陆表海碳酸盐岩台地沉积期微地貌恢复方法研究①——以四川盆地磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A层为例
2011-12-13谭秀成赵路子张本健
谭秀成 聂 勇 刘 宏 周 彦 李 凌 赵路子 张本健 冯 钰,5
(1.油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室西南石油大学 成都 610500; 2.西南石油大学资源与环境学院 成都 610500;3.西南油气田分公司勘探处 成都 610051; 4.西南油气田分公司川西北气矿 四川江油 621709;5.西南油气田分公司川中油气矿 四川遂宁 629000)
陆表海碳酸盐岩台地沉积期微地貌恢复方法研究①
——以四川盆地磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A层为例
谭秀成1,2聂 勇2刘 宏2周 彦2李 凌2赵路子3张本健4冯 钰4,5
(1.油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室西南石油大学 成都 610500; 2.西南石油大学资源与环境学院 成都 610500;3.西南油气田分公司勘探处 成都 610051; 4.西南油气田分公司川西北气矿 四川江油 621709;5.西南油气田分公司川中油气矿 四川遂宁 629000)
陆表海碳酸盐岩台地沉积期微地貌起伏差异小,难于确定。分析了沉积期微地貌控制着颗粒滩储层的发育及分布,因此,可通过对颗粒滩储层的研究,反演微地貌起伏。按此原理,建议具体研究步骤为:颗粒岩沉积为主体的等时地质体选取、储层成因确定、暴露时间确定、沉积期地貌恢复,以及成果检验应用。以四川盆地磨溪气田嘉陵江组嘉二2亚段A层为例,利用丰富的钻孔取心资料进行了实例研究,取得良好效果,表明该方法值得推广应用,尤其适用于钻探程度高、资料老、缺乏三孔隙度测井系列的盆地老区,这对于储层预测和新层挖潜具有重要参考意义。
陆表海 碳酸盐岩台地 沉积期微地貌 颗粒滩 嘉陵江组 三叠系 磨溪气田 四川盆地
含油气盆地沉积期古地貌的恢复是认识区域岩相古地理及其油气地质意义的重要关键,对于相对高差较大的地貌单元,通常可采用回剥法[1]、沉积学分析方法[2,3]、层序地层学方法[4,5](包括高分辨率层序地层学方法[6])等实现;相比而言,在陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内部,由于次一级地貌起伏较小[7],导致在某一时间段内小区域中形成的地层多为米级差异[7,8],从而使得应用常用的方法难以准确刻划这种地貌差异。实际上,在陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内部,微地貌高地在海退期暴露几率较高,因此储层质量较之相对低洼区要好,据此理论而言,通过对储层的研究,可以反演地层沉积期的古地貌,然而,这在过去的研究中,尚未得到系统工作。
四川盆地磨溪气田位于盆地川中古隆中斜平缓构造带南部,是近年来盆地天然气勘探开发的重点地区之一[9]。在早三叠世嘉陵江期,以发育陆表海碳酸盐岩台地为特征,台地内部具有次一级的地貌起伏[10],但迄今少有精确的恢复工作。目前,在磨溪构造的主体280 km2内,揭穿嘉二段钻井共42口(资料截止2005年),其中嘉二段全取芯井16口,并且在区内分布较均匀,因此,井网合理分布的大量钻孔资料为沉积期微地貌恢复研究提供了有利条件[7]。本文以该段为例,开展陆表海碳酸盐岩台地沉积期微地貌的恢复研究,主要目的是探索一种具有普遍意义的恢复方法,以供同类研究类比参考。
