Ki67、CyclinD1在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及其意义
2011-03-06郑发著穆芳张利沈鸿彬
郑发著 穆芳 张利 沈鸿彬
Ki67、CyclinD1在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及其意义
郑发著 穆芳 张利 沈鸿彬
目的探讨Ki67、CyclinD1在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达意义及与食管鳞癌发生发展之间的关系。方法 应用流式细胞术方法(flow cytometry,FCM)检测60例食管鳞状细胞癌及食管正常组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白的表达情况,并检测食管癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达与不同临床参数之间的关系。FCM方法检测食管癌组织中Ki67与CyclinD1蛋白表达的相关性。结果 流式细胞术方法检测到食管癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达水平显著高于正常食管组织(P<0.05)。食管癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达水平与食管鳞癌细胞分化程度、有无淋巴结转移、癌浸润深度有关(P<0.05),与患者的性别及年龄无关(P>0.05)。食管癌组织中Ki67与CyclinD1蛋白表达呈正相关性。结论 Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白在食管癌组织中的高表达可能参与了食管癌的发生与发展,其高表达使细胞具有旺盛增殖能力,促进肿瘤发生。联合检测Ki67、CyclinD1可作为食管癌诊断指标。
流式细胞术;食管鳞状细胞癌;Ki67;CyclinD1
食管癌是较常见的恶性肿瘤,我国是食管癌的高发区,尤其在河北的磁县和河南的林县发病率较高,严重影响了人们的生命健康,目前食管癌的发病机制仍为阐明,研究食管癌发生、发展机制对食管癌早期诊断具有重要的意义。细胞周期的紊乱与肿瘤的发生具有密切的关系,Ki67及CyclinD1是细胞周期调控因子[1-4],可以调控细胞周期从G1期向S期过渡,从而使细胞呈现旺盛增殖能力,促进肿瘤的发生[5,6]。本实验主要研究食管癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1表达意义及与食管癌发生、发展之间的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料 收集河北医科大学第四医院2003年1月至2004年12月食管鳞状细胞癌手术切除标本120例,所有患者术前未接受过化疗和放疗。每例标本分别取癌组织及手术切缘正常食管黏膜(距癌边缘5 cm以上)。每个组织分为两份,分别固定于4%多聚甲醛(用于HE病理诊断)和70%乙醇(用于流式细胞术检测)。所有标本临床病理资料完整,全部经病理检查确诊。从中选出60例食管鳞状细胞癌(B组)和正常食管黏膜组织(A组),用于FCM的检测,男40例,女20例;年龄38~83岁,平均年龄(58±7)岁。食管鳞癌组织中45例为高中分化鳞癌,15例为低分化鳞癌;42例侵及纤维膜,18例未达到纤维膜;19例淋巴结转移,41例未转移。
