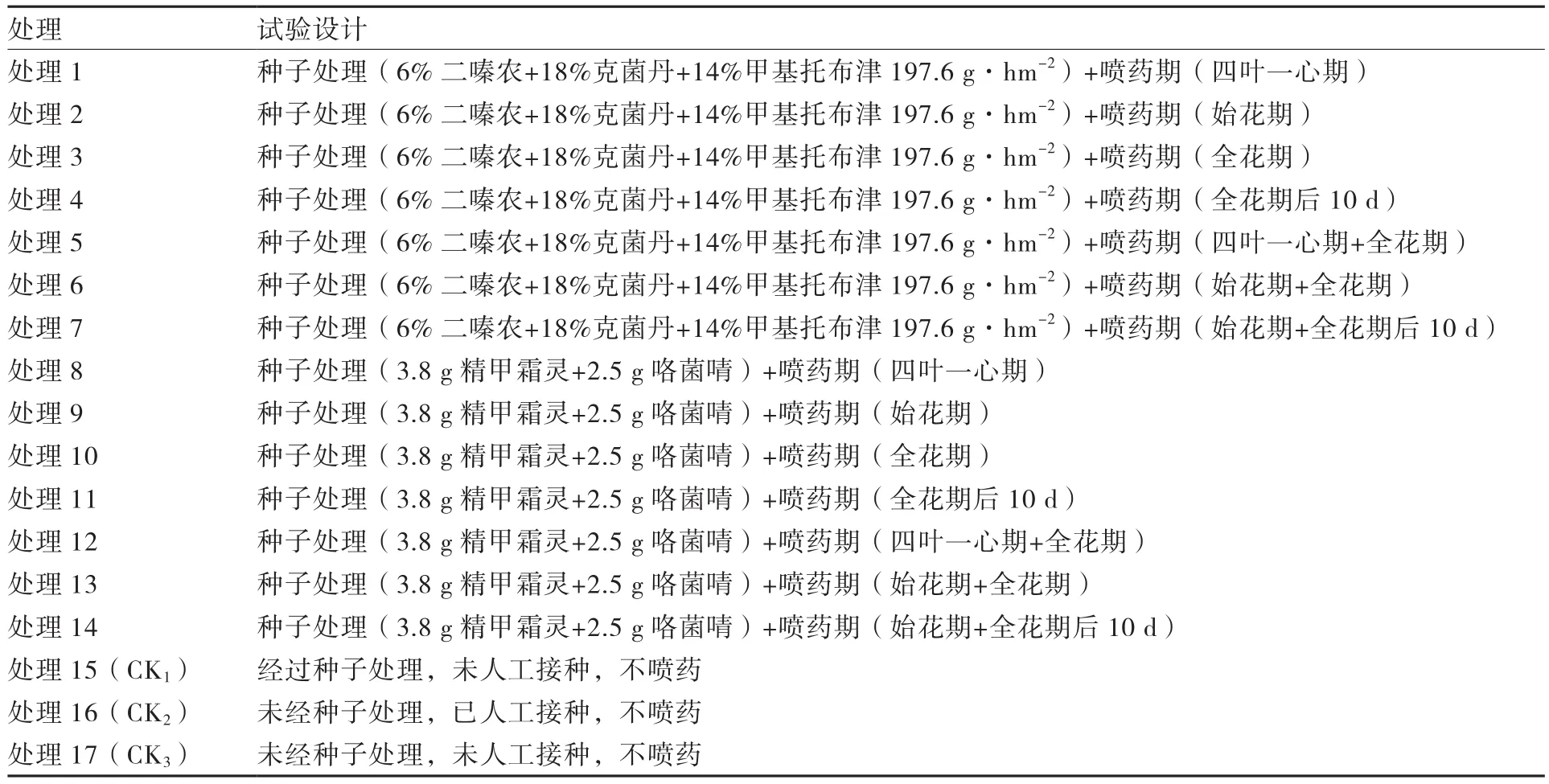
表1 具体试验设计
试验结果表明,菜豆种子带病斑和适合发病的环境条件均对后期植株炭疽病的发生和发展起促进作用。而种子处理可以针对带病斑种子,以杀灭病原菌;全生育期关键时期施用杀菌剂,可有效防治环境条件引起的炭疽病的发生和发展。处理6和处理5,即种子采用6%二嗪农+18%克菌丹+14%甲基托布津197.6 g·hm-2进行处理,始花期+全花期或四叶一心期+全花期2次喷施杀菌剂,防治菜豆炭疽病效果最佳。说明种子处理与正确时间点杀菌剂联合使用对控制炭疽病的发生和提高菜豆产量十分重要。
2 启示
目前,我国蔬菜种植过程中存在一些问题,使得病害发生比较频繁。例如,连作逐渐导致土壤结构恶化,土壤和周围环境中病原菌残留等,直接影响到下茬蔬菜的生产,极易造成病害爆发。此外,种子生产管理粗放,种子带菌比率升高。现在蔬菜整个生育期基本上离不开农药,农药使用量呈逐渐上升的趋势。这不仅使农民的生产成本提高,对环境造成破坏,而且蔬菜上残留的农药对人体也会造成极大的危害。通过对Gillard等的精准施药法的介绍,对蔬菜病害的化学防治有了新的认识:如将此经验扩大应用到其他病害的防治上,只要找到病原菌与寄主植物之间相互作用的关键点,并在此关键点加以防治,就可以起到事半功倍的防治效果,但这还需要不断探索求证。
Bradley C A.2008.Effect of fungicide treatments on stand establishment,seedling disease,and yield of soybean in North Dakota.Plant Dis,92:120-125.