1 原理与方法
陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内部浪基面浅,一般小于5 m[7],总体扰动深度小,因此在相对海退时期,微地貌高地易处于浪基面之上,从而发育颗粒滩[7]。颗粒滩的沉积速率高于台地内其它微相区[11],因此,地貌差异得到强化。此外,颗粒滩沉积之后,由于上覆沉积物的加积,颗粒沉积物在物理压实的影响下,形成颗粒格架支撑,压实率要远低于细粒沉积物,从而使不同微相区的地貌差异导致的沉积厚度差异得到进一步强化[8],这同时也表明台地内部沉积期的微地貌近似恢复可以不考虑压实校正。总而言之,某一时间段内形成的颗粒岩厚度可用于近似恢复其形成时的微地貌起伏。
对于非暴露浅滩区,微地貌高地的颗粒滩始终较其它区域沉积速率快,其颗粒岩累计厚度可用来近似表征微地貌起伏(图1a)。而陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内多数时期形成的颗粒滩,发育深度较小,沉积物的可容空间也相应较小,并由于其海平面变化特征为快速海侵-缓慢海退,颗粒滩的快速生长使得微地貌高地的颗粒沉积物极易在同生期暴露(暴露浅滩),使微地貌高地颗粒滩终止发育,颗粒滩向微地貌低地迁移(图1b,c)。
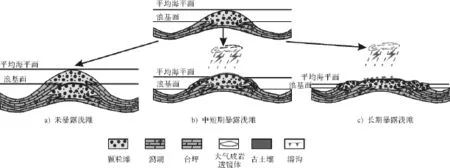
图1 水下及暴露浅滩叠置迁移模式Fig.1 Superposed migration pattern of submarine and exposed shoals
如图1b,1c,对于同生期暴露浅滩,可以分为中短期暴露和长期暴露两种情形。其中,中短期暴露时间一般小于50 000 a,缺乏岩溶特征,并以发育选择性的粒内溶蚀和早期淡水胶结物为特征[12],此时,地貌高地的剥蚀不明显,连续取芯见不到明显的不整合面,颗粒滩在海退时期向低地迁移,但其厚度仍小于地貌高地(图1b),因此,颗粒滩中短期暴露形成的大气成岩透镜体储层与颗粒滩的累计厚度呈正相关关系。相比而言,长期暴露的浅滩,其暴露时间大于130 000 a,以发育古土壤和不规则溶沟、溶缝为特征[12],此时,地貌高地的颗粒岩存在不同程度的剥蚀,并且颗粒滩向微地貌低地迁移,低洼处的颗粒岩累计厚度可能大于微地貌高地,大气成岩透镜体的厚度与颗粒滩厚度不具正相关关系(图1c)。因此,若同生期暴露时间长,就会干扰颗粒滩累计厚度对沉积期地貌的判断,尤其是等时地质体选取的时间段越长,越难消除这种因素的影响。因而,暴露时间的确定成为利用颗粒滩厚度法恢复微地貌的关键。尽管准确的年龄界限目前还难以实现,但仍可以根据成岩组构与宏观地质特征区别暴露的时间,如具有以下特征的通常反映短期暴露(反之则为长期暴露):①不整合特征不明显,缺乏古土壤;②缺乏不规则溶沟、溶缝;③粒内溶蚀极其发育;④早期淡水胶结物与胶结不整合的出现;⑤大气成岩透镜体成因储层与颗粒岩累计厚度呈正相关。
综上所述,在陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内部,可以通过精细的宏微观分析寻找符合条件的等时地质体,利用颗粒岩厚度法对暴露浅滩期的微地貌进行近似恢复。具体可以分为如下几个步骤:①选取以颗粒岩沉积为主体的等时地质体;②确定储层成因;③暴露时间确定;④沉积期地貌恢复;⑤成果检验与应用。需要注意的是,根据以上分析,未暴露和中短期的暴露滩研究效果要比长期的暴露滩研究效果好。
