Study on Mutant Induction of Gladiolus by in vitro Culture of Petals
2012-03-01LiCaihuaFanJinpingGongShufangandCheDaidi
Li Cai-hua ,Fan Jin-pingGong Shu-fangand Che Dai-di*
1 College of Horticulture,Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin 150030,China
2 Economic Crops Research Institute,Heilongjiang Land Reclamation Academy of Science,Harbin 150086,China
Introduction
Gladiolus is a monocotyledonous bulb crop which ranks fifth in cut-flower sale worldwide (United States Department of Agriculture 1995-1996).Gladiolus is propagated by corms resulting in continual virus spread to progenies.Zhao (1999) reported petals tissue culture could get rid of virus effectively.
Petal tissue culture is different from shoot tip culture.It needs to experience the process of dedifferentiation and redifferentiation (Qiu,1982;Qiu et al.,1983).Earle and Langhans (1974) first found the phenomenon that mutants were easy to occur from plantlets differentiated from petals.Skirvin and Janick (1976) found that the further explants existed from organ of differentiation or the longer time explants need to differentiate,the higher rate of somaclonal variation occurred.They suggested the potential use of clonal variation for improvement of horticultural plants.New varieties has been obtained by using petals in vitro culture which has been reported in many horticultural crops.Petal culture in vitro could be used as an effective auxiliary mean to breed new varieties (He,1992).Keeping these in view,the present research used petal as explants to establish regeneration system,expecting to create new Gladiolus varieties.
Materials and Methods
Petal callus induction
Young inflorescences of 'Rose Supreme'in 5-leaf stage were used as initial explants.The inflorescences were cut from stem base,stripped out bracts.Young petals were surface disinfested with 75% (v/v) ethanol for 0.5 min,rinsed with sterile water,stirred for 5 min in 0.1% HgCl2with two drops of Tween 80 and rinsed three times with sterile water.Superfluous water was absorbed with sterile filter paper and young petals were cut into 3-5 pieces,inoculated on MS medium supplemented with different concentrations of auxins and cytokinins: (1) MS+2,4-D 4.0 mg • L-1+6-BA 0.5 mg • L-1;(2) MS+NAA5.0 mg • L-1;(3) MS+2,4-D 1.0 mg • L-1+KT2.0 mg • L-1;(4) MS+ZT2.0 mg • L-1.Cultures were maintained in a growth chamber at 25℃ under a 16-hlight photoperiod for 4 weeks,the situation of induction of callus on the medium was observed.
Induction of somatic embryo
Better loose texture of the callus was chosen and cut into squares of 0.5 cm.They were inoculated on MS solid medium supplemented with different concentrations of 2,4-D,6-BA,TDZ.Three factors 3 levels L9(34) orthogonal experimental design in Table 1 was used to select the best medium to induce somatic embryo.Total 40 explants were inoculated in each treatment.Cultures were maintained in dark chamber at 25℃ for 3 weeks,somatic embryo induction rate were calculated (somatic embryo induction rate=number of somatic embryo/number of explants).