1.2 主要试剂与仪器 流式细胞仪,美国Beckman Coulter公司;鼠抗人Ki67、CyclinD1抗体,购自北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司;二抗为FITC标记的山羊抗鼠IgG,购自Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratiries Inc。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 实体组织单细胞悬液的制备:网搓法制备单细胞悬液,将细胞悬浮计数并调整细胞浓度为1×107/ml时,此悬浮液为单分散细胞悬液。
1.3.2 Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白的免疫荧光标记:取单细胞悬液0.1 ml(含1×106个细胞),分别加入1∶100稀释的鼠抗人Ki67、CyclinD1抗体0.1 ml,室温放置30 min,加入PBS 10 ml洗涤一次,1 000转,5 min低速离心,弃上清,分别加入羊抗鼠FITC-IgG二抗工作液 100 μl,避光室温放置 30 min,加入 PBS 10 ml 1 000转,5 min低速离心,弃上清以除去未结合的荧光二抗,上机检测前加入PBS 1.0 ml,经300目尼龙网过滤后上机检测。
1.3.3 流式细胞术检测蛋白表达方式:流式细胞术检测Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达量以平均荧光强度(Mean Fluorescence Intensity)表示。
1.4统计学分析应用SPSS 11.5统计软件,计量资料以±s表示,组间比较采用t检验分析,相关性分析采用Peason相关分析,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 不同食管组织中Ki67蛋白的表达情况 流式细胞术检测结果显示,Ki67蛋白在食管癌组织中的表达显著高于食管正常组织(P <0.05)。见表1,图1。
2.2 不同食管组织中CyclinD1蛋白的表达情况 流式细胞术检测到CyclinD1蛋白在食管癌组织中的表达显著高于食管正常组织(P <0.05)。见表2,图2。
2.3 食管癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达与临床病理特征的关系 Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白表达量在低分化者、浸润深度达到纤维膜者、有淋巴结转移者显著高于中高分化者、浸润深度未达到纤维膜者、无淋巴结转移者(P<0.05)。年龄和性别之间表达量差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。

表1 流式细胞术检测Ki67蛋白在不同食管组织中的表达
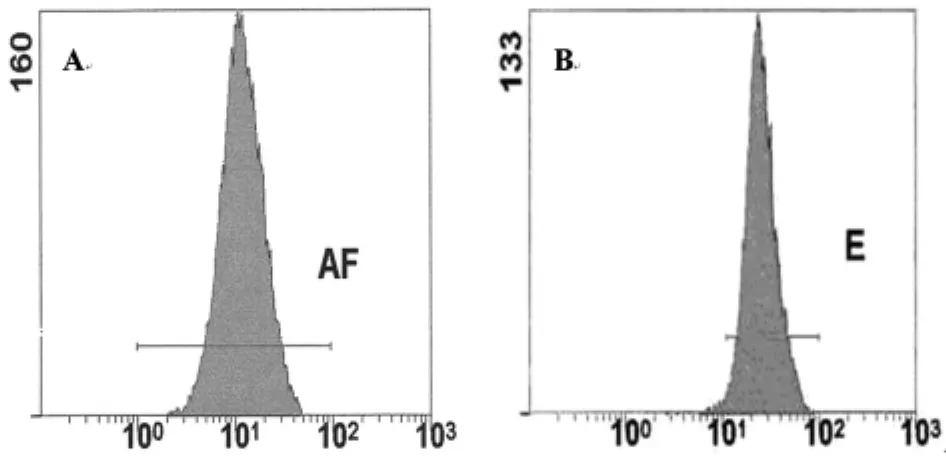
图1 流式细胞术检测不同食管组织中Ki67蛋白的表达
表2 流式细胞术检测CyclinD1蛋白在不同食管组织中的表达n=60,±s
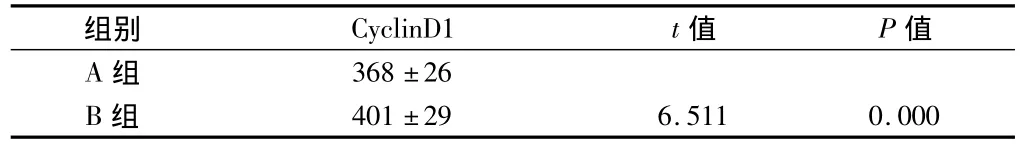
表2 流式细胞术检测CyclinD1蛋白在不同食管组织中的表达n=60,±s
组别 CyclinD1 t值 P值A组368±26 B组401±29 6.511 0.000
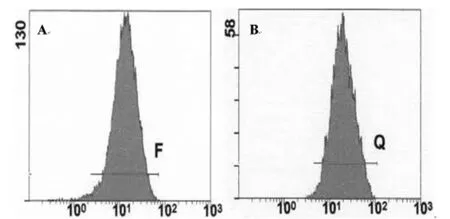
图2 流式细胞术检测不同食管组织中CyclinD1蛋白的表达
表3 食管鳞癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白的表达与不同临床参数之间的关系±s
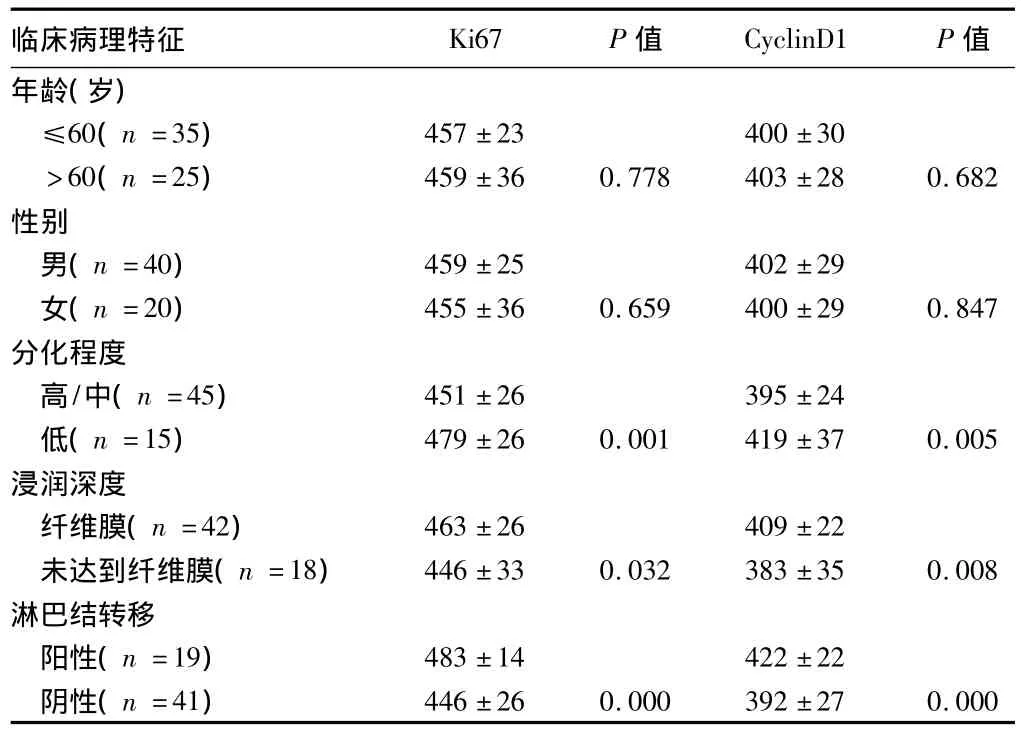
表3 食管鳞癌组织中Ki67、CyclinD1蛋白的表达与不同临床参数之间的关系±s