2 实例应用
2.1 等时地质体选择与储层成因
磨溪气田嘉二段主要由海相碳酸盐岩、蒸发岩和少量陆源碎屑岩组成,钻厚从104 m到120 m不等,总体上表现出东厚西薄的变化趋势。本区嘉二沉积期的沉积体系为陆表海碳酸盐岩台地,以发育局限-蒸发海台地沉积为特征,其中的嘉二2亚段A层以发育台内颗粒滩亚相为特征,主要包括滩核及滩核-滩缘微相[13]。滩核微相主要由鲕粒灰岩组成,具有颗粒岩累计厚度和单滩体厚度较大的特点,是本期沉积最有利的储集微相带[7]。因此,以嘉二2亚段A层为例展开重点研究。
如图2,嘉二2亚段A层下部为蓝灰色泥岩频夹薄层砂屑灰岩,中上部为浅灰色鲕粒灰岩夹薄层泥晶灰岩或泥晶云岩,局部井区夹灰黑色块状硬石膏岩,上部为深灰色泥晶灰岩,储层主要发育于鲕粒灰岩中[14]。研究表明,磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A小层为近乎等时的地质体,并以颗粒岩沉积为主体[15],储集空间类型以粒内溶孔和铸模孔为主,属同生期岩溶成因[14]。因此,开展沉积期古地貌恢复,嘉二2亚段A层具有翔实的基础资料条件。
2.2 暴露时间确定
通过嘉二段丰富的取心资料观测发现,嘉二2亚段A小层各向上变浅序列间未见明显的不整合现象;岩芯上针孔状粒内溶蚀极其发育,而未见溶沟溶缝现象(图3);镜下可见到大气水成岩环境形成的刃状方解石(图4)。据此,对比前文归纳总结的判识标准,初步表明颗粒滩的暴露时间不长。
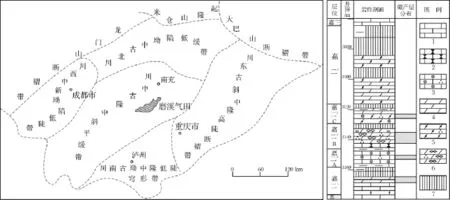
图2 研究区地理位置图1.硬石膏岩;2.泥晶云岩;3.砂屑云岩;4.粉晶云岩;5.泥晶灰岩;6.瘤状灰岩;7.鲕粒灰岩Fig.2 Geographical location of the study area

图3 鲕粒灰岩,逆粒序,铸模孔,磨206井, 3186.69~3187.01 m,嘉二2 AFig.3 Oolitic limestone,inverse grading,moldic pore,Well Mo206, 3186.69~3187.01 m,the layer A of Jia22 submember.
此外,具有大气成岩透镜体成因的储层与颗粒岩累计厚度呈正相关,也表明了滩体的暴露时间不长。研究表明,本区储层段随粒屑滩生长,加上受海平面变化等因素的影响,几十厘米厚的单滩体也可出露水面,接受大气淡水的淋滤作用,以颗粒岩的原生粒间孔隙为通道进行溶蚀,使得刚沉积不久的颗粒由外向内发生强烈的溶蚀作用,形成粒内溶孔发育的颗粒岩,往往成为良好的孔隙型储层[16]。通过对磨溪和邻区18口嘉二段全取心井的精细观测统计,发现粒屑滩的累计厚度与针孔鲕粒灰岩的累计厚度存在明显的正相关关系(图5)。

图4 鲕粒灰岩,两期方解石胶结物,磨13井, 3124.71 m,X50(-),嘉二2亚段A层Fig.4 Oolitic limestone,two-period calcite cements,Well Mo13, 3124.71 m,X50(-),the layer A of Jia22 submember
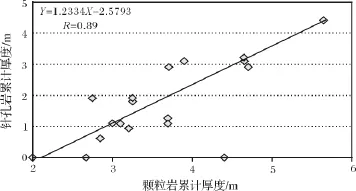
图5 颗粒岩累计厚度与针孔岩累计厚度相关关系图Fig.5 The correlation graph of gross thinkness between grainstones and pinhole rocks.