Conner R L,McAndrew D W,Balasubramanian P,Kiehn F A,Dongfang Y.2006.Influence of growth habit,row spacing,and seed infection on bean anthracnose development.Can J Plant Pathol,28:411-418.
Conner R L,Chen Y,Hou A,Balasubramanian P M,McLaren D L,McRae K B.2009.Seed-borne infection affects anthracnose development in two dry bean cultivars.Can J Plant Pathol,31:449-455.
Gillard C L,Ranatunga N K,Conner R L.2012.The control of dry bean anthracnose through seed treatment and the correct application timing of foliar fungicides.Crop Protection,37:81-90.
Pastor-Corrales M A,Tu J C.1989.Anthracnose//Schwartz H F,Pastor-Corrales M A.Eds.Bean production problems in tropics,seconded.Cali:Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical:77-104.
Tu J C.1981.Anthracnose(Colletotrichumlindemuthianum)on white bean (PhaseolusvulgarisL.) in southern Ontario:spread of the disease from an infection focus.Plant Dis,65:477-480.
Tu J C.1983.Epidemiology of anthracnose caused byColletotrichumlindemuthianumon white bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in southern Ontario:survival of the pathogen.Plant Dis,67:402-404.
Tu J C.1988.Control of bean anthracnose caused by the delta and lambda races ofColletotrichumlindemuthianumin Canada.Plant Dis,72:5-8.
Tu J C.1996.Re-evaluation of DCT seed reatment against the new alpha-Brazilrace of bean anthracnose caused byColletotrichum lindemuthianum.Annu Rep Bean Improv Coop,39:294-295.
Comment on Paper “The Control of Dry Bean Anthracnose through Seed Treatment and The Correct Application Timing of Foliar Fungicides”
GU Yu,HAN Qi-hou,YU Hai-long,XIA Jun-feng,LIU Hui-jing,YUE Xin,LANG Lang
(Tianjin Kernal Vegetable Research Institute,Tianjin 300384,China)
This article coments on the paper published in《Crop Protection》by Prof. Gillard C L from Guelph University,Canada,and named “The control of dry bean anthracnose through seed treatment and the correct application timing of foliar fungicides”.Taking chemical fungicides to treat seed before sowing as contrast,Prof.Gillard C L designed several fungicides application times,so as to find out the interactions between crop and harmful bacteria,and disease development time points,aiming at postpone and improve the controlling effect of pesticides on anthracnose,to increase dry bean(Phaseolus vulgarisL. )yield and quality,to save farmers investment,and to protect the environment.The content of the paper is new and unique with good maneuverability and guidance significance on production practise.We wish to provide for domestic colleagues more references on concepts about controlling anthracnose through the introduction of the paper test contents and achievements.
Bean;Anthracnose;Accurate chemical pesticides application time
S643.1
A
1000-6346(2013)08-0001-03
2012-11-07;接受日期:2013-02-01
天津市应用基础与前沿技术研究计划重点项目(10JCZDJC18100),天津市经济技术开发区企业博士后工作站科润公司分站专项
古瑜,女,副研究员,专业方向:蔬菜遗传育种,E-mail:guyu-bohang@163.com