临床病理特征 Ki67 P值 CyclinD1 P值年龄(岁)446±26 0.000 392±27 0.000≤60(n=35) 457±23 400±30>60(n=25) 459±36 0.778 403±28 0.682性别男(n=40) 459±25 402±29女(n=20) 455±36 0.659 400±29 0.847分化程度高/中(n=45) 451±26 395±24低(n=15) 479±26 0.001 419±37 0.005浸润深度纤维膜(n=42) 463±26 409±22未达到纤维膜(n=18) 446±33 0.032 383±35 0.008淋巴结转移阳性(n=19) 483±14 422±22阴性(n=41)
2.4 食管癌组织中Ki67与CyclinD1蛋白表达的相关性分析流式细胞术结果显示,食管癌组织中Ki67蛋白表达与CyclinD1蛋白表达呈正相关(Pearson相关系数 =0.275,P=0.034)。
3 讨论
食管癌是我国较常见的恶性肿瘤,发病率及病死率高,严重威胁着人们的生命健康,阐明食管癌的发生机制对食管癌的早期诊断具有重要的意义。研究发现,细胞周期紊乱能够导致肿瘤的发生[7,8],是肿瘤发生的促使因素。Ki67和CyclinD1是调控细胞周期的重要因子。
Ki67是一种核增殖抗原[9],存在于细胞周期的 G1、S、G2、M期,G1后期开始出现,在S期和G2期逐渐升高,M期达到高峰,但G0期无表达。而且还发现Ki67在S期聚集,尤其是在后半期表达率明显增高,故Ki67只表达于增殖期细胞,而不表达于静止期细胞。Ki67表达的高低反映了细胞增殖状态,是目前应用最广泛的增殖细胞标记之一。Ki67在细胞中的高表达可以使细胞具有增值旺盛的能力,促使肿瘤的发生,本实验中,应用流式细胞术方法检测食管癌组织中Ki67蛋白的表达显著高于食管正常组织,Ki67的高表达可能参与了食管癌的发生。同时检测了食管癌组织中Ki67的表达与不同临床参数之间的关系发现,Ki67表达量在低分化者、浸润深度达到纤维膜者、有淋巴结转移者显著高于中高分化者、浸润深度未达到纤维膜者、无淋巴结转移者,提示Ki67可能参与了食管癌恶性度转化过程,可作为食管癌恶性度及预后判断的指标。
研究发现,在细胞周期进程中,CyclinD1主要功能是调控细胞周期从G1期进入 S期[10],促进细胞增殖,当CyclinD1蛋白在细胞中表达异常增高时,将引起细胞增殖周期失调,从而导致肿瘤的发生。本实验中,检测到食管癌组织中CyclinD1蛋白的表达显著高于食管正常组织,CyclinD1的高表达可促使细胞周期从G1期过渡至S期,使细胞呈现旺盛的增值能力,参与了食管癌的发生。同时检测了食管癌组织中CyclinD1表达水平在低分化者、浸润深度达到纤维膜者、有淋巴结转移者显著高于中高分化者、浸润深度未达到纤维膜者、无淋巴结转移者,提示CyclinD1可能参与了食管癌恶性度转化过程,可作为食管癌恶性度和预后判断的指标。而且经统计学分析,食管癌组织中Ki67蛋白的表达与CyclinD1蛋白表达具有正相关性。肿瘤发生是多基因、多因素引起的,Ki67、CyclinD1在细胞中的异常表达可能共同参与了食管癌的发生及发展。
综上所述,提示Ki67与CyclinD1蛋白在食管组织细胞中的异常高表达可能参与了食管癌发生及发展,联合检测这两个指标对食管癌的早期诊断具有一定的临床意义,而且为食管癌的靶向治疗提供新的研究方向。
1 Morimoto K,Kim SJ,Tanei T,et al.Stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive breast cancers are characterized by negative estrogen receptor,positive human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2,and high Ki67 expression.Cancer Sci,2009,100:1062-1068.