上述特征表明,磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A小层颗粒岩早期暴露时间为中-短期。大气淡水淋溶形成的针孔状颗粒岩发育程度与古地形高低密切相关,位于古地形高处,同生期暴露几率较大,颗粒岩接受大气淡水淋溶改造时间较长,因此,针孔岩发育区域即为沉积时的古地貌高地,如位于现今构造高部位的磨151井、磨13井等井,岩心观察发现嘉二2A层针孔状颗粒岩极为发育。而位于现今构造低部位的磨16井、磨47井等岩芯观察表明该层针孔状颗粒岩不发育,面孔率极低,说明这些区域古地形较低,颗粒岩暴露几率少,很难接受大气淡水的淋溶改造。因此,可利用该套颗粒岩厚度变化来表征嘉二2A期沉积期微地貌。
2.3 沉积期地貌恢复
基于上述原理,用颗粒岩厚度法来恢复磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A层沉积期古地貌。除磨溪16口全取芯井直接统计外,其余未取心井则通过测井相获取颗粒岩厚度[17],根据岩芯观察和测井相统计出了42口井嘉二2A层颗粒岩的累计厚度,绘制出颗粒岩累计厚度等值线图,并以此为标准恢复了嘉二2A沉积期的古地貌起伏形态,形成如图6的认识:①微地貌高地呈近东西向展布;②微地貌高地与现今构造具一定协调性,说明磨溪构造为一同沉积水下高地,只是南部由于后期喜山运动的改造而沉降;③水下高地内部隆、凹分异明显,出现高地和洼地等次一级微地貌单元。高地发育在Mo24-Mo205东井区、Mo206井南侧、Mo207井周缘、Mo151井-Mo36井区、Mo208井区及南部、Mo48井和Mo202井区北侧等(7个)。洼地发育在Mo12-Mo201、Mo005-2-Mo150、Mo22井南及Mo206井东等(4个)。
2.4 成果检验
嘉二2初期四川盆地遭受到一次较强海侵,沉积了一套区域上稳定分布的、富含叶肢介的蓝灰色泥岩,导致嘉二2A期少见蒸发岩沉积,表明盆内海水盐度基本正常[18]。然而有意义的是,在Mo005-2井-Mo150井一带,以及Mo207井区却出现了较厚的水下膏岩沉积(膏岩为深灰色块状,未见暴露标志)[7],其周缘是反映微高地的粒屑滩颗粒岩沉积。这反映了由于周缘微高地上滩体的生长,导致相对低洼的滩间海环境封闭受限,水体蒸发浓缩,从而形成膏岩沉积。这表明,利用颗粒岩厚度恢复出的古地貌得到了岩相沉积的支持,因此是可信的。
2.5 成果应用I:指导相邻层系的沉积微相分析
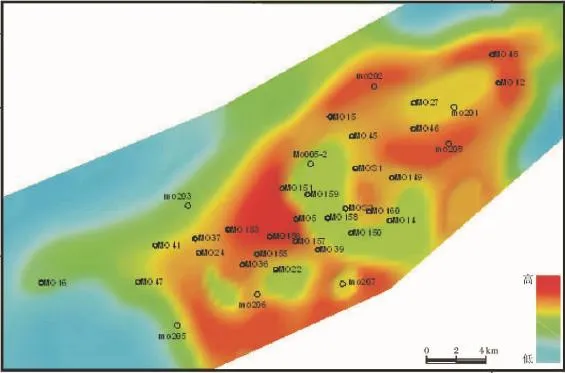
图6 磨溪气田嘉二2亚段A期古地貌示意图Fig.6 The palaeogeomorphic sketch of the layer A of Jia 22 submember,Moxi gas field
对于以中短期的早期暴露为主的陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内部古地貌,利用此方法恢复的沉积期地貌在较长时间内具有一定的继承性,并控制其沉积微相的展布。如以嘉二2A沉积期后的嘉二2A期为例,图7给出了根据实际取心资料绘制的沉积相图,如图可见,云坪、云坪和潮上膏云坪夹坪洼微相的沉积微地貌更高[14],沉积微相分布表明海水盐度向北东增加,导致蒸发矿物含量增高,对比图6,可见这种地貌特征是对嘉二2A期的继承发展,说明该方法恢复的地貌可以指导相邻层系的沉积微相研究。
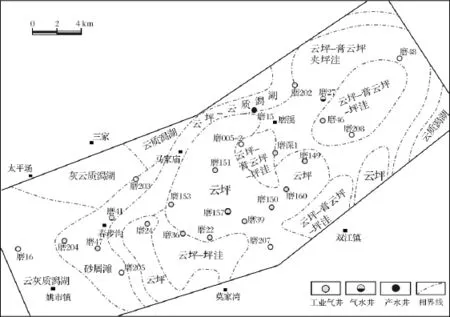
图7 磨溪嘉二2 B期沉积微相平面分布特征(据文献[13])Fig.7 Microfacies distributional characteristics of the layer B of Jia22 submember,Moxigas field
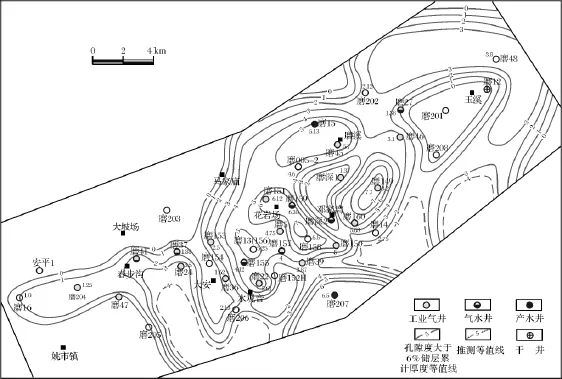
图8 磨溪气田嘉二2 B期孔隙度>6%的储层累计厚度等值线图Fig.8 Gross thinkness contourmap of reservoirs(porosity is higher than 6%) in the layer B of Jia22 submember,Moxigas field
2.6 成果应用II:指导储层精细研究及勘探开发部署
岩芯实测物性统计表明,位于古地貌高处的区域,储层孔隙度值在5%~18%之间,平均孔隙度在9%左右,储层有效厚度大;相比而言,位于古地貌低处的区域,水动力条件弱,颗粒岩不发育,储层质量差,孔隙度值仅在3%左右,储层有效厚度小。
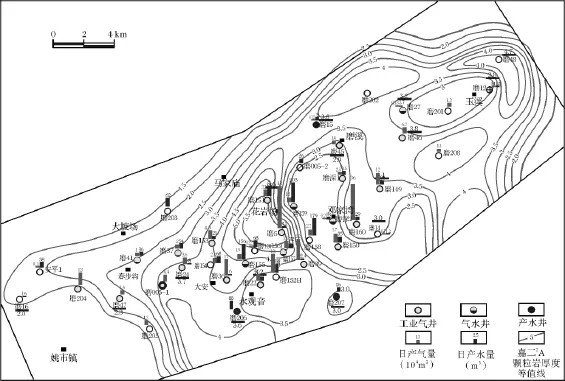
图9 磨溪嘉二气田产能分布图Fig.9 Capacity distribution of Moxi gas field
考虑到微地貌具有继承性发展特征,因此微地貌高地也会控制相邻时期优质储层的分布格局,如根据嘉二2B期孔隙度大于6%的储层累计厚度,优质储层的分布与嘉二2B期的古地貌高地具明显的相关性,虽然由于嘉二2B晚期向北东方向盐度增加,膏质沉淀充填导致储层相对变差,但不改变其分布格局(图8),该期的优质储层相应发育于磨151-磨22及磨207等高地。
受沉积期盐度向北东增加的影响,储层质量和厚度与之相适应,东北部的高地相对储层较差,而中部高地盐度较低,储层质量好,实际试油资料也表明嘉二气藏产能高的井基本上都位于中部磨151-磨22、磨160这两个古地貌高地及附近,气井日产能一般在十几万立方米/日~几十万立方米/日(图9)。因此,古地貌恢复结果可对生产提供指导。
3 结论
(1)陆表海碳酸盐岩台地沉积期古地貌的恢复可利用等时地质体内的颗粒岩累计厚度来近似恢复,特别是对于未暴露和中短期暴露滩效果尤佳,具体研究步骤为:颗粒岩沉积为主体的等时地质体选取、储层成因确定、暴露时间确定、沉积期地貌恢复,以及成果检验应用。
(2)在磨溪气田嘉二2B期的应用结果表明,陆表海台地内沉积期微地貌在较长时间内可继承发展,并控制相邻层序沉积、储层的分布格局,其生产应用效果良好,说明对于井网密度大的开发阶段气田的沉积、储层精细描述是一种有效辅助手段。