Table1 Factors and levels of experiment design
Developmental characteristics of petal plantlets and screening of mutants in M1 generation
Petal somatic embryo calli were transferred to MS medium supplemented with 6-BA 0.5 mg • L-1and NAA 0.1 mg • L-1to induce shoots (Zheng,2007).
Developmental characteristics of petal plantlets were observed during formation process of petal callus and shoots.Shoots were transferred to MS medium supplemented with IBA 1.0 mg • L-1,PP3330.3 mg • L-1and sucrose 60 mg • L-1(Ma et al.,1994).Lids of the bottles were taken off in greenhouse for 2 days when the roots reached 1.5 cm in length or shoots had 1-2 euphylla.Medium on the roots was washed off.All the seedlings were transferred to soil in greenhouse and watered with 1/2MS nutrient solution every 10 days.Leaf-DNA of every single seedling was extracted for ISSR analysis by using primer (TGT GTG TGT GTG TGT GA) we had screened.The mutants were cultured with tags after preliminary genetic analysis.
Observation of traits in M3 generation
Traits of mutants were observed in M2and M3generations in order to verify the accuracy of ISSR analysis in M1generation.
Results
Induction of petal callus
Although petal callus could be induced on each treatment according to Table 2,the induction results were different apparently.Red or white loose granular callus could be formed on treatment 1 (Fig.1A).Red or brown callus could be formed on treatment 2 and treatment 3,but most callus could't develop into plantlets (Fig.1B and C).White shoots could be formed earlier on treatment 4 than other three treatments,but these shoots were difficult to survive with subsequent culture (Fig.1D).Therefore,treatment 1 was selected as the best medium to induce petal callus.
Petal callus could be induced on medium supplemented with 2,4-D and 6-BA or KT hormone combination,but the induction result of 6-BA was better than that of KT.Callus also could be induced on treatment 2,but callus turned brown during subsequent culture.2,4-D 4.0 mg • L-1+6-BA 0.5 mg • L-1was the best hormone combination to induce petal callus.The color of the callus was red and white.Most of them grew rapidly (Fig.1).
Induction of petal embryogenic callus
The results of 3 factor 3 level L9(34) orthogonal experimental design showed that the highest somatic embryo induction rate was 65% when medium contained 2,4-D 1.0 mg • L-1,6-BA 0.5 mg • L-1and TDZ 0.3 mg • L-1according to Table 3.Induction rate was 52.5% when medium contained 2,4-D 1.0 mg • L-1,6-BA 0 mg • L-1and TDZ 0.1 mg • L-1and induction rate was 55% when medium contained 2,4-D1.5 mg • L-1,6-BA 0 mg • L-1and TDZ 0.3 mg • L-1.The induction rate was 0 when medium contained no TDZ.So we know that TDZ was an important factor to induce somatic embryo and the suitable concentration of TDZ was 0.3 mg • L-1.The concentration of 6-BA almost had no influence on somatic embryo induction.As a result,MS medium supplemented with 2,4-D 1.0 mg • L-1and TDZ 0.3 mg • L-1was the best induction medium to induce somatic embryo.

Table2 Characteristics of induced petal callus in different treatments

Fig.1 Growth of petal callus on different treatments
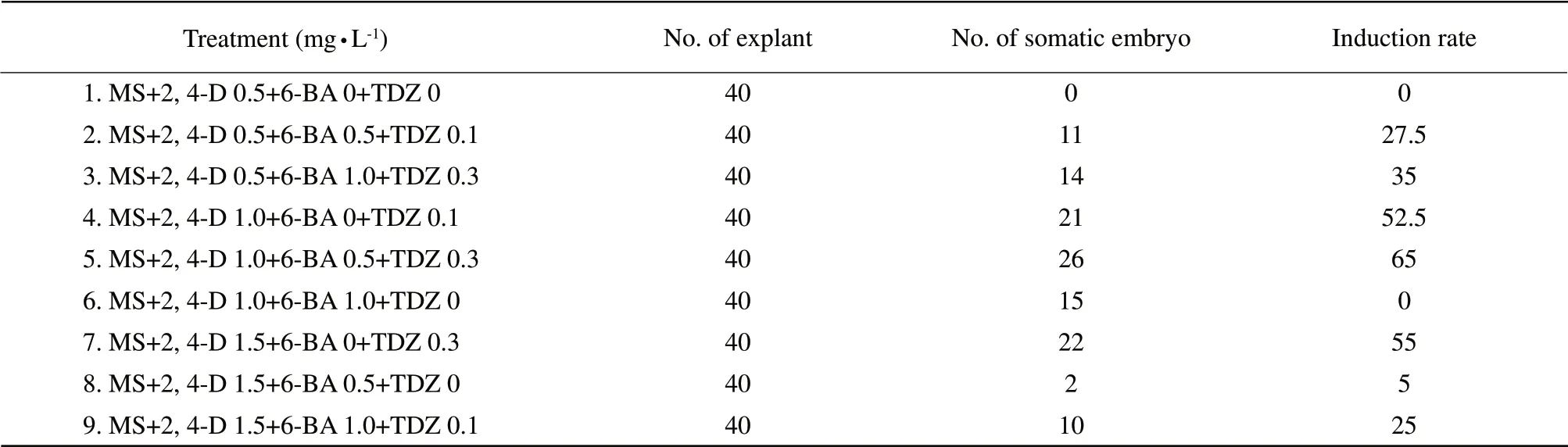
Table3 Somatic embryo induction rate of different treatments
Development characteristics of shoots from petal embryogenic callus
After petal callus had been inoculated on medium for shoot differentiation for 2 weeks,different seedlings appeared on the callus and the color of explants appeared on parts of the seedlings like sheath,top end of the leaf (Fig.2A and B).It showed that pigment in petals has been passed down to new organs with cell division.The subsequent development of seedlings was similar to the seedlings derived from other organs.This reflected that the genes that control color of the flower expressed with the developing stage of the plant.Some seedlings derived from petal callus only had red color on the stem (Fig.2C).
After petal callus had been transferred to MS medium supplemented with 6-BA 0.5 mg • L-1and NAA 0.1 mg • L-1for 4 weeks,we found that petal callus not only differentiated into plantlets whose sheath had the same color as explants,but also differentiated into petals or petal analogues exactly same as explants again (Fig.3),but they couldn't differentiate into plantlets.Petals and petal analogues derived from petal callus withered like natural petals after being cultured further.The reason of this phenomenon might be that petal callus in vitro were affected by certain factors such as temperature,phytohormone and osmotic pressure inside the tube which resulted in the genes that control petal color development were activated,the growth direction of some cells still followed the flowering controlled genes according to the spatiotemporal order that petal explants followed.Specific reason of this depended on further researches on organogenesis and molecular mechanism of plant growth.