2 Dayan D,Vered M,Sivor S,et al.Age-related changes in proliferative markers in labial salivary glands:a study of argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions(AgNORs)and Ki-67.Exp Gerontol,2002,37:841-850.
3 Mineta H,Miura K,Ogino T,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)expression correlates with p53 and ki-67 expressions in tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res,2002,22:1039-1044.
4 Saha A,Halder S,Upadhyay SK,et al.Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Facilitates G1-S Transition by Stabilizing and Enhancing the Function of CyclinD1.PLoS Pathog,2011,7:e1001275.
5 Kwak YT,Radaideh SM,Ding L,et al.Cells Lacking IKK{alpha}Show Nuclear Cyclin D1 Overexpression and a Neoplastic Phenotype:Role of IKK{alpha}as a Tumor Suppressor.Mol Cancer Res,2011,9:341-349.
6 Tsai MH,Tsai CW,Tsou YA,et al.Significant association of cyclin D1 single nucleotide polymorphisms with oral cancer in taiwan.Anticancer Res,2011,227-231.
7 Hayakawa Y,Hirata Y,Nakagawa H,et al.Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and cyclin D1 compose a positive feedback loop contributing to tumor growth in gastric cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2011,108:780-785.
8 Li W,Jiang HR,Xu XL,et al.Cyclin d1 expression and the inhibitory effect of celecoxib on ovarian tumor growth in vivo.Int J Mol Sci,2010,11:3999-4013.
9 Winking H,Gerdes J,Traut W.Expression of the proliferation marker Ki-67 during early mouse development.Cytogenet Genome Res,2004,105:251-256.
10 Dubova EA,Podgornova MN,Schegolev AI.Expression of adhesion molecules and cyclin d1 in cells of solid-pseudopapillary tumors of the pancreas.Bull Exp Biol Med,2009,148:908-910.
Expression and significance of Ki67 and CyclinD1 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
ZHENG Fazhu,MU Fang,ZHANG Li,et al.Department of Surgery,Handan People’s Hospital,Hebei,Handan 056001,China
ObjectiveTo investigate the expression and significance of Ki67 and CyclinD1 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma,and to explore the correlation between the expressions of Ki67,CyclinD1 protein and pathogenesis as well as progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.MethodsThe levels of Ki67,CyclinD1 protein expression in 60 cases of normal esophageal mucosa and esophageal carcinoma tissues were detected by flow cytometry.The correlation between the expression of Ki67,CyclinD1 protein and clinicopathological characteristics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma was analyzed.ResultsThe expression levels of Ki67,CyclinD1 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma were significantly higher than those in normal esophageal tissues(P <0.05).The expression levels of Ki67,CyclinD1 protein in esophageal cancer were closely correlated with the degrees of differentiation,metastasis of lymph node and the invasive depth of the tumor(P <0.05).There was no significant correlation between Ki67,CyclinD1 protein expression in esophageal cancer and the patients'gender,age(P >0.05).There was a positive correlation between ki67 protein expression and CyclinD1 protein expression in esophageal cancer.ConclusionThe high-expression of Ki67 and CyclinD1 may be involved in the pathogenesis and advancement of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma,which may induce the high proliferation of cells,then result in the tumorigenesis.The combination detection of Ki67 and cyclinD1 can be used as valuable diagnosis indexes for esophageal carcinoma.
flow cytometry;esophageal squamous cell carcinoma;Ki67;cyclinD1
R 735.1
A
1002-7386(2011)09-1293-03
10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2011.09.004
056001 河北省邯郸市人民医院外科
沈鸿彬,056001 河北省邯郸市人民医院外科;E-mail:laoyindy1010@163.com
2011-02-18)
·论著·