(3)由于台地内滩相薄储层厚度小于地震的垂直分别率,因此采用沉积期古地貌恢复这一方法间接预测储层发育概率,尤其适用于钻探程度高、资料老、缺乏三孔隙度测井系列的老区,对于储层预测和新层挖潜具有重要意义。
References)
1 代金友,何顺利。鄂尔多斯盆地中部气田奥陶系古地貌研究[J]。石油学报,2005,26(3):37-43[Dai Jinyou,He Shunli.Ordovician paleokarst landform of central gas field in Ordos basin[J].cta Petrolei Sinica,2005,26(3):37-43]
2 赵俊兴,陈洪德,时志强。古地貌恢复技术方法及其研究意义——以鄂尔多斯盆地侏罗纪沉积前古地貌研究为例[J]。成都理工学院学报,2001,28(3):260-261[Zhao Junxing,Chen Hongde,Shi Zhiqiang.The way and implications of rebuilding palaeogeomorphology-taking the research of palaeogeomorphology of the Ordos ba-sin before Jurassic deposition as example[J].hengdu University of Technology News,2001,28(3):260-261]
3 吴丽艳,陈春强,江春明,等。浅谈我国油气勘探中的古地貌恢复技术[J]。石油天然气学报,2005,27(4):559-563[Wu Liyan, Chen Chunqiang,Jiang Chunming,et al.Paleogeomorphic restoring techniques in China's hydrocarbon exploration[J].ournal of Oil and Gas Technology,2005,27(4):559-563]
4 王家豪,王华,赵忠新,等。层序地层学应用于古地貌分析——以塔河油田为例[J]。地球科学,2003,28(4):426-430[Wang Jiahao,Wang Hua,Zhao Zhongxin,et al.Sequence stratigraphy in paleogeomorphy analysis:An example from the Tahe oilfield[J].arth Science,2003,28(4):426-430]
5 樊太亮,李卫东。层序地层应用于陆相油藏预测的成功实例[J]。石油学报,1999,20(2):12-20[Fan Tailiang,LiWeidong.A successful case on sequence stratigraphy applied to the prediction of non marine oil reservoir[J].cta Petrolei Sinica,1999,20(2):12-20]
6 赵俊兴,陈洪德,向芳。高分辨率层序地层学方法在沉积前古地貌恢复中的应用[J]。成都理工大学学报:自然科学版,2003,30 (1):76-82[Zhao Junxing,Chen Hongde,Xiang Fang.The possibility of rebuilding paleogeomorphy before basin deposition by high resolution sequence stratigraphy[J].hengdu University of Technology News:Science Edition,2003,30(1):76-82]
7 谭秀成,刘晓光,陈景山,等。磨溪气田嘉二段陆表海碳酸盐岩台地内滩体发育规律[J]。沉积学报,2009,27(5):56-62[Tan Xiucheng,Liu Xiaoguang,Chen Jingshan,et al.Shoal development within the epicontinental carbonate platform,Jia2 Member,Lower Triassic,Moxigas field,central Sichuan Basin[J].cta Sedimentologica Sinica,2009,27(5):56-62]
8 赵路子。碳酸盐岩隐蔽滩相储层特征及预测模型[D]。成都:成都理工大学博士论文,2008[Zhao Luzi.Characteristics and Forecast Model of Carbonate Subtle Shoal Reservoir[D].hengdu:Doctoral Dissertation for Chengdu University of Technology,2008]
9 李鹭光。立足新起点,再创新辉煌-写在四川油气田建成千万吨级大油气田之际[J]。天然气工业,2007,27(1):1-3[Li Luguang.Standing on the jumping-off point,looking forward to a new success: Written by the time 10 million tons-level Sichuan oil and gas field was built up[J].atural Gas Industry,2007,27(1):1-3]
10 四川油气区石油地质编写组。中国石油地质志(卷10。四川油气区)[M]。北京:石油工业出版社,1989:87-109[Petroleum Geology Compiling Panel of Sichuan Oil and Gas Field.Petroleum Geologyof China(volume 12,Sichuan Oil and gas field)[M].eijing:Petroleum Industry Press,1989:87-109]