Fig.2 Characteristics of petal seedlings developed from embryogenic callus

Fig.3 New petals and petal analogue formed from petal callus directly
Mutants ISSR screening in M1 generation and observation in M3 generation
Plantlets derived from petals were transplanted into pots in greenhouse after rooting in tubes.Leaf-DNA of each plantlet was extracted for ISSR analysis.The result showed there were two mutants in M1generation of petal somatic lines (Fig.4A).Traits were observed in M3generation.Two mutants appeared different from the control (Fig.4B).Compared with the control,the mutants had regular blocky pigmentzone on petals.Anther,the base part of the petal was purple and the petal color of the mutants was lighter than that of the control (Fig.4C and D).

Fig.4 ISSR map of mutants and differences between 'Rose Supreme'and its mutants
Conclusions
The study showed that petal regeneration system of Gladiolus could be established successfully.Pigment of parents appeared,while plantlets were formed from petals.New petals could be formed from petal callus directly.Two mutants were identified from petal somatic line with assistant of ISSR analysis in early generation and the traits observation of the mutants in M3generation verified the results of ISSR analysis.
Earle E D,Langhans R W.1974.Propagation of Chrysanthemum in vitro.Amer Soc Hort Sci,4: 352-358.
He X D.1992.Variation of Chrysanthemum petals somatic lines.Journal of Botany,6: 28-28.
Ma G H,Zhang Q M.1994.The effect of paclobutrazol on gladiolus in tissue culture.Acta Horticulturae Sinica,21(3): 288-292.
Qiu W D.1982.Studies on quick propagation of rare variety Chrysanthemum "green paeony" in vitro.Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University,8(1): 89-94.
Qiu W D,Li X S.1983.In vitro propagation of rare Chrysanthemum varieties.Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University,9(2): 105-l14.
Qiu W D,Li X S,1983.Some new types obtained from petal tissue culture of chrysanthemum.Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural University,9(3): 243-246.
Skirvin R M,Janick J.1976.Tissue culture-induced variation in scented Pelargoniura spp.Amer Soc Hort Sci,101: 281-290.
Zhao X M.1999.Preliminary reports on propagation of gladiolus by using petal as explants.Gansu Agr Sci and Techn,4: 45-46.
Zheng Y.2007.Establishment of plant regeneration system and study on agrobacterium-mediated gladiolus transformation of NPR1 gene.Northeast Agricultural University,Harbin.
杂志排行
Journal of Northeast Agricultural University(English Edition)的其它文章
- Regulatory Network of Transcription Factors in Response to Drought in Arabidopsis and Crops
- Comparison of Net Photosynthetic Rate in Leaves of Soybean with Different Yield Levels
- Multiplex PCR System Optimization with Potato SSR Markers
- Analysis on Combining Ability for Characters of Male Sterile Lines in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.)
- Research on Tobacco Transformation of Vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit c Gene from Iris lacteal
- Genome-wide Analysis of Ovate Family Proteins in Arabidopsis