11 Wilson J L.Carbonate Facies in Geologic History[C].ew York: Springer-Verlag,1986:471。
12 Arthur H Sallerdeng,Dickson J A D,Fumiaki Matsuda.Evolution and distribution of porosity associated with subaerialexposure in Upper Paleozoic platform limestones,West Texas[J].APG Bulletin, 1999,83(11):1835-1854
13 谭秀成,邹娟,李凌,等。磨溪气田嘉二段陆表海型台地内沉积微相研究[J]。石油学报,2008,29(2):219-225[Tan Xiucheng, Zou Juan,Li Ling,et al.Research on sedimentarymicrofacies of the epicontinental sea platform of Jia 2 Member in Moxigas field[J].cta Petrolei Sinica,2008,29(2):219-225]
14 周彦,谭秀成,刘宏,等。磨溪气田嘉二段鲕粒灰岩储层特征及成因机制[J]。西南石油大学学报,2007,29(4):30-33[Zhou Y, Tan Xiucheng,Liu Hong,et al.Oolitic limestone reservoir characteristics and its genetic mechanism of Jia 2 Member in Moxi gas field [J].outhwest Petroleum University Acta,2007,29(4):30-33]
15 谭秀成,罗冰,李凌,等。碳酸盐岩台地多旋回沉积小层精细划分对比方法研究——以川中磨溪构造嘉二段为例[J]。地层学杂志,2008,32(2):207-212[Tan Xiucheng,Luo Bing,Li Ling,et al.Fine subdivision and correlation ofmulti-cycle carbonate platform successions:A case study of the second member of the Jialingjiang Formation in the Moxi structure,central Sichuan province[J].ournal of Stratigraphy,2008,32(2):207-212]
16 Laboratory simulation ofmoldic porosity formation(in AAPG 2006 annual convention;abstracts volume,Anonymous,)[C].bstracts: Annual Meeting-American Association of Petroleum Geologists,2006: 15-46
17 刘宏,谭秀成,周彦,等。颗粒碳酸盐岩测井相及其对滩相储层的指示意义[J]。天然气地球科学,2007,18(4):30-33[Liu Hong,Tan Xiucheng,Zhou Yan,et al.Logging facies of granular carbonate rocks and its implication on reservoir evaluation[J].atural Gas Geoscience,2007,18(4):30-33]
18 谭秀成。多旋回复杂碳酸盐岩储层地质模型——以川中磨溪构造嘉二气藏为例[D]。成都:成都理工大学博士论文,2008[Tan Xiucheng.Geological Model of Complicated Carbonate Reservoir with Multi-cycle[D].hengdu:Doctoral Dissertation for Chengdu University of Tecnology,2008]
Research on the M ethod of Recoverying M icrotopography of Epeiric Carbonate Platform in Depositional Stage:A case study from the layer A of Jia 22Member in Moxi Gas Field,Sichuan Basin
TAN Xiu-cheng1,2NIE Yong2LIU Hong2ZHOU Yan2LILing2ZHAO Lu-zi3ZHANG Ben-jian4FENG Yu4
(1.State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exp loitation,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu 610500; 2.College of Resovoir and Environment,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu,610500; 3.Exp loration Department Southwest Oil and Gas Field Com pany,Chengdu,610051; 4.Northwest Sichuan M ining District,Southwest Oil and Gas Filed Com pany,PetroChina Jiangyou,Sichuan 621700; 5.Central Sichuan M ining District,Southwest Oil and Gas Field Com pany,PetraChina Suining,Sichuan 629000)
Themicrotopography difference of the epeiric carbonate platform in the depositional stage is so tiny,as a result,it is too hard to identify.This paper is then,firstly,mainly based on the development dominating factors of the grain shoal within the platform,and then points out that the microtopography highland tends to be beyond the wave base in the relative-regression stage,where the grain shoal develops.The depositional rate is higher than any othermicrofacies area within the platform,hence,the topography differencewas enhanced at that stage.Besides,after the sedimentation of the grain shoal,the grain-supported framework forms under the influence of physical compaction,where the compaction rate ismuch lower than the finer sediments,so the depositional thickness resulted from the topography difference of variousmicrofacies areas is also further enhanced,which shows that the grainstone thicknesswithin a certain period of time can be used,approximately,in recovering itsmicrotopography prominence when it began to present,and that the compaction correction can be ignored when approximately recovering themicrotopography within the platform at the depositional stage.It then further analyses the effects on the grain shoal construction and reservoir development by the exposure process during the depositional stage,and it divides the shoalwithin the epeiric platform into three genetic types:unexposed shoal,short-medium-term exposed shoal and long-term exposed shoal,meanwhile, pointing out that themethod of grainstone gross-thicknesswhich is used,approximately,in recovering the depositional palaeogeomorphology of epeiric carbonate platform is preferable for the unexposed and short-medium-term exposed shoals,where themain characteristics of the short-medium term exposed shoal can be concluded as follows(contrarily be long-term exposure):①unconformity characteristic limited,palaeosol lacks;②irregular karren and corroded fissure lack;③intargranular solution extremely develops;④the freshwater cements in early stage and cementunconformity exist;⑤lens-diagenesis reservoir of atmospheric genesis positively associates with the grainstone gross-thickness.Based on this,the paper then takes the view thatmicrotopography prominence can be inverted by the reservoir study of the grain shoal.Followed by that principle,italso suggestes that the concrete study procedure can be like this:the isochronous geologic body to be chosen as themain body of grainstone deposition,the confirmation of reservoir genesis and exposured time,the topography recovering during depositional stage and the application of achievement verification.
Sichuan Basin was characterized by developing epeiric carbonate platform during the period of Jialingjiang in early Triassic.The basin was also hit by an fierce transgression in the period of early Jia 22,which made the salinity of the seawater normal on the whole.Moxi gas field locates in the south of gentle-oblique tectonic zone of the palaeohigh in the central of the basin,where the tectonic body is about 280 km2,and the exploration wells penetrating the Jia 2 member sum up to42(data by 2005),ofwhich the total cored wells of Jia 2member sum up to 16,besides,the distribution is relatively uniform.Hence,the gas field was used in the case study,where the result indicates that highland mainly develop in the well areas of eastern side of Mo 24-Mo 205,southern side of Mo 206,the rim of Mo 207,Mo 151-Mo 36,Mo 208 and its southern part,Mo 48,Northern part of Mo 202(7 in all),which distribute in the direction of southwest-northeast,swalesmainly develop in Mo 12-Mo 201,Mo 005-2-Mo 150,southern part ofMo 22 and eastern part of Mo 206.here is thick deposition of underwater-gypsum(dark-gray and massive gypsum,no exposed marks found)developing in the well areas of Mo 005-2-Mo 150,Mo 207,which has come into being by the shoal development around themicro-highland,resulting in the sealing restrict of the low-lying environment of interbank sea and the evaporation and concentation of the waterbody,the gypsum deposition therefore comes into being.It can be believed from the above that the recovery of the palaeogeomorphology by taking advantage of the grainstone thickness can be supported by the lithofacies deposition。
According to the graph of sedimentary facies compiled by actual cored data of B Formation,Jia 22Sub-member, the palaeogeomorphology during early sedimentary stage carries on developing in the stage of Jia 22B.dominating the distributing framework of its sedimentation and reservoir.The result indicates that this sort ofmethod used in recovering themicrotopography during depositional stage is applied to the characteristics of lithofacies and so on。,besides, the recovered microtopography in the sedimentary stage can not only continue to successively develop over a long period of time and can also dominate the deposition of adjacent stratigraphy and the framework of reservoir distribution, furthermore,relatively speaking,its production application effect is good,which also indicates that dedicate description of sedimentation and reservoir is an effective and adjuvantmeasure for those gas fields at developing stage with high density ofwell pattern and that this kind ofmethod should be widely popularized,especially for those maturing basin fieldswith high level ofwell exploration,data that is out of date,rare tri-porosity logging series,all of these are significant and also has referenced significance for the reservoir prediction and tapping the new potential formation。
Epeiric Sea;carbonate platform;microtopography during depositional stage;grain shoal;Jialingjiang Formation;Triassic,Moxi Gas Field;Sichuan Basin
谭秀成 男 1970年出生 博士 副教授 储层沉积学 E-mail:tanxiucheng70@163.om
P512.2
A
1000-0550(2011)03-0486-09
①四川省重点学科建设项目(编号:SZD0414)资助。
2010-05-26;收修改稿日期:2010-08-20
